INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name and index number in the spaces provided above.
- Sign and write the date of examination in the spaces provided above.
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
- KNEC Mathematical tables and electronic calculators may be used.
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary.
- Candidates should check the paper carefully to ascertain that all pages are printed and that no questions are missing.
FOR EXAMINER’S USE ONLY
|
QUESTION |
MAXIMUM SCORE |
CANDIDATES SCORE |
|
1-26 |
80 |
|
QUESTIONS
-
- State the condition under which a Bunsen burner produces a non-luminous flame. (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction that takes place in a luminous flame assuming the laboratory gas is butane. (1mk)
- One of the regions in the non-luminous flame is the unburnt gas region. Describe how the presence of this region can be shown using a piece of paper. (1mk)
- The diagram below is a section of a model of the structure of element T.
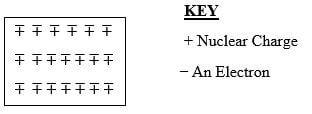
- State the type of bonding that exist in T. (1mk)
- In which group of the periodic table does element T belong? Give a reason. (2mks)
- A radioactive isotope of lead undergoes radioactive decay in two stages as shown below:
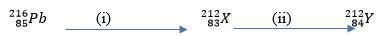
- Identify the particle emitted at each stage. (2mks)
- State one use of radioactive isotopes. (1mk)
-
- State the observations made when Hydrogen Sulphide gas is bubbled through aqueous Lead (II) Nitrate solution. (1mk)
- Write an ionic equation for the reaction above. (1mk)
- The set up below was used to investigate the reaction between dry hydrogen gas and Copper (II) Oxide.
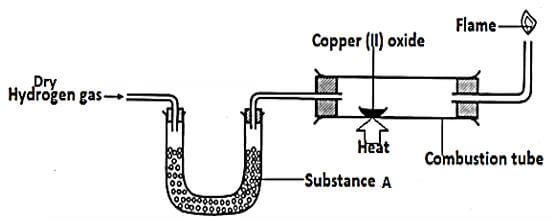
- Name substance A. (1mk)
- State the observation made in the combustion tube. (1mk)
- Explain the observation in (b) above. (1mk)
-
- Consider the following equation.
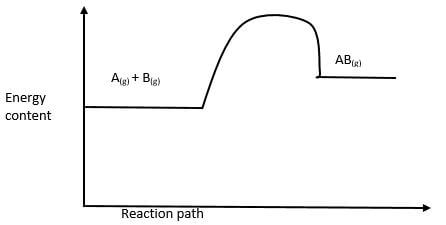
On the same axis, sketch the graph when a catalyst is added. (1mk) - Hydrazine
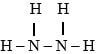 is used as a fuel in rockets. Using the bond energies in the table below. Calculate the enthalpy change for combustion of hydrazine. (3mks)
is used as a fuel in rockets. Using the bond energies in the table below. Calculate the enthalpy change for combustion of hydrazine. (3mks)
N2H4(l) + O2(g) → N2(g) + 2H2O(g)
Bond
Bond energy kJ/mol
N – H
N – N
O = O
N Ξ N
O – H
388
163
496
944
463
- Consider the following equation.
- The diagram below represents large scale manufacture of hydrochloric acid. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
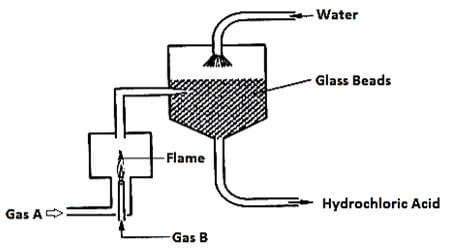
- Identify
- Gas A (1mk)
- Gas B (1mk)
- Write the chemical equation for the reaction between gas A and gas B. (1mk)
- State the role of glass beads in the process. (1mk)
- Identify
- Use the following information on substances S, T, V and Hydrogen to answer the question that follow.
- T displaces V from a solution containing V ions.
- Hydrogen reacts with the heated oxide of S but has no effect on heated oxide of F.
- Arrange substances S, T, V and Hydrogen in order of increasing reactivity. (2mks)
- If T and V are divalent metals, write an ionic equation for the reaction in (i) above. (1mk)
- Describe how the PH of anti-acid (Actal tablet) can be determined in the laboratory. (3mks)
-
- A student electroplated a spoon with copper metal. Write an equation for the reaction at the cathode. (1mk)
- Calculate the time in minutes required to deposit 1.184 grams of Copper if a current of 2A was used. (1 Faraday = 96500 coulombs, Cu = 63.5) (2mks)
- When steam was passed over heated charcoal as shown in the diagram below, hydrogen gas and Carbon (II) oxide were formed.
