QUESTIONS
SECTION A (25 MARKS)
-
- Give two evidences supporting the Nebula Cloud theory on the origin of the earth. (2marks)
- The diagram below represents the revolution of the earth.
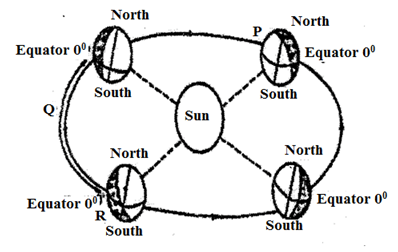
Give three climatic conditions in Europe when the earth is in position R. (3marks)
-
- Give two forces that may cause faulting process. (2marks)
- Describe how a block mountain is formed through compressional forces. (3 marks)
-
- What is natural vegetation? (2 marks)
- Identify the temperate grassland in the following countries
Argentina (1mark)
South Africa (1 mark)
Australia (1 mark)
-
- Name two types of tides. (2marks)
- State three conditions necessary for formation of a beach. (3marks)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
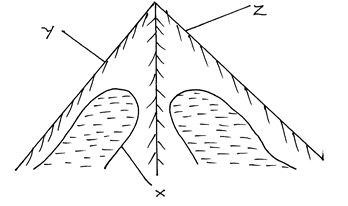
- Name the features marked
X (1 Mark)
Y (1 Mark)
Z (1 Mark) - Identify two processes through which the feature marked X is formed. (2 marks)
- Name the features marked
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section.
- Study the map of Nyeri 1: 50 000 (sheet 120/4) provided and answer the following questions.
-
- Identify the sheet number of the map provided (1mark)
- Convert the scale of map into a statement scale. (2marks)
- What is the bearing of the trigonometrical station 1906 in grid square 6860 from the trigonometrical station 1865 in grid square 6957. (2 marks)
-
- Identify three physical features found in grid square 6259. (2 marks)
- Give the latitudinal extent of the area covered by the map. (2 marks)
- Identify two districts in the area covered by the map. (2 marks)
-
- Using a scale of 1 cm represents 20m, draw a cross section from Easting 68 to Easting 74 along Northing 64 . (4 marks)
On it mark and name
- A hill top (1mark)
- A stream/river (1 mark)
- All weather road loose surface (1mark)
- Calculate the vertical exaggeration of the cross-section. (2 marks)
- Using a scale of 1 cm represents 20m, draw a cross section from Easting 68 to Easting 74 along Northing 64 . (4 marks)
- Citing evidence from the map, identify two social services offered in Mweiga Township. (4 marks)
-
-
- What is climate (2 marks)
-
- Explain two effects of climate change on the physical environment. (4 marks)
- State four characteristics of the hot desert climate. (4 marks)
- Using a well-labelled diagram, explain the formation of anabatic winds. (5 marks)
-
- Define micro climate. (2 marks)
- Explain four human activities that can lead to aridity and desertification. (8 marks)
-
- Identify two types of earthquake waves. (2 marks)
-
- Describe two ways in which the strength of an earthquake is measured. (4 marks)
- State three human causes of earthquakes. (3 marks)
- Explain four effects of earthquakes on physical environment. (8 marks)
- Students from Karatina School carried out a field study of an area affected by earthquake.
- Identify three effects they noticed on human environment. (3 marks)
- State three advantages of collecting information in the area using photographs? (3 marks)
- Give two problems they are likely to experience (2 marks)
-
-
- Distinguish between the river system and river interfluves (2 marks)
- Give three types of river erosion. (3 marks)
-
- What is a waterfall? (2 marks)
- Give four types of waterfalls. (4 marks)
- Describe each of the following drainage patterns.
- Dendritic pattern (4 marks)
- Trellis pattern (4 marks)
- Your class is required to carry out a field study on the lower course of a river.
- Give three advantages of dividing the class into groups. (3marks)
- List three features the students would identify. (3marks)
-
-
-
- Define the term ‘leaching’. (2 marks)
- State two factors that contribute to the leaching of soils. (2 marks)
-
- Explain how laterization (ferrallization) occur. (6 marks)
- State three types of soils degeneration. (3 marks)
-
- Explain four ways in which vegetation protects the soils and prevents soil erosion. (8 marks)
- State four advantages of mulching soil using organic matter. (4 marks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- All planets undergo rotation and revolution.
- Temperatures of the planets increases with the increase in depth.
- Material making up the Nebula were hot hence planets nearer the centre of the solar system have higher temperature than those far away. (2x1 = 2mks)
- The diagram below represents the revolution of the earth.
-
-
- High temperatures
- High rainfall
- Convergence of winds
- Low atmospheric pressure
- High humidity
- It is cloudy (3x1 = 3mks)
-
-
-
-
- Tensional forces
- Compressional forces
- Vertical forces (2x1 = 2mks)
-
- Earth crustal rock are subjected to compressional forces developing reversed faults.
- Continued subjection to compressional forces on crustal rocks triggers off vertical forces.
