Questions
Instructions
- Answer ALL questions in the spaces provided
- Show your working clearly.
- Electronic calculators and Mathematical tables may be used.
- All answers must be written in English language
- Below is a table showing the solubility of salts Q and R at different temperatures.
Temperature °C 0 10 20 30 40 50 Solubility in grams per 100g of water Salt Q 3.0 5.0 7.4 10.0 14.0 19.0 Salt R 15.0 17.0 20.7 25.7 28.7 33.0 - Define the term “Solubility of salt” (1mk)
- If both salts Q and R are present in 100cm3 of saturated solution at 50°C, what willbe the total mass of crystals formed if the solution was cooled to 20°C? (2mks)
- Name two areas where knowledge of solubility curves is applied (2mks)
- Two samples of hard water C and D were boiled. When tested with drops of soap, sample D formed lather easily while C did not:-
- Name the possible salt that caused hardness in sample D(1mk)
- Explain how distillation can remove hardness in sample C (1mk)
- Give two advantages of hard water (1mk)
- You are provided with a mixture of Lead (II) Chloride, ammonium chloride and sodium chloride. Explain how you would separate all the three solids (3mks)
- Sodium Carbonate Decahydrate crystals were left exposed on a watch glass for two days.
- State the observations made on the crystals after two days.(1mk)
- Name the property of salts investigated in the above experiment (1mk)
- When water reacts with potassium metal the hydrogen produced ignites explosively on the surface of water.
- What causes this ignition?(1mk)
- Write an equation to show how this ignition occurs (1mk)
- How does the pH value of 0.25M KOH (aq) compare with that of 0.25M ammonia solution? Explain (2mks)
-
- State Gay Lussac’s law. (1mk)
- 10cm3 of methane (CH4) gas is exploded with 150cm3 of air containing 20% oxygen and 80% nitrogen. The products were allowed to cool to room temperature. What will be the total volume of the gases at the end of the reaction (3mks)
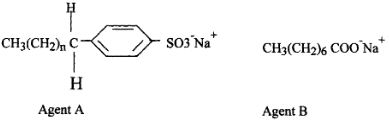
- The formulae below represents active ingredients of two cleansing agents A and B
- Name the class to which each of the cleansing agent belongs(2mks)
- Which one of the cleaning agent above is not environmental friendly? Explain (2mk)
- Which one of the cleansing agent would be suitable to be used in water containing magnesium hydrogen carbonate? Explain (2mks)
- During Saponification process, a small amount of Sodium Chloride is added Give a reason (1mk)
-
- Write an equation showing how ammonium nitrate may be prepared starting with ammonia gas (1mk)
- Calculate the maximum mass of ammonium nitrate that can be prepared using 5.3kg of ammonia (H=1, N=14, O=16) (2mks)
- Plastics and rubber are extensively used to cover electrical wires.
