INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name and index number in the spaces above.
- Sign and write the date of examination in the spaces provided above.
- Answer all questions in the spaces provided.
- KNEC Mathematical tables and silent non-programmable electronic calculators may be used.
- All working MUST be clearly shown where necessary.
FOR EXAMINER’S USE ONLY
|
QUESTION |
Maximum Score |
Candidate’s Score |
|
1 |
12 |
|
|
2 |
12 |
|
|
3 |
13 |
|
|
4 |
10 |
|
|
5 |
10 |
|
|
6 |
10 |
|
|
7 |
13 |
|
|
Total Score |
80 |
QUESTIONS
- Use the table below to answer the questions that follow. (The letters are not the actual symbols of the elements )
Element
Atomic number
Melting point (0C)
A
11
97.8
B
13
660
C
14
1410
D
17
-101
E
19
63.7
- Write the electronic arrangement for the ions formed by the elements B and D
B ( ½ mark)
D ( ½ mark ) - Select an element which is
- a poor conductor of electricity . ( ½ mark )
- most reactive metal . ( ½ mark)
- Explain briefly how the atomic radii of element B and C compare. (2 marks )
- Use dots (•) and crosses (x) to represent outermost electrons and show the bonding in the compound formed between C and D. ( 2 marks )
- Explain why the melting point of element B is higher than that of element A. (2 marks)
- Write an equation for the reaction that takes place between element A and water. (1 mark)
- Describe how a solid mixture of the sulphate of element E and lead (II) sulphate can be separated into solid samples. (3 marks)
- Write the electronic arrangement for the ions formed by the elements B and D
-
-
- State Hess’s law. (1 mark)
- Use the thermochemical equations given below to calculate the enthalpy of formation of ethane. (3 marks)
C2H6 (g) + 7/2 O2 (g) → 2CO2 (g) + 3H2O (g) ΔH = -1560 kJmol-1
C (graphite) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) ΔH = -394 kJmol-1
H2(g) + ½ O2 (g) → H2O (g) ΔH = -286 kJmol-1
- The table below gives the volumes of oxygen gas produced at different times when hydrogen peroxide solution decomposed in the presence of a catalyst.
Time in seconds
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
Volume of oxygen (cm3)
0
66
98
110
119
120
120
- Name the catalyst used for this reaction. (1 mark)
- Write the chemical equation for the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide. (1 mark)
- On the grid provided, draw the graph of the volume of oxygen gas ( vertical axis ) against time (horizontal axis). (3 marks)
- Using the graph, determine the rate of decomposition of hydrogen peroxide 24th second and 34th second. (2 marks)
- Give a reason why the total volume of oxygen gas produced after 50 seconds remain constant. (1 mark)
-
-
- The diagram below is a set-up to prepare ethyne gas.
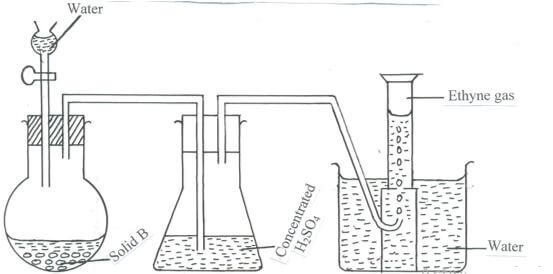
- Name solid B . (1 mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction taking place between solid B and water. (1 mark)
- State the property that makes the gas to be collected by the method shown in the diagram. (1 mark)
- State the main commercial use of ethyne. (1 mark)
- The scheme below represents some reactions of ethyne. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
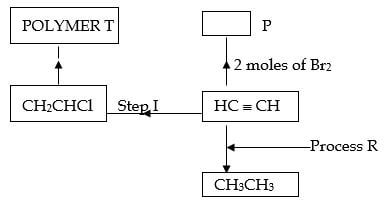
- Name compound P and draw it’s structural formula. (1 mark)
- Name the reagents used in:
- Process R .. . (½ mark)
- Step I . (½ mark)
- Draw the repeating unit in polymer T. (1 mark)
- Name polymer T (1 mark)
- Give one use of T (1 mark)
- Ethanol and ethanoic acid react according to the following equation under condition M and process N to form product Z.