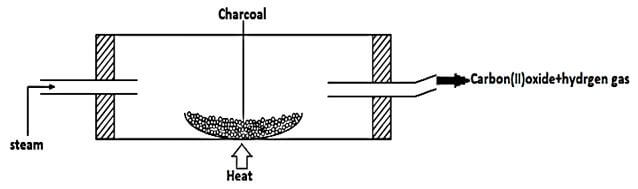
- Write a balanced equation for the reaction which takes place in the combustion tube. (1mk)
- Name two uses of Carbon (II) oxide gas, which are also the uses of hydrogen gas. (2mks)
- A given sample of ink is a mixture of red dye, blue dye and orange dye. The blue dye is least absorbed than the rest and the red dye is the most sticky.
- Complete the paper chromatogram below showing their separation. (1½mks)
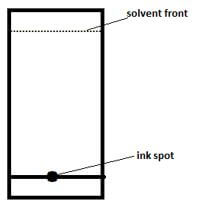
- The above dyes are soluble in water. Describe how a pure sample of blue dye can be obtained. (1mk)
- Name the solvent used in paper chromatography. (½ mk)
- Complete the paper chromatogram below showing their separation. (1½mks)
- In an experiment to investigate the conductivity of substances, a student used the set up shown below.
The student noted that the bulb did not light.- What had been omitted in the set up. (1mk)
- Explain why the bulb lights when the omission is corrected? (2mks)
- The results of an experiment to determine the solubility of potassium chlorate in water at 30ºC were as follows.
Mass of dish = 15.86g
Mass of dish + saturated solution at 30ºC = 26.8g
Mass of dish + solid chlorate after evaporation to dryness = 16.68g
Calculate the mass of saturated solution containing 60g of water at 30ºC. (3mks) -
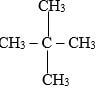
- Give the systematic names of the following compounds. (2mks)
- CH3CΞCCH2CH3
- Describe a chemical test that can be carried out inorder to distinguish between.
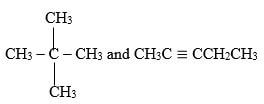
(2mks)
- Give the systematic names of the following compounds. (2mks)
-
- Draw a labelled diagram showing the atomic structure of 2311Na (2mks)
- The atomic number of phosphorous is 15. Draw a dot (˖) and cross (x) diagram for the compound formed when phosphorous react with chlorine. (1mk)
-
- State Gay-Lussaic’s Law. (1mk)
- 15cm3 of a gaseous hydrocarbon reacted completely with 45cm3 of Oxygen gas. 30cm3 of carbon (IV) oxide were formed. Determine the formula of the hydrocarbon given that all volume of gases were measured under same conditions of temperature and pressure. (2mks)
- Consider the following reactions
N2(g) + 3H2(g) ↔ 2NH3(g)
The enthalpy is -92.4kJ per mole of nitrogen.- Give the enthalpy change per mole of ammonia. (1mk)
- State and explain how each of the following affects the yield of ammonia: (2mks)
- Increase in temperature. (1mk)
- Finely divided iron. (1mk)
- Excess iron was allowed to rust in dm3 of moist air remaining was measured at 1 atmospheric pressure each day. The results were as follows.
Day
0
1
3
4
5
6
7
8
Volume (cm3)
2000
1900
1720
1660
1620
1600
1600
1600
- Write an equation for the formation of rust. (1mk)
- On which day was the reaction complete. Explain. (1mk)
- What is the percentage volume of oxygen in air. Show your working. (1mk)
- 20. Element P3+ and Q2- belong to period three of the periodic table.
- Write the electronic arrangement of their atoms. (2mks)
- Write the formula of the compound formed by P and Q. (1mk)
-
- Give the IUPAC name of the following:
CH3CH2COOCH2CH3 (1mk) - Give the chemical name to which the compound you have named in (i) above belongs.(1mk)
- Name the two substances used in the formation of the compound in (i) above. (1mk)
- Give the IUPAC name of the following:
- The set up below was used to investigate some properties of two gases M and N.
