QUESTIONS
- You are provided with :-
- Sulphuric (VI) acid, solution P
- 0.25M sodium hydroxide, solution S
- Solid R
You are required to determine the concentration of sulphuric (VI) acid in moles per litre
PROCEDURE I
Using a burette, place 50.0cm3 of sulphuric (VI) acid, solution P in a 100ml beaker. Measure the temperature of the solution after every half – minute and record the values in table 1. At exactly 1 ½ minute, add solid R to the acid. Stir the mixture gently with the thermometer ensuring the solid is intact in the solution and note the temperature of the mixture after every half – minute and record the values in table 1.- Table 1
Time (minute) 0 ½ 1 1½ 2 2½ 3 3½ 4 4½ 5 5½ 6 Temperature (ºC) -
- Plot a graph of temperature ( y – axis) against time. (3mks)
- Using the graph, determine the highest change in temperature. (1mk)
- Calculate the heat change for the reaction (Assume that the specific heat capacity of the mixture is 4.2Jg-1 k-1 and density of the mixture is 1g/ cm)3. (2mks)
- Given that the molar heat of reaction of sulphuric (VI) acid with solid R is 320 kJ mol-1, calculate the number of moles of sulphuric acid that were used during the reaction. (2mks)
PROCEDURE II
Transfer ALL the contents of the 100 ml beaker used in procedure I into a 250ml volumetric flask. Add distilled water to make up to the mark. Label this solution Q.
Rinse the burette and fill it with sodium hydroxide, solution S
Using a pipette and a pipette filler, place 25.0 cm3 of solution Q into a 250ml conical flask. Add two or three drops of phenolphthalein indicator and titrate against sodium hydroxide. Record your results in table 2. Repeat the titration two more times and complete table 2.
Table 2
(4mks)Experiment I II III Final burette reading (cm3) Initial burette reading (cm3) Volume of solution S used (cm3) - Calculate the :-
- Average volume of solution S used.
- the number of moles of sodium hydroxide used.
- Sulphuric (VI) acid in 25cm3 of solution Q (1mk)
- Sulphuric (VI) acid in 250cm3 of solution Q. (1mk)
- Calculate the number of moles of sulphuric (VI) in 50cm3 of solution P.
- Calculate the concentration of the original sulphuric (VI) acid solution P in moles per litre (2mks)
- Calculate the :-
- Table 1
- You are provided with solution Q. Carry out the tests shown below and answer the questions that follow.
- Dip a clean glass rod in solution Q provided and heat it using a non-luminous flame.
Divide the above solution Q into four portionsObservations Inferences (1 mark) ( 1mark) - To about 1cm3 of the solution add 2M sodium hydroxide dropwise until excess.
Observations Inferences (1 mark) ( 1mark) - To the second portion add 2M ammonia solution dropwise until excess.
Observations Inferences (1 mark) ( 1mark) - To 1cm3 of solution Q add a few drops of Lead (II) nitrate solution.
Observations Inferences (1 mark) ( 1mark) - To 1cm3 of solution Q add four drops of barium nitrate solution followed by a few drops of 2M nitric (V) acid.
Observations Inferences (1 mark) ( 1mark)
- Dip a clean glass rod in solution Q provided and heat it using a non-luminous flame.
- You are provided with substance E. Carry out tests on it.
-
- Place about one third of solid E on a metallic spatula and ignite it in a flame.
Place the remaining solid E boiling tube and add about 5cm3 of distilled water. Shake the contents and divide into 3 portions.Observations Inferences (1 mark) ( 1mark) - To portion one add 3 drops of Universal indicator
Observations Inferences (1 mark) ( 1mark)
- Place about one third of solid E on a metallic spatula and ignite it in a flame.
- To the second portion add all the sodium carbonate provided
Observations Inferences (1 mark) ( 1mark) - To third portion add 2 drops of acidified potassium manganate (VII) solution. Warm the mixture
Observations Inferences (1 mark) ( 1mark)
-
CONFIDENTIAL
In addition to the apparatus and the fitting found in a chemistry laboratory, each candidate will required the following
- About 70cm3 of solution P.
- About 80cm3 of solution S
- Exactly 7.5 cm solid R (May be fold twice)
- One thermometer -10ºC - 110ºC
- One stop watch / clock
- One 100ml plastic beaker
- One burette 0 – 50ml
- One pipette 25ml and a pipette filler
- One volumetric flask 250 ml
- About 500cm3 of distilled water supplied in a wash bottle
- One label
- Two conical flasks
- 10ml measuring cylinder
- Five clean dry test – tube in a test tube rack.
