INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name and Adm.No. in the spaces provided.
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided
- Candidates should check to ascertain that all pages are printed as indicated and that no questions are missing.
FOR EXAMINERS USE ONLY
|
QUESTION |
MAXIMUM SCORE |
CANDIDATE’S SCORE |
|
1 |
||
|
2 |
||
|
3 |
||
|
TOTAL |
40 |
|
QUESTIONS
- You are provided with solutions labeled L1,L2 and L3. L3 is the same as L2 except that L3 has been boiled.
Label three test tubes A,B and C. into the test-tube labeled A, add 1ml of solution L1.
Into the test tube labeled B, add 1ml of L1 and 1ml of L2.
Into the test tube labeled C, add 1ml of L1 and 1ml of L3.- Withdraw a drop from test tube A and place in on a white tile. To the drop, add one drop of iodine solution. Record your observation in the table below. (3mks)
Repeat the procedure with contents in test-tubes B and C. record your observations in the table. Place the three test tubes labeled A,B and C into a water bath at 37ºC. Ensure that the temperature of the water bath does not fall below 35ºC or exceed 38ºC. Leave the set up for about 30 minutes.Test tube
Observation
conclusion
A
B
C
- After 30 minutes, test the contents of each of the test tubes labeled A,B and C following the procedure in (a) above. Record your observations in the table below. (3mks)
Test tube
Observation
conclusion
A
B
C
- Account for the results at the end of the experiment in the test tube labeled:
- B (1mk)
- C (2mks)
-
- Suggest the identity of solution L2. (1mk)
- Give reasons for your answer in d(i) above. (3mks)
-
- Suggest where the process being investigated in this experiment would take place in:-
an animal
a plant - Give a reason for your answer in e(i) above. (1mk)
- Suggest where the process being investigated in this experiment would take place in:-
- Withdraw a drop from test tube A and place in on a white tile. To the drop, add one drop of iodine solution. Record your observation in the table below. (3mks)
- You are provided with a piece of petiole of kale, two unknown liquids labeled E1 and E2, means of cutting and means of timing.
- Using the blade split the pieces lengthwise into halves and then into quarters.
- Place two of the splits in liquid E1 and the other two in liquid E2.
- Allow the set up to stand for 30 minutes
- Record the appearance of the splits placed in:
- Liquid E1 (1mk)
- Liquid E2 (1mk)
- Account for the appearance of the split placed in
- Liquid E1. (4mks)
- Liquid E2. (3mks)
- State the importance of the physiological process in the above experiment in plants.(3mks)
- Record the appearance of the splits placed in:
- The photograph below is specimen from the same animal of two different bones each shown in two views. Examine them.
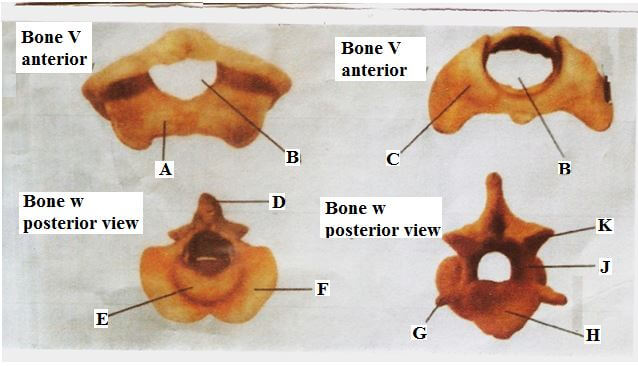
- Identify the two specimens. (2mks)
Specimen V
Specimen W - Give four observable differences between bones V and W. (4mks)
- Name the structure that articulated with part labeled A. (1mk)
- State two roles of opening labeled B. (2mks)
- Name the part labeled E. (1mk)
- State the function of each part labeled H and J on bone W. (2mks)
H
J
- Identify the two specimens. (2mks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
-
Test tube
Observation
Conclusion
A
B
C
Blue black
Blue black
Blue black
Starch present;
Starch present;
Starch present;
-
Test tube
Observation
Conclusion
A
B
C
Blue black
Brown / Orange / yellow colour of iodine solution
Blue black
Starch present;
Starch absent;
Starch present;
-
- B – Colour of iodine solution remains since starch has been digested / hydrolysed; acc; glucose / simple sugar / monosaccharide / disaccharide. (1mk)
- C – Blue-black since starch is present since Boiling denatured / destroyed L2 therefore no conversion; (2mks)
-
- Salivary amylase / starch digesting enzyme / ptydlin / diastase; (1mk)
- It has digested starch
Can be denatured / destroyed by boiling
Acts within a narrow range of temperature / act at 35ºc – 38ºc / acts at suitable / optimum comparative. (3mks)
-
- Animal – mouth / duodenum / small intestine; rej. Gut / digestive system / alimentary canal / intestine. (1mk)
Plant – leaf of plant / Geminating seeds;
Acc; correct storage organ (1mk) - Starch is digested there / starch digesting enzyme is there / diastase enzyme is present there / amylase enzyme is there; (1mk)
- Animal – mouth / duodenum / small intestine; rej. Gut / digestive system / alimentary canal / intestine. (1mk)
-
-
-
- The split curves with the cortex on the outside / with the epidermis on the inside. (1mk)
- The split curves with the epidermis on the outside / with the cortex on the inside. (1mk)
-
- The splits were placed in a hypotonic solution; the cortical cells gained water by osmosis; became turgid; the epidermal cells are covered with a water proof cuticle; therefore did not gain water the curvature with the cortex on the outside. (4mks)
- The splits were placed in a hypertonic solution; the corical cells lost water big osmosis; become flaccid; the epidermal cells are covered with a water proof cuticle hence the curvature with epidermis on the outside. (3mks)
-
- Support due to turgidity
- Opening and closing of stomata
- feeding in insectivorous plants
- Absorption of water. (3mks)
-
-
- V – Atlas;
W – Axis; -
Bone V
Bone W
i) Broader transverse processes
ii) Absence of odontoid process
iii) Smaller Centrum
iv) Small neural spine
v) Wider neural canal
i) Smaller transverse processes;
ii) Presence of odontoid process;
iii) Larger centrum,
iv) Broad neural spine;
v) Narrower neural canal
- Occipital Condyle;
- Allow passage of the spinal cord;
Articulates with the odontoid process of the axis; - Odontoid process;
- H – Support / bears the weight of the vertebrae above;
J – Protects the spinal cord;
- V – Atlas;
Download Biology Paper 3 Questions and Answers - Mincks Group of Schools Mock Examinations 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
