QUESTIONS
- You are provided with the following
Sodium hydroxide solution A
0.1M HCl labelled B
An alkanoic acid labelled C
You are required to- Standardize solution A
- Determine the mole ratio of reaction between sodium hydroxide and the alkanoic acid
- Calculate the molarity of solution C
- Determine the molar enthalpy of neutralisation of the alkanoic acid and sodium hydroxide
PROCEDURE 1
Using the pipette, place 25cm3 of solution A into a 250ml volumetric flask .Add distilled water as you shake up to the 250ml mark .Label the solution formed as D.
Fill the burette with solution B .Rinse the pipette and use it to transfer 25cm3 of solution D into a conical flask. Add 3 drops of phenolphthalein indicator and carry out titration .Repeat the procedure twice to obtain concordant values .Record the results below
(4mk)1 2 3 Final burette reading (cm3) Initial burette reading (cm3) Volume of solution B used (cm3) - Determine the average titre volume (1mk)
- Calculate the number of moles of
- HCl that reacted (1mk)
- NaOH in the 25cm3 of solution D ( 1/2mk)
- Molarity of NaOH solution A (1mk)
- PROCEDURE 2
Rinse the burette and fill it with solution C .Run 16cm3 of solution C into a 100ml plastic beaker .Using a thermometer measure its temperature and record it in the table 2 below as initial .Add 4cm3 of solution A using a syringe .Stir with the thermometer immediately and note the highest temperature reached .Record it in the table as final temperature .Repeat the procedure with other volumes of A and C as shown in the table and complete it . Rinse the beaker and the thermometer after each experiment
Volume of solution (cm3) 16 12 8 6 4 2 Volume of solution A (cm3) 4 8 12 14 16 18 Final temperature (ºC) Initial temperature (ºC) Change in temperature - On the grid below, plot the graph of change in temperature against volume of sodium hydroxide solution A (3mks)
- From your graph determine,
- The volume of sodium hydroxide solution A required to neutralize the alkanoic acid (1/2mk)
- Highest change in temperature DT (1/2mk)
- Determine the volume of the alkanoic acid solution C, used in the neutralization (1/2mk)
- Calculate the;
- Concentration of the alkanoic acid solution C, given that the ratio of volume of alkali to the volume of acid is also the mole ratio(2mks)
- Molar enthalpy of neutralisation of the acid by sodium hydroxide(2mks)
(C=4.2J/g/k, density of solution =1g/cm3)
- You are provided with solid P .Carry out the following tests and write your observations and inferences in the spaces provided
- Place all the solid P in a boiling tube .Add about 10cm3 of distilled water and shake the mixture thoroughly .Filter the mixture into another boiling tube .Retain the filtrate for use in the test 2 (b) below and dry the residue using a filter paper
- Transfer about half of the residue in a dry test tube .Heat the residue strongly and test any gas produced using a burning splint
Observations Inferences - Place the rest of the residue in a dry test tube .Add 2cm3 of 2M hydrochloric acid .Retain the mixture for test (iii) below
Observations Inferences - To the solution formed in (ii) above, add aqueous ammonia drop wise till in excess
Observations Inferences
- Transfer about half of the residue in a dry test tube .Heat the residue strongly and test any gas produced using a burning splint
-
- To above 2cm3 of the filtrate obtained in a) above add aqueous ammonia drop wise until in excess
Observations Inferences - To about 2cm3 of the filtrate, add about 2cm3 of 2M hydrochloric acid
Observations Inferences - To 2cm3 of filtrate add two drops of barium nitrate solution(2mks)
Observations Inferences
- To above 2cm3 of the filtrate obtained in a) above add aqueous ammonia drop wise until in excess