- What Name is used to describe plastic and rubbers used in this way? (1mk)
- Explain why plastics and rubbers are used for this purpose (1mk)
- G grams of a radioactive isotope take 120days to decay to 3.5grams. The half-life period of the isotope is 20days
- Find the initial mass of the isotope (2mks)
- Give two applications of radioactivity in medicine (2mks)
- Uranium -238 disintegrates by emitting an alpha particle to form substance Y. Nuclide Y emits a beta particle to form substance Z. Write down nuclear equations to show how substance Y and Z are formed (U=92) (2mks)
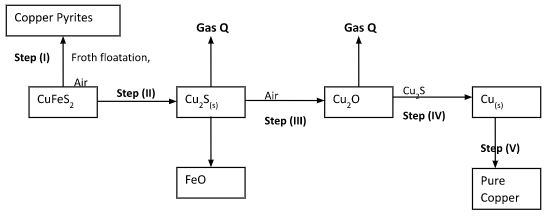
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow:
- Name gas Q(1mk)
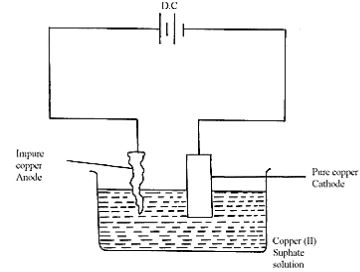
- With the help of diagram, describe how step (V) is carried out (3mks)
- During purification of copper by electrolysis, 1.48g of copper were deposited when a Current was passed through aqueous copper (II) sulphate for 2 ½ hours. Calculate the amount of current passed (Cu = 63.5 1Faraday = 9650°C) (3mks)
- What is meant by the term Froth Floatation(2mks)
- Name two impurities present in the ore of copper (1mk)
- State two properties of Duralumin that make it suitable for use in making aircraft parts?(1mk)
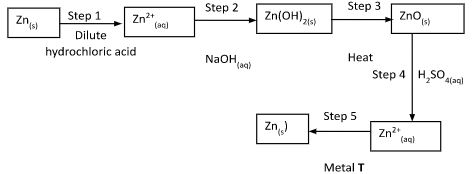
- The flow chart below shows a sequence of chemical reactions starting with Zinc. Study it and answer the questions that follow:-
- In step 1, excess 3M hydrochloric acid was added to 0.5g of Zinc powder
- State one observation which were made when the reaction was in progress ( ½ mks)
- Explain why hydrogen gas is not liberated when dilute nitric acid is used in step 1 (1mk)
- Write an ionic equation for the reaction that took place in step 1 (1mk)
- Calculate the volume of 3M hydrochloric acid that was needed to react completely with0.5g of Zinc powder (Zn = 65.0) (2mks)
- In step 1, excess 3M hydrochloric acid was added to 0.5g of Zinc powder
- Briefly describe how a pure sample of lead ii iodide can be prepared in the lab given Distilled water, solid lead ii nitrate and solid Potassium iodide (3mks)
- Use equations only to explain how slag is formed in the Blast furnace during the extraction of iron (2mk)
- Using dots and crosses to represent electrons draw the structure Phosphorous chloride (PCl3) (1mk)
- Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow:
(The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements)
Element Electronic configuration Ionization energy KJmol-1 P 2:1 519 Q 2:8:1 494 R 2:8:8:1 418 - What is meant by ionization energy? (1mk)
- Element R has the lowest ionization energy. Explain. (1mk)
- When a piece of element Q is placed on water it melts and a hissing sound is produced as it moves on the water surface. Explain these observations. (1 1/2mks)
- Write the equation for the reaction between element Q and water.(1mk)
- Chlorine has a higher boiling point than Argon. Give a reason (1mk)
-
- State Graham’s Law of diffusion (1mk)
- Gas B takes 110 seconds to diffuse through a porous pot, how long will it take for theSame amount of ammonia to diffuse under the same conditions of temperature and pressure?
