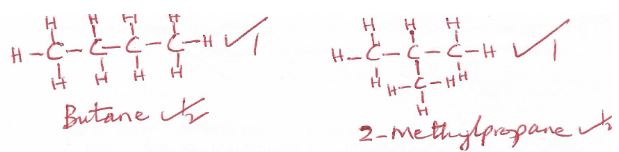Questions
Instructions to candidates
- Answer ALL questions
- KNEC Mathematical tables and silent non – programmable electronic calculators may be used.
- All working MUST be clearly shown where necessary.
- Candidates should answer the questions in English.
- A luminous flame produces more light than a non-luminous flame. Explain. (2 marks)
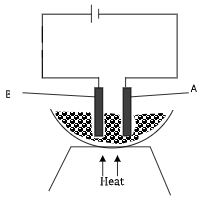
- The diagram below was used to electrolyze molten copper (II) chloride using graphite electrodes at s.t.p.
- Explain the role of heat on the above set up. (1 mark)
- Write equations at electrode A and B. (2mark)
- Dry ammonia was passed over heated copper (II) oxide in a combustion tube.
- State and explain the observation that was made. (2 marks)
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction above. (1 mark)
-
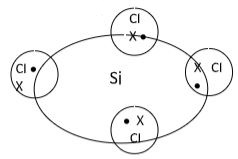
- Use dots (∙) or crosses (x) to show bonding in the silicon chloride (1mark)
- Ethanol and dimethylether have both molecular formulae Explain why ethanol boils at 78.20C and dimethyl ether has a boiling point -240C. (2 marks)
- When 17.2 g of hydrated calcium sulphate was heated to a constant mass, 13.6g of the residue was obtain. Find the value of n in . (3 marks)
(Ca = 40, S = 32, O = 16, H = 1) - In an experiment, ammonium chloride was heated in a boiling tube with a moist red and blue litmus paper at the mouth of test tube. State and explain the observation made. (3 marks)
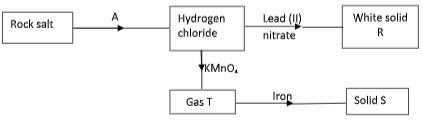
- Study the chart below and answer the questions that follow.
- Name reagent used in step A. (1 mark)
- Write the ionic equation for formation of white solid R. (1 mark)
- Write an equation for formation of solid S. (1 mark)
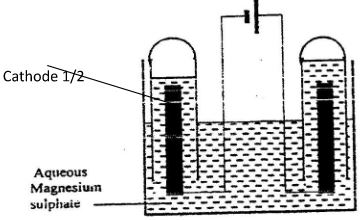
- The set-up below was used during the electrolysis of aqueous magnesium sulphate using inert electrodes.
- On the diagram label the cathode. (½mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction that took place at the cathode. (1 mark)
- Explain the change that occurred to the concentration of magnesium sulphate solution during the experiment. (1½ marks)
- The equation below shows the oxidation of Sulphur (IV) oxide to Sulphur (VI) oxide in the contact process.
2SO2(g) + O2(g ) → 2SO3(g) ∆H = -196kJ/mol-
State and explain the effect on the yield of Sulphur (IV) oxide when:- the temperature increased. (1½ marks)
- the amount of oxygen is increased. (1½marks)
- Dry carbon (II) oxide is passed over heated iron (III) oxide.
- Name the type of reaction between carbon (II) oxide and iron (III) oxide. (1mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction between carbon (II) oxide and iron (III) oxide (1mark)
- Name a suitable drying agent for carbon (II) oxide (1mark)
- Thermochemical equation for combustion of ethanol is shown below;
C2H5OH (l) + 3 O2 (g) ———> 2 CO2 (g) + 3 H2O (I), AH = - 1337kJmol- Determine the heating value for ethanol? (2 mark)
( C= 12, H = 1, O = 16 ) - Draw the structural formula for 2-methylprop-l-ene {1 mark)
- Determine the heating value for ethanol? (2 mark)
-
- Define oxidation in terms of electrons (1mark)
- Determine the oxidation state of (1mark)
- Suphur in SO32- ion
- Phosphorous in PO43- ion (1mark)
- Labels on acid solutions indicated the following:-
Acid 1 :0.1M, 6.5% ionized
Acid 2 :0. 2M, 1.3% ionized- Identify the strong acid (1 mark)
- If 25cm3 of distilled water are added to 50cm3 of acid 2, what is its new concentration? (2 mark)
- When 0.05 mole of magnesium were added to 100cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid at 25°C, 25kJ of heat energy were released. The acid was in excess.
