INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name, class, school and admission number in the spaces provided.
- All your answers must be written in the spaces provided in your question paper.
- This paper consists of section A and B. Answer all the questions in section A, question 6 and any other two questions in section B.
- All answers must be written in English.
FOR EXAMINER’S USE ONLY
|
|
CANDIDATE’S SCORE |
MAXIMUM SCORE |
|
Section A Question 6 Question 7 Question 8 Question 9 Question 10 |
|
|
|
TOTAL SCORE
|
|
100 |
QUESTIONS
SECTION A
-
- The diagram below shows the internal structure of the earth. Use it to answer question a (i).
-
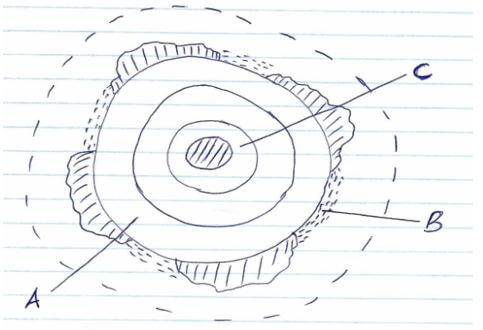
Name the parts labeled A, B and C. (3marks) - Mention two layers of disconuities found in the internal structure of the earth. (2marks)
-
- The diagram below shows the internal structure of the earth. Use it to answer question a (i).
-
- Differentiate between soil catena and soil profile. (2marks)
- State three importances of soil water. (3marks)
-
- Outline two types of river erosion. (2marks)
- State three factors influencing river transportation. (3marks)
-
- Define an earthquake. (2marks)
- State three effects of earthquakes on built-up areas. (3marks)
-
- What is a sea breeze. (2marks)
- State three effects of sea breeze on adjacent areas. (3marks)
SECTION B
-
-
- Give two types of scales used in map extract. (2marks)
- Give the longitudinal extent of the map. (1mark)
-
- Calculate the area of Nyeri Hill forest. (2marks)
- Citing evidence, state the social function of Nyeri. (6marks)
-
- Using a scale of 1cm to represent 40meters, draw a cross-section along Northing 57from grid reference 640570 to 700570 (4marks)
On it mark and label the following.- Boundary (1mark)
- Dry weather road (1mark)
- River Muringato (1mark)
- State two factors that have influenced trade in the area covered by the map. (2marks)
- Using a scale of 1cm to represent 40meters, draw a cross-section along Northing 57from grid reference 640570 to 700570 (4marks)
- Describe settlement in the area covered by the map. (5marks)
-
-
-
- What is vulcanicity. (2marks)
- Apart from sill, name three other intrusive features. (3marks)
- The diagram below shows a composite volcano.
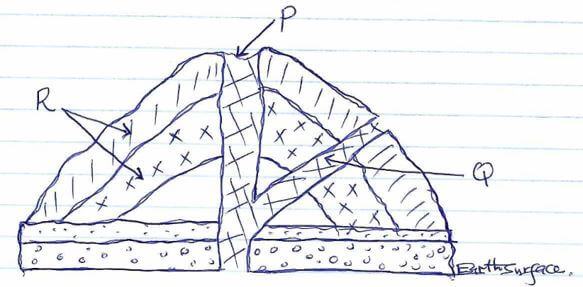
- Name the features marked P, Q, and R. (3marks)
- State three characteristics of the above volcano. (3marks)
- You are required to carry out a field study in a region affected by vulcanicity.
