- This paper has two sections: A and B Answer all questions in section A.
- In Section B answer Question 6 and any other TWO questions.
SECTION A
Answer all the questions in this section.
-
- Give two examples of game sanctuaries in Kenya. (2mks)
- State three problems experienced by Kenya in conservation of wildlife. (3mks)
-
- Name two major forest blocks found along the Kenyan Coast. (2mks)
- State three factors contributing to deplation of forests in Kenya. (3mks)
-
- Outline two characteristics of plantation farming in Kenya. (2mks)
- State three physical conditions that favours tea growing in Kenya. (3mks)
-
- Name two minerals that occur as weathered products. (2mks)
- State three uses of soda ash. (3mks)
-
- State two factors which have contributed to decline in infants mortality in Kenya. (2mks)
- Identify three problems resulting from decline in population in industrialized countries. (3mks)
SECTION B
Answer Question 6 and any other two questions.
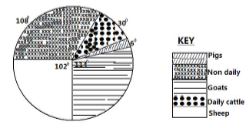
- The table below shows total livestock in Kenya in 2007.
Type of Livestock Number in Millions
Non-Dairy cattle 9.0
Dairy cattle 2.5
Sheep 8.5
Goats 9.5
Pigs 0.5
Total 30.0- Using a radius of 5cm, draw a pie chart to represent the above information (7mks)
-
- Name three pastoralist communities in Kenya (3mks)
- State four characteristics of nomadic pastoralism (4mks)
- Explain four ways in which the kenya government assists nomadic pastoralists to improve the quality of their livestock. (8mks)
- State three problems facing ranching in the tropical areas. (3mks)
-
-
- Explain three conditions that favour irrigation farming in Kenya (6mks)
- State five problems experienced in irrigation farming in Kenya (5mks)
- Describe the stages in the reclamation of land from the sea in Netherlands (6mks)
-
- Apart from irrigation name two other methods of land reclamation.(2mks)
- Explain three factors that influenced the location of Perkerra Irrigation Scheme (6mks)
-
-
-
- Apart from deep shaft mining, name three other mining methods(3mks)
- Describe how deep shaft mining is carried out (6mks)
- Explain four ways in which the exploitation of minerals contributes to the economy of Kenya. (8mks)
-
- What is dereliction? (2mks)
- State three ways that can be used to combat dereliction (3mks)
- A part from dereliction state three other negative effect of mining.(3mks)
-
-
-
- Identify three characteristics of pelagic fish. (3mks)
- State three reasons why marine fishing is not developed in Kenya. (3mks)
- Why should the Government of Kenya encourage fish farming. (4mks)
-
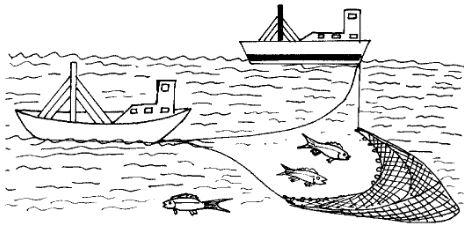
- Identify the fishing method shown below. (1mk)
- Describe how the above method is used in Lake Victoria (4mks)
- State two problems facing fishing in Japan. (2mks)
- Identify the fishing method shown below. (1mk)
- Explain four factors that favour fishing in the pacific fishing grounds. (8mks)
-
-
-
- State two advantages of railway transport over road transport (2mks)
- Describe two conditions of Kenyan roads which contribute to road carnage (4mks)
- Apart from different railway gauges, give three reasons why railway links among African countries are underdeveloped. (3mks)
-
- State two physical factors which favour the location of settlements (2mks)
- Give two differences in the functions of New York and Nairobi cities (4mks)
-
- Compare the ports of Mombasa and Rotterdam under the following Headings:
- Transport to the interior (2mks)
- The size of the hinterlands (2mks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Give two example of game sanctuaries in Kenya.
- OlArtiNyiro sanctuary
- Ngulia Rhino sanctuary
- Maralal. 2 x 1=2mks
- State three problems experienced by Kenya in conservation of wildlife.
- Poaching especially for game trophies meat, skins and hides.