- Calculate the highest temperature of the reaction mixture. (2mark)
(specific heat capacity for water is 4.2J/g/ °C, density of the solution is lg/cm3) - Calculate the molar heat of reaction for the reaction below (1 mark}
Mg (s) + 2HCI (aq) ———> MgCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)
- Calculate the highest temperature of the reaction mixture. (2mark)
- Hydrogen sulphide is a highly toxic and flammable gas and is usually prepared in the fume chamber.
- Name any two reagents that can be used to prepare hydrogen sulphide in the laboratory. (1mk)
- Hydrogen sulphide could be used to produce sulphur as shown in the equation below:
2H2S(g) + SO2(g) → 3S(s) + 2H2O(l)
In the equation above, identify the reducing agent and give a reason for your answer. (1mk) - Other than Vulcanization of rubber, identify any other uses of Sulphur. (1mk)
- The following table shows the PH values of solutions A ,B and C
Solution A B C pH 2 7 11 - Which solution is likely to be magnesium chloride? Give a reason. (1mk)
- Identify the solution in which a sample of aluminium chloride is likely to be when dissolved in water. Explain (2mks)
- Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow (The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements)
Ionization Energy KJ/Mole-1 Element Electronic configuration 1st ionization energy 2nd ionization energy A 2.2 900 1800 B 2.8.2 736 1450 C 2.8.8.2 590 1150 - What is ionization energy (1mk)
- Explain why the 2nd ionization energy is higher than the 1st ionization energy. (1mk)
- An element K has relative atomic mass of 40.2. It has two isotopes of masses 39 and 42. Calculate the relative abundance of each isotope. (3mks)
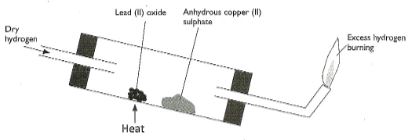
- Use the diagram below to answer the questions that follow.
- After the experiment has been running for some time, record two major observations made in the tube. (2mks)
- Write an equation for the reaction that takes place in the dish containing lead (II) oxide. (1mk)
-
- Name two ores of iron. (1mks)
- Give the name of the suitable method used in extracting iron from the ore. (1mk)
- Name one impurity present in pig iron and state one effect of the impurity in the physical property of iron. (1mks)
- The table below gives two samples of mixtures. Study the table and answer the questions that follow
Mixture 1 components Mixture components Silver chloride Iron(III) Chloride Lead Chloride Iron (III) Oxide Water - State the main property that makes components of Mixture 1 separable (1mk)
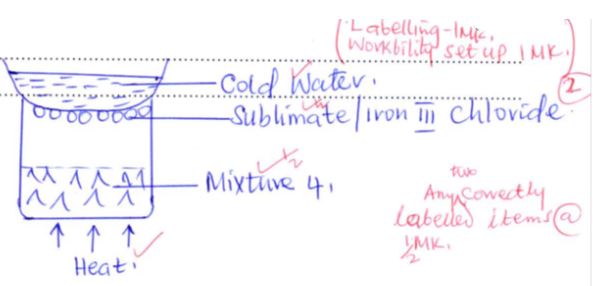
- Draw a well labeled diagram of a simple laboratory set up which can be used to separate the components of Mixture 2 (2mks)
-
- What name is given to group one elements ? (1mk)
- Explain why there is a general increase in the atomic radii of the elements down a group of the periodic table. (2 mks)
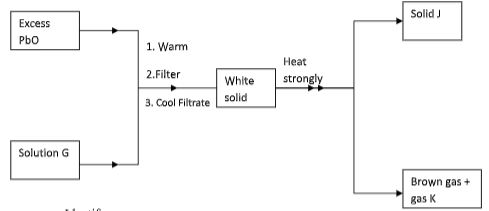
- Study the flow chart below and answer the question that follows.
Identify: (3mks)- Solution G
- Solid J
- Gas K
- Draw and name structural formulae of two isomers whose molecular formula is C4H10. (3mks)
- The concentration of a solution of aluminium sulphate is 0.02M. How many sulphate ions are contained in 150 cm3 of the solution? (3 mks)
(Avogadro’s constant= 6.0 x 1023) - Explain why a solution of hydrogen chloride gas in methylbenzene does not conduct electricity but solution of the gas in water conduct electricity. (2mks)
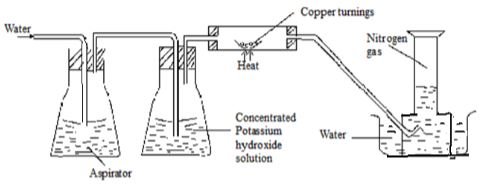
- Nitrogen gas can be obtained from air as shown below.
