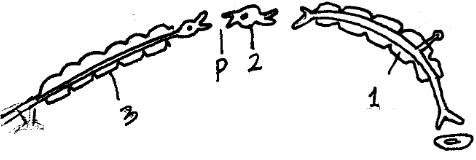- This paper consists of two sections, section A and section B. Answer ALL the questions in section A in the spaces provided on the question paper. In section B, answer question 6 (compulsory) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question 8
- Be brief and precise. Unnecessary information and wrong spellings especially of technical terms shall be penalized
- All answers must be written in the English language
SECTION A
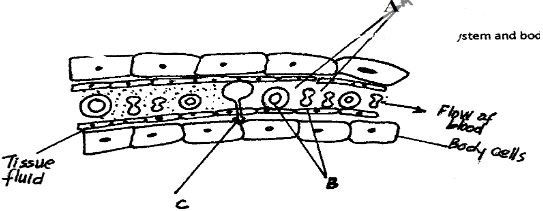
- The diagram below shows the exchange site between circulatory system and body cells.
- State two adaptations of the capillaries. (2mks)
-
- Name the blood cells labeled B. (1mk)
- State the gas that diffuses from B to the tissue cells. (1mk)
- State two functions of the part labeled A. (2mks)
- Name the blood vessel with the highest concentration of;
- Oxygen. (1mk)
- Urea. (1mk)
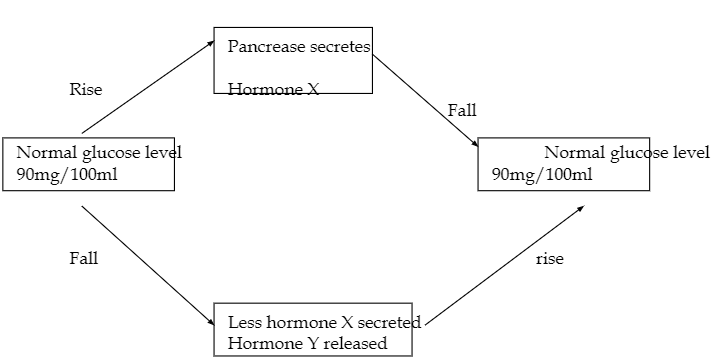
- The diagram below shows how blood glucose in mammalian body is regulated.
- Name the hormone X and Y (2mks)
- State two ways by which hormone X lowers glucose level in the blood when it rises above 90mg/100ml (2mks)
- Name the organ that produces hormone Y (1mk)
- Suppose there is deficiency of hormone X, state the disease the person would suffer from (1mk)
- Explain how the disease mentioned in (d) above can be controlled. (2mks)
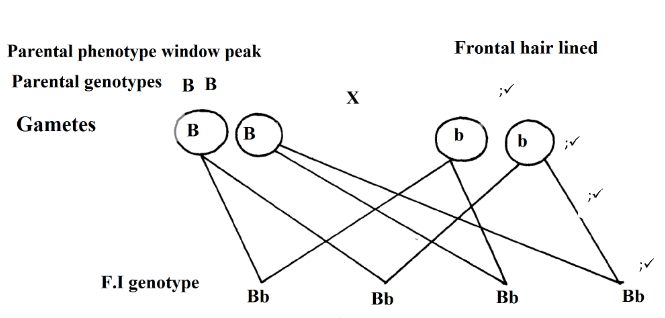
- In human beings, a downward pointed frontal hairline (“windows peak”) is a heritable trait. A person with windows peak always has at least one parent who has his trait; whereas persons with frontal hairline may occur in families in which one or even both parents have windows peak. Using B and b to symbolize genes for this trait.
- Determination the f1 generation if a homozygous windows peak male parent is married to a Homozygous frontal hairline female parent. (4mks)
- State two causes of variations. (2mks)
- Name two examples of discontinuous variation. (2mks)
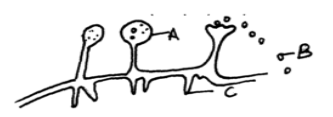
- The drawing below represents a mature bread mould (rhizopus).Study it and answer the questions which follow.
- Name the structures labeled A, B and C. (3mks)
- Identify the type of asexual reproduction represented in the diagram (1mk)
- Give one function of structure C. (1mk)
- Define the term fertilization. (1mk)
- Compare an ovum cell and a zygote. (2mks)
- The diagram below shows three different types of neurons along a reflex.