- Glass rod
- One boiling tube
- One spatula
- One test – tube holder
- Filter funnel
- PH chart
- 5ml of solution Q
- About 0.5g of anhydrous sodium carbonate
- About 0.5g of solid E
Access to:
- Bunsen burner
- 2M sodium hydroxide provided with a dropper
- Phenolphthalein indicator supplied with a dropper
- Lead (II) nitrate solution supplied with a dropper
- Barium nitrate solution supplied with a dropper
- 2M aqueous ammonia
- Universal indicator solution
- Acidified potassium manganate (VII)
- 2M Nitric (V) acid
NOTE
- Solution P is prepared by adding exactly 27.2 cm3 of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid of specific gravity ( density) 1.84g / cm3 to about 600cm3 of distilled water and diluting to one litre of solution
- Sodium hydroxide is prepared by dissolving exactly 10g of sodium pellets in about 800cm3 of distilled water and diluting to one litre of solution
- Solid R is exctaly 7.5cm magnesium ribbon
- Lead (II) Nitrate solution is prepared by dissolving 33.1g of lead (II) Nitrate solid to 1 litre of distilled water
- Barium Nitrate solution is prepared by dissolving 26.1g of Barium Nitrate in 1 litre of distilled water.
- Solution Q made by mixing sodium sulphate and zinc sulphate in the ratio of 1:1 and dissolving in 10ml of distilled water
- 2M Nitric (V) acid is prepared by dissolving 134cm3 of concentrated Nitric (V) acid of specific gravity 1.42 g/cm3 to about 600cm3 of distilled and diluting to 1 litre of solution
- 2M sodium hydroxide solution is prepared by dissolving 80g of sodium hydroxide pellets to about 800cm3 of distilled water and diluting to 1 litre of solution
- Solution Y -Acidified Potassium Manganate (VII)prepared by dissolving 9g of solid Potassium Manganate (VII) in about 600cm3 of 2M Sulphuric (VI) acid and adding distilled water to make a litre of solution.
- Solid E is oxalic acid

MARKING SCHEME
-
- CT = Complete table ….1mk
Table to be filled completely
If at time 0min a student records temperature as 0 or any reading is more than 40 penalize half mark.
D.P = decimal point ……. ½mk
All values to be recorded as whole numbers OR with a decimal as 0 or 0.5 only if any other figure is used award 0mk for d.p
Accuracy.Consider reading at time 0min if +/- 2oC of school value award ½mk, if beyond award 0mk
Trend 1 mk
For time t= 0to 1½ values to be constant. ½ mk
For time t = 2 ½ to 6 ½mk
Values to be rise and be higher than those of t = 0 to t = 1 ½ .the last values to drop - Graph
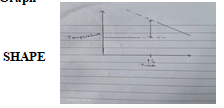
Labeled axes …. ½mk
Axes to be labeled with quantities
Scale ………….½mk
Plot to cover ¾ of the given grid.
Plots …………..1mk
To be plotted accurately, 10-12 (1mk), 9plots (½ mk)
Plots for t =0 to 1 ½ to be joined by straight line …. ½mk. Draw line for drop and extrapolate ½mk- ½ mk for using graph ( must show dotted line on graph or blocked liner)
½ mk for correct answer
If not shown in graphs penalize fully. - MCΔT
M ≡ 50 x 1.0g/cm3 = 50g ½ mk
= 50 x 4.2 x higher of ans b(ii) // 50 x 4.2 xΔt 1mk
= ans ½ mk
Penalize ½ mk for omitting units or wrong units in final answer
Accept J or kJ units - Value obtain in b(iii)
320
Procedure II
Table 2
CT – 1mk
Decimal – 1mk
Accuracy – 1mk
Principle of averaging – 1mk
Final answer – 1mk-
- I : ans a(i) x 0.25 ½ mk = ans ½ mk
1000 - Moles ratio between H2SO4 and NaOH = 1 : 2// ½ mk
Moles of H2SO4in 25cm3 = ½ x ans a(ii)
= ans ½ mk - ans a(iii) x 250 ½ mk = ans
25
- I : ans a(i) x 0.25 ½ mk = ans ½ mk
- Moles of procedure I b(iv) + procedure II a(iv)
- Ans part (d) x 1000
50
-
- ½ mk for using graph ( must show dotted line on graph or blocked liner)
- CT = Complete table ….1mk
- Observation Inference
Observations Inferences Yellow flame 1mk
Whit ppt. forms ½mk soluble in excess ½mk
Whit ppt. ½mk soluble in excess ½mk
White ppt 1mk
white ppt ½mk insoluble in the acid ½mkNa+ present 1mk
Zn2+ , Al3+ , Pb2+ present
Zn2+ present
SO42-, CO32- , SO32-, CI- present
SO42- 1mk - Observation Inference
Observations Inferences Burns with sooty yellow flame
pH = 4 - 6
Bubbles evolved // Effervescence
purple KMnO4decolourizedunsaturated organic compound // 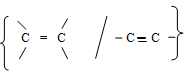
Weakly acidic (½mk)
–COOH present (½mk)
R - OH ½ mk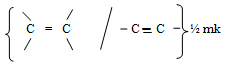
Download Chemistry Paper 3 Questions and Answers - Kakamega Evaluation Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
