INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:-
- Write your name, index number and school in the spaces provided above.
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided above.
- You are supposed to spend the first 15 minutes of the 2 ½ hours allowed for this paper reading the whole paper carefully before commencing your work
- Marks are given for a clear record of the observations actually made their suitability, accuracy and the use made of them.
- Candidates are advised to record their observations as soon as they are made.
- Non- programmable silent calculators and KNEC Mathematical tables may be used.
|
QUESTION |
PART |
MAXIMUM SCORE |
CANDIDATE’S SCORE |
|
1 |
A |
05 |
|
|
B |
15 |
||
|
2 |
A |
10 |
|
|
B |
10 |
||
|
40 |
|||
QUESTIONS
QUESTION 1
You are provided with the following apparatus;
- A carbon resistor labelled X .
- A carbon resistor labelled Z
- A voltmeter (0 – 5V)
- An ammeter (0 – 1A)
- 5 10Ω carbon resistors.
- Centre zero galvanometer.
- 2 new dry cells and cell holder.
- 8 connecting wires at least 4 with crocodile clips at one end.
- Jockey
- A resistance wire labelled AB mounted on mm scale.
- A switch.
PART A
- Set up the circuit below.
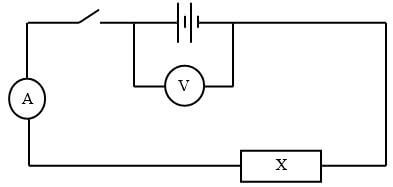
- Record the voltmeter reading E when the switch is open.
E = …………………………………………………………….V (1mk) - Close the switch and record the voltmeter and Ammeter readings V and I respectively.
V = ………………………………………………………….V (1mk)
I = …………………………………………………………..A (1mk) - Account for the difference between E and V. (1mk)
- Calculate the resistance R for resistor X. (1mk)
PART B
- Set up the circuit as shown in the figure below.
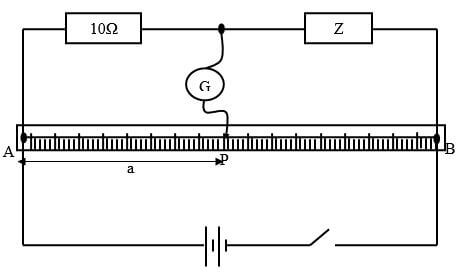
- Close the switch. Tap the jockey at various points on the wire AB and locate point P at which the galvanometer shows zero deflection. Measure and record in the table below the length a where a = AP.
- Repeat procedure b) using two 10Ω resistors in series, then three resistors in series, then four resistors in series and five resistors in series.
- Record your readings in the table below and complete the table where X is the effective resistance for the series combination. (5mks)
Number of 10Ω carbon resistors
One
Two
Three
Four
Five
X (Ω)
a (cm)
1/X (Ω-1)
1/a (cm-1)
- Plot a graph of 1/a (cm-1) against 1/X (Ω-1) (5mks)
- Determine the slope m of the graph. (3mks)
- Given that 1/a=R/K .1/X+1/K where K = 100cm, use the graph to determine R. (2mks)
QUESTION B
PART A
You are provided with the following;
- Metre rule.
- Screen
- Glass beaker (250ml)
- Water plasticine.
- A candle.
Proceed as follows;
- Add a volume V= 200ml of water into the beaker.
- Measure the value of h, the height of water in the beaker.
h = ………………………………………………cm (1mk) - Calculate the value of internal radius R of the beaker using the formula
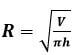 where π=22/7 (2mks)
where π=22/7 (2mks)
R = ……………………………………………… - Fill the beaker with water and set the apparatus as shown below.
