Instructions to Candidates:
- Write your Name, School and Admission number in the spaces provided
- Answer any FIVE questions in the spaces provided.
- All questions carry equal marks.
FOR EXAMINERS USE ONLY
|
QUESTIONS |
MAXIMUM SCORE |
CANDIDATE’S SCORE |
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
TOTAL SCORE |
100 |
|
QUESTIONS
Answer any FIVE questions in the spaces provided.
-
- Explain five ways of making face to face communication effective. (10mks)
- Discuss five advantages of trade restriction to a Country. (10mks)
-
- Explain five circumstances under which an insurance contract may be terminated. (10mks)
- Explain five differences between commercial banks and the non-banking financial Institutions. (10mks)
-
- Using a well labeled diagram explain the effect of a decrease in the cost of production on the equilibrium price and quantity of a commodity. (10mks)
- Kyalo started a hardware business on 1st Jan. 2019. The following is a summary of his transactions during the month.
Invoice received
2019: Jan 2: Jirani Ltd Ks.80,000
18: Chuma Ltd Ksh.140,000
26: Mwanaisha traders Ksh.160,000
Invoice Issued2019: Jan 5: Mungi Traders Ks.50,000
20: Moto traders Ksh.150,000
25: Jua Kali traders Ksh.70,000Credit notes issued
2019: Jan 10: Mungi Traders Ks.6,000
28: Jua Kali traders Ksh.4,000Credit notes received
2019: Jan 12: Jirani Ltd Ks.3,000
24: Chuma Ltd Ksh.8,000
30: Mwanaisha traders Ks.12,000Additional information
2019: Jan 10: Sold machinery on credit to Kima traders sh50,000
9: Bought electronics equipment on credit from Lowland traders sh.18,000.
Prepare relevant journals to record the above transactions. (10mks)
-
- Explain five uses of the national income statistics. (10mks)
- Explain five factors that may lead to business success. (10mks)
-
- Explain five benefits that a private Ltd Company may enjoy by changing to a Public Limited Company. (10mks)
- Explain five factors that the government should consider when deciding on a good tax system. (10mks)
-
- Yoder is an horticultural Company producing flowers. Explain five factors that may influence the choice of a channel for distributing its’ products. (10mks)
- The following information was extracted from the books of Sunway stores.
Opening stock Sh.60,000
Closing stock Sh.120,000
Cost of sales Sh.40,000
Debtors Sh.75,000
Creditors Sh.106,000
Returns inwards Sh.25,000
Sales Sh.52,500
Bank overdraft Sh.24,000
Required:
Determine- Purchases (2mks)
- Mark up (2mks)
- Profit margin (2mks)
- Working capital (2mks)
- Rate of stock turn over (2mks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Ways of making face to face communication effective.
- Ensuring clarity of message when speaking - to avoid misunderstanding.
- Having positive attitude - of the message/sender/receiver.
- Ensuring good listening skills – to make the receiver get the message being sent.
- Proper timing by the sender – to make it conducive. And acceptable for both sender and receiver.
- Making the message brief – to avoid unnecessary details.
- Use of non-verbal gestures- to reinforce the verbal messages.
- Proper planning by the sender – to enhance understanding of the message.
Any 5 well explained @ 2 = 10 mks
- Advantages of trade restriction to a Country.
- Protection of infant or news industries – from unfair/stiff competition from superior/higher quality goods from other Countries.
- Allows expansion of domestic market – due to increased demand for locally manufactured goods.
- Enables correction of balance of payment deficit – it helps reduce volume of imports reducing payment out of the Country.
- Discourage dumping of goods – from more developed Countries which are of lower/inferior quality as they may affect people’s health negatively.
- Creation of employment – due to establishment of more local firms to produce the more demanded local goods.
- Reduces dependency of a country on another – hence the Country becomes safe incases of misunderstanding.
- Enables a country fully exploit its resources – due to increased business ttrading activities.
- Increased government revenue – due to increased customs duty/which can be used to finance development projects in the Country.
Any 5 well explained @ 2 = 10 mks
- Ways of making face to face communication effective.
-
- Circumstances under which an insurance contract may be terminated.
- Where the principle of utmost good faith was violated – some important/vital information was not revealed about the subject matter.
- Where the insured ceases to have insurable interest in the subject matter – where the property is sold to another person to new owner is the one who should be compensated.
- Incase of life assurance where to policy matures - and the insured is compensated/settled.
- Incase of default in payment of premiums – the policy becomes null and void and its not in force.
- Incase of a court order – ordering the termination of the policy/contract incase of an illegal activity is property that was insured.
- Where the insurance company becomes insolvent – is unable to pay/compensate its clients.
Any 5 well explained @ 2 = 10 mks
- Differences between commercial banks and the non-banking financial Institutions.