(RMM of B = 34 RMM of ammonia = 17) (2mks)
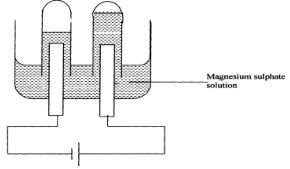
- The setup below was used to carry out the electrolysis of Magnesium sulphate solution using
- Name a suitable pair of electrode that can be used in the above process. ( ½ mk)
- State and explain the changes on the concentration of magnesium sulphate solution as the process proceeds. (1mk)
- Label on the diagram the Cathode and anode(1mk)
-
- Bond energies for some bonds are tabulated below:-
Use the bond energies to estimate the enthalpy for the reactionBOND BOND ENERGY KJ/mol H - H 436 C = C 610 C - H 410 C - C 345
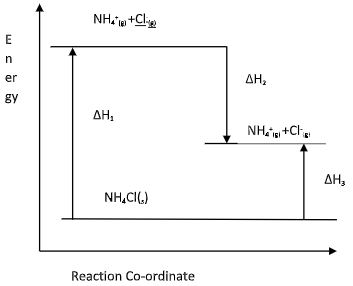
C2H4(g) + H2(g) → C2H6(g) (2mks) - Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow:
What do ∆H1 and ∆H2 represent? (1mk) - Write an expression to show the relationship between ∆H1, ∆H2 and ∆H3.(1mk)
- Bond energies for some bonds are tabulated below:-
-
- Name one substance that is added to Aluminium oxide during electrolysis in the manufacture of Aluminium metal ( ½ mk)
- Give a reason why the substance named above is added (1mk)
-
- State Le Chatelier’sPrinciple (1mk)
- An equilibrium exists in the Haber process as shown in the equation below
N2(g) + 3H2(g) → 2NH3(g) ΔH = -92kJ - State and explain the effect of the following factors on the yield of Ammonia
- Increase in Pressure (1 ½mks)
- Increase in Temperature (1 ½ mks)
Marking Scheme
- Below is a table showing the solubility of salts Q and R at different temperatures.
- Define the term “Solubility of salt” (1mk)
- The maximum mass of solute required to saturate 100g of solvent at a given temperature;
- If both salts Q and R are present in 100cm3 of saturated solution at 50°C, what will be the total mass of crystals formed if the solution was cooled to 20°C? (2mks)
- Q 19.0 - 7.4 = 11.6
- R 33.3 – 20.7 = 12.6
Total mass= 24.2
- Name two areas where knowledge of solubility curves is applied (2mks)
- Extraction of Trona and Sodium Chloride on Lake Magadi
- Separation of Soda ash and Ammonium Chloride in the Solvay process
- Define the term “Solubility of salt” (1mk)
- Two samples of hard water C and D were boiled. When tested with drops of soap, sample D formed lather easily while C did not:-
- Name the possible salt that caused hardness in sample D (1mk)
- Magnesium hydrogen carbonate
- Calcium hydrogen Carbonate
- Explain how distillation can remove hardness in sample C (1mk)
- When water is heated to boil, it evaporates and the vapour is condensed, distilled water free of Calcium and Magnesium ions is obtained.
- Give two advantage of hard water (1mk)
- Calcium ions are necessary for strong bones and teeth
- Good for beer brewing
- Name the possible salt that caused hardness in sample D (1mk)
- You are provided with a mixture of Lead (II) Chloride, ammonium chloride and sodium chloride. Explain how you would separate all the three solids (3mks)
- Heat the mixture in a beaker covered with a watch glass containing ice cold water
- Ammonium chloride sublimes and is deposited as a sublimate
- Add water and stir to dissolve Sodium chloride
- Filter, Lead ii chloride as residue, sodium chloride as filtrate
- Heat to saturate the filtrate, Cool to crystallize
- Dry the sodium chloride crystals between filter papers
- Sodium Carbonate Decahydrate crystals were left exposed on a watch glass for two days.
- State the observations made on the crystals after two days.(1mk)
- Dry/loses their water of crystallization
- Name the property of salts investigated in the above experiment (1mk)
- Efflorescence
- State the observations made on the crystals after two days.(1mk)
- When a small piece of potassium metal is dropped in cold water, it bursts into a flame on the surface of water.