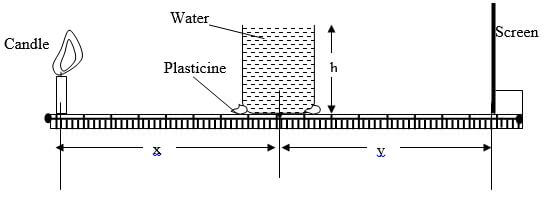
- Position the candle which acts as an object above the metre rule and 10R from the centre of the water ‘lens’.
- Measure the object distance x. (1mk)
x = …………………………………………………………….cm - Move the screen towards or away from the water lens to obtain a sharp and focused bright image (line) on the screen.
- Measure the value of image distance y. (1mk)
y = ………………………………………………………..cm - Repeat the experiment for the other values of x in the table below and note and record the corresponding values of y. Complete the table.
Beaker position
10R
9R
8R
x
y
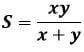
- Determine the average value of S. (2mks)
- What does S represent. (1mk)
PART B
You are provided with the following;
- Vernier calipers. (can be shared)
- Micrometer screw gauge (can be shared)
- Boiling tube.
- Test tube.
- Some water in a beaker
- Half metre rule.
- 2 ball bearings.
- Some sand.
- Spatula
- Complete retort stand.
- Measure and record the diameter of one ball bearing using the micrometer screw gauge.
d = ……………………………………………mm (1/2mk) - Determine the volume V of the ball bearing. (1mk)
V = …………………………………………………..cm3 - Measure and record the outer diameter D of the test tube using the vernier calipers.
D = ………………………………………………….. (1/2mk) - Calculate the cross-sectional area A of the tube. (1mk)
A …………………………………………………….cm2 - Mount the boiling tube on the clamp as shown below and put some water to a height of about 8.5cm from bottom.
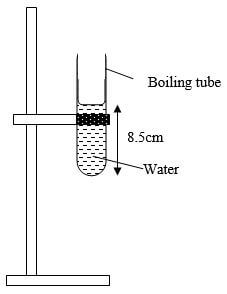
- Gently lower the test tube into the water in the boiling tube.
- Add some sand into the test tube bit by bit until the test tube floats upright in the water.
- Note and record height ho of the water in the boiling tube from the bottom.
ho = …………………………………………………cm (1mk) - Gently lower one ball bearing into the test tube and note and record the new level h in the table below.
- Add the other ball bearing and note and record the corresponding height h.
- Compute the values of h- ho and complete the table. (2mks)
No. of ball bearings (N)
Height h (cm)
h – ho (cm)
1
2
- Calculate S the average value of X where
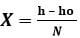 (1mk)
(1mk) - Given that
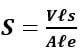 where ℓs is the density of steel and ℓe the density of water, determine the ratio of ls/le (2mks)
where ℓs is the density of steel and ℓe the density of water, determine the ratio of ls/le (2mks) - What is the significance of the ratio ls/le (1mk)
MARKING SCHEME
QUESTION 1
You are provided with the following apparatus;
- A carbon resistor labelled X .
- A carbon resistor labelled Z
- A voltmeter (0 – 5V)
- An ammeter (0 – 1A)
- 5 10Ω carbon resistors.
- Centre zero galvanometer.
- 2 new dry cells and cell holder.
- 8 connecting wires at least 4 with crocodile clips at one end.
- Jockey
- A resistance wire labelled AB mounted on mm scale.
- A switch.
PART A
- Set up the circuit below.

- Record the voltmeter reading E when the switch is open.
E = ……3.0 ± 0.2…………….V (1mk) - Close the switch and record the voltmeter and Ammeter readings V and I respectively.
V = ……2.7 ± 0.2……………….V (1mk)
I = ………0.26 ± 0.02……………..A (1mk) - Account for the difference between E and V. (1mk) Lost voltage
- Calculate the resistance R for resistor X. (1mk)
R = V/i = 2.7/0.26 = 10.38Ω
(student's work ..... answer with correct units to 4 s.f or exact)
PART B
- Set up the circuit as shown in the figure below.