Any matching 5 differences @ 2 = 10 mksCommercial banks
Non – banking finance institutions
(i) Operate savings, fixed and current accounts
(i) Operate savings accounts only
(ii) Issues cheque books
(ii) Do not issue cheque books
(iii) Gives short term and medium term loans
(iii) Gives long term loans
(iv) Participates in the clearing house.
(iv) Do not Participates in the clearing house.
(v) No restrictions on loans given.
(v) Loan given have restrictions on sectors to be given.
(vi) Normally operates in the money market.
(vi) Operates in the capital market.
(vii) Provide overdraft facilities
(vii) Do not offer overdraft facilities
(viii) Provides safekeeping facilities for valuable items
(viii) Do not provides safekeeping facilities
(ix) Buy and sell foreign exchange.
(ix) Do not sell/buy foreign exchange.
(x) Are used by Central bank to regulate money supply
(x) Are not used since they are not under direct control of Central bank.
(xi) Provides letter of credit to their clients.
(xi) Do not provides letter of credit to their clients.
(xii) Are under the control of the Central bank
(xii) Are not under direct control of the Central bank
- Circumstances under which an insurance contract may be terminated.
-
- Effect of a decrease in the cost of production on the equilibrium price and quantity of a commodity.
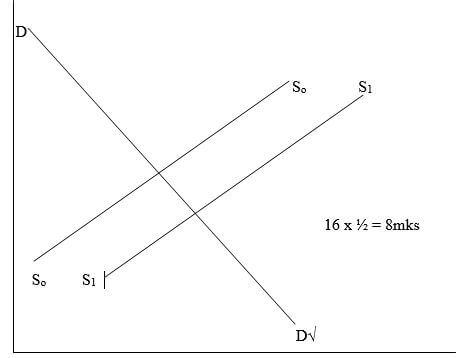
- Decrease in cost of production causes increase in supply of goods.√
- Increase in supply without a change in demand causes excess supply in the market.√
- The excess supply forces traders to lower the price of the commodity in order to sell more and avoid wastage.√
- The new/lower prices enables the buyers to buy more since the commodity is now cheaper√
4 x ½ = 2mks 10 mks
- Summary of transactions during the month.
Purchases Journal
Sales JournalDate
Particulars
Invoice
L.F
Amount
2/1/19
Jirani ltd
PL
80,000 √
18/1/19
Chuma ltd
PL
140,000√
26/1/19
Mwanaishi traders
pL
160,000√
Total posted to purchase acc. (Dr)
380,000√
Sales Returns JournalDate
Particulars
Invoice
L.F
Amount
5/1/19
Mungi traders
SL
50,000√
20/1/19
Moto traders
SL
150,000√
25/1/19
Jua kali
SL
70,000√
Total posted to sales acc. (cr)
270,000√
Purchases returns JournalDate
Particulars
Credit note
L.F
Amount
10/1/19
Mungi traders
SL
60,000√
28/1/19
Jua Kali traders
SL
40,000√
Total posted to return invoicesacc. (Dr)
100,000√
GENERAL JOURNALDate
Particulars
Credit note
L.F
Amount
12/1/19
Jirani ltd
PL
3,000√
24/1/19
Chuma ltd
PL
8,000√
30/1/19
Mwanaishi traders
PL
12,000√
Total posted to returns outwards acc. (cr)
23,000√
(10mks)Particulars
DR
CR
Kima traders A/c
Machinery A/c
(Being sale of machinery to Kima on credit)
50,000√
50,000√
Electronic Equipment A/c
Lowland traders A/c
(Being purchase of equipment on credit from lowland traders)
18,000√
18,000√
- Effect of a decrease in the cost of production on the equilibrium price and quantity of a commodity.
-
- Uses of the national income statistics.
- Indicator of people’s living standards.- An improvement/increase in size of national income indicates higher/better living standards and vice varsa.
- Used to compare standards of living between Countries – Country with higher national income are deemed to have higher standards of living compared with one with lower national income and vice varsa.
- Used to compare people’s living standards between different years/periods – the year/period with higher national income is deemed to have higher living standards and vice varsa.
- Used to calculate per capital income – by dividing total national income with total people/to measure people’s living standards.
- Used by government for economic planning – by comparing performance of different sectors/regions helps the government in the planning for better/efficient allocation/use of resources.
- Used to attract investment/for investment decisions – data obtained can be used by entrepreneurs to make decisions on the sector/when amount of capital to invest/growth in national income will encourage investors and vice varsa.
- Provides information on distribution of income – helps the government address income disparities/identify sectors or regions not performing to their expectations.
- Used to attract foreign aid/funding – when a country show strong economic growth/when experiencing challenges to finance its development.
Any 5 well explained @ 2 = 10 mks
- Factors that may lead to business success.
- Adequate capital/funds – to start/run/expand/sustain business.
