QUESTIONS
Section A: (20 marks)
(Answer all the questions in the spaces provided)
-
- Study the illustration given and answer the questions that follow.

- Mention the appropriate technique that was used to produce it. (1mk)
- Mention any one tool and material used. (2mks)
- Explain the smearing technique of drawing forms. (1mk)
- State and explain any material that is used in clay correction during the preparation process. (2mks)
- How can ornaments be used to preserve a nation’s heritage? (1mk)
- Give any two factors to consider in packaging design. (2mks)
- State any four tools used in weaving. (2mks)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
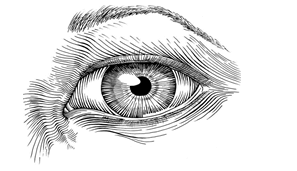
- State the most outstanding element used in the picture. (1mk)
- Explain one use of the above-mentioned element. (1mk)
- Distinguish between a monochromatic colour scheme and an analogous colour scheme. (2mks)
- Illustrate and state the importance of a view finder in Art. (2mks)
- Explain the 3 techniques of making marks on a surface. (3mks)
- Study the illustration given and answer the questions that follow.
Section B : 25mks
-
- Identify the stage and approach of drawing the illustration given is. (1mk)

Stage……..
Approach………… - Highlight any two advantages of using the above mentioned approach and 2 disadvantages. (4mks)
- Identify the stage and approach of drawing the illustration given is. (1mk)
-
- Differentiate between tritik and discharge technique of decorating fabric in terms of the process. (2mks)
- Explain the importance of using shellac on a silk screen as opposed to varnish. (1mk)
- Define serigraphy as a printing process and mention two techniques used under the process. (2mks)
-
- Identify the types of illustrations shown. (3mks)
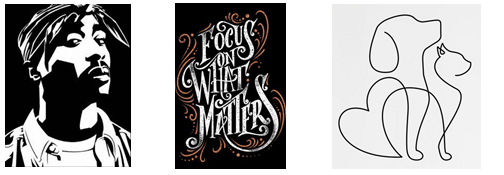
- Explain the importance of illustrations in a graphic artwork. (2mks)
- Identify the types of illustrations shown. (3mks)
-
- Explain the mosaic technique under the following:
- support (1mk)
- pasting (1mk)
- materials (1mk)
- Outline the importance of interstices in a Mosaic artwork. (2mks)
- Explain the mosaic technique under the following:
-
- Differentiate between visual symbols and corporate symbols. (1mk)
- Identify and list four components of a badge. (4mks)
Section C: (15mks)
(Answer only one question in this section in the space provided after question 9)
-
- Define the batik technique. (1mk)
- Explain how wax is molten for the batik process. Why? (2mks)
- Discuss how you would produce a decorated fabric in 3 colours using the batik technique. (10mks)
- Outline how to finish the fabric. (2mks)
-
- What do you understand by the term printmaking (1mk)
- Explain the following printing techniques (8mks)
- Relief printing
- Intaglio
- Serigraphy
- Lithography
- Mention and explain the tools used in any three techniques mentioned above. (6mks)
-
- Discuss the following hand building techniques. (12mks)
- Slab
- Pinch
- Scoop
- Outline the importance of: (3mks)
- Slaking day
- Kneading
- Storing day
- Discuss the following hand building techniques. (12mks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- Pottery
- Material- Clay, water, grog, slip.
Tool- loop tool, kidney scrappers, cutting wire, brush, sponge
- Using wet media such as ink or paint, dye etc; to produce a drawn composition.
- Grog- used to help in hardening the clay thus making it less plastic to enhance it’s workability. It is added in the kneading stage in the preparation process.
- Open ended as long as it sound logical.
-
- The type of item to be packed.
- Advertisement
- Durability
- Size and shape of the product
-
- Shuttle
- Shed stick
- Loom
- beater
-
- Lines
-
- Enclose shapes
- Define form
- Create depth
- Create mood, express feelings
- Monochromatic- different shades of the same/one colour (colours with same varied hues)
Analogous- colour placed next/ besides each othe in the colour wheel, and appear to belong in the same family, - Used to limit the area under study in landscape drawings and paintings.
- Smearing a mark using wet media
Etching/ cutting /scraping the surface
Pressing dry media such as charcoal, chalk or pencil
-
-
- Stage - drawing as a study
Approach - drawing from observation - Advantages- good capturing of details
Improves keenness, curiosity
Disadvantages- limits creativity
Monotony
- Stage - drawing as a study
-
- Tritik- use of a needle and thread to make detailed stiches if the design to be produced on the fabric,
Discharge- using a substance o dis-colour he fabric thus altering the initial colour giving it an effect of design. - It is washable thus the screen can be used to print different design unlike varnish which is not washable thus more permanent making the screen only usable for one given design only.
- Serigraphy the printing process that is done thru a surface,
Stencil printing
Silk screen printing
- Tritik- use of a needle and thread to make detailed stiches if the design to be produced on the fabric,
-
- silhouette
typographic
line art - To help in aiding the message with an actual image thus making it easy for the audience to understand what is being communicated.
Make the work more appealing.
- silhouette
-
-
- The supporting surface onto which the work is carried out on.
- The technique of attaching the tesserae being used.
- The actual material being used to produce the artwork referred to as the tesserae.
- Helps to give the work a shimmering effect and also create the web-like effect that enhances the appearance of the work, this making it look unique.
-
-
- Visual symbol- is an image or sign that is used to stand for something.
Corporate symbol- designs derived from visual symbols and are used mostly for office stationaries. - Shield
Emblem
Motto
Name of institution or organization.
- Visual symbol- is an image or sign that is used to stand for something.
-
- Duplication/ transfer of images from one surface to another.
-
- Planography/ lithography; printing from a flat surface
- Serigraphy; printing through a surface e.g silk screen printing
- Relief; printing from a raised surface.
- Intaglio/ gravure; printing from a sunken surface e.g etching, engraving
- computer assisted printing
- photographic printing
-
- To spread the ink evenly on a flat surface.
Transfer the ink onto the printing block. - Illustration 1mk
Labeling 2 mks
- Handle
- Roller
- To spread the ink evenly on a flat surface.
- -ve and +ve
-
- Tritik; a fabric is stitched and dyed to produce intricate designs.
-
- Remove excess dye
- Remove starch
- Remove dirt
-
- Vat
- Dylon
- Procion
- Reactives
-
- collect materials
- measure, mark and cut the fabric into required size
- wash and dry the fabric
- tie the fabric as required
- prepare the dye bath (starting with the lightest colour)
- immerse the fabric in the bath as desired and allow it to get the required shade (stir if necessary)
- remove the fabric and oxidise it
- wash the fabric to remove excess dye
- repeat the process for the second colour
- untie, dry the fabric, iron and present it.
-
- Keramos
‘potter’s clay’ - Residual; found near the original rock source, they are the purest types
Sedimentary; have been carried away from the original source by water, erosion etc. They are impure since they contain a lot of other substances. - Digging (wet) – getting the clay from the source
Crash (dry) – turn the dry clay to small fragments.
Slake- soak the clay in water for about 2 days
Mix- stir to mix into a porridge like consistency
Seive- to remove any impurities, after grog is added if necessary or any other ingridients needed to make a working clay body eg. Kaolin
Wedge/ knead- the clay is kneaded to expel all the air in it to render it into a smooth consistency. All air must be removed to prevent the form from cracking during firing.
Store- kneaded clay can be stored in plastic buckets, polythen bags or polythene.
- Keramos
Download Art Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Cekenas Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