- What causes this ignition?(1mk)
- Heat produced ignites the hydrogen gas being produced
- Write an equation to show how this ignition occurs (1mk)
- 2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(g)
- What is the colour of the flame (1mk)
- Lilac
- What causes this ignition?(1mk)
- How does the pH value of 0.25M KOH(aq) compare with that of 0.25M ammonia solution? Explain (2mks)
- pH of 0.25M KOH is Higher
- KOH is a strong base/ completely or fully Dissociates/ionizes in water to produce more hydroxide ions
-
- State Gay Lussac’s law. (1mk)
- When gases combine, they do so in volumes which bear simple ratios to one another and to the product if gaseous
- 10cm3 of methane (CH4) gas is exploded with 150cm3 of air containing 20% oxygen and 80% nitrogen. The products were allowed to cool to room temperature. What will be the total volume of the gases at the end of the reaction (3mks)
CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(l)- Vol ratios 1 2
- Total volume of oxygen in air 20/100 *150 = 30cm3
- Volume of O2 that reacted with methane 2/1*10 =20cm3
- Unreacted O2 30 - 20 =10cm3
- Volume of CO2 formed 1/1*10= 10cm3
- Volume of N2 150 - 30= 120cm3
- Volume of gases mixture at end 120 + 10 + 10=140cm3
- State Gay Lussac’s law. (1mk)
- The formulae below represents active ingredients of two cleansing agents A and B
- Name the class to which each of the cleansing agent belongs(2mks)
- A Soapless detergent/detergent
- B Soapy detergent/soap
- Which one of the cleaning agent above is not environmental friendly? Explain (2mk)
- B
- Which one of the cleansing agent would be suitable to be used in water containing magnesium hydrogen carbonate? Explain (2mks)
- A
- During Saponification process, a small amount of Sodium Chloride is added Give a reason (1mk)
- To help precipitate the soap/reduce its solubility in glycerol
- Name the class to which each of the cleansing agent belongs(2mks)
-
- Write an equation showing how ammonium nitrate may be prepared starting with ammonia gas (1mk)
- NH3(g) + HNO3(aq) → NH4NO3(aq)
- Calculate the maximum mass of ammonium nitrate that can be prepared using 5.3kg of ammonia (H=1, N=14, O=16) (2mks) (accept direct method)
- Moles of Ammonia 5300/17 = 311.76471 ½ mk
- Moles of Ammonium nitrate 1/1*311.76471=311.76471 ½ mk
- Mass Ammonium nitrate 311.76471*96=29929.4112g/ 29.929kg 1mk
- Write an equation showing how ammonium nitrate may be prepared starting with ammonia gas (1mk)
- Plastics and rubber are extensively used to cover electrical wires.
- What Name is used to describe plastic and rubbers used in this way? (1mk)
- Insulators
- Explain why plastics and rubbers are used for this purpose (1mk)
- They are Non conductor
- What Name is used to describe plastic and rubbers used in this way? (1mk)
- G grams of a radioactive isotope take 120days to decay to 3.5grams. The half-life period of the isotope is 20days
- Find the initial mass of the isotope (2mks)
- No of half lifes 120/20 =6 ½ mk
1 2 3 4 5 6
3.5 → 7 → 14 → 28 → 56 → 112 → 224g 1 ½ mks
Or Remaining mass = (½) n *Original mass ½ mk
3.5=(½)6*Om
Om=3.5/(½)6 ½ mk
=224g ½ mk
- No of half lifes 120/20 =6 ½ mk
- Give two applications of radioactivity in medicine (2mks)
- Gamma rays are used to detect bone fractures and healing(any 2 correct, with correct example)
- Gamma rays are used to sterilize surgical equipment
- Iodine 331 treatment of hyperthyroidism
- Cancer treatment/Radiotherapy/kll malignant tumors- gamma radiation
- Uranium -238 disintegrates by emitting an alpha particle to form substance Y. Nuclide Y emits a beta particle to form substance Z. Write down nuclear equations to show how substance Y and Z are formed (U=92) (2mks)
- 238 92U → 23490 Y + 42He (accept the greek symbols of the particles)
- 234 90 → Y 23491Z + 0-1e
- Find the initial mass of the isotope (2mks)
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow:
- Name gas Q (1mk)
- Sulphur iv oxide
- With the help of diagram, describe how step (V) is carried out (3mks)
- Workable diagram 1mk
- Labels 1mk
- Impure copper is the Anode while pure copper is cathode. During electrolysis copper ions migrate/attracted to the cathode where they are discharged as pure copper 1mk (accept equation)
Cu2+ + 2e → Cu(s)