- Vertical forces pushes the middle block up at higher level while the side block remains at the original positions.
- The raised middle block that is above the surrounding sides blocks forms block mountains.
-
-
- It is the plant cover that grows wildly on the earth’s surface without interference from man and his animals. (2x1 = 2mks)
-
- Argentina - Pampas
- South Africa - Veldts
- Australia – Downs
(3x1 = 3mk)
-
-
- Spring tides
- Neap tides
- Apogean tides
- Perigean tides
(2x1 = 2mks)
-
- Presence of abundant supply of material to be deposited.
- Presence of a shallow shore/ continental shelf
- A relatively weak long shore current
- Gently sloping land at the sea shore
- A weak backwash/ constructive wave.
-
-
- X – Corrie/ cirque (1 Mark)
Y - Arete (1 Mark)
Z – Pyramidal peak (1 Mark) - Abrasion
Plucking
- X – Corrie/ cirque (1 Mark)
-
-
- 120/4
- 1 : 50000 = 0.5
100000
Therefore 1 cm rep 0.5km or 1 cm rep ½km - 338º ± 1 or N22º W
-
-
- Stream/river
- River/valley
- Scrub vegetation
- Woodland vegetation
- 18.3cm = 5'
5.7cm = ?
5 x 5.7 = 1.5
18.3
1 min = 60sec
0.5 = 30sec
5.7cm = 1'30''
0º20'00''
1'30''
0'18'30''
Latitudinal extent = 0'18'30''s = 0º30's - Nyeri district
Laikipia district
-
-
-
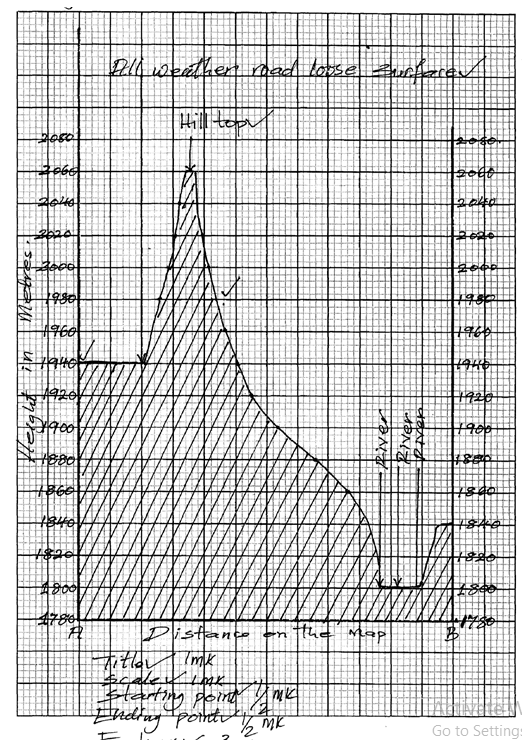
- V.E = V.S
H.S
= 1 ÷ 1
20m 50000cm
= 1 x 50000
2000 1
= 25times
-
-
- Recreation services as evidenced by presence of youth club
- Education as evidenced by presence of school
- Medical/ Health as evidenced by presence of dispensary
- Administration as evidence by the chief’s office
- Security as evidenced by presence of police station.
-
-
- Climate is the average weather conditions of a place over a long period of time.
-
-
- Global warming and increase in temperatures.
- Increased temperature may lead to melting of ice caps and ice sheets leading to rising sea level.
- Increase in temperatures may result to high evaporation leading to drought.
- May cause changes in rainfall patterns in different parts of the world.
-
- High temperatures during the day and low temperatures during the night due to high terrestrial radiation.
- High diurnal range of temperature
- Clear and cloudless skies
- Receives less than 250mm of rainfall annually
- Receive short and torrential rains which cause flash floods
- Humidity is low and evaporation rate is high
- Sandstorms are very common
- High wind velocity due to the frictional force.
-
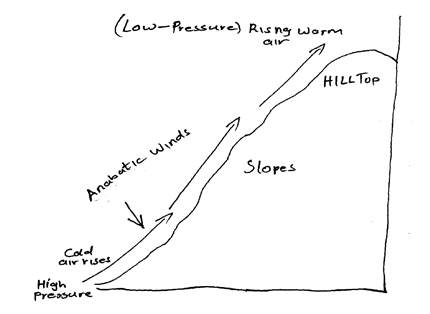
- During the day, mountain slopes are heated and warm faster than in the valley bottoms.
- Low pressure develops on mountain slopes than at the valley bottoms
- The air on the mountain slopes expands and rises by convection.
- The cool air from the valley bottom rises as anabatic wind to take its place
-
- Climate experienced within a small or restricted area which is different from general climate in the region.
-
- Clearing of vegetation for settlement and agriculture interfering with the water cycle causing drying up.
- Overstocking that leads to overgrazing leaving the land bear exposing to soil erosion.
- Poor agricultural practices such as over- cultivating, monoculture, slashing and burning leading to soil erosion.
