INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper has two sections A and B.
- Answer all the questions in section A, in section B answer question 6 and any other two questions.
- All answers must be written in the answer sheets provided.
For Examiner’s Use Only
|
Section |
Question |
Maximum Score |
Candidate’s Score |
|
A |
1 – 5 |
25 |
|
|
B |
6 |
25 |
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
|
Total score |
|
||
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
-
- Explain the origin of the earth and the solar system according to the Nebular cloud theory. (4mks)
- Name two other theories that explain the origin of the earth and the solar system apart from the Nebular cloud theory. (2mks)
-
- List two zones of transition in the atmosphere. (2mks)
- Give three evidences that the interior of the earth is hotter. (3mks)
-
- Define the following terms.
- River divide (1mk)
- A confluence (1mk)
- A river profile (1mk)
- List three factors that influence the formation of a river. (3mks)
- Define the following terms.
- How is an oasis formed? (4mks)
- List four characteristics of Mediterranean climate. (4mks)
SECTION B
ANSWER QUESTION 6 AND OTHER TWO QUESTION FROM THIS SECTION
Study the map of Nyeri (1:50,000) sheet 120/4 provided and answer the questions that follows
-
-
- Give the latitudinal and the longitudinal position of the south west corner of the map extract (2mks)
- Calculate the magnetic declination of the map extract (2mks)
-
- Which adjoining sheet is to the S.E of the area covered by the map? (1mk)
- What is the general flow of river Chanya (2mks)
- Give three social function of Nyeri town (3mks)
- Calculate the area of Nyeri Forest to the East of Easting 69 and North of Northing 56. (Give your answer in Kilometre squared(Km2) (2mks)
- Citing evidence from the map. Give
- Two reasons why the area is covered by the map is suitable for coffee growing (4mks)
- Two factor that favor saw milling in the area covered by the map (4mks)
- Describe drainage of the area covered by the map (5mks)
-
-
-
- What is faulting? (1mk)
- With the use of a well labeled diagram explain how a reverse fault occurs. (5mks)
- State two other types of faults apart from reverse faults. (2mks)
- Describe how a rift valley forms through tensional forces. (4mks)
- Explain three ways in which features resulting from faulting are of economic importance to man. (6mks)
- You intend to carry out a field study of the landforms around your school.
- State two hypotheses you are likely to formulate for the study. (2mks)
- Apart from dividing your class into groups, in what three other ways will you prepare for the study. (3mks)
- In what two ways is dividing the class into groups important? (2mks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between intrazonal and azonal soils. (2mks)
- Give three examples of a zonal soils (3mks)
-
- Explain four factors that influence soil formation. (8mks)
- Give two factors that determine the colour of soil (2mks)
-
- What is soil erosion. (2mks)
- Explain four ways in which vegetation prevents soil erosion. (8mks)
-
-
-
- Name a country in Africa where temperate grassland is found. (1mk)
- State four characteristics of temperate grasslands. (4mks)
-
- Explain four ways in which trees in the coniferous forests have adapted to the environmental conditions of the region. (8mks)
- You are required to carry a field study on a forest near your school. Describe the methods you would use to determine each of the following aspects of the trees in the forest.
- Age of the trees. (3mks)
- Height of the trees. (3mks)
- Tree species (3mks
-
- The figure below shows underground zones of saturation. Use it to answer question a (i)
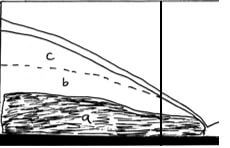
-
- Identify the zones marked a, b, and c. (3mks)
- Name four sources of groundwater. (4mks)
- Explain four ways in which groundwater is of significance to human activities. (8mks)
-
- Give two examples of lakes in East Africa that have formed due to crustal warping. (2mks)
- Describe how the process of crustal warping leads to formation of lakes. (5mks)
- State three other processes that lead to formation of lakes apart from crustal warping. (3mks)
-
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Origin of the solar system and the earth according to the Nebular Cloud Theory
- There existed a big cloud (Nebular of hot gases and dust)
- This cloud which was rotating at a very high speed flattened into a disk due to centrifugal force.