- During purification of copper by electrolysis, 1.48g of copper were deposited when a Current was passed through aqueous copper (II) sulphate for 2 ½ hours. Calculate the amount of current passed (Cu = 63.5 1Faraday = 96500C) (3mks)
- 63.5g= (96500*2) C ½ mk
1.48= (96500*2*1.48)/63.5 ½ mk
=4498.267C ½ mk
I=Q/t
4498.267/(2.5*60*60) ½ mk =0.4998A 1mk
Or
Moles of copper deposited 1.48/63.5 = 0.02331moles ½ mk
Quantity of charge used 193000 (½ mk )*0.02331 = 4498.83C ½ mk
I=Q/t
4498.83/ (2.5*60*60) ½ mk =0.4998A 1mk
- 63.5g= (96500*2) C ½ mk
- What is meant by the term Froth Floatation(2mks)
- Involves crushing the ore into fine powder, ( ½ mk) dissolving the powder in a suitable solvent such as oil, water or detergent solution,( ½ mk) then air is blown into the mixture (½ mk)A froth which is a more concentrated ore floats on the surface and is separated. ( ½ mk)
- Name two impurities present in the ore of copper (1mks)
- Gold
- Silver
- Name gas Q (1mk)
- State two properties of Duralumin that make it suitable for use in making aircraft parts? (1mk)
- Low density/light (any two ½ mk each)
- High tensile strength/tough
- Resistant to corrosion
- Malleable and ductile
- The flow chart below shows a sequence of chemical reactions starting with Zinc. Study it and answer the questions that follow:-
- In step 1, excess 3M hydrochloric acid was added to 0.5g of Zinc powder
- State one observation which were made when the reaction was in progress (1mk)
- Effervescence
- Explain why hydrogen gas is not liberated when dilute nitric acid is used in step 1 (1mk)
- Hydrogen produced is oxidized to water
- Write an ionic equation for the reaction that took place in step 1 (1mk)
- Zn (s) + 2H+(aq) → Zn2+(aq) +H2(g)
- State one observation which were made when the reaction was in progress (1mk)
- Calculate the volume of 3M hydrochloric acid that was needed to react completely with0.5g of Zinc powder (Zn = 65.0) (2mks
- Moles of Zinc 0.5/65 =0.007692 moles ½ mks
- Moles of HCl 2* 0.007692 = 0.015385moles ½ mks
- Volume of HCl (1000*0.015385)/3 (½ mks)
=5.1cm3 ½ mks
- In step 1, excess 3M hydrochloric acid was added to 0.5g of Zinc powder
- Briefly describe how a pure sample of lead ii iodide can be prepared in the lab given Distilled water, solid lead ii nitrate and solid Potassium iodide (3mks)
- Add water to the two solids ½ mk
- Mix the two solutions to form a yellow precipitate of lead ii iodide ½ mk
- Filter to obtain the precipitate ½ mk
- Wash the precipitate with distilled water 1mk
- Dry the precipitate between filter papers ½ mk
- Using equations explain how slag is formed in the extraction of iron (2mks)
- CaO(s) + SiO2(s) → CaSiO3 (l)
- CaO(s) + Al2O3(s) → Ca Al2O4 (l)
- Using dots and crosses to represent electrons draw the structure of Phosphorous chloride (PCl3) (1mk)
- Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow:
(The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements)- What is meant by ionization energy? (1mk)
- Minimum amount of energy required to completely remove a loosely held electron from an atom in gaseous state
- Element R has the lowest ionization energy. Explain. (1mk)
- Largest atomic size/radius/ valence Electron far away/greatest distance from nucleus ( ½ mk) hence its loosely held/require least energy to be removed/experiences weak nuclear force of attraction ( ½ mk)
- When a piece of element Q is placed on water it melts and a hissing sound is produced as it darts on the water surface. Explain these observations. (1 1/2mks)
- Melts – exothermic/ heat is produced
- Hissing sound- production of hydrogen gas
- Darts on water surface- less dense than water
- Write the equation for the reaction between element Q and water.(1mk)
- 2Q (s) + 2H2O(l) → 2QOH(aq) + H2 (g)
- What is meant by ionization energy? (1mk)
- Chlorine has a higher boiling point than Argon. Give a reason (1mk)
- Chlorine gas has larger Diatomic molecules which experience stronger intermolecular forcesmthan the smaller monoatomic molecules of Argon
-
- State Graham’s Law of diffusion (1mk)
- Under similar conditions of temperature and pressure, the rate of diffusion of a gas is inversely proportional to the square root of Its density
- Gas B takes 110 seconds to diffuse through a porous pot, how long will it take for the
Same amount of ammonia to diffuse under the same conditions of temperature and pressure?
