QUESTIONS
SECTION A (30 MARKS)
Answer ALL Questions in this section
- List three aspects of light a farmer should consider when deciding on a crop to grow. (1½mks)
- State four factors which determine the depth of ploughing. (2mks)
- Give four reasons why it is advantageous to use farm yard manure instead of straight fertilizer. (2mks)
- State four methods of reclamation farmers can carry out. (2mks)
- State four benefits of land consolidation. (2mks)
- State four factors that determine the spacing of maize crops. (2mks)
- State four factors which may affect the quality of hay. (2mks)
- State four factors that affect the effectiveness of a pesticide. (2mks)
- List any four types of records a crop farmer should keep. (2mks)
- State four importance of practicing agroforestry. (2mks)
- State four characteristics of a good site for a nursery bed. (2mks)
- Name four methods of farming. (2mks)
- Name four natural factors that may influence soil erosion. (2mks)
- State two conditions that should be observed when harvesting to ensure that cotton picked is of high quality. (2mks)
- State four uses of water on the farm. (2mks)
- List three types of surface irrigation in crop production. (1½mks)
- Differentiate between coppicing and pollarding as used in Agroforestry. (1mk)
SECTION B (20MARKS)
Answer ALL questions in this section
- Below are filed practices. Study them carefully and answer the questions that follow.
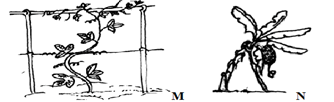
- Identify the above practices. (2mks)
- State three reasons for carrying out practice M. (3mks)
- Below are common weeds found on the farm. Use them to answer the questions that follow.

- Identify the weeds R, S, T, U. (2mks)
- State the reason why S and U are difficult to control. (2mks)
- Why is weed R not suitable on dairy animals. (½mk)
- Which weed is parasitic to cereals? (½mk)
- The diagram below shows a silo. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
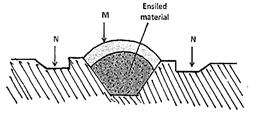
- Identify the type of silo shown on the diagram. (1mk)
- State the use of the part labelled M and N. (2mks)
- Give two ways of ensuring that anaerobic conditions are achieved during silage making process. (2mks)
- The illustrations below represents types of soil structures. Study them carefully and answer the questions that follow.
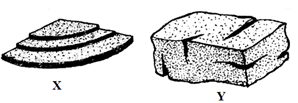
- Identify the soil structures X and Y shown above. (2mks)
- Which of the soil structure you have named above is not suitable for growing maize. (1mk)
- Give two methods of improving the soil structure you have mentioned in (ii) above. (2mks)
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
Answer any two questions from this section
-
- Explain how farmers overcome risks and uncertainties in a farming business. (5mks)
- Explain how various practices carried out in the field help to control crop diseases. (8mks)
- Transplanting of seedlings. (7mks)
- Study the following information which was extracted from Mr. Rono’s farm record on 31st December 2021 and answer the questions below.
Item
Debts receivable 18,000
Loans payable to bank 300,000
Cows 250,000
Chicken 80,000
Goats 30,000
Debts payable to cooperative 20,000
Buildings and structures 600,000
Wages payable to workers 19,000
Cattle feed in store 10,000
Animal drugs in store 4,000
Breakages to repair 30,000
Cash at hand 20,000
Cash in bank 30,000
Farm equipment 12,000- Prepare a balance sheet for Rono’s farm using the information above. (10mks)
- Describe the properties of nitrogenous fertilizers. (15mks)
- Describe five problems farmers face in marketing of water melon. (5mks)
-
- Describe cabbage production under the following sub-headings.
- Ecological requirements. (2mks)
- Field management practices. (3mks)
- State five advantages of using seeds as planting material. (5mks)
- Describe process of chemical water treatment before storage. (10mks)
- Describe cabbage production under the following sub-headings.

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Light wavelength
- Light intensity
- Light duration (½ x 3= 1 ½mks)
-
- Type of crop/ rooting system of crop
- Type of implement available
- Type of soil
- Soil moisture content during ploughing time
- Presence of certain types of weeds e.g. couch grass
- Source of power (½ x 4= 2mks)
-
- Supplies a variety of plant nutrients
- Has a longer residual effect
- Promotes microbial activities in the soil
- It is locally/ easily available
- Moderates the soil pH/ increases aeration exchange capacity
- Farm yard manure improves soil structure/ improves soil water holding capacity. (½ x 4= 2mks)
-
- Draining the land
- Controlling of soil erosion
- Irrigation
- Afforestation/ re- afforestation
- Control of tsetse flies (½ x 4= 2mks)
-
- There is proper supervision of the farm
- Reduces costs on travelling
- Rotational program can be easily affected
- Mechanization is possible because the areas are large
- Easy to get extension services
- Allows good farm planning
- It enhances proper pests, diseases and weed control
- Encourages long term investments (½ x 4= 2mks)
-
- Soil moisture content
- Soil fertility
- Machinery to be used
- Intended use of the crop
- Prevalence of pests and diseases
- Cropping system used
- Number of seeds per hole. (½ x 4= 2mks)
-
- Stage at which the grass is cut/ harvested
- Efficiency in preparation / how well the grass is dried/ turned
- Methods of storage/ storage conditions
- Species/ type of forage crop/ nutritional composition of forage
- Length of drying period/ extent of drying
- Weather conditions during drying period (½ x 4= 2mks)
-
- Concentration of the pesticides
- Weather conditions during application
- Stage of development of the pesticide
- Rate of application of pesticide
- Mode of action of the pesticide. (½ x 4= 2mks)
-
- Field operation records
- Crop production records
- Inventory records/ consumable goods inventory/ permanent goods inventory
- Marketing records
- Labour records (½ x 4= 2mks)
-
- Remedy for deforestation/ source of firewood
- Source of income when timber/ fodder/ poles/ fruits are sold
- Aesthetic value/ beauty
- Labour saving
- Environment benefits/ control soil erosion/ improve water retention/ enrich soil through leaf litter and nitrogen fixation/ improve water catchment.