- What is the purpose of concentrated potassium hydroxide solution? (1mk
- Write the equation for the reaction that takes place in the chamber containing copper turnings (1 mk)
- The nitrogen gas obtained above is not pure. Identify one gaseous impurity in the gas. (1mk)
- Radioactive, polonium, 21684 Po , decays as shown below:-
216 208
Po → Pb + M α + n β
84 82
Determine the values of M and N. (2 marks)
Marking Scheme
- A luminous flame produces more light than a non-luminous flame. Explain. (2 marks)
- Presence of unburnt (1)carbon which glow (1)
- The diagram below was used to electrolyze molten copper (II) chloride using graphite electrodes at s.t.p.
- Explain the role of heat on the above set up. (1 mark)
- Keep CuCl2 in molten form so as the ions are mobile to conduct electricity.
- Write equations at electrode A and B. (2mark)
- A Cu2+(l) + 2e → Cu(s)
- B 2CI-(l) → Cl2(g) + 2e
- Explain the role of heat on the above set up. (1 mark)
- Dry ammonia was passed over heated copper (II) oxide in a combustion tube.
- State and explain the observation that was made. (2 marks)
- Black copper (II) oxide changed to brown - ammonia reduces copper (II) oxide to copper//
- Colourless liquid forms on cooler parts of combustion tubes- Ammonia is oxidised
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction above. (1 mark)
- 3CuO(s)+2NH3(g) → 3Cu(s) + 3H2O + N2(g)
- State and explain the observation that was made. (2 marks)
- Use dots (∙) or crosses (x) to show bonding in the following molecules.
- Silicon chloride
- Ethanol and dimethylether have both molecular formulae C2H6O. Explain why ethanol C2H6OH boils at 78.20C and dimethyl ether CH3OCH3 has a boiling point -240C. (2 marks)
- Ethanol contains hydrogen bond which are strongerbonds than Van der Waal forces in dimethyl ether.
- Silicon chloride
- When 17.2 g of hydrated calcium sulphate was heated to a constant mass, 13.6g of the residue was obtain. Find the value of n in CaSO4 nH2O. (3 marks)
(Ca = 40, S = 32, O = 16, H = 1)
n = 2CaSO4 H2O Mass 13.6 3.6 R.A.M 136 18 No. of moles 13.6/136 3.6/18 Mole ratio 0.1
0.1/0.10.2
0.2/0.21 2 - In an experiment, ammonium chloride was heated in a boiling tube with a moist red and blue litmus paper at the mouth of test tube. State and explain the observation made. (3 marks)
- First Moist red litmus changed to blue and both the moist blue litmus papers later changed to red.
- When ammonium chloride is heated it decomposes into ammonia and hydrogen chloride gases.
- Ammonia is light hence diffuses faster changing the litmus to blue. HCl diffuses slower changing the two litmus back to red. (W.T.T.E)
- Study the chart below and answer the questions that follow.
- Name reagent used in step A. (1 mark)
- Concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid
- Write the ionic equation for formation of white solid R. (1 mark)
- Pb2+(aq) + 2Cl-(aq) → PbCl2(s)
- Write an equation for formation of solid S. (1 mark)
- 2Fe(s) + 3Cl2(g) → 2FeCl3(s)
- Name reagent used in step A. (1 mark)
- The set-up below was used during the electrolysis of aqueous magnesium sulphate using inert electrodes.
- On the diagram label the cathode. (½mark)
- Write an equation for the reaction that took place at the cathode. (1 mark)
- 2H+(aq) + 2e- → H2(g) ✓1
- Explain the change that occurred to the concentration of magnesium sulphate solution during the experiment. (1½ marks)
- Concentration increased✓½ because the amount of water decreased✓½ as it was decomposed to hydrogen and oxygen gases which escaped✓½
- On the diagram label the cathode. (½mark)
- The equation below shows the oxidation of Sulphur (IV) oxide to Sulphur (VI) oxide in the contact process.