- Place all the solid P in a boiling tube .Add about 10cm3 of distilled water and shake the mixture thoroughly .Filter the mixture into another boiling tube .Retain the filtrate for use in the test 2 (b) below and dry the residue using a filter paper
- You are provided with solid E carry out the following test and record your observations and inferences in the spaces provided
- Place about one half of solid E in a dry test tube .Retain the other half for use in (b) below .Add all of the absolute ethanol provided to solid E in a test tube shake the mixture
Divide the mixture formed into two portions- Determine the pH of the first portions
Observations Inferences - To the second portion, add about one half of sodium hydrogen carbonate provided
Observations Inferences
- Determine the pH of the first portions
- Place the remaining solid E in a boiling tube 10cm3 of distilled water and shake. Boil the mixture and divide it into 3 portions while still warm
- To the first portion add the remaining sodium hydrogen
Observations Inferences - The second portion add three drops of acidified K2Cr207 (1mks)
Observations Inferences - To the third portion add 5 drops of Bromine water(1mk)
Observations Inferences
- To the first portion add the remaining sodium hydrogen
- Place about one half of solid E in a dry test tube .Retain the other half for use in (b) below .Add all of the absolute ethanol provided to solid E in a test tube shake the mixture
CONFIDENTIAL
- Solution A-120cm3
- Solution C -60cm3
- 5cm3 of absolute ethanol
- About 0.5gms NaHC3
- About 0.2g solid E
- About 1g solid P
- Pipette
- Pipette filler
- 250ml volumetric flask
- Means of labelling
- Burette
- Filter funnel
- Conical flasks – 2pcs
- 100 ml plastic beaker
- Thermometer
- 20ml syringe
- Boiling tube -2pcs
- Filter paper -2pcs
- 6 test tubes in a rack
- Wooden splint
- Distilled water in wash bottle
- Metallic spatula
- Test tube holder
Access to;
- Phenolphthalein indicator
- Source of heat
- 2M NH3
- 2M HCl
- Ba(NO3)2
- Universal indicator and pH chart
Preparation of solutions
- Solution A -0.8 M NaOH
- Solution C -1M H2SO4
- Solid P –mixture of ZnCO3 and ZnSO4 in the ratio 2:1
- Solid E is 0.2 grams Maleic acid

MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- HCl that reacted (1mk)
= correct answer A - iNaOH in the 25cm3 of solution D( 1/2MK)
Correct answer (i) above - Molarity of NaOH solution A (1MK)
Ans in (ii) → 25cm3
? = 250cm3
= Ans B
Ans B x 1000
25
= correct ans
- HCl that reacted (1mk)
- LA =1/2
Scale =1/2
P=1
Line=1 -
- (To be read from the correct graph)
- (To be read from a correct graph)
- 20 –Ans in (i) above
-
- vol of NaOH ;Acid
2 :1
Moles of sodium hydroxide
Ans in (e) (ii) above x Ans in b(iii)
1000
=ans in c
Moles of acid = Ans C/2
Ans C x 1000
2
Ans in F
=Correct answer - Heat change for reaction 20 x 4.2 x Ans in e (ii) above
= Correct answer (K) in joules
Moles of acid = Ans in (F) above x correct Ans in g (i) above
1000
= Ans M
=Correct Ans K /Ans M = - Correct Ans J/mole
- vol of NaOH ;Acid
-
Observations Inferences a)i)Effervescence ,burning splint extinguished
Residue, yellow hot white when cold
ii)Effervescence/ bubbles of a colourless gas
iii)White precipitate soluble in excess
b)i) White precipitate soluble in excess
ii) No effervescence
No white precipitate
iii) White precipitateCO32-
Zn²+
CO32-
Zn2+
Zn2+
CO32-, SO32- absent
Pb2+ Ag+ absent
SO42-
Observations Inferences a)Soluble
i)pH7
ii)No effervescence/bubbles
b)i)Effervescence
ii)Orange colours of H+/ K2Cr2O7 changes to green
iii)Yellow bromine water decolourises/ changes to colourlesspolar
neutral
RCOOH/ /H3O+/H+ Absent
RCOOH/H3O+
R-OH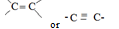
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 3 Questions and Answers - Cekenas Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