- Very hot materials concentrated at the centre of the rotating cloud and led to the formation of the sun
- Some masses of gases and dust were thrown off as the cloud continued to rotate
- The particles consolidated, cooled and contracted to form planets
1 x 4 = 4mks
- Other theories
- The twin star theory/ big bang
- The passing star theory
- Biblical/ creation theory
1 x 2 = 2mks
- Origin of the solar system and the earth according to the Nebular Cloud Theory
-
- Transitional zones of the atmosphere
- Tropopouse
- Stratopause
- Mesopause
1 x 2 = 2mks
- Evidences that the interior of the earth is hotter
- During volcanic eruptions hot material (magma) are ejected onto the surface
- Occurrence of hot springs on the ground
- Progressive increasing heat experienced as mines and borings get deeper
- The molten state of rocks in the mantle
1 x 3 = 3mks
- Transitional zones of the atmosphere
-
- Defining
- River divide – It is a ridge line/ hill ground that separates two or more river basins
- A confluence – The point at which a tributary joins the main river
- A river profile – This is the longitudinal cross section of a river from the source to the mouth.
1 x 3 = 3mks
- Factors that influence the formation of a river
- Vegetation cover
- Climate
- Nature of rocks
- The degree of slope
- Land use systems e.g. irrigation
1 x 3 = 3mks
- Defining
- How an oasis forms
- A pre-existing depression is deepened by eddy action/ deflation
- Gradually the depression is excavated through wind abrasions
- The surface is lowered until it reaches the water bearing rock/ aquifer / table
- Water oozes out of the ground and collects in the depression to form an oasis
1 x 4 = 4mks
- Characteristics of mediterranean climate
- Summers are hot with temperatures of about 21ºC
- Winters are mild/ cold with temperatures of about 11ºC
- Mean annual rainfall moderate varies between 500 – 900 mm with most of it falling in winter
- The region mainly experiences cyclonic rainfall
- Trade winds are offshore in summer and onshore westerlies dominate in winter
- Hot and cold local winds are common 1 x 4 = 4mks
-
-
- Give the latitudinal and the longitudinal position of the south west corner of the map extract (2mks)
- Latitude: 0º 30’S
- Longitude 36º45’E
- Calculate the magnetic declination of the map extract (2mks)
- 1º31
- Give the latitudinal and the longitudinal position of the south west corner of the map extract (2mks)
-
- Which adjoining sheet is to the S.E of the area covered by the map? (1mk)
- Fort Hall(Muranga)
- What is the general flow of riverChanya
- Eastwards / West to East 1x2=2mk
- Give three social function of Nyeri town
- Educational centre
- Religious centre
- Health centre
- Recreational centre
- Adminisrative centre 1x3=3mks
- Which adjoining sheet is to the S.E of the area covered by the map? (1mk)
- Calculate the area of Nyeri Forest to the East of Easting 69 and North of Northing 56. (Give your answer in Kilometresquared(Km2) (2mks)
- Complete = 2
- Incomplete = 20
Area =2+20/2 = 12Km2
- Citing evidence from the map. Give
- Two reasons why the area is covered by the map is suitable for coffee growing
- The area receive high rainfall suitable for crop farming as evidenced by many permanent rivers/forest vegetation.