-
- Near a reliable water source
- Well drained area with deep fertile soils
- Gently sloping area
- Secure area
- Sheltered area
- Should not have been used for the same crop species in the previous season
- Should be accessible (½ x 4= 2mks)
-
- Shifting cultivation
- Nomadic pastoralism
- Organic farming
- Mixed farming
- Agroforestry (½ x 4= 2mks)
-
- Amount of rainfall/ rainfall intensity
- Slope/ topography
- Type of soil
- Size of water shed/ catchment
- Length of the slope
- Vegetation cover
- Wind velocity/ strength of the wind
- Soil depth (½ x 4= 2mks)
-
- Do not pick the lint when it is wet
- Pick on weekly basis
- Avoid dry twigs or leaves contaminating the cotton
- Do not use sisal bags to hold cotton as the sisal fibres may contaminate lint. (½ x 4= 2mks)
-
- For diluting/ mixing chemicals used to control pests, diseases, weeds
- For watering livestock e.g drinking
- Watering plants I.e. irrigation
- In processing farm produce e.g. coffee, carrots etc.
- Domestic use e.g. drinking, cooking
- For rearing fish
- Mixing concrete in construction
- Recreation e.g. swimming pool
- Cooling and running machine engines (½ x 4= 2mks)
-
- Furrow irrigation
- Basin irrigation
- Flood irrigation (½ x 3= 1½mks)
- Pollarding is cutting the branches and the tree crown
Coppicing is cutting main stem completely at a height of 30cm above the ground. (1x1= 1mk) -
- M – Trelishing
N – Propping -
- Enhance production of clean fruits/ improves quality of fruits
- Help in controlling diseases
- Facilitates spraying/ harvesting of the crop
- Prevents infestation by soil borne pests (1x 3= 3mks)
- M – Trelishing
-
- R – Mexican Marigold
S – Bristly fox tail / love grass
T – Witch weed/ Striga spp
U – Double thorn (½ x 4= 2mks) - S – Easily dispersed by animals
U – Has thorns which injure the workers. (1 x 2= 2mks) - Taints the milk (½ x 1= ½mk)
- T
- R – Mexican Marigold
-
- Type of silo – Trench Silo (1 x1 = 1mark)
- Use of part M and N
M – Prevents entry of water into the silage
N – Drains away water (1x 2= 2mks) -
- Fast filling of silo
- Proper compaction
- Sealing with polythene paper and soil. (1x 2= 2mks)
-
- X – Platy soil structure
Y – Blocky structure (1 x 2= 2mks) - X / platy structure (1x 1= 1mk)
-
- Add organic matter/ organic manure to the soil/ F.Y.M/ Compost manure.
- Add liming materials / Calcium Ammonium Nitrate
- X – Platy soil structure
-
-
- Diversification of enterprises to avoid total loss
- Insurance against losses- for compensation in case of failure.
- Inventory marketing/ strategic farming keeping farm product and selling at when prices are favourable
- Flexible enterprises- engaging in enterprises that can be stopped or changed
- Rationing of inputs – use of sufficient inputs such that losses are not too high
- Contract farming – making arrangements with marketing agencies in advance to cater for price fluctuations
- Selecting more certain enterprises – selection of enterprises that do well in the area/ tried through research.
-
- Crop rotation- helps to break life cycles of disease causing organisms
- Rogueing- to prevent further spread of the disease.
- Planting disease free planting materials/ use of certified seeds- prevents introduction of pathogens in the field.
- Close season- helps to break the life cycle of pathogens.
- Timely/early planting- help crop to establish faster before attack
- Proper spacing- creates unfavorable micro-climate for some pathogens.
- Weed control- eliminate weeds that could be alternate hosts for particular pathogens.
- Use of resistant varieties- ensure crop is not attacked by the pathogen.
- Use of clean equipment/tools- reduces contamination with disease causing organisms hence prevent spreading of the disease from one plant to the other.