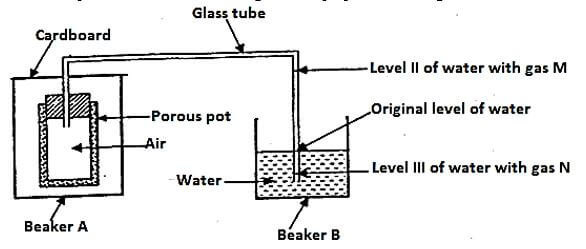
When beaker A was filled with gas M, the level of water in the glass tube rose to point II. When the experiment was repeated using gas M, the level of water dropped to point III. Explain these observations. (2mks) - Nitric (V) acid may be prepared in the laboratory by the action of concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid on a suitable nitrate and distilling off the nitric V acid.
- Why is the apparatus used in the preparation of nitric (V) acid made of glass. (1mk)
- Pure nitric (V) acid is colourless but the products in the laboratory preparation is usually yellow. Explain. (2mks)
- Starting with copper metal, describe how a pure sample of Copper (II) carbonate can be prepared. (3mks)
- Aluminum is both malleable and ductile.
- Differentiate between malleable and ductile. (2mks)
- State one use of aluminium based on:
- Malleability (1mk)
- Ductility (1mk)
- Sulphur (IV) oxide and nitrogen (IV) oxide reacts as shown in the equation below.
SO2(g) + NO2(g) -SO3(g) + NO(g)- Using the oxidation numbers of either sulphur or nitrogen, show that this is redox reaction. (2mks)
- Identify the reducing agent. (1mk)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- When air hole is completely/fully closed.
- C4H10 (g) + 4O2 (g) → C(s) + 3CO(g) + 5H2O(l) /(g)
Or
C4H10 (g) + 3O2(g) → C(s)+CO2(g) + 5H2O(l)/ (g) 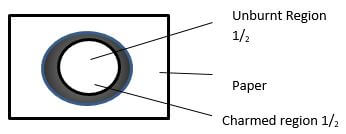
Or
Slip a piece of paper across the middle point of the flame. Several times. Remove and observe ½
The central part remains unburnt while other part burns. ½ Accept wooden splint
-
- Metallic bond
- Group I (1mrk) Each action contains one electron in the outermost energy level (1mrk)
-
-
- Alpha (a)
- Betta (-Ie)
-
- Cancer treatment
- Detecting cracks in metals
- Carbon dating of plants and animals
-
-
- Black Precipitate
- Pb2+(aq)+ S2-(aq) → Pbs(s)
-
- Anhydrous calcium chloride
- Black CuO changes to brown solid
- Hydrogen reduces CuO to copper metal which is brown
Colorless liquid forms on the cooler parts of the combustion tube.
-
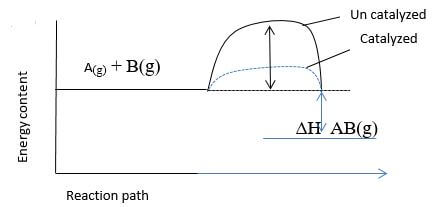
- N2H4 + O2 (g) → N2(g)+ 2H2 O(l)
Bond Breaking Bond Formation
4x 388 = 1552 1x944= 944
1x163 4x464= 1856
1x 496=496 -2800 kJ
+2211 kJ
ΔH = -589kJ
-
- A - chlorine
B – Hydrogen - H2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g)
- To increase surface area for dissolution of hydrogen
Chloride gas in water. No present sucking back.
- A - chlorine
-
- S, Hydrogen, V, T
- T(s) + V2+ (aq) → V(s)+ T2+(aq)
- Crush the tablet with mortex and pistle ½, add water stir to dissolve ½, add the universal indicator ½ , match the color with that of PH chart ½, determine the PH 1mrk.