CH3 CH2 OH (l) + CH3 COOH (aq) → Z (l) + H2O (l)
Name:- Condition M . (½ mark)
- Product Z . (½ mark)
- Draw the structural formula of product Z. (1 mark)
- State any 1 difference between the above reaction and that of an hydroxide and an acid. (1 mark)
- Butane is often used as the main component in domestic gas fuels. Calculate it’s heating value ( H = 1, C = 12, HC (C4H10) = 2877.0 k Jmol-1 ) (1 mark)
- The diagram below is a set-up to prepare ethyne gas.
- The flow chart below shows the extraction of zinc. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
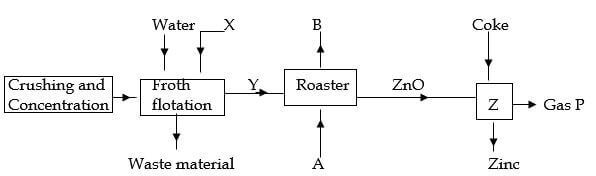
-
- Identify substance X . (1 mark)
- Give one waste material of the froth flotation process. (1 mark)
- Identify substances A and B.
A (½ mark)
B (½ mark) - Write equation for the reaction taking place in the roaster. (1 mark)
- Identify gas P and write an equation for it’s formation. ( 1 ½ marks)
- Use the standard electrode potentials given below to answer the questions that follow.
Half reactions Electrode potential, Eθ (V)
D+ (aq) + e- D (s) + 0.80
E2+ (aq) + 2e- E (s) + 0.34
F 2+ (aq) + 2e- F (s) -0.13
G 2+ (aq) + 2e- G (s) -0.76- Construct an electrochemical cell that will produce the lowest emf. (3 marks)
- Calculate the emf of the cell constructed in (i) above. (1 mark)
- From the half reactions listed in the table in (b) above select strongest oxidizing agent. (½ mark)
-
-
- Fractional distillation of liquid air is mainly used to obtain nitrogen and oxygen.
- Name one substance that is used to remove carbon (IV) oxide from the air before it is changed into liquid. (1 mark)
- Describe how nitrogen gas is obtained from the liquid air.
(Boiling points nitrogen = -196ºC, Oxygen = -183ºC ) (3 marks)
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow.
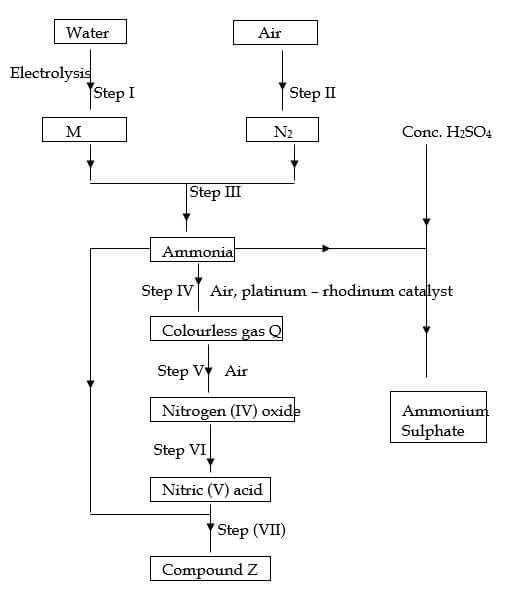
- Name substance M . (1 mark)
- Identify gas Q (1 mark)
- State one use of compound Z (1 mark)
- A fertilizer manufacturing industry uses 1400dm3 of ammonia gas per hour to produce ammonium sulphate. Calculate the amount of ammonium sulphate produced in kg for one day if the factory operates for 18 hours.
( N = 14, H = 1, S = 32, O = 16, 1 mole of gas = 24dm3 ) (3 marks)
- Fractional distillation of liquid air is mainly used to obtain nitrogen and oxygen.