- State three objectives you would formulate for the study. (3marks)
- Apart from preparing a route map, how would you prepare for the field study. (3marks)
- Explain four significances of vulcanicity to human activities. (8marks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between a mineral and a mineral ore. (2marks)
- Describe the following characteristics of minerals;
- Colour (2marks)
- Lustre (2marks)
- Density (2marks)
-
- Name two examples of plutonic rocks. (2marks)
- Explain how mechanically-formed sedimentary rocks are formed. (4marks)
- Name the type of rock which results from the metamorphism of:
- Clay (1mark)
- Coal (1mark)
- Limestone (1mark)
- Explain four benefits of rock in the economy of Kenya. (8marks)
-
-
- What is weathering? (2marks)
-
- State three agents of weathering. (3marks)
- Describe how block disintegration occurs. (5marks)
- Explain how the following factors influence weathering
- Time (2marks)
- Nature of the rock (3marks)
- Action of plants. (2marks)
- Your class decided to carry out a field study on the area affected by weathering around your school.
- State three reasons for seeking permission. (3marks)
- Give three methods you would use to collect data. (3marks)
- State two follow up activities you are likely to engage in after the study. (2marks)
-
- Name three types of glaciers. (3marks)
-
- Explain three processes in which glacier erodes. (6marks)
- The diagram below shows features resulting from glaciation.
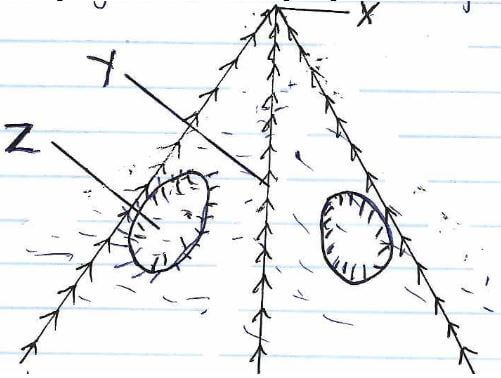
Name the features marked X, Y and Z.
-
- Name three types of glacier moraines. (3marks)
- List three depositional features on glaciated lowlands. (3marks)
- Explain four positive effects of glaciation. (8marks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Parts labeled A, B and C
- A – Mantle
- B – Hydrosphere
- C – Outer-core
(3x1=3marks)
- Layers of discontinuity of the internal structure of the earth.
- Gutenburg discontinuity
- Mohonovicic/moho discontinuity
(2x1=2marks)
- Parts labeled A, B and C
-
- Differentiate between soil catena and soil profile
- Soil catena is the horizontal arrangement of soil from the top of the hill to the valley bottom/down a slope while soil profile is the vertical arrangement of soil layers from the surface downward to the parent rock.
(2x1=2marks)
- Soil catena is the horizontal arrangement of soil from the top of the hill to the valley bottom/down a slope while soil profile is the vertical arrangement of soil layers from the surface downward to the parent rock.
- Importance of soil water
- Regulates temperatures of the soil
- Dissolves minerals in the soil making them easily absorbed by plants.
- Plants absorbs soil water which helps maintain their turgidity of the cells.
- Supplies water for the living organisms in the soil.
(3x1=3marks)
- Differentiate between soil catena and soil profile
-
- Types of a river erosion
- Head ward erosion
- Vertical erosion
- Lateral erosion
(any 2x1=2marks)
- Factors influencing river transportation
- Nature and amount of load
- Speed/velocity of river water
- Volume of water in the river
- The slope of the land
(any 3x1=3marks)
- Types of a river erosion
-
- Definition of earthquake
- Sudden and rapid movement/vibration of crustal rocks caused by seismic waves as a result of sudden release of energy from earth crust.
(2x1=2marks)
- Sudden and rapid movement/vibration of crustal rocks caused by seismic waves as a result of sudden release of energy from earth crust.
- Effects of earthquakes on built-up areas
- Causes damage of structures, building and destruction of property.
- Causes landslides leading to loss of lifes and destruction of Agriculture land
- May lead to destruction of nuclear plants causing pollution which affect human health
- Tsunami causes flooding causing displacement of people.
(any 3x1=3marks)
- Definition of earthquake
-
- What is a sea breeze
- Mass of warm air blowing from the sea to the land during the day.
(2x1=2marks)
- Mass of warm air blowing from the sea to the land during the day.