2SO2(g) + O2(g ) → 2SO3(g) ∆H = -196kJ/mol-
State and explain the effect on the yield of Sulphur (IV) oxide when:- the temperature increased. (11/2 marks)
- Yield decreases 1 backward reaction is favoured which endothermic//lower temperature 1/2
- the amount of oxygen is increased. (11/2marks)
- Yield increases 1 Oxygen reacts with Sulphur (IV) oxide forming more Sulphur (VI) oxide//equilibrium shifts to the right to lower concetration of oxygen.
- the temperature increased. (11/2 marks)
- Dry carbon (II) oxide is passed over heated iron (III) oxide.
- Name the type of reaction between carbon (II) oxide and iron (III) oxide. (1mark)
- Redox reaction ( 1 mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction between carbon (II) oxide and iron (III) oxide (1mark)
- Fe2 O3(s) + 3 CO → 2Fe (s) + 3 CO2 (g)
- Name a suitable drying agent for carbon (II) oxide (1mark)
- Concentrated sulphuric acid// anhydrous calcium chloride// calcium oxide
- Name the type of reaction between carbon (II) oxide and iron (III) oxide. (1mark)
- Thermochemical equation for combustion of ethanol is shown below;
C2H5OH (l) + 3 O2 (g) ———> 2 CO2 (g) + 3 H2O (I), AH = - 1337kJmol- Determine the heating value for ethanol? (2 mark)
( C= 12, H = 1, O = 16 )- 1337kj/46g (1mark)
= 29.07 kJg-1 (1mark)
- 1337kj/46g (1mark)
- Draw the structural formula for 2-methylprop-l-ene {1 mark)
- Determine the heating value for ethanol? (2 mark)
-
- Define oxidation in terms of electrons (1mark)
- Oxidation is lose of electrons
- Determine the oxidation state of (1mark)
- Suphur in SO3 -2 ion
- x +3 (-2) =- 2
x – 6 = -2
x = + 4
- x +3 (-2) =- 2
- Phosphorous in PO43- ion (1mark)
- x + 4 ( - 2) = -3
x – 8 = - 3
x= +5
- x + 4 ( - 2) = -3
- Suphur in SO3 -2 ion
- Define oxidation in terms of electrons (1mark)
- Labels on acid solutions indicated the following:-
Acid 1 :0.1M, 6.5% ionized
Acid 2 :0. 2M, 1.3% ionized- Identify the strong acid (1 mark)
- Acid 1
- If 25cm3 of distilled water are added to 50cm3 of acid 2, what is its new concentration? (2 mark)
- M1V1 = M2 V2
M2 = M₁V₁ = 0.2M X 50CM³ = 0.133M
V2 75cm3
- M1V1 = M2 V2
- Identify the strong acid (1 mark)
- When 0.05 mole of magnesium were added to 100cm3 of dilute hydrochloric acid at 25°C, 25kJ of heat energy were released. The acid was in excess.
- Calculate the highest temperature of the reaction mixture. (2mark)
(specific heat capacity for water is 4.2J/g/ °C, density of the solution is lg/cm3)- ∆H = mc∆T
25000 J = 100g x 4.2Jg-1k-1 x ∆T
∆T = 25000J
100g x 4.2Jg-1 K-1
= 59. 52
Highest temperature reached
59.52 + 25 = 84.520C
- ∆H = mc∆T
- Calculate the molar heat of reaction for the reaction below (1 mark}
Mg (s) + 2HCI (aq) ———> MgCl2 (aq) + H2 (g)- 0.05moles 25kJ
1 mole x
X = 1 mole x 25kj = -500kJ mol-1
0.05moles
- 0.05moles 25kJ
- Calculate the highest temperature of the reaction mixture. (2mark)
- Hydrogen sulphide is a highly toxic and flammable gas and is usually prepared in the fume chamber.