- The chart below represents the main steps in the large-scale manufacture of sodium carbonate.
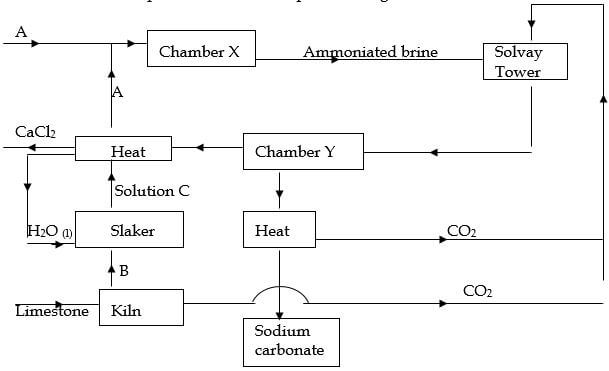
- Name substances A and B.
A . (1 mark)
B . (1 mark) - Write down the chemical equation leading to formation of C. (1 mark)
- A stream of cold water is made to circulate around chamber X. What does this suggest about the reaction taking place. (1 mark)
- Name the process that takes place in chamber Y. (1 mark)
- State any 2 by-products recycled in the process. (2 marks)
- In an experiment, wood charcoal was mixed with concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid in a test-tube. The mixture was then placed over a Bunsen-burner flame for some time.
- Write down the chemical equation of the reaction that takes place. (1 mark)
- State the property of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid investigated in (i) above. (1 mark)
- Mention any 2 uses of sodium carbonate. (1 mark)
- Name substances A and B.
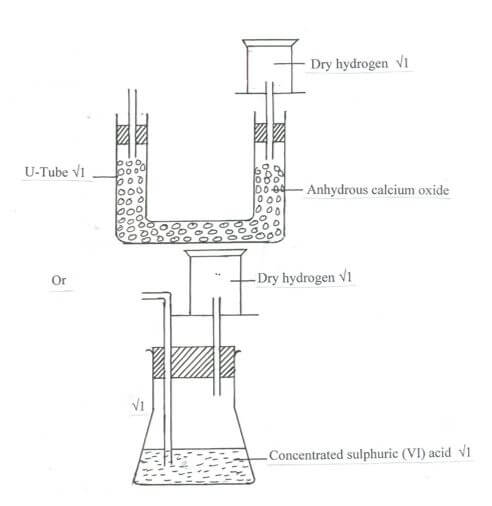
- The set up below shows the reagents that can form hydrogen gas in a laboratory.
- Complete the diagram to show how a dry sample of hydrogen gas can be collected. (3 marks)
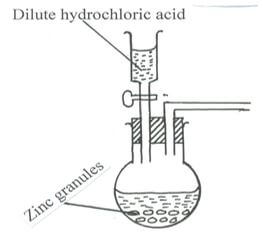
- Write the chemical equation for above reaction. (1 mark)
- Why is it not advisable to use calcium in this method to prepare hydrogen? (1 mark)
- Why is it advisable to discard the first jar of the gas collected? (1 mark)
- The set-up below was used to investigate the properties of hydrogen gas.
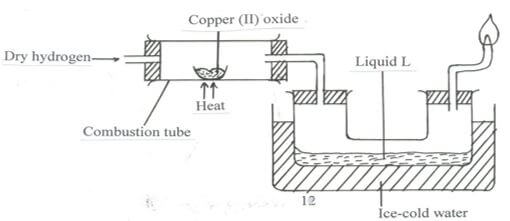
- State the observation made in the combustion tube. (1 mark)
- Write down the equation leading to formation of liquid L. (1 mark)
- What property of hydrogen is being investigated? (1 mark)
- Why is potassium oxide not used to investigate this property of hydrogen gas. (1 mark)
- Hydrogen gas is used in hydrogenation of oils. What do you understand by the term hydrogenation? (1 mark)
- Give any 2 other industrial uses of hydrogen gas. (2 marks)
- Complete the diagram to show how a dry sample of hydrogen gas can be collected. (3 marks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- B – 2 : 8 ½
D – 2 : 8 : 8 ½ -
- D ½
- E ½
- Atomic radius of B is larger 1 than that of C. C has more protons. The outer energy level electrons are pulled 1 strongly to the nucleus reducing the atomic size.
