Instructions for candidates
- Answer any five questions in the spaces provided.
For Examiner’s Use Only
|
Question No |
1a |
1b |
2a |
2b |
3a |
3b |
4a |
4b |
5a |
5b |
6a |
6b |
|
Marks |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
QUESTIONS
-
- Explain negative effects of any five macro environmental factors on a business. (10 marks)
- Explain five uses of National Income statistics to an economy. (10marks)
-
- Explain any five features of a good filing system. (10 marks)
- The following transactions relate to Koko Traders for the month of September 2010.
Sept. 2 Sold goods on credit to Chui Shs. 12,000 and Jane Shs.16,000
Sept. 8 Bought goods on credit from Shah Traders Shs. 40,000.
Sept. 12 Chui returned goods worth Shs. 2,000.
Sept. 15 Purchased goods on credit from Tanui Shs. 34,000 and Peter Shs. 31,050.
Sept. 20 Goods worth Shs. 6,000 were returned to Shah Traders and goods
worth Shs. 3,000 to Tanui.
Sept. 23 Goods sold on credit to Chui Shs. 8,000, Tom Shs. 11,000 and Joseph
Shs. 13,000.
Sept. 27 Goods returned by Tom Shs. 2,000.
Required:
Prepare the relevant Journals and balance them off. (10marks)
-
- Explain five principles of insurance. (10marks)
- Explain five problems a developing country will encounter in the implementation stage of development planning. (10marks)
-
- Kenya experienced a general increase in prices of goods and services due to Covid-19 pandemic. Explain five negative effects of this to the Kenyan economy (10 marks)
- Explain five causes of unfavourable balance of payment for most developing countries. (10 marks)
-
- With the aid of a suitable diagram, explain the effects of a decrease in supply on the equilibrium price and quantity of a product (10 marks)
- Explain five roles of central bank in an economy (10 marks)
-
- Explain five Benefits of an enclosed office plan. (10 marks)
- On 1st July, 2016 Ekalale Traders had cash in hand sh. 85,200 and cash at bank sh.40,000 (Cr). During the month, the following transactions took place:
July
2 cash sales sh. 42,630 was paid directly into the bank
5 Received a cheque of sh. 14,100 from Ruth in full settlement of her account.
9 Bought goods worth sh. 26,240 cash.
12 Cash sales sh. 42,950 payment received by cheque
15 Paid Ndoigo’s account of sh. 25,000 in cash less 5% cash discount.
17.Paid wages sh. 24,000 in cash
18 Withdrew sh. 16,000 from bank for office use.
20 Bought stationery sh.850 cash
22 Cheque received from Ruth was dishonoured.
28 Received a cheque of sh. 9,500 from Kemamo after he deducted a 5% cash discount
31 All cash was banked except sh.10,000.
Required:
Prepare a three column cash book duly balanced. (10 marks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Negative effects of any five macro environmental factors on a business
- Demographic population/population changes – Declining population leads to reduced demand for a product
- Economic factors (money) – if the people’s purchasing power declines, demand for the products may decline.
- Social cultural factors – if the customers/ values/beliefs shared by a society protest a given product less of it will be ought.
- Political factors – Political instability may lead to destruction of business property
- Legal factors such/changes in laws and regulations – Legislations against a business may lead to its closure
- Physical factors – Adverse climate may lead to reduced supply of raw material
- Competitors – increased competition may take away business customers leading to reduced sales
- Intermediaries should be carefully chosen and monitored otherwise the goods and services produced by the business may fail to reach the intended users leading to loss of market
- Technological changes – Outdated technology leads to production of relatively low quality products hence reduced demand..
- Explain five uses of National Income statistics to an economy. (10marks)
- Indicator/measure of standard of living/ an improvement/increase in national incoming indicates higher/improved standards of living/improved welfare.
- Comparing standards of living between countries. Those with higher national income are believed to have higher standards of living.
- Measure/indicator of economic growth/assessing performance of the economy over time. The period with higher national income is considered better.
- Economic planning by comparing performance in different sectors for better /efficient allocation of resources.
