QUESTIONS
- Name the antigens present in red blood cells of a person whose blood group is B positive. (2mks)
- Give reasons for the following structural modifications in axial skeleton of humans
- Fused sacral vertebrae (1mk)
- Long transverse process in lumbar vertebrae. (1mk)
-
- What is adaptive radiation? (1mk)
- State two ways in which Homo sapiens differs from Homo habilis (2mks)
- State three characteristics of class Reptilia. (3mks)
- The diagram below represents the structure of a yeast cell as seen under a light microscope.
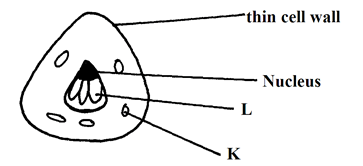
Name parts labeled L & K(2mks) - Which part of plant normally shows
- Increased growth at lower auxin concentration (1mk)
- Decreased growth at lower auxin concentration (1mk)
- State the functions of the following parts of a light microscope.
- Fine adjustment knob (1mk)
- Condenser (1mk)
- Give a reason for the following features present in human trachea
- Ring of cartilage (1mk)
- Presence of cilia (1mk)
- The diagram below shows a plant supportive tissue
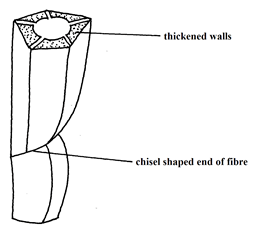
- Identify the tissue (1mk)
- State two similarities between tissue named in 9(a) above and one conducting water in dicotyledonous plants
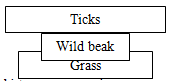
- A wild beast in Masai Mara National Park was found to be infested with a lot of ticks. State the trophic level occupied by the following organisms:
-
- Wild beast (1mk)
- Ticks (1mk)
- Sketch a pyramid of numbers to represent above feeding relationship. (1mk)
-
-
- Name the causative agent of the following diseases in humans.
- Bilharziasis (1mk)
- Syphillis (1mk)
- Describe the following defects:
- Varicose veins (1mk)
- Thrombosis (1mk)
- Name the causative agent of the following diseases in humans.
- The flow chart below shows the movement and fate of carbohydrate synthesized by green plants.

- Name the type of carbohydrate that is
- Transported from leaf to other parts of plant (1mk)
- Found in storage tissues (1mk)
- Name two main photosynthetic tissues found in a leaf (2mks)
- Name the type of carbohydrate that is
- State the roles of the following cell organelles in a cell
- Lysosomes (2mks)
- Centrioles (1mk)
- Name the physiological process involve in the movement of the following substances in and out of the cell.
- Mineral salts (1mk)
- Water (1mk)
- Below is the dental formula of an organism
i3/3 C1/1 Pm4/4 m2/3- Calculate the total number of teeth in the jaw of the animal (2mks)
- With a reason, identify the type of dentition for the organism (2mks)
- The diagram below shows a section through a plant organ
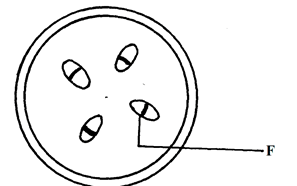
- Name the class of the plant from which the section was obtained (1mk)
- Give a reason for your answer in a(i) above (1mk)
-
- Name two structures for gaseous exchange in aquatic plants. (2mks)
- State one adaption of the above named structures. (1mk)
- During a biological trip, plants that had flowers drew the attention of students
- Name the subdivision of the plants (1mk)
- Name two possible characteristics that students would use to conclude that they were insect pollinated. (2mks)
- Define the following terms
- Homologous structures (1mk)
- Vestigial structures (1mk)
- Name the type of responses exhibited by the following
- Pollen tube growth towards the embryo sac (1mk)
- Maggot moving from the lit part of boiling tube to the part painted black (1mk)
- Folding of the leaves of the Mimosa Pudica plant on touch (1mk)
- Insulin is a hormone synthesized using bacteria DNA. It is possible to obtain from hospitals because of the new technology
- Name the technology used in the case above. (1mk)
- Why were bacteria preferred in the medicine production (2mks
-
- State the role of the following parts of ear in the hearing process
- Ear drum (1mk)
- Cochlea (1mk)
- Explain why the body temperature of a healthy human being may rise up to 390C on a hot humid day. (3mks)
- State the role of the following parts of ear in the hearing process
- Explain what happens to human body when glucose level is above normal (3mks)
- Name three mechanisms that ensure cross pollination takes place in flowering plants. (3mks)
- State the functional difference between sensory and motor neurons (1mk)
- Give two reasons why class insecta is the most numerous among members of phylum arthropoda. (2mks)
- The diagram below shows the appearance of a plant cell after it had been placed in a strong salt solution
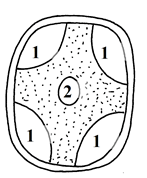
- Name the process that occurred in the cell shown above. (1mk)
-
- Which substance is present in the regions marked 1? (1mk)
- Give reasons for your answer in b(i) above (2mks)
- State two roles of a fruit to a plant (2mks)
- What is the importance of the following in an ecosystem?