- Name any two reagents that can be used to prepare hydrogen sulphide in the laboratory. (1mk)
- iron(II)sulphide and dilute hydrochloric acid// any metal sulphide and an acid
- Hydrogen sulphide could be used to produced sulphur as shown in the equation below:
2H2S(g) + SO2 (g) → 3S(s) + 2H2O(l)
In the equation above, identify the reducing agent and give a reason for your answer. (1mk)- H2S – oxidation number of sulphur decreases from +4 to 0
- Other than Vulcanisation of rubber, identify any other uses of Sulphur. (1mk)
- Manufacture of sulphuric (VI)acid// any other correct use
- Name any two reagents that can be used to prepare hydrogen sulphide in the laboratory. (1mk)
- The following table shows the PH values of solutions A ,B and C
- Which solution is likely to be magnesium chloride. Give a reason. (1mk)
- B- it is neutral
- Identify the solution in which a sample of aluminium chloride is likely to be when dissolved in water. Explain (2mks)
- A – hydrolyses in water to produce hydrochloric acid which is a strong acid
- Which solution is likely to be magnesium chloride. Give a reason. (1mk)
- Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow (The letters do not represent the actual symbols of the elements)
- What is ionization energy (1mk)
- Minimum amount of energy required to remove an electrom from an atom in the gaseous state
- Explain why the 2nd ionization energy is higher than the 1st ionization energy. (1mk)
- Once an electron is removed from an atom, the remaining electrons are held more strongly by the net charge than the first one
- What is ionization energy (1mk)
- An element K has relative atomic mass of 40.2. It has two isotopes of masses 39 and 42. Calculate the relative abundance of each isotope. (3mks)
- 39 x + 42(100-x) = 40.2
100
4020 = 39x + 4200 – 42x
3x = 180
X = 60
K39 = 60%
K42 = 40%
- 39 x + 42(100-x) = 40.2
- Use the diagram below to answer the questions that follow.
- After the experiment has been running for some time, record two major observations made in the tube. (2mks)
- Red lead (II) oxide turns grey
- White copper (II) sulphate turns blue
- Write an equation for the reaction that takes place in the dish containing lead (II) oxide. (1mk)
- PbO(s) + H2(g) → Pb(s) + H2O(l)
- After the experiment has been running for some time, record two major observations made in the tube. (2mks)
-
- Name two ores of iron. (1mks)
- haematite
- magnetite
- siderite any two
- Give the name of the suitable method used in extracting iron from the ore. (1mk)
- reduction
- Name one impurity present in pig iron and state one effect of the impurity in the physical property of iron. (1mks)
- Carbon//silicon – makes iron brittle
- Name two ores of iron. (1mks)
- The table below gives two samples of mixtures. Study the table and answer the questions that follow
- State the main property that makes components of Mixture 1 separable (1mk)
- lead(II) chloride dissolves in warm/hot water
- Draw a well labeled diagram of a simple laboratory set up which can be used to separate the components of Mixture 2 (2mks)
- State the main property that makes components of Mixture 1 separable (1mk)
-
- what name is given to group one elements ? (1mk)
- Alkali metals
- Explain why there is a general increase in the atomic radii of the elements down a group of the periodic table. (2 mks)
- There is increase in number of occupied energy levels which leads to a weaker force of attraction for valence electrons
- what name is given to group one elements ? (1mk)
- Study the flow chart below and answer the question that follows.
Identify: (3mks)- Solution G
- Dilute nitric(V) acid// HNO3
- Solid J
- Lead(II)oxide// PbO
- Gas K
- Oxygen//O2
- Solution G
- Draw and name structural formulae of two isomers whose molecular formula is C4H10. (3mks)
- The concentration of a solution of aluminium sulphate is 0.02M. How many sulphate ions are contained in 150 cm3 of the solution? (3 mks)
(Avogadro’s constant= 6.0 x 1023)- Moles of AI2(SO4)3 = 150 x 0.02
1000
= 0.003moles(1)
Moles of SO42- = 0.003 x 3 = 0.009moles(1)
No. of SO42- ions = 0.009 x 6.0 x 1023
= 5.4 x 1021 ions(1)
- Moles of AI2(SO4)3 = 150 x 0.02
- Explain why a solution of hydrogen chloride gas in methylbenzene does not conduct electricity but solution of the gas in water conduct electricity. (2mks)
- Methylbenzene is a non- polar compound hence hydrogen chloride in it does not ionize // exist as a molecule substance but in water hydrogen chloride ionizes to give H+ and cl- ions that’s why it conduct electricity in water.
- Nitrogen gas can be obtained from air as shown below.
- What is the purpose of concentrated potassium hydroxide solution? (1mk)
- Absorb carbon(IV) oxide gas.
- write the equation that takes place in the chamber containing copper turnings
- 2Cu(s) + O2(g) → 2CuO(s) (1 mk)
- The nitrogen gas obtained above is not pure. Identify one gaseous impurity in the gas.
- Argon (1mk)
- What is the purpose of concentrated potassium hydroxide solution? (1mk)
- Radioactive, polonium, 216 Po , decays as shown below:-
Determine the values of M and N.- M =2
- N=2
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Mathioya Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students