- Effects of sea breeze on adjacent areas
- Lowers temperature in adjacent areas
- May result to increased rainfall
- Lead to increased humidity in the adjacent areas
(3x1=3marks)
- What is a sea breeze
-
-
- Two types of scales
- Linear scale
- Ratio scale
(2x1=2marks)
- Longitudinal extent.
- 360451E to 370001E
- Two types of scales
-
- Area of Nyeri Hill forest
- Complete squares + Incomplete square’s
2
2+20 10
2
12 km2 ± 0.5
(1x2=2marks)
- Complete squares + Incomplete square’s
- Social function of Nyeri
(any 3x2=6marks)Social function
Evidence
Religious function
Administrative function
Education function
Health function
Trading
Recreation
presence of churches
presence of police station
Ads offices, D.O, Chief centre
presence of schools, colleges
presence of hospitals
presence of market/shops
presence of stadium/golf course
Social welfare
Presence of youth centre
GRAPH PAPER (CROSS- SECTION)
- Area of Nyeri Hill forest
-
- Transport – There is presence of many roads which enhance faster movement of goods and people.
- Settlements – Dense settlement which provide ready market and labour.
- Availability of market evidenced by the presence of dense settlement which provide consumers thus promoting trade.
(any 2x2=4marks)
- Description of settlement.
- There are no settlements in the forest due to government policies.
- Linear settlements along roads for easy accessibility.
- Few settlements on steep slope which discourages construction of buildings/Agriculture.
- Many settlements on gentle slope – encourage construction of houses/well drained.
- There no settlement in Aberdare national park due to conservation policy.
(any 5x1=5marks)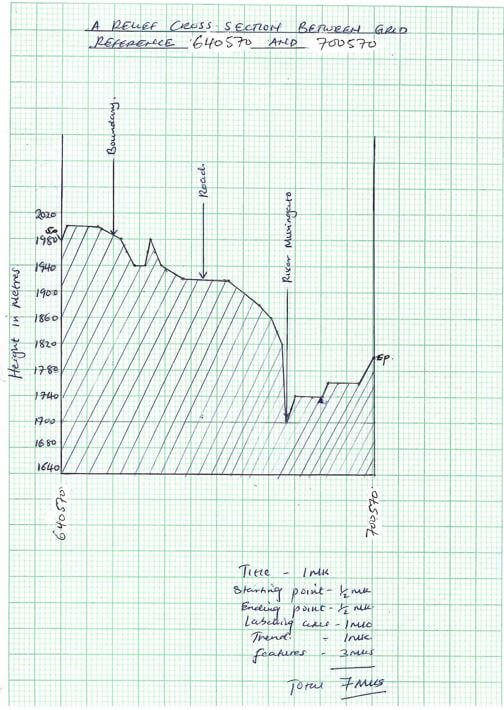
-
-
-
- Definition of vulcanicity
- Vulcanicity is the process by which solids, liquids and gases are intruded into crustal rock of reach the earth surface.
(2x1=2marks)
- Vulcanicity is the process by which solids, liquids and gases are intruded into crustal rock of reach the earth surface.
- Other intrusive features
- Batholith
- Laccolith
- Lapolith
- Dyke
- Phacolity
(any 3x1=3marks)
- Definition of vulcanicity
-
- Parts marked P, Q and R
- P – Crater
- Q – Side vent
- R – Layers of lava and pyrodasts/volcanic ash
(3x1=3marks)
- Characteristics of the feature
- Has alternating layers of lava and pyroclasts
- Has a side vent
- Has a crater at the top
- Has steep or gentle slopes depending on nature of lava involved
- Has parasitic cones/side cones
- Has a central rent
(any 3x1=3marks)
- Parts marked P, Q and R
-
- Objectives of the study
- To find out the possibility of the region becoming a tourist attraction.
- Establish whether volcanicity in the region is active dormant or extinct.
- To find out the volcanic features present in the area.