- Quarantine-prevent introduction of pathogens into the farms
- Heat treatment- kills the pathogens.
- Pruning- creates unfavorable microclimate for some pathogens/minimizes prevent spread of diseases.
- Destroy crop residue- kills the pathogen.
- Control the vectors — helps to slop spread of pathogens.
- Proper plant nutrition — helps plants resist disease attack/ control deficiency diseases.
- Use of appropriate chemicals e.g. fungicides- to kill pathogens
-
- Water nursery thoroughly before transplanting
- Dig the planting holes at appropriate depth
- Select healthy seedlings
- Lift the seedlings carefully with as much soil as possible to avoid root damage/ use a garden trowel
- Transport seedling careful/v to the end field using appropriate means
- Transplant on a cloudy day or late in the afternoon
- Place insecticide in the hole to control soil borne pests
- Place the seedling in the planting holes at the same depth they were in the nursery bed
- Fill the holes with soil and firm around the seedlings
- Apply mulch or erect a shade
- Water the seedling thoroughly
-
-
- Mr.Rono’s farm balance sheet as at 31st December 2021
ASSETS LIABILITIES Kshs. Cts Fixed Assets Long term liabilities Building and structures 60000 00 Loan payable to bank 300000 Cows 250000 00 Chicken 80000 00 Goats 30000 00 Farm equipment 12000 00 Sub total 972000 00 Current assets Current liabilities Cattle feeds in store 10000 00 Animal drugs in store 4000 00 Wages to workers 19000 Debts receivable 18000 00 Breakages and repair 30000 Cash at hand 20000 00 Cash at bank 30000 00 Sub total 82000 00 Sub total 69000 Total Assets 1054000 00 Total Liabilities 369000 Net worth/ owner’s equity/ net capital/ balance 685,000 TOTAL 1,054,000 TOTAL 1,054,000 -
- Highly soluble in soil water therefore should be applied in an already established crop.
- Have short residual effect, thus should be applied frequently.
- They have a scorching effect burning effect therefore should not come into contact with the plants.
- The fertilizers are hygroscopic/abs orb moisture from atmosphere therefore it should be stored in dry conditions
- The fertilizers are corrosive therefore they should not be handled with bare hands/stored in easily corroded containers
- Are easily leached therefore they should be applied to a vigorously growing crop/already established crop
- The fertilizers are Volatile therefore they should be applied on moist soils.
- The fertilizers are Volatile therefore they should be applied on moist soils.
-
- Perishability of produce-farmers incur losses of produce due to extra costs for transportation/ storing
- Bulkiness-hence occupy large space or require expensive or heavy transport.
- Transportation- due to poor infrastructure in various farming communities and lack of vehicles, transportation is a big problem.
- Seasonality of produce create storage problems, especially during peak seasons/under or over supply leading to fluctuation of prices.
- Storage is difficult- because of bulkiness/perishability of the produce, large space and special storage facilities are required, which is very costly
- Changes in market demand- there is time lag between decision to produce and actual availability of the product. This makes it difficult for a farmer to respond immediately to market demand.
- Change in supply- caused by under or overproduction/ competition from cheap imports causing price fluctuation.
- Lack of perfect market Information of market situation-many farmers are ignorant about the prevailing prices of their produce in other parts of the country making selling difficul
- Mr.Rono’s farm balance sheet as at 31st December 2021
-
-
- Altitude – 900 – 2700m above sea level
Temperature – cool conditions
Rainfall – 750-2000m per annum, well distributed throughout the growing period
Soils- Deep, fertile, well drained soils. (Any 2 x 1= 2mks) -
- Control weeds by hand; care should be taken not to break the leaves
- Top dressing when cabbages are 20 -25cm in height using one table spoonful of S.A/CAN
- Control pests such as Aphids, cutworms, cabbage saw fly by spraying appropriate pesticide
- Control diseases such as damping off, black rot and downy mildew by use of appropriate fungicide, crop rotation.
- Gapping by replacing the dead/ dry seedlings
- Irrigation to ensure proper growth. (3 x 1= 3mks)
- Altitude – 900 – 2700m above sea level
-
- Seeds are easy to treat against soil borne pests and diseases.
- Seeds are less bulky hence storage is easy
- Easy to handle during planting making operation faster
- When planting seeds, it is easy to use machines like seeds planters and drillers
- Easy to mechanize fertilizers and manures
- Pesticide to apply manures and fertilizers together with seeds during planting
- It is possible to develop new crop varieties due to cross pollination (1 x 5= 5mks)
- Water is passed through a series of sieves with different meshes to trap large particles
Softening of water
Soda ash/ sodium bicarbonate is added to soften water
Coagulation and sedimentation
Alum/ Aluminum sulphate is added to coagulate solid particles
Water stays here for 36 hours to kill bilharzia worms
Aeration of water is done by perforations on top of the tank.
Filtration II
Water is passed through different layer sizes of gravel and sand on top to remove solid particles left behind.
Chlorination
Small quantities of chlorine is added to kill microorganisms in water
-
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Cekenas Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