- Drought/ unfavourable climatic conditions which causes drying up of pastores/ vegetation, water courses and water holes.
- Land use conflicts e.g with pastoralists over pastures, intrusion of wild animals on farmlands.
- Inadequate capital for maintenance of parks and sanctuaries resulting into loss of wildlife.
- Inadequate trained personnel to manage the wildlife.
- Environmental pollution e.g water bodies.
- Bush fires and pests and diseases
- Migratory habits of many animals and birds makes if difficult for the country to protect them from poachers. 3 x 1=3mks
- Give two example of game sanctuaries in Kenya.
-
- Name two major forest blocks found along Kenyan coast.
- Shimba hills
- Tana river
- Boni/Dodori
- Arubukosokoke
- Mangrove forests.
- Kaya forests. 2 x 1=2mks
- State three factors contributing to deplation of forests in Kebya.
- Natural calamities that destroy forests.
- Pests and diseases that destroy forests.
- Development of towns result into reduction of areas under forest.
- Pollution from industrial wastes.
- Increase in population and need for land for agriculture and settlement
- Illegal logging for charcoal.
- Uncontrolled fires that destroy forests 3 x 1=3mks
- Name two major forest blocks found along Kenyan coast.
-
- Outline two characteristics of plantation farming in Kenya.
- Crops are raised on large estates of more than 40 hac.
- Most estates are foreign owned e.g by U.S.A , British and French companies.
- There is scientific management e.g through mechanization use of specialized skills.
- Heavy capital outlay for establishment of infrastructure/administration, replanting restocking. 2 x 1 = 2mks.
- State three physical conditions that favours to a growing in Kenya.
- Warm / cold temperature throughtout the year
- High rainfall of between 1000-2000m
- Well distributed of rainfall through out the year
- Areas free from frost
- Acidic volcanic soils.
- Deepness drained soils
- High altitude of between 1000-1500m. 3 x 1=3mks
- Outline two characteristics of plantation farming in Kenya.
-
- Name two minerals that occur as weathered products.
- Bauxite
- Manganese 2 x 1=2mks
- State three uses of soda ash.
- Glass making
- Manufacture of paper
- Fixing dyes in the textile industry.
- Softening of water
- Oil refining . 3 x 1=3mks
- Name two minerals that occur as weathered products.
-
- State two factors which have contributed to decline in infant mortality in Kenya.
- Improved medical facilities
- Improved diet for mother infants.
- Improved education for parents especially mothers. 2 x 1=2mks
- Identify problems resulting from decline in population in industrialized countries.
- Shortage of manpower which makes labour expensive
- Underfilisation of social facilities such as school.
- High old age dependence ratio
- There is rural depopulation due to increased urbanization. 3 x 1=3mks
- State two factors which have contributed to decline in infant mortality in Kenya.
SECTION B
-
- Non dairy
30 = 360°
9.0 = 9.0 × 360 = 108°
30
Dairy
30 = 360°
2.5 = 2.5 × 360 =30°
30
Pigs
30 = 360°
0.5 = 0.5 × 360 = 6°
30
Sheep
30 = 360°
8.5 = 8.5 × 360 =102°
30
Goats
30 = 360°
9.5 = 9.5 × 360 = 114°
30 -
- Pastoral Communities in Kenya
- Maasai
- Turkana
- Boran
- Gabbra
- Samburu
- Somali
- Pokot
- Sakuyu 3 x 1 = 3mks
- Characteristics of nomadic pastoralism
- Practiced in areas of low and inreliable rainfall
- Movement with livestock in search of water and pasture (seasonal)
- Animals are community grazed
- Quantity as opposed to quality is emphasized
- Different types of animals are kept.