- Good/appropriate marketing strategies – leading to high sales/more customers/retain/attract customers.
- Fair/healthy competition – which the business can cope with.
- Adequate/skilled/experienced labour – which leads to high quality/quantity goods/services
- Adequate/appropriate technology – which leads to high quality/quantity goods/services.
- Favourable government policies – that reduces the cost of doing business/that makes it ease to start businesses/that leads to emergence/expansion of businesses.
- Adequate demand/market – for selling the goods/services.
- Good pricing strategies – which attracts more buyers/fair/reasonable prices maintains customers.
- Political stability/security – that ensures confidence of investors and provides security of goods/properties of the investors.
- Development infrastructure – that facilitates easy/faster movement of goods/services/lowers the cost of transport.
- Goods customer relations – leading to increase/expansion of the market.
- Good choice of business – that exploits the available market gaps.
Any 5 well explained @ 2 = 10 mks
- Uses of the national income statistics.
-
- Benefits that a private Ltd Company may enjoy by changing to a Public Limited Company.
- Ability to raise more capital – by selling share to the Public through stock exchange market.
- Easy transfer of shares – without restrictions through the stock exchange market.
- Increased transparency – as shareholders must approve company’s annual audited accounts which are published.
- Increased public confidence by owners – as shareholders have no direct managerial control over company’s activities.
- Increased professionalism – since the company can afford to hire professional mangers.
- Higher continuity – since shares can be transferred freely without affecting the business.
- Can enjoy economics of scale – due to increased scale by production.
- The company can be quoted in the stock exchange market – leading to sound management.
- Can advertise sale of shares – to the public in the media which attract new investors.
- Enhanced ability to borrow funds – by selling debentures.
- Better management – since its run by competent board of directors/professionals.
Any 5 well explained @ 2 = 10 mks
- Factors that the government should consider when deciding on a good tax system.
- Certainity – the tax payer and tax collector should be aware/knows the amount payable/collectable as tax they should know when to pay/collect the tax.
- Convenience – the taxpayer should pay the tax when he has the money to pay.
- Economy – the tax revenue should be more that the cost of collecting the tax.
- Equity – should be fairness – high income earners should be taxed more, low income earners should be taxed less/one should be taxed according to level of income.
- Elasticity – the tax revenue should expand with increase in economic activities automatically.
- Flexibility – the rates should be able to be raised is lowered according to the needs of the economy.
- Diversity – there should be a variety of taxes inorders to generate more tax revenue/should be broad based.
Any 5 well explained @ 2 = 10 mks
- Benefits that a private Ltd Company may enjoy by changing to a Public Limited Company.
-
- Factors that may influence the choice of a channel for distributing its’ products.
- Cost/affordability – the cost of different channel should be considered and the most affordable one/cost effective should be used.
- Extent/coverage/distance/proximity of the market – if consumers are wide spread. Then long channels may be necessary to reach them.
- Taste/preferences of consumers/consumers may have specific preferences/consumer specification – which might require the personal attention of the producer hence use of short channel.
- Quantity/output/volume/scale of production – if the quantity of flower to be sold is large, then more middlemen/intermediaries may be required/where volume is small choose a short/direct channel.
- Availability of technical personnel – if the producer does not have the required technical personnel, then he may have to use a longer channel/middlemen/agents. If available short/direct channels are used.
- Availability of intermediaries/agents – if there is no middlemen then shorter channel is used, if available longer channel is used.
- Government policy – where the government policy requires that a certain channel be used then the firm will have to comply.
- Size of the market/number of consumers – if small few, short channel will be used. If large/many a longer channel may be used.
- Risk involved- where there is need to spread risk, the firm should use longer channel/agents/intermediaries.
Any 5 well explained @ 2 = 10 mks
-
- Cost of sales = Opening + Purchase – closing stock
40,000 = 60,000 + P – 120,000√
Purchases = 40,000 + 120,000 – 60,000√
= 100,000√√ 4 x ½ = 2mks - Mark up = GP x 100
COS
Gp = (525,000 - 25,000 ) – 40,000
= 460,000 10,000√
10,000 25
M.U = 100,000 X 100 = 25,000 √ 4 x ½ = 2mks
40,000 - Profit margin = GP x 100
N. sales
= 10,000√ x 100 = 20,000√√ 4 x ½ = 2mks
50,000√ - Working capital = C.A – C.L
(120,000 + 75,000 ) – (106,000 + 24,000) √√
= 195,000 – 130,000 4 X ½ = 2mks
= 65,000.√ - Rate of stock turn over
= Costs of sales
Average stock
= 40,000
90,000
= 0.44 times. 4 x ½ = 2mks
- Cost of sales = Opening + Purchase – closing stock
- Factors that may influence the choice of a channel for distributing its’ products.
Download Business Studies Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Mincks Group of Schools Mock Examinations 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