- Identify the neuron labeled 1, 2 and 3 (3mks)
- Using arrow show the direction of impulse transmission on the diagram. (1mks)
- Name the part of the spinal cord where the cell bodies of neuron 2 and 3 are located. (1mk)
- Describe the transmission impulses across the part labeled P. (3mks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6(compulsory) in the spaces provided and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after 8.
- During germination and growth of a cereal, the dry weight of endosperm, the embryo and the total dry weight were determined at two day intervals. The results are shown in the table below:
Time after planting (days) Dry weight of endosperm (mg) Dry weight of embryo (mg) Total dry weight (mg) 0 43 2 45 2 40 2 42 4 33 7 40 6 20 17 37 8 10 25 35 10 6 33 39 - Using the same axes, draw graphs of dry weight of endosperm, embryo and the total dry weight against time. (7marks)
- What was the total dry weight on day 5 (1mark)
- Account for
- Decrease in dry weight of endosperm from 0 to 10 (2marks)
- Increase in dry weight of embryo from day 0 to day 10 (2marks)
- Decrease in total dry weight from day 0 to day 8 (1mark)
- Increase in total dry weight after day 8 (1mark)
- State two factors within the seed and two outside the seed that cause dormancy
- Within the seed. (2marks)
- Outside the seed (2marks)
- Give two characteristics of meristematic cells (2marks)
- Explain how abiotic factors affect plants. (20marks)
- Discuss eye accommodation. (10mks)
- Discuss the process of hearing in man. (10mks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Adaptations of capillaries.
- Their walls are made up of an endothelium only which allows only part of the blood to move into the intercellular spaces;✔
- They are numerous thus creating a large S.A for exchange of materials;✔
- Have narrow lumen that maintains high blood pressure;✔
- Have sphincter muscle at the arteriole end enabling regulation of blood flow;✔
-
- Blood cells labeled B.
- Red blood cells;✔
- Oxygen gas;✔
- Blood cells labeled B.
-
- Transport of food nutrients;✔Metabolic wastes;✔antibodies involved in defense against diseases;✔
- Distribution of body heat;✔
-
- Pulmonary vein;✔
- Hepatic vein;✔
- Adaptations of capillaries.
-
- X – Insulin;
-
Y – Glucagon;
- X – Insulin;
-
-
-
Stimulates conversion of glucose to glycogen/fats;
-
Oxidation of glucose to release energy;
-
-
Pancreas;
-
Diabetes mellitus;
-
Regular insulin injection; with controlled diet and exercise;
-
-
- Gene for the window peak is dominant over gene for frontal hair lined.
Accept pun net square but genotypes must be present in order to score. -
- Gamete formation-independent assortment;✔
- Crossing over;✔
- Fertilization;✔
- Mutations;✔
-
- Tongue rolling;✔
- Sex;✔
- ABO (blood group);✔
- Free ear lobe and attached one;✔
- Pawpaw (male and female pawpaw);✔
- Are genes located on the sex chromosomes and are transmitted together with those that are transmitted together with those that determine sex;✔
- Gene for the window peak is dominant over gene for frontal hair lined.