- Gentle sloping landscape for proper drainage as evidenced by widely spaced contours
- High altitude above 1500 metres that provides cool condition suitable for coffee farming
- Availability of transport as evidenced by many roads
- Availability of labor evidenced by dense settlements 1x4=4mks
- Two factor that favor saw milling in the area covered by the map
- Presences of extensive forest to provide raw materials
- Availability of transport by roads for transporting sawn timber and logs
- Presence of many settlements which provide markets for products 1x4=4mks
- Two reasons why the area is covered by the map is suitable for coffee growing
- Describe drainage of the area covered by the map
- The main drainage features are rivers
- There are many permanent rivers
- Most of the rivers form dendritic drainage pattern
- The main rivers in the area are the river Chanya and Ambani
- Most of the river flow from Abardere forest
- Most of the rivers flows to the East of the area covered by map 1x5=5mks
-
-
-
- What is faulting
- It is the fracturing/ cracking of crustal rocks 1
- Formation of reverse fault
- Formed when crustal rocks are exposed to compressional forces
- A reverse fault develops
- Continued pushing of compressional forces lead tone block being pushed over the other to form a reverse fault
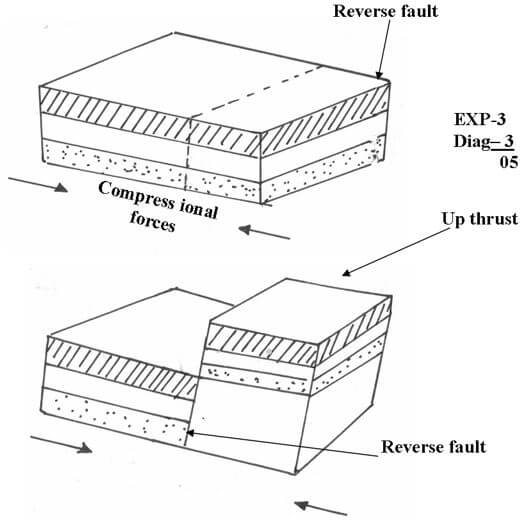
- Other types of faults
- Normal faults
- Shear/ tear/ slip/ strike slip/ wrench/ trancurrent
- Thrust fault/ over throw
- Anticlinal faults 1 x 2 = 2mks
- What is faulting
- How a rift valley forms through tensional forces
- Layers of rocks in a region are subjected to tensional forces
- Lines of weakness develop, resulting in the development of normal faults
- As the forces pull the side blocks away, the middle block sinks
- The block that has sunk forms the floor of the rift valley
1 x 4 = 4mks
- Economic importance of features formed through faulting
- Block/ horst mountains are a source of rivers which provide water for HEP production e.t.c
- Rift valley formation has led to the exposure of minerals e.g. diatomite which are mined on the rift valley floor
- Rift valley lakes formed through faulting are important fishing grounds
- Faulted features provide scenery which promote tourist industry
- Block mountains attract rainfall which favour agriculture/ settlement
2 x 3 = 6mks
-
- Hypotheses
- Most landforms near my school have resulted from faulting
- Presence of block mountains around my school has influenced tourism
- Mountains are the dominant landforms around my school
Any relevant points 1 x 2 = 2mks
- Other ways of preparing for the study
- Seeking permission from relevant authorities
- Conducting a pre-visit/ reconnaissance
- Preparing a questionnaire
- Holding discussions in class
- Preparing a working schedule
- Reading through relevant books
- Gathering the required tools 1 x 3 = 3mks
- Importance of dividing into groups
- It eases congestion/ overcrowding in areas they have to visit
- It helps in ensuring that required data is collected within the time frame given
- It creates order when carrying out the field study
- Ensures that everybody is involved in the study
1 x 2 = 2mks
Total = 25 marks
- Hypotheses
-
-
-
- Difference between intrazonal and azonal soils
- Intrazonal soils are those soils that are formed under poor drainage conditions e.g. water logged areas whereas azonal soils are those soils that have not had adequate time to develop. They are thus immature soils.
- The difference must come out clearly to score
- Examples of azonal soils
- Mountain/ scree soils
- Alluvial soils
- Glacial soils
- Loess
- Volcanic soils recently formed
- Difference between intrazonal and azonal soils
-
- Factors that influence soil formation
- Parent rockF
- Nature of the rock influences the rate of weathering EX hard rocks weather slowly while soft rocks weather fast
- The rock determines the soil texture e.g. large grained rocks produce large grained soils
- Living organismsF
- They assist in the breaking down of rocks through burrowing EX
- The roots of bigger plants break up the soil as they grow and allow water to pass through
- Topography
- It determines the rate of weathering e.g. steep slopes encourages high rate of weatheringEX
- It influences soil depth e.g. gentle slopes have deep soils while steep slopes have thin soils
- It influences soil drainage e.g. where land is flat soils are poorly drained
- ClimateF
- Affects the rate and type of weathering that takes place EX
- Determines the rate of leaching
- Elements of climate i.e. Temperature accelerates weathering leading to soil formation
- TimeF
- For soil to reach maturity, time is requiredEX
F = max 04 EX = max 04 Total = 8mks
- For soil to reach maturity, time is requiredEX
- Parent rockF
- Type of parent material
- Chemical composition of the soil
- Drainage of the area