- Attract investment/for investment decision. Data obtained can be used by entrepreneurs to make decisions on which sector to invest in.
- Provide information on distribution/contribution of national income. This helps the government to address income disparities. Calculate/determine per capita income by dividing national income by population. 5x2=10
- Negative effects of any five macro environmental factors on a business
-
- Features of a good filling system
- Cost effectiveness – cheap /economical in terms of installation and maintenance
- Safety – ensure documents are secured against theft/damage
- Compactness – ensure minimal sue of space
- Simplicity – easy to understand
- Accessibility – ensure easy location/retrieval of documents
- Elasticity – easy to expand whenever need arises
- Confidentiality – guard against unauthorized access to documents
-
Sales Journal
Purchases JournalDate
Particulars
Inv. No.
L.F
Amount
2010
Sept 2
2
23
23
23
Chui
Jane
Chui
Tom
Joseph
Total credit sales to be posted to sales a/c (cr) in the general ledger.
SL1
SL2
SL1
SL3
SL3
12,000P
16,000P
8,000P
11,000P
13,000P
60,000P
Sales Returns JournalDate
Particulars
Inv. No.
L.F
Amount
Sept 8
15
15
Shah Traders
Tanui
Peter
Total credit purchases to be posted to purchases a/c (Dr) in the general ledger.
PL1
PL2
PL3
40,000
34,000
31,050
105,050
Purchases Returns JournalDate
Particulars
Inv. No.
L.F
Amount
Sept 12
27
Chui
Tom
Total Sales returns to be posted to sales return a/c (Dr) in the general ledger.
SL1
SL3
2,000
2,000
4,000
Purchases journalsDate
Particulars
Inv. No.
L.F
Amount
Sept 20
20
Shah Traders
Tanui
Total Purchases returns to be posted to purchases return a/c (Cr) in the G.L
PL1
PL2
6,000
3,000
9,000
Sales journalsDate
Details
Invoice Number
Ledger Folio
Amount Kshs.
2010
May 1
1
1
6
6
6
18
Ben
Martha
Atuti
Masha
Martha
Saudoka
Dume
Total posted to purchases A/C (Dr)
25,000
30,000
40,000
10,000
35,000
50,000
70,000
260,000
Purchase returns journalsDate
Details
Invoice Number
Ledger Folio
Amount Kshs.
2010
May 4
4
8
8
8
26
Kola
Otieno
Kaka
Kola
Kaki
Kola
Total posted to sales A/C (Dr)
16,000
20,000
60,000
26,000
45,000
54,000
221,000
Date
Details
Invoice Number
Ledger Folio
Amount Kshs.
2010
May 13
13
13
Ben
Masha
Saudoka
Total posted to purchases returns A/C (Dr)
4,000
1,500
3,000
8,500
Sales returns journals
Date
Details
Invoice Number
Ledger Folio
Amount Kshs.
2010
May 22
22
31
31
Kola
Otieno
Kaki
kola
Total posted to purchases returns A/C (Dr)
1,000
2,400
2,000
4,000
9,400
- Features of a good filling system
-
- Explain five principles of insurance. (10marks)
- Principle of utmost good faith.
- This principle requires a person taking out insurance cover to disclose all the necessary information to the insurer when filing proposal form.
- Principle of insurable interest
- One should only insure property he/she stands to suffer a direct financial loss in case the risk insured against occurs.
- Principal of indemnity
- This aims at compensating the insured and not benefiting from the misfortune. It is putting one in original financially state before risk occurred.
- Principal of proximate cause.
- This states that for the insured opt be compensated there must be a very close relationship between loss suffered and risk insured against.
- Principle of subrogation
- Under this principle, whatever remains of the property insured after the insured has been compensated becomes the property of the insurer.
- Principle of contribution
- This operates in a situation where the insured has taken policies with two or more insurance companies hovering the same risk and in event of loss the companies contribute equally to indemnify the insured.
Any 5 points @ 2 mks = 10mks
- This operates in a situation where the insured has taken policies with two or more insurance companies hovering the same risk and in event of loss the companies contribute equally to indemnify the insured.
- Principle of utmost good faith.