- Poor irrigation methods leading to evaporation and salts brought from below to the surface and deposited on the top soil making soils salty and unable to support plants.
- Industrial release of greenhouse gasses like CO2 to the atmosphere which absorb heat rising earth’s temperatures.
-
-
- Primary waves
- Secondary waves
- Longitudinal waves/L waves
-
-
- The strength of an earthquake is measured by its intensity.
- Intensity measures how strong and hard an earthquake shakes the ground
- It is measured on the Mercalli scale or Rossi Farrell scale
- The strength is measured by its magnitude
- Magnitude measures the amount of energy released by an earthquake.
- It is measured on the Ritcher scale
-
- Use of explosives
- Underground nuclear tests
- Construction of large reservoirs
- Movement of trains
-
-
- It causes landslides/slumps
- It causes raising or lowering of land
- It causes faulting of the crust
- It causes lateral or vertical displacement of rocks
- It causes rising and lowering of the sea level.
-
-
- Cracks in buildings
- Landslides covering crops etc.
- Collapse of weak buildings
- Panic and fear amongst people
- Death and destruction of properties due to falling objects
-
- They are easy to take
- Cheap to produce
- Can be stored for future references
- Easy to extract information of well-labelled
- Features portrayed are realistic
-
- Inaccessibility of the area due to massive destruction
- The rubble may obscure the evidence
- Lack of informers because people may have evacuated
-
-
-
-
- River system is the main river and its tributaries while river interfluves is the high areas in between the tributaries.
-
- Head ward erosion
- Vertical erosion
- Lateral erosion
-
- A waterfall is the sharp break in the river channel over which the river falls
-
- Waterfalls formed where a river channel passes over underlying hard rock
- Waterfall formed where there is vertical hard work along the river channel.
- Waterfall formed where the river course flows over a fault scarp.
- Waterfall formed where a river enters a coastal plain from a plateau
- Waterfall as a result of river rejuvenation
- Waterfall formed where a river channel flows over underlying volcanic dykes, lava dorms or plugs
- Waterfall formed where a river enters the sea through a cliff.
- Waterfall formed in a glaciated upland where a river flows from a hanging valley and plunges into a u-shaped valley.
-
-
- The pattern develops in areas where rocks have uniform structure.
- The direction of flow is influenced by the slope of the land
- The tributaries join the main river at acute angles.
- The tributaries join the main river forming a shape like that of a tree and its branches.
- Rivers join the main river from many directions.
-
- The pattern develops where soft and hard rocks alternate vertically.
- The tributaries join the main river at right angles.
- The consequent streams are parallel to the main river.
- Some consequent streams flow to the opposite direction of the main river.
- The main river and its tributaries form a rectilinear pattern.
-
-
-
- The class would be able to study the entire course of the river.
- It will enable them to obtain detailed information on the river.
- It will enable the field study to be carried in an orderly way.
- It will encourage participation of all the members of the class
- It will facilitate more interaction among the group members.
-
- Alluvial fan
- Meanders
- Oxbow lakes
- Natural levees
- Deferred tributaries
- Braided channels
- Flood plains
- Delta
- Distributaries
-
-
-
-
- It is the removal by rainwater on soluble mineral matter in solution from the upper horizon or the soils (horizon A) to the lower horizons of the soils.
-
- Nature of the soils especially its texture and solubility or its minerals
- High rainfall in the rain season alternating with a dry season
- Topography
-
-
- It occurs in areas which experience alternating wet and dry seasons especially the warm hot humid tropical regions.
- During the wet season mineral salts in the A- horizon dissolve in percolating rain water.
- The dissolved minerals percolate from A – horizon downwards i.e. leached out.
- The soil solution also cause removal or silica in a process called desilication.
- The dissolved minerals are deposited in the lower layer in a process known as precipitation.
- Insoluble minerals such as iron and aluminum oxides accumulate in A – horizon to form a crust known as laterite.
- There is rapid circulation or bases between the soil and the vegetation because or abundance of leaf litter and its rapid decay.
-
- Physical degeneration
- Chemical degeneration
- Biological degeneration
-
-
-
- The leaf cover helps to reduce the force or rain drops which would otherwise loosen and remove soil particles if their force was not checked.
- vegetation cover increases the rate or infiltration or rainwater and thus reduces surface run-off
- Plant roots which penetrate the soil create space through which water percolates deep into the ground.
- A wide – spreading and deeply penetrating root system is very effective in binding the soil particles together.
- Plant cover breaks the force of wind at ground and reduces evaporation which would otherwise dry and loosen the soil.
- Decayed vegetable matter provides humus which binds the soil particles together.
-
- It reduces the rate of evaporation of water from the soil
- It protects the soil from erosion
- It increases the humus content of the soil when they disintegrate
- Increases the rate of infiltration of water into the soil
- The mulch provide suitable habitat for borrowing animals which churn the soil and improve its texture and capacity
-
-
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Geography Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Cekenas Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