- Factors that influence soil formation
-
- What is soil erosion
- The process by which the top soil is removed/ detached and carried away by various agents at a rate that is faster than it is being replaced by the soil forming processes
- Way vegetation prevents soil erosion
- The leaf cover helps to reduce the force of raindrops which would otherwise loosen and remove soil particles if the force is not checked
- The rate of infiltration of rainwater into the soil is increased by vegetation cover thus reducing surface run off
- Plant cover breaks the force of wind at the ground level and reduces the transportation of soil particles/ reduces the evaporation which would dry and loosen the soil
- Decayed vegetation matter provides humus which binds the soil particles together
2 x 5 = 10mks
Total = 25 marks
- What is soil erosion
-
-
-
- A country in Africa where temperate grassland is found
- South Africa
- 4 characteristics of temperate grasslands
- Treeless except along water courses
- Grass is short and tough in the drier areas
- Grass is tall in the moist areas
- Grass withers in Autumn and dies in Winter
- Grass sprout in springs
- Grass is nutritious
1 x 4 = 4mks
- A country in Africa where temperate grassland is found
-
- Ways in which trees in the coniferous forests have adapted to the environmental conditions
- The trees have a conical shape and flexible branches to allow snow to slide off easily thus minimizing damage to the trees
- Most trees are evergreen so as to have maximum utilization of sunlight during the short drowing season
- Needle like leaves help to reduce the loss of water from the trees in winter when there is no moisture to be absorbed from the soil
- The tree trunks are flexible to enable them sway without breaking during the strong winter winds.
- The leaves have a tough waxy skin which protects them from the winter cold
- The trees have a widely spread root system for utilizing moisture from the top soil since most of the time the subsoil is frozen 2 x 4 = 8mks
- Factors that determine zoning of mountain vegetation
- Altitude
- Aspect
- Slope
- Temperature
- Moisture availability
1 x 3 = 3mks
- Ways in which trees in the coniferous forests have adapted to the environmental conditions
-
- Methods likely to be used in determining:
- Age of trees
- Asking the local people / forest officer / when the trees may have been planted
- Observing the rings on the tree stump and counting them to find out the age of the trees
- By estimating the age of trees
- Refering to available records to know when the trees were planted
1 x 3 = 3mks
- Height of trees
- By estimating the height
- By measuring the exact height of samples of trees and generalising
- Calculate using the ratio of height of near short object in relation to height of its, relate to the shadow of the tree in relation to its height.
1 x 3 = 3mks
- Tree species
- By walking through the forest observing and noting the various species
- By interviewing the local people / forester
- By reading through available records
1 x 3 = 3mks
Total = 25 marks
- Asking the local people / forest officer / when the trees may have been planted
- Age of trees
- Methods likely to be used in determining:
-
-
-
- The zones marked
- a – zone of permanent saturation/ phreatic zone
- b – zone of intermittent saturation
- c – zone of non – saturation 1 x 3 = 3mks
- Sources of ground water
- Rain water
- Lake/ sea water
- Melt water
- Magmatic/ plutonic water 1 x 4 = 4mks
- The zones marked
- Significance of ground water
- Sources of rivers – Many springs are sources of river that provide water for industrial / domestic use
- Ground water is used for irrigating the land all over the world thus promotes agriculture
- Ground water influences the development of settlements
- Hotsprings are a tourist attraction
- At the mouths of many hotsprings, valuable mineral salts are deposited and people exploit them for economic gain 2 x 4 = 8mks
-
- Lakes that have formed due to crustal warping in East Africa
- Lake Victoria
- Lake Kyoga
- Lake Wamala
- Lake Kachira
1 x 2 = 2mks
- How crustal warping leads to the formation of lakes
- Earth movements cause crustal downwarping
- This leads to the formation of a basin like depression
- Uplifting of landmasses around the depression diverted the flow of rivers into the depression causing reversed drainage
- Deposition onto the depression resulted in to further downwarping
- Water from the rivers accumulated in the depression to form a lake
1 x 5 = 5mks
- Other processes that lead to formation of lakes
- Faulting
- Vulcanicity
- Erosion
- Deposition
- Meteorite falling
- Human activities
1 x 3 = 3mks
Total = 25 marks
- Lakes that have formed due to crustal warping in East Africa
-
Download Geography Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Sunrise 2 Evaluation Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