- Bacteria and fungi (1mk)
- Predators (1mk)
- Outline three roles of active transport in the human body. (3mks)

MARKING SCHEME
- Antigen B; rej. Small b
Antigen Rhesus; (1mk) -
- for support / to transmit weight of stationery animal to the rest of body; (1mk)
- To increase surface area for attachment of large abdominal of muscles (to maintain posture and flex spine); (1mk)
-
- Situation where organisms have homologous structures / structures with common embryonic origin but modified to perform different functions; to adapt organisms to different functions; to adapt organisms to different habitats / niches; (1mk)
- Standing upright / erect posture ; high intellectual capacity / thinking capacity hig; communicate through speech / language; acc correct comparison (2mks)
-
- Body covered with dry scaly skin;
- Majority have four limbs with snakes having no limb
- Eggs have leathery shell (to reduce desiccation)
- Have lungs for gaseous exchange
- Heart is three chambered two atric and partially divided ventricle or four chambered; (3mks)
- L – Glycogen granule; rej Plural
K – Vacuole; (2mks) -
- Root; (1mk)
- Shoot; (1mk)
-
- Moves the body through small distances to bring image / specimen / object into sharper focus;
- Concentrates light (from mirrow) into object on stage; (2mks)
-
- to keep it open / provide mechanical strength
- to propel dust / bacteria / mucus out of trachea. (2mks)
-
- Trachaid?
- thickened with lignin;
Has tapered ends (tracheids); (3mks)
-
-
- Primary consumer;
- Secondary consumer; (2mks)
-
-
-
-
- Schistosoma mansoni;
- Treponema pallidum; (2mks)
-
- Swellings in veins due to weakened / defective valves resulting into accumulation of blood;
- Formation of (a blood) clot in the blood vessels; (2mks)
-
-
-
- Sucrose ; (2mks)
- Starch;
- Pollisade;
Spongy; (2mks)
-
-
- Burst / break drum to release lytic enzyme; to digest dead and worm out cell organelles;
- Form spindle during cell division/ formation of cilia and flagella; (1mk)
-
- Active transport / Diffusion; (1mk)
- Osmosis ;(1mk)
-
- 10 x 2 = 20 ;
11 x 2 = 22
= 42 teeth; (2mks) - Heterodont;
Reason – Has different types of teeth; OWTTE.
- 10 x 2 = 20 ;
-
- Dicotyledonae; rej wrong spelling Dicot, dicotyledonae
- Vascular bundles arranged in (concentric) ring around the pith; presence of pith; (1mk)
-
- Aerenchyma (tissue); (2mks)
Pneumatophores; rej breathing roots - Have large air spaces for circulation of air / gaseous exchange; (1mk)
- Aerenchyma (tissue); (2mks)
-
- Spermatophyte
- brightly coloured petals scented nectar guides
-
- Structures from the same (embryonic) origin / ancestry but modified to perform different functions; (1mk)
- Structures that have ceased to function over long period of time hence become reduced in size; (1mk)
-
- Chemotropism
- (Negative) photo taxis;
- Haptonasty / Thigmonasty;
-
- Genetic engineering;
- Reproduce of very fast; hence producing more lormures;
-
-
- Currents sound waves to sound vibrations; transmit sound vibrations to ear obscicles;
- Currents vibrations into impulses (for hearing)
- More sweat produced; but does not evaporate; due to humid conditions, hence more leaf retained;
-
- Pancreas secreted insulin hormone; hormone activates liver cells; to convert excess glucose to glycogen fats / increase in the rate of metabolism to break down glucose into energy; (3mks)
-
- Protogyny and protandry (3mks)
- Self sterility / incompatibility
- dioecious plant where distillate and staminate flower are born on different plants.
- Sensory neuron - Transmit impulses from receptors to CNS
Motor neuron - Transmit impulses from CNS to effectors; (1mk) -
- Ability to fly;
- Can inhabit most types of habitats;
- Have varied mouth past for feeding
-
- Plasmolysis (1mk)
-
- Strong salt solution; (1mk)
- The salt solution passed through the cell wall because it is fully permeable; but cannot pass through the cell membrane which is semi permeable; (2mks)
- Protect the seeds; As a storage organ; Aids in seed dispersal; Max (2mks)
-
- Decomposition / recycling of nutrients;
- requlate population of he prey / herbivores; (1mk)
-
- Reabsorption of salt and sugar in kidney nephrons;
- Absorption of digested food;
- Excretion of waste products from body cells
- Sodium pump in the nervous system
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Kakamega Evaluation Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