- Characterized by frequent raids by neighbouring communities 4 x 1 = 4mks
- Ways the Kenya government is helping pastoralists
- Setting up demonstration ranches to educate the pastoralists on better ways of keeping livestock
- Construction of cakes dips to control pasts
- Provision of extension services
- Construction of boreholes and dams to provide water to the livestock
- Construction of roads to ease transportation of livestock to market
- Encouraging group ranches to enable them see livestock keeping as a commercial activity 4 x 2 = 8 mks
- Pastoral Communities in Kenya
- Problems facing tropical ranches
- Seasonal shortage of pasture
- Poor communication network within the ranches
- Lack of good local market for products
- Frequent attacks by pests and diseases
- Expensive to feed animals. 3 x 1 = 3mks
- Non dairy
-
-
- Conditions favouring irrigation farming in Kenya
- Topography
- Getting sloping land permits flow of water by gravity hence reducing costs of pumping water to the fields.
- Presence of clay / black cotton soil with high water retention capacity. This avails water for use by crops.
- Presence of rivers/reservoirs / lakes which provide regular water supply /permanent/constant. Thus make sit possible to irrigate land through out the year.
- Availability of large tract .............. for irrigation
- Sparsely populated areas reduce cost of resettlement for the displaced.
- Low and unreliable rainfall in most parts of the ground. 3 x 2 = 6mks for well explained point.
- Topography
- Problems facing irrigation farming in Kenya
- Siltation of canals / pipes/reservoirs
- High rate of evaporation
- Salinisation of soil
- Presence of parts
- Clogging of canals by weeds
- Waterborne diseases such as molar and bilharzias
- Poor marketing strategies
- Delay marketing strategies
- Delay payments and ....... mismanagement
- Expensive farm inputs. 5 x 1 = 5mks
- Conditions favouring irrigation farming in Kenya
- Reclamation of land from sea – Netherlands
- Protective dykes / sea walls are constructed enclosing part of the sea to be reclaimed.
- Pumping stations are installed to pump out water from the area enclosed by dyke.
- Water is then pumped out.
- Reeds are planted to help dry the land
- Drainage ditches and more pumping stations are made on the land being reclaimed
- Drainage pipes are bid below the soil
- Area is divided into regular portions using inner dykes
- Soil is treated with chemicals to lowed salinity
- The land is then flush with fresh water to remove salt.
- Pumping continues throughout to avoid accumulation of water. 6 x 1 = 6 mks
NB: The sequence must be followed.
-
- methods of land reclamation
- Drainage
- Afforestation
- Drought resistant crops 2 x 1 = 2mks
- Factors influencing the location of Perkerra
- The need to control floods along river Perkerra which used to devastate the area
- Presence of flat gently sloping land which enables easy flow of water by gravity. This reduces costs
- The area is and this leaves irrigation as the only source.
- Presence of fertile loamy soils reduces use of fertilizers. 3 x 2 = 6mks
- methods of land reclamation
-
-
-
-
- Stripping /Dredging
- Hillslope ...... Hydraulic
- Solution
- Adit/Drift
- Alluvial/places 3 x 1 = 3mks
- Deep shaft Mining
- Vertical shafts are sunk/dug into ground
- Horizontal tunnels are dug to reach the mineral
- Props are erected to support the roof
- The mineral as blasted /dug out /drilled
- It is transported on light rail tracks/conveyers to the bottom of the surface.
- Cranes are used to transport the ore 6 x 1 = 6mks
-
- Role of mining to the economy
- Provides raw materials for manufacturing industrial /chemical and building and construction industries.
- Stimulates development of transport /infrastructure opening up remote areas.
- The industry generator employment opportunites which raises the standard of living.
- Promotes agriculture by purchasing market
- It facilitates provision of social amenities in mining areas.
- Encourages development of skills which can be applied in other sectors.
- Leads to development of related industries. Any 4 x 2 = 5 mks
-
- Dereliction refers to the process whereby land that has been exhausted of minerals is abandoned in state where it has stagnant pools of water.
- Ways to combat dereliction
- Enactment of laws forcing miners to rehabilitate land
- Proper disposal of wastes from mines
- Reclamation of affected land 3 x 1 = 3mks
- Negative effects of mining
- Exploitation of producing countries by multi natural corporators
- Leads to neglecting of other sectors of the economy
- Price fluctuation affects the economy due to over dependency 3 x 1 = 3mks
-
-
-
- Characteristics of Pelagic fish.
- Live near the water surface / live at shallow depths.