(any 3x1=3marks)
- How you would prepare for the field study
- Carry out a pre-visit
- Read widely on the topic
- Discuss the topic in class
- Gather relevant tools/equipment’s for the study
- Seek permission from relevant authorities
- Dividing into groups
- Prepare objectives and hypotheses
(any 3x1=3marks)
- Objectives of the study
- Significances of vulcanicity to human activities
- Volcanic mountains receive high rainfall on windward side promoting Agriculture and forestry
- Volcanicity lead to formation of beautiful sceneries that attract tourists earning a country foreign exchange.
- Volcanic rocks disintegrate to form deep and well drained volcanic soils which support crop farming.
- The high rainfall received on windward side of volcanic mountains leads to formation of rivers which promote fishing, irrigation, navigation and HEP generation.
- Volcanicity results to formation of craters which when filled with water form lakes used for fishing.
- Hot springs and geysers formed during volcanity may be used as spas for health purposes.
- Geysers formed through volcanicity may be harnessed to generate geothermal power used in industries and homes for lighting.
(any 4x2=8marks)
-
-
-
- Difference between a mineral and a mineral ore.
- Mineral is an inorganic substance with a definite chemical composition found as or beneath the surface of the earth while mineral ore is a rock bearing a valuable mineral with the rocks of the crust.
(2x1=2marks)
- Mineral is an inorganic substance with a definite chemical composition found as or beneath the surface of the earth while mineral ore is a rock bearing a valuable mineral with the rocks of the crust.
- Characteristics of minerals
- Colour
- Different minerals have different colours for example gold is yellow.
(2x1=2marks)
- Different minerals have different colours for example gold is yellow.
- Lustre
- Minerals differ in their brightness depending on how their surfaces reflect light. Some have smooth surfaces which are shinny while others have rough surfaces which are dull.
(2x1=2marks)
- Minerals differ in their brightness depending on how their surfaces reflect light. Some have smooth surfaces which are shinny while others have rough surfaces which are dull.
- Density
- Minerals have specific gravity/density. Some minerals are heavier while others are light.
(2x1=2marks)
- Minerals have specific gravity/density. Some minerals are heavier while others are light.
- Colour
- Difference between a mineral and a mineral ore.
-
-
-
- Examples of plutonic rocks.
- Gabbro
- Diorite
- Peridotite
- Granite
- Syenite
(any 2x1=2marks)
- Formation of mechanically formed sedimentary rocks. They are formed when eroded rock sediments are transported by wind, water or ice.
- The sediments are deposited in layers on land or in the sea. Over a long period of time, the deposited sediments are compacted and cemented to form sedimentary rocks.
(1x4 = 4marks)
- The sediments are deposited in layers on land or in the sea. Over a long period of time, the deposited sediments are compacted and cemented to form sedimentary rocks.
- Examples of plutonic rocks.
- Rock which result from metamorphism of:
- Clay – slate
- Coal – graphite
- Limestone – marble
(1x3 = 3marks)
- Benefits of rocks to the economy of Kenya
- Some rocks form unique features such as granitic tors which attract tourists earning the country foreign exchange. Which is used to fund other sectors of economy such as Agriculture, education.
- Some rocks such as granite are extracted to provide building and construction materials
- Some sedimentary rocks contain fosil fuels which provide energy for domestic and industrial use.
- Some rocks such as soapstone in Kisii county are used for earning which is sold to earn an income.
- Some rocks such as rock salt are used as food by people and provide salt licks for livestock.
(any 4x2=8marks)
-
-
- Weathering is the breakdown/disintegration and decomposition or rocks at or near the earth’s surface without movement. (2marks)
-
- Agents of weathering
- Water
- Moving ice
- Temperature
- Living organisms
(any 3x1=3mark)
- Occurrence of block disintegration
- This is the breakdown of blocks of rocks from huge rock masses
- A huge mass of rock is subjected to high temperature during the day and very low temperatures at night.
- This causes cracks to form in the rocks.
- The rocks successively expand during the day and contract at night.