- Close the switch. Tap the jockey at various points on the wire AB and locate point P at which the galvanometer shows zero deflection. Measure and record in the table below the length a where a = AP.
- Repeat procedure b) using two 10Ω resistors in series, then three resistors in series, then four resistors in series and five resistors in series.
- Record your readings in the table below and complete the table where X is the effective resistance for the series combination. (5mks)
Number of 10Ω carbon resistors
One
Two
Three
Four
Five
1 mk
± 2.0 cm @ 1/2 max
2 mks
1 mk
1 mk 4 s.f or exact
X (Ω)
10
20
30
40
50
a (cm)
9.1
16.5
23.0
24.1
29.5
1/X (Ω-1)
0.1
0.05
0.03333
0.025
0.02
1/a (cm-1)
0.1099
0.06061
0.04348
0.04149
0.03390
- Plot a graph of 1/a (cm-1) against 1/X (Ω-1) (5mks)
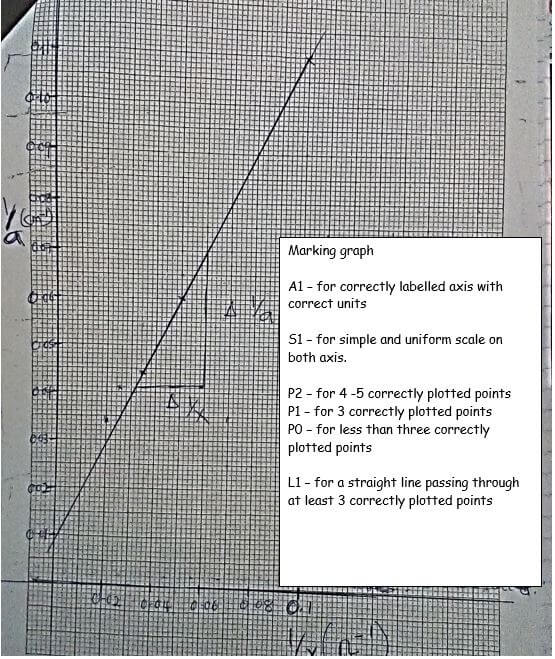
- Determine the slope m of the graph. (3mks)
slope = 0.07 - 0.041
0.06 - 0.31
= 0.029 = 1Ω/cm
0.029
follow student's work
Deny if L mark is 0
Answer correct to 4 s.f. or exact with units.
Deny 1/2 mk if no units - Given that 1/a=R/K .1/X+1/K where K = 100cm, use the graph to determine R. (2mks)
R/K = slope
R/100 = 1
R = 100 Ω/cm
Follow student’s work.
Answer correct to 4 s. f. or exact with units.
Deny ½ mk if no units
QUESTION B
PART A
You are provided with the following;
- Metre rule.
- Screen
- Glass beaker (250ml)
- Water plasticine.
- A candle.
Proceed as follows;
- Add a volume V= 200ml of water into the beaker.
- Measure the value of h, the height of water in the beaker.
h = …7.0 ± 0.5……cm (1mk) - Calculate the value of internal radius R of the beaker using the formula
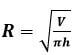 where π=22/7 (2mks)
where π=22/7 (2mks)
R = ………………………………………………
Follow student’s work.
Answer correct to 4 s. f. or exact with units.
Deny ½ mk if no units - Fill the beaker with water and set the apparatus as shown below.

- Position the candle which acts as an object above the metre rule and 10R from the centre of the water ‘lens’.
- Measure the object distance x. (1mk)
x = ……30.2 ± 0.2……….cm - Move the screen towards or away from the water lens to obtain a sharp and focused bright image (line) on the screen.
- Measure the value of image distance y. (1mk)
y = ………6.0 ± 0.2………..cm - Repeat the experiment for the other values of x in the table below and note and record the corresponding values of y. Complete the table.