- Live in large groups.
- Small in size
- Move in shoals.
- Reasons why Marine fishing is not developed in Kenya.
- lack of enough capital.
- Small market along the coast /sparse population.
- Stiff competition from foreign fishermen.
- Use of small boats discourage deep sea fishing/ poor technology.
- Warm waters of the tropics discourage fish breeding.
- Narrow continent shelf.
- Shallow waters due to the presence of coral reefs. 3x1 =3mks
- Characteristics of Pelagic fish.
- Why the government of Kenya should encourage fish farming.
- It occupies less space.
- Fish supply protein.
- Creates job opportunities.
- Some fish from the ponds are exported to earn foreign exchange.
- May lead to the development of fish related industries.
- Its free from international disputes. 4x1=4mks
-
- Seining 1x1= 1mks
-
- Fishing boat with the help of another boat(Dory) spread out the seine net in the Lake.
- Nets are held in position using floats.
- Nets are tied to some weights to keep it in water.
- The Net is attached to the boats which surround a shoal of fish.
- The net is pulled from both ends.
- The net is hauled over and fish emptied. 4mks
- Problems facing fishing in Japan
- Over fishing depleted some fish species.
- Industrial pollution of Japanese waters.
- Restrictions imposed on Japanese fleets by her neighbours.
- Factors favouring fishing in the North west pacific grounds
- Convergence of the cold OyasiwoKamchtaka current and warm Kurosiwo.
- Broad continental shelf favours the growth of Planktons.
- The indented North East Asian coastline with several Islands.
- The mountainous landscape hinder agriculture making fishing the only alternative source of food.
- Availability of large ready market High Asian population provide market and
- Labour.
- Advance technology.
- Modern and efficient transportation facilities.
-
-
-
- Advantages of railway transport over road transport
- Railways can carry more goods over long distances at once
- Railway are cheaper than roads
- Railways are less susceptible to traffic jams
- Once built, railways do not require frequent relaying unlike roads, which are frequently resurfaced
- Railways are more efficient because they operate on rigid timetable
- Railways are free to accidents
- Conditions of Kenyan roads contributing to road carnage
- Some roads have potholes/ uneven road surface...
- Some roads are steep/ have sharp bends.
- Some roads are slippery.
- Some roads are not marked/ absence of road signs.
- Some roads have loose surface/ dusty.
- Some roads are narrow.
- Some roads have potholes/ uneven road surface...
- Advantages of railway transport over road transport
- Reasons why railway links among african counries are underdeveloped
- African countries have railways of different gauges, which make it difficult for them to join
- The countries were colonized by different European powers who constructed railways to transport raw materials from the interior to the ports within their own colonies
- Political differences/ differences/ different political ideologies/ political instability among African countries hinder efforts to construct railway line to link them
- African countries produce similar goods hence there is limited trade between them. ( this does not warrant construction of railway lines)
- Railways are expensive to construct/ most African countries are poor/ inadequate capital and hence expensive to construct/ expand
- Parts of Africa are unproductive so it would be uneconomical to construct railway lines
- African countries have railways of different gauges, which make it difficult for them to join
-
- Physical factors which favour the location of settlements
- Availability of water supply/ good drainage
- Availability of land/space
- Nature of relief
- Suitability of climate/good rainfall
- Absence of pest and diseases/health environment fertile soils
- Availability of water supply/ good drainage
- Difference in functions betwenn New York and Nairobi cities
Nairobi New York It is an inland/dry port
It is a national capital
It is a regional commercial centreIt is a sea port It is a state capitalIt is an international commercial centre
- Physical factors which favour the location of settlements
- Compare the ports of Mombasa and Rotterdam under:
- Transport to the interior - Mombasa relies on road, railway, air and pipeline to the interior while Rotterdam has in addition, river Rhine and canals Rotterdam is a major transshipment centre.
- The size of the hinterlands - Both ports have extensive hinterlands. Mombasa’s hinterland extends to DRC congo while Rotterdam serves the continental Europe.
-
Download Geography Paper 2 Questions and Answers - ACK Diocese Mumias Joint Evaluation Mock 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students