- This enlarges the joints and eventually the rocks break into smaller blocks a process called block disintegration.
(5x1=5marks)
- Agents of weathering
- Factors influencing weathering
- Time
- Rocks exposed to the agents of weathering for a long time are more broken than those exposed for a short time.
- Long periods may lead to deep rock weathering compared to short period which leads to shallow weathering.
(2x1=2marks)
- Nature of the rocks
- The chemical composion, rock hardness, texture, permeability of rocks, jointed rocks, influence weathering. Jointed rocks allow water to enter, increasing the rate of weathering.
- Dark minerals in rocks absorb more heat than light ones thus increasing the rate of weathering.
(2x1=2marks)
- Action of plants
- Plants roots grow deep into the ground and penetrate into joints, thus opening them up, hence encouraging physical weathering. Organic aerials released by decomposing plants and in chemical weathering.
(2x1= 2marks)
- Plants roots grow deep into the ground and penetrate into joints, thus opening them up, hence encouraging physical weathering. Organic aerials released by decomposing plants and in chemical weathering.
- Time
-
- Reasons for seeking permission
- It is an official requirement
- It helps the school authority to organize for transport.
- It helps to avoid being denied permission to carry out the study.
- It helps to inform the school authorities of any absence in order to make adjustments.
- It helps the authorities in the place of visit to organize for a guide.
(any 3x1=3marks)
- Methods of date collection
- Observation
- Administering questionnaires
- Conducting interviews
- Photographing
- Video taking
(any 3x1=3marks)
- Follow up activities
- Holding discussions in class address issues observed and recorded during the study.
- React further on the topic to fill gaps identified
- Presentations by various groups
- Drawing maps and diagrams of the area studied
- Displaying the samples collected from the field
- Displaying photographs taken from the field
(any 2x1=2marks)
- Reasons for seeking permission
-
- Types of glaciers
- Valley glacier
- Grque glacier
- Piedmont glacier
- Continental glacier/ice sheet
- Hanging glacier
(any 3x1=3marks)
-
- Processes of glacier erosion
- Plucking – rock particles on the floor of or sides of the valley are removed by the force of the moving glacier and are carried away by ice.
- Abrasion – The moraines carried by glacier scraps the floor and sides of the valleys, loose rocks are removed and carried away by the moving glacier.
- Nivation – ice produces alternate freezing and thawing of rocks causing them to disintegrate. Melt water removes the resulting rock debris.
(3x2 = 6marks)
- Parts labeled X, Y and Z
- X – Pyramidal peak
- Y – arete
- Z- cirque
- Processes of glacier erosion
-
- Lateral moraine
- Medial moraine
- Terminal moraine
- Ground moraine/sub-glacial moraine
- Englacial moraine
(any 3x1=3marks)
- Depositional features on glaciated lowlands.
- Outwash plain/boulder train
- Till/morraines
- Drumline
- Eskers and kames
- Erratic boulders.
(any 3x1=3marks)
- Lateral moraine
- Positive effects of glaciation
- Glacial till provide deep well drained soils for crop cultivation.
- The scouring effects of the moving ice reduce the land surface exposing the mineral seams which become easy exploit. Minerals are sold earning an income.
- Outwash plains comprises of sand and gravel which provide materials for building and construction.
- Glaciated features such as pyramidal peaks create unique features which attract tourist earning a foreign exchange.
- Lakes formed through glaciation have various economic uses such as fishing and provide water for domestic use. Glaciated lowlands are generally flat due to erosion and deposition and ideal for construction of building and transport network/roads.
- Glaciated mountain slopes provide rich pastures for grazing of animals in summer.
- Glaciated coasts provide fiords which give good natural harbours for shipping.
- Glaciated features such as hanging valleys form waterfall which are suitable sites for generation of hydro-electric power.
(any 4x2=8marks)
- Types of glaciers
Download Geography Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Mincks Group of Schools Mock Examinations 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