-
- Ca2+(aq) + 2e- → Cu(s)
- 63.5g of Cu → (96500x2)C
Thus 1.184g Cu = 1.184g x 193000
63.5
= 3598.66
Quantity = It → 3598.66
2t = 3598.6
2
= 1799. 3 Sec
=30 sec
-
- C(s) + H2O(g) → CO(g) + H2(g)
- Reducing agent
Together with oxygen is used as fuel
-
-
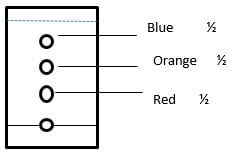
- Wash the blue spot in the chromatogram with plenty of water ½
Evaporate the water to obtain the dye ½ - Ethanol/ Propanol
-
-
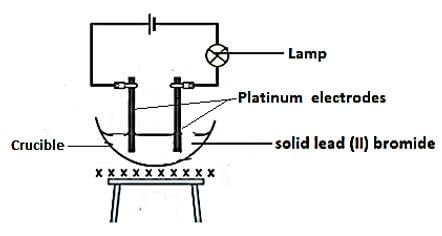
- Source of heat
- The solid Pb Br2 melts to form Pb2+ and Br – ½
These mobile ions ½ conducts electric current ½ Then Bulb lights ½
- Mass of KClo3 = 16.86 – 15.86 = 1g ½
Mass of water = 26.86 – 16.86 = 10g ½
1g of KClO3 saturates 10g of water at 30ºC ½
X(g) of K ClO3 saturates 60g of water at 30ºC = 60x1 = 6g ½
10
Mas of saturated solution = 6+ 60
= 66g -
-
- 2, 2 – dimethyl propane
- Pent – 2 – yne
- Add acidified KMnO4 solution to both separately
CH3C = CCH2 CH3 will change purple acidified KMnO4
Colourless.
CH3 (CH2)2 CH3 doesn’t ½
-
-
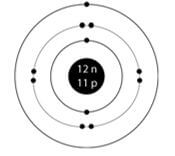
11P ½
12N ½ 3 energy levels ½
11 electrons ½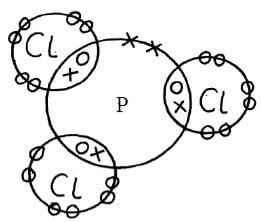
-
- When gases react they do so in volumes which bears simple whole number ratio to one another and to the volume of products if gaseous when temperature and pleasure remains constant 1mrk
- Cx Hy + O2(g) → CO(g) + H2 O(g)
15 45 30 30
15 15 15 15
1 3 2 2
C Hy + 3O2 → 2CO2(g) + 2H2 O(g)
Cx Hy = C2 H4 ½
-
- -92.4 = -46.2kJmol-1 penalize ½ for missing sign or 2 wrong units
2 -
- Lowers the yield ½ forward reaction is exothermic/ Backward reaction is endothermic ½
Penalize for backward reaction is favoured - No effect ½ catalysts have no effect on the position of Equilibrium. ½
- Lowers the yield ½ forward reaction is exothermic/ Backward reaction is endothermic ½
- -92.4 = -46.2kJmol-1 penalize ½ for missing sign or 2 wrong units
-
- 4Fe(s) + 3O2(g) + NH2O → 2Fe2 O3.NH2O
- 6th day ½, volume of air remains constant ½
- % of oxygen gas = 2000 – 1600 x100 ½
2000
=20% ½
-
- 2. 8. 3
2. 8. 6 - P2Q3
- 2. 8. 3
-
- Ethyl propanoate
- Ester/ Alky/alkanoate
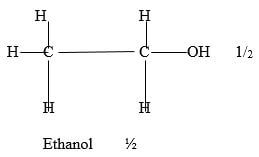
Ethanol ½
- Gas m is lighter than air hence creating low pressure, water will rise to occupy space left as gas m escapes to the atmosphere. Gas N is denser than air so air enter the porus pot hence increasing the pressure hence pushing water down.1mrk
-
- Nitric acid is a strong oxidizing agent and attacks rubber corks and rubber tubes.
- Contain dissolved nitrogen (IV) oxide which reacts from decomposition of nitric (V) acid
- Heat copper metal in air to form copper (II) oxide, 1mrk,
React excess copper (II) oxide with dilute H2SO4(aq) to obtain copper (II) sulphate solution. 1mrk Heat the solution to Saturation ½ and allow it to cool to form copper (II) sulphate Crystals ½ -
- Malleable material that can be hammered into sheets while ductile is the material that can be drawn into wires
-
- Used in making of cooking utensils.
- Used to make overhead cables
-
- SO2(g) + NO2(g) →SO3(g) + NO(g)
+4 +4 +6 +2
Oxidation number of sulphuric increases from +4 to +6
Oxidation of number of nitrogen decreases - Sulphur – dioxide/ SO2
- SO2(g) + NO2(g) →SO3(g) + NO(g)
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Mincks Group of Schools Mock Examinations 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