-
- Element B has stronger metallic 1 bond ( has more delocalized electrons ) than A, hence higher amount of heat 1 energy is needed to break the bond.
- 2A(s) + 2H2O (l) → 2AOH (aq) + H2 (g)
- Reject fully if unbalanced
- Award ½ mk if states are missing or any one state is wrong.
- Add water ½ to the mixture and stir.
Filter ½ to obtain lead (II) sulphate as ½ residue and sulphate of E as filtrate
Dry the residue ½ to obtain lead (II) sulphate.
Evaporate ½ the filtrate to dryness ½ to obtain the solid sulphate of E.
- B – 2 : 8 ½
-
-
- The energy change in converting reactants to products is the same regardless of the route by which chemical change occur.
- 2CO2 (g) + 3H2O (g) → C2H6 (g) + 7/2 O2 (g) ΔH = + 1560 kJmol-1
2C (s) + 2O2 (g) → 2CO2 (g) ΔH = -788 kJmol-1
+ 3H2 (g) + 3/2 O2 (g) → 3H2O (g) ΔH = -858 kJmol-1
2C (s) + 3H2 (g) C2H6 (g) ΔHθf = -86 kJmol-1
OR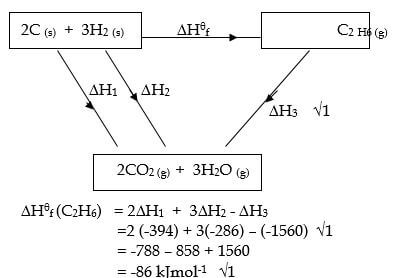
-
- Manganese (IV) oxide
- 2H2O2 (aq) → 2H2O (l) + O2 (g)
-
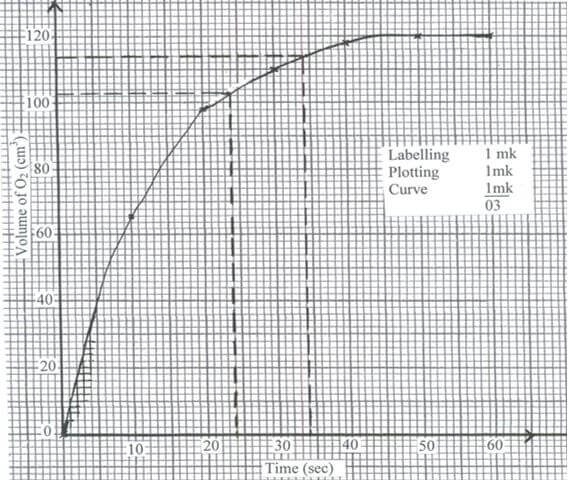
- Average rate = 114 – 103 = 11 = 1.1 ± 0.1cm3 s-1
34 – 24 10
Missing units in the answer penalize ½ mk on correct answer. - The reactant have been used up
-
-
-
- Calcium (II) carbide ½
- CaC2 (s) + 2H2O (l) → Ca (OH)2 (aq) + C2H2 (g)
- Ethyne gas is insoluble in water
- A mixture of oxygen and ethyne gas forms oxyacetylene flame used for welding and cutting of metals
-
- 1,1,2,2-tetrabromoethane ½
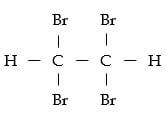
-
- Hydrogen gas ½
- Hydrogen chloride (HCl) ½
-
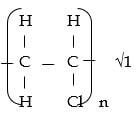
- Polychloroethane
-
- Making crates and boxes
- Making plastic ropes
- Making water pipes
- Insulation for electrician wires
Any 1 correct use
- 1,1,2,2-tetrabromoethane ½
-
- Concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid ½ Reject sulphuric (VI) acid
- Ethylethanoate ½
-
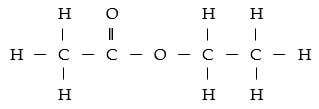
- Esterification Neutralization
Reaction is slow - Reaction is fast
Reaction is reversible - Reaction is irreversible
Forms esters(molecular) - Forms salts (ionic)
Any 1 correct each 1 mark - Heating value = molar enthalpy of combustion
Molar mass of compound
= 2877 kJmol ½
58g
= 49.603 kJ g-1 ½
-
-
-
- Frothing agent / vegetable oil
- Sand / clay or galena (PbS) or slurry
- A – Air ½