(RMM of B = 34 RMM of ammonia = 17) (2mks)- T NH3/TB = MNH3/MB
T NH3 = MNH3/MB * TB formula ½ mk, subt= ½ mk
= 0.70710*110
=77.78seconds 1mk
- T NH3/TB = MNH3/MB
- State Graham’s Law of diffusion (1mk)
- The setup below was used to carry out the electrolysis of Magnesium sulphate solution using
- Name a suitable pair of electrode that can be used in the above process. ( ½ mk)
- Platinum/Carbon/Graphite
- State and explain the changes on the concentration of magnesium sulphate solution as the process proceeds. (1mk)
- Increases- H+ and OH- ions of water are being discharged
- Label on the diagram the Cathode and anode(1mk)
- Name a suitable pair of electrode that can be used in the above process. ( ½ mk)
-
- Bond energies for some bonds are tabulated below:-
Use the bond energies to estimate the enthalpy for the reaction- C2H4(g) + H2(g) → C2H6(g) (2mks)
- 2686 ( ½ mk) - 2805 ( ½ mk) = -119 kJ (1mk)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow:
What do ∆H1 and ∆H2 represent? (1mk)- ∆H1 Lattice ½ mk
- ∆H2 Hydration ½ mk
- Write an expression to show the relationship between ∆H1, ∆H2 and ∆H3. (1mk)
- ∆H1 + ∆H2 = ∆H3
- Bond energies for some bonds are tabulated below:-
-
- Name one substance that is added to Aluminium oxide during electrolysis in the manufacture of Aluminium metal ( ½ mk)
- cryolite /sodium hexafluoroaluminate
- Give a reason why the substance named above is added (1mk)
- Lower the melting point from 2015°C to about 800°C (½ mk)to save on the electrical energy needed( ½ mk)
- Name one substance that is added to Aluminium oxide during electrolysis in the manufacture of Aluminium metal ( ½ mk)
-
- State Le Chatelier’s Principle (1mk)
- if a stress/change is applied to a system in dynamic equilibrium, the system readjust/shift/move/behave so as to remove/ reduce/ counteract/ oppose the stress/change
- An equilibrium exists in the Haber process as shown in the equation below
N2(g) + 3H2 (g) → 2NH3 (g) ΔH = -92kJ
State and explain the effect of the following factors on the yield of Ammonia- Increase in Pressure (1 ½ mks)
- shift the equilibrium forward/to the right ½ mk where there is less volume/molecules ( ½ mk) More/higher yield of ammonia is attained ( ½ mk)
- Increase in Temperature (1 ½ mks)
- shift the equilibrium to the left/favours reverse reaction ½mk because forward reaction is exothermic(ΔH = -92kJ) ½ mk . Ammonia formed decomposes back to Nitrogen and Hydrogen/ a less yield of ammonia is formed ½ mk
- Increase in Pressure (1 ½ mks)
- State Le Chatelier’s Principle (1mk)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - ACK Diocese Mumias Joint Evaluation Mock 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students