- Explain five problems a developing country will encounter in the implementation stage of development planning. (10marks)
- Reduce on donor funding
- The less developed countries that base their development plans on expected aid form develop countries may find it difficult when such aid is denied.
- Lack of domestic resources
- Lack of skilled personnel, finance and capital equipment may hamper implementation
- Failure to invoice local people in planning
- If local people expected to implement plans are left out they may fall to support the plan at implementation.
- Natural calamities
- Direct or indirect natural calamities like floods or drought may make it difficult to implementation projected plans as funds are diverted to handle calamities.
- Inflation
- Increased prices may negatively affect implementation.
- Over ambitious plans
- Plans meant to impress donors so that they release foreign aid may be unrealistic and difficult to implement.
- Lack of cooperation among the executing parties
- Lack of cooperation among expected experts may lead to conflict and result to difficulty in implementation
- Lack of political will
- If there is no political commitment to implement the plans will remain in paper plan and fall to be executed.
Any 5 points @ 2 mks = 10mks
- If there is no political commitment to implement the plans will remain in paper plan and fall to be executed.
- Reduce on donor funding
- Explain five principles of insurance. (10marks)
-
- Kenya experienced a general increase in prices of goods and services due to Covid-19 pandemic. Explain five negative effects of this to the Kenyan economy (10marks).
- Reduction in profits
- Rise in prices of commodities may lead to reduced sales volume for firms as many customers may not afford the high prices. This in turn may reduce the firms’ profits.
- Discourages savings
- During inflation, people tend to spend most of their earnings leaving little or nothing to save.
- Retardation of economic growth
- Inflation may create a situation where investors are not willing to take risks, invest in new ventures, expand production or hire more workers. This would bring about retardation in economic growth.
- Loss to creditors
- Creditors lend out when the value money is high. At time of payment, the creditors receive less in real money terms since the money value has been eroded by inflation.
- Decline in standards of living
- During inflation, consumers’ purchasing power decrease. This is so especially for people who earn fixed incomes such as pensioners. The reduction in purchasing power bring about a decrease in standards of living.
- Loss of confidence in the monetary system
- High levels of inflation may lead to loss of confidence in money both as a medium of exchange and a store of value. This may lead to collapse of the monetary system.
- Wastage of time
- Inflation can be wasteful in that individuals and firms may waste a lot of time shopping around for reasonable prices. The time so wasted can be an extra cost to the individual/firm.
- Conflicts between employers and employees
- Adverse effects on the balance of payments
Any 5 @ 2 = 10marks
- Adverse effects on the balance of payments
- Reduction in profits
- Causes of unfavorable balance of payment for most developing countries.
- Reliance on Primary products which fetch low prices in the international market.
- Heavy importation of finished goods, whose value are very high hence spend more on them.
- Low level of technology which compromises the quality of their exports and lowering their value.
- Too much reliance on foreign borrowing-Such loans are repaid with heavy interest.
- Susceptibility to natural calamities like drought which adversely affect their production.
- Preference towards foreign goods – most consumers in developing countries prefers foreign goods in the belief that they are of better quality.
- Unfavorable world economic order - Developing countries have very little say in international trade forums and cannot influence the world economic order in their favors.
- Kenya experienced a general increase in prices of goods and services due to Covid-19 pandemic. Explain five negative effects of this to the Kenyan economy (10marks).
-
- With the aid of a suitable diagram, explain the effects of a decrease in supply on the equilibrium price and quantity.
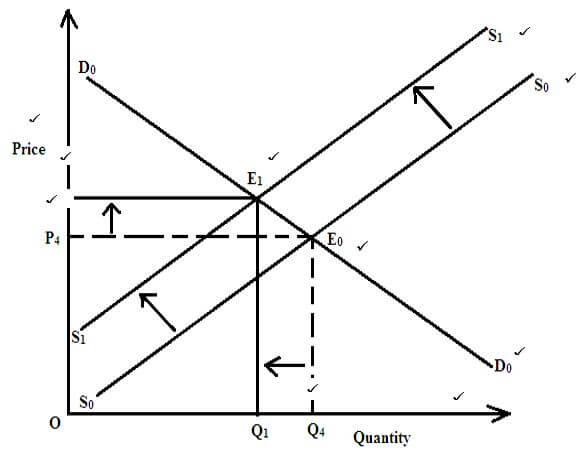
Diagram 8 marks then explanation 2 marks= 10 marks - Explain five roles of central bank in an economy (10 marks)
- Issue of currency; it issues new currencies both notes and coins into the economy and also replaces worn out currencies
- Banker to commercial banks; accept deposits from commercial banks for safe keeping of their money.