B – Sulphur (IV) oxide ½ - 2ZnS (s) + 3O2(g) → 2ZnO(s) + 2SO2 (g)
- Carbon (II) oxide ½
ZnO (s) + C (s) → Zn (s) + CO (g)
-
-
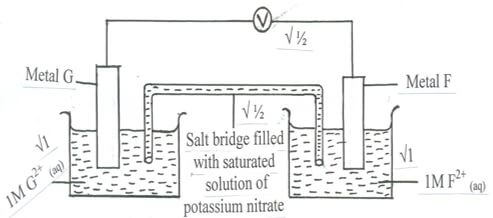
- Emf of cell = 0 - 0.13 – ( -0.76)
= -0.13 + 0.76 ½
= + 0.63V ½ - Ag+ (aq) ½
-
-
-
-
- Potassium hydroxide solution 1 (KOH) or sodium hydroxide solution (NaOH)
- Heat / boil the liquid air // warm / raise the temperature of liquid air.
Nitrogen comes out first because it has a lower boiling point than oxygen.
NB: If word heating / boiling / warming not mentioned penalize fully.
-
- Hydrogen (H2)
- Nitrogen (II) oxide 1 Reject nitrogen monoxide
- Fertilizer 1 Reject manufacture of fertilizers
- 2NH3 (g) + H2SO4 (l) → (NH4)2 SO4 (s) ½
Number of moles of NH3 used per day = 1400 x 18 = 1,050
24
Mole ratio NH3 : (NH4)2SO4 = 2 : 1
Moles of (NH4)2SO4 produced = 1050 = 525 ½
2
4
Mass of (NH4)2SO4 produced per day = 525 x 132 = 69.3kg
1000
-
-
- A – Ammonia
B – Calcium oxide - CaO (s) + H2O (l) → Ca(OH)2 (aq)
- ) Reaction is exothermic
- Filtration
- Ammonia
Carbon (IV) oxide -
- C (s) + 2H2SO4 (l) → CO2 (g) + 2H2O (l) + 2SO2 (g)
- Oxidising property
-
- Manufacture of glass
- Softening of hard water
- Making of soaps and detergents
- For making sodium hydrogen carbonate used in baking soda and fire extinguishers
Any 2 correct answers each ½ mk
- A – Ammonia
-
-
- Zn (s) + 2HCl (aq) → Zn Cl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
- Reaction between calcium and acid is explosive and dangerous.
- It contains impurities i.e. other gases e.g nitrogen, neon present in air
-
- Copper (II) oxide changes from black ½ to brown solid ½ .
- CuO (s) + H2 (g) → Cu (s) + H2O (l)
- Reducing property
- Potassium cannot ½ be displaced from it’s oxide by hydrogen because it is high ½ in the reactivity series.
- It is hardening of oils to form fats 1 by passing hydrogen gas in presence of nickel catalyst.
-
- A mixture of oxygen and hydrogen burns to produce oxy-hydrogen flame used in welding and cutting of metals.
- Manufacture of ammonia is haber process.
- Manufacture of hydrochloric acid
- As a fuel cells
- As a fuel in rockets
Any 1 each 1 mark
-
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Sunrise 2 Evaluation Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