± 0.2cm ½ mk @ in columns 2 n 3Beaker position
10R
9R
8R
x
30.2
27.1
24.0
y
6.0
8.8
9.8
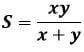
5.005
6.643
6.959
1mk correct to 4 s.f. or exact all values- Determine the average value of S. (2mks)
Saverage = 5.005 + 6.643 + 6.959 = 6.202
3
Follow student’s work.
Answer correct to 4 s. f. or exact with units.
Deny ½ mk if no units - What does S represent. (1mk)
Focal length of the water lens
- Determine the average value of S. (2mks)
PART B
You are provided with the following;
- Vernier calipers. (can be shared)
- Micrometer screw gauge (can be shared)
- Boiling tube.
- Test tube.
- Some water in a beaker
- Half metre rule.
- 2 ball bearings.
- Some sand.
- Spatula
- Complete retort stand.
- Measure and record the diameter of one ball bearing using the micrometer screw gauge.
d = ……5.78 ± 0.02………mm (1/2mk) - Determine the volume V of the ball bearing. (1mk)
V = ……0.1011………..cm3
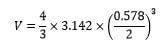
Follow student’s work.Answer correct to 4 s. f. or exact with units.
Deny ½ mk if no units - Measure and record the outer diameter D of the test tube using the vernier calipers.
D = ……1.85 ± 0.02…….. (1/2mk) - Calculate the cross-sectional area A of the tube. (1mk)
A ………2.688……………….cm2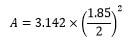
Follow student’s work.
Answer correct to 4 s. f. or exact with units.
Deny ½ mk if no units - Mount the boiling tube on the clamp as shown below and put some water to a height of about 8.5cm from bottom.

- Gently lower the test tube into the water in the boiling tube.
- Add some sand into the test tube bit by bit until the test tube floats upright in the water.
- Note and record height ho of the water in the boiling tube from the bottom.
ho = ……13.0 ± 0.5…cm (1mk) - Gently lower one ball bearing into the test tube and note and record the new level h in the table below.
- Add the other ball bearing and note and record the corresponding height h.
- Compute the values of h- ho and complete the table. (2mks)
1mk for correct evaluation of both values of (h – ho)No. of ball bearings (N)
Height h (cm)
h – ho (cm)
1
13.5 ± 0.2 0.5 2
14.0 ± 0.2 1.0 - Calculate S the average value of X where
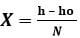 (1mk)
(1mk)
0.5 + 0.5 = 0.5 cm
2
Follow student’s work.
Answer correct to 4 s. f. or exact with units.
Deny ½ mk if no units - Given that
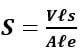 where ℓs is the density of steel and ℓe the density of water, determine the ratio of ls/le (2mks) 13.29
where ℓs is the density of steel and ℓe the density of water, determine the ratio of ls/le (2mks) 13.29 - What is the significance of the ratio ls/le (1mk)
relative density of steel
CONFIDENTIAL
Question 1
- A carbon resistor labelled X (10Ω)
- A carbon resistor labelled Z (10kΩ)
- A voltmeter (0 – 5V)
- An ammeter (0 – 1A)
- 5 10Ω carbon resistors (unlabelled)
- Centre zero galvanometer.
- 2 new dry cells - size D
- Cell holder.
- 8 connecting wires at least 4 with crocodile clips at one end.
- Jockey
- A resistance wire labelled AB (A at 0)mounted on mm scale. (diameter 0.29mm)
- A switch.
Question 2
- Metre rule.
- Screen
- Glass beaker (250ml)
- Water
- A candle.
- Vernier calipers. (can be shared)
- Micrometer screw gauge (can be shared)
- Boiling tube.
- Test tube.
- Some water in a beaker
- Half metre rule.
- 2 ball bearings. (size ¼’’)
- Some sand.
- Spatula
- Complete retort stand.
Download Physics Paper 3 Questions, Answers and Confidential - Mincks Group of Schools Mock Examinations 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