- Banker to the government; it provides banking services to the government by receiving deposits and making payments on behalf of the government.
- Maintains an account for foreign exchange services. It sells foreign exchange to commercial banks and other institutions dealing with foreign exchange.
- Advisor to the government; it gives advice to the government on monetary/economic issues
- Managing the public debt; money borrowed by the government from internal and external sources is administered and repayments made through the central bank.
- Lender of the last resort to commercial banks when they have no other sources from which they can borrow.
- Controls commercial banks; it has the authority and power to direct, control and supervise financial activities of commercial banks and other financial institutions.
- Research and statistics; it collects and publishes financial data which is vital for the country’s economy.
- Acts as a link bank to other central banks and international financial institutions for the purpose of settling financial transactions arising from economic activities.
- Credit control; the central bank regulates the amount of money in the economy by controlling the lending activities of commercial banks and other financial institutions.
- Acts as a central clearing house to facilitate the clearing of cheques arising from inter-bank activities.
(Any 5 x 2 = 10 marks)
- With the aid of a suitable diagram, explain the effects of a decrease in supply on the equilibrium price and quantity.
-
- Demerits of direct taxation. ( 10mrk)
- Encourage avoidance and evasion; it can be easily evaded by tax payers by either falsifying information about their incomes or just ignoring payments.
- Deterrent to savings as it reduces peoples’ ability to save due to less disposable incomes left with them.
- Deterrent to work; e.g. progressive tax on personal incomes would make an individual opt for leisure time instead of working overtime to get extra income. This is because the more they earn the more tax they pay.
- Deterrent to investment; heavy taxation on profits may deter entrepreneurs from investing in highly risky but profitable areas. This is because an entrepreneur can only invest in risky areas if there is a possibility of making huge profits.
- May inconvenience the tax payer especially where he/she has to comply with complicated formalities relating to sources of income as well as expenses incurred while generating it.This may make the tax payers to involve experts which is an extra cost.
- Not imposed on all citizens as low income earners who do not fall within the tax brackets are exempted hence not contributing anything to the state in form of tax.
(Any 5 x 2 = 10 marks)
- Masaku Investments books of original entry
SALES JOURNAL
PURCHASES JOURNALDATE
DETAILS
INVOICE NO.
AMOUNT
2016 May
3
22
Kyalo
Musyoki
Total Posted to Sales a/c (Cr)
Shs. 60,000
150,000
210,000
PURCHASES RETURNS JOURNALDATE
DETAILS
INVOICE NO.
AMOUNT
2016 May 8
16
Musau
Musau
Total Posted to Purchases A/C (Dr)
Shs. 120,000
160,000
210,000
SALES RETURNS JOURNALDATE
DETAILS
INVOICE NO.
AMOUNT
2016 May 12
Musau
Total posted to purchases returns A/c (cr)
Shs. 6,000
6,000
GENERAL JOURNALDATE
DETAILS
INVOICE NO.
AMOUNT
2016 May 24
Kyalo
Total Posted to Sales
Returns A/C (Dr)
Shs. 10,000
10,000
10 ticks x 1 = 10 marksDATE
DETAILS
DR.
CR.
2016 May 23
Motor Van A/c.
Mashiriki Motors A/c. (Being purchase of Motor Vehicle on credit)
3,200,000
3,200,000
2016 May 29
Chap Chap Ltd A/c.
Equipment
(Being sale of Equipment on credit)
840,000
840,000
NB: For the general journal, the candidate must indent the account to credit to earn the mark.
- Demerits of direct taxation. ( 10mrk)
Download Business Studies Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Sunrise 2 Evaluation Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