-
-
- A-Sporangium;✔
- B-Spore; ✔(rej; spores)
- C-Rhizoid; ✔(rej. Rhizoids)
- Sporulation/spore formation;✔
- Absorption of water and mineral nutrients from decaying materials;✔
- Process by which female and male gamete nuclei fuse to form a diploid zygote;✔
-
OvumOvum Zygote Haploid Diploid ✔ Lower mass Higher mass ✔
-
-
-
- Sensory /Afferent Neuron;✔
- Relay/intermediate Neuron;✔
- Motor/Efferent Neuron;✔
-
- Grey matter;✔
- Impulse reaching the dendrite end of relay neuron causes the synaptic vesicle to release a acetylcholine;✔(transmitter substance) that diffuse across the cliff ;✔and causes the depolarization of the motor neuron;✔
-
-
- Graph
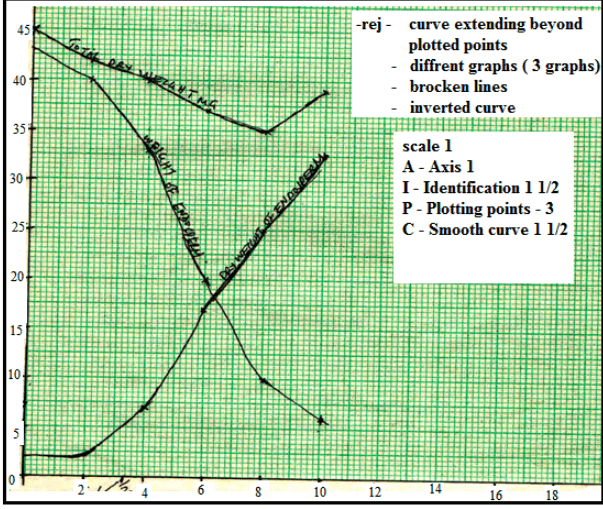
- Total dry weight 38.5mg; acc ±0.5
-
- Hydrolysis of starch into simple sugars/glucose which are translocated to the embryo;
Oxidation/respiration of( simple sugars) to the embryo;
CO2/energy/heat; acc water vapor - New cells/tissues materials are synthesized (from proteins);bring about growth of embryo
- The rate of respiration is faster than that of synthesis of materials for growth;
- First leaf carried out photosynthesis; (leading to growth
- Hydrolysis of starch into simple sugars/glucose which are translocated to the embryo;
-
-
- Presence of absissic acid; (ABA)
- Presence of germination inhibitors;
- Embryo not fully developed/immature embryo;
- Absence of hormones/enzymes that stimulate germination;
Acc inactivity of hormones/enzymes inhibitors; - Impermeable seed coat;
Acc for germination hormones such as cytokines, gibberellins;
-
- Unsuitable temperatures/lack of suitable/unfavorable temperatures; absence of light; lack of O2 Rej lack of air
- Lack of water
-
-
- Dense cytoplasm; thin cell walls
- Absence of vacuoles (cell sap)
- Graph
-
- Wind;
- Windy conditions transpiration;
- Wind disperses fruits/seeds/spores; an agent of pollination;
- Temperature;
- Change in temperature affect rate of photosynthesis/other biochemical reactions/ metabolic/enzymatic reactions; rise in temperature rises transpiration.
- Light;
- (Green) plants need light for photosynthesis;
- Some plants need it for flowering;
- ome seeds (like lattice) require it for germination;
- Humidity
- When humidity is low, transpiration rate risPH
- Each plant requires specific PH to grow well;
- Acidic or alkalinity or neutraSalinity
- Plants with salt tolerant tissues (e.g. mangrove) grow in saline area; plants in estuaries adjust to salt fluctuations;
- Topography
- North falling slopes in temperate lands have more plants than south facing slopes;
- Windward side plants have stunted and distorted growth; leeward side plants are stunted/wind ward normal growth;
- Rainfall/water
- Few plants in dry areas/where rainfall is less;
- Water for germination;
- Water as a raw material for photosynthesis;
- Water as solvent for mineral salts;
- Provides turgidity;
- Water for dispersal;
- A medium of transport of plant nutrients;
- Mineral salts
- Plants thrive (grow well in soils with mineral salts)
- Plants living in soil with deficiency of particular element have special methods of obtaining it. Legumes obtain nitrogen by nitrogen fixation /carnivorous plants/insectivorous plants, carnivorous trees obtain their nutrients from mycorrhizal association;
- Wind;
-
- Accommodation is the ability of the eye to focus both far and near objects;
- For accommodation of a distant object ciway Muscles realx; creating a tension on suspensory ligametns /suspensory ligments contract; the lens become flattened otr less convex; minimizing the refractive power of lens; bringing light rays from afar object to focus on the retina;
- For a accommodation of a neat object aliany muscles contracts relaxing lesion on suspensory ligametns/sensory ligaments spherical in shape; this increase the refractive power of lens; that brings light rays from a near object to focus on the retina; funnel shaped pinna collects sound waves; and directs them to the auditory meatus/ear drum;
- Ear drum vibrates and transforms sound wave into vibrations; the vibrations core transmitted to the ear ossiclis where they are amplified and transmitted to the oral window. Vibrations front eh oral windo. Vibrations from the oral window creates pressure waves on the fluid/perlymph in cochlea; movement of fluid in cochlea causes sensory hairs to be stimulated /torched; generating an impulse; the impulse is transmitted to the brains via auditory nerve for interpretation on pitch. intensity and direction of sound;
- Accommodation is the ability of the eye to focus both far and near objects;
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Sunrise 2 Evaluation Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students