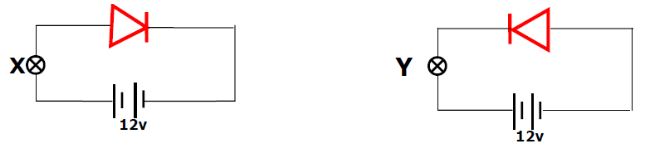Questions
INSTRUCTION TO CANDIDATES.
- This paper contain two sections; Section I and Section II.
- Answer all the questions in section I and II. In the spaces provided
- All workings and answers must be written on the question paper in the spaces provided below each question.
- Marks may be given for correct working even if the answer is wrong.
- Calculators and KNEC Mathematical tables may be used EXCEPT where stated otherwise.
- Show all the steps in your calculations, giving your answers at each stage in the spaces below each question.
SECTION A 25 MKS
- Give a reason when light strikes a mirror at 900, it is reflected along the same path (1 mark)
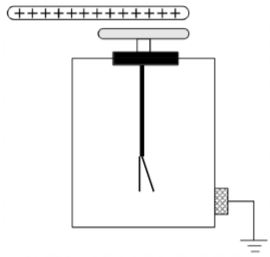
- The figure below shows an electroscope that is being charged.
If the final charge on an electroscope is positive- State the method of charging that produces the above electroscope to be positively charged (1 mark)
- Explain how the final charge was acquired (2 marks)
- Give the formula relating to the Emf of a cell, the internal resistance, r, and the terminal voltage, V and the current, I in a closed circuit (1 mark)
- Give a reason why parabolic reflectors are used as car headlight lamps. (1 mark)
- A current of 2A flows through a conductor for 2.5minutes. If the electronic charge is 1.6 x 10-19 C, calculate the number of electrons involved. (3marks)
- Give one reason why Ultra sound is used in pulse echo techniques in determining the depth of the sea. (1 mark)
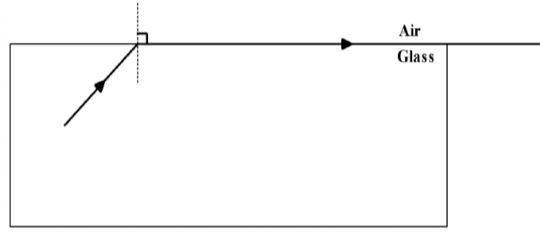
- The figure below is drawn to scale. Use this information on the figure to answer the questions that follow;
Determine the refractive index of the glass material. (2 marks) -
-
- What is a virtual image? (1 mark)
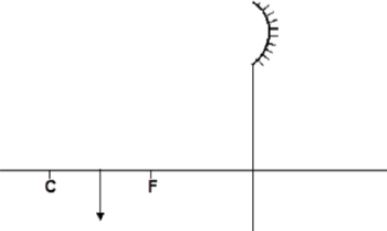
- Complete the ray diagram in figure 3 below so as to form an image. (3 marks)
-
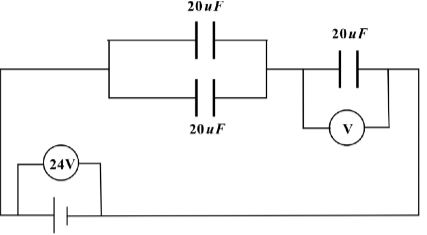
- Three capacitors of capacitance 20μF are arranged as shown below. Find the Reading on the voltmeter across the 20μF shown in the following diagram. (3 marks)
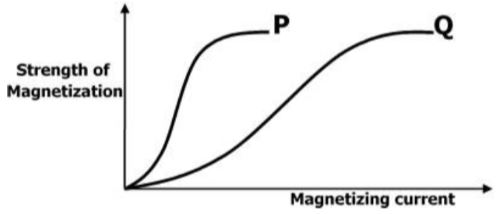
- In an experiment to magnetize two substances P and Q using electric current, two curves were obtained as shown below. State with a reason which substance will be used as an armature in an electric bell. (2 marks)
- State the function Argon and Nitrogen in a fluorescent lamp. (1 mark)
- Distinguish between thermionic emission and photoelectric effect. (1mark)
- The following is part of a radioactive decay series.
234 β a α 230
Bi → X → Y
83 4 b
Determine the values of a and b (2mark)
SECTION B
-
- Explain in terms of flow of electric charges why a thin wire feels warmer than copper leads in the same current (1 mark)
-
- State the main energy changes that take place in a filament lamp (1 mark)
- Name any two factors affecting the heating effect of an electric current (2 marks)
- Give a reason why tungsten wire is used in a filament bulb. (1 mark)
- A light bulb is found to have a resistance of 950Ω. When operating normally on a 240V mains.
Calculate- Power rating of the Bulb (2 marks)
- Electric energy converted to heat and light when the bulb operates for 2 hours (3 marks)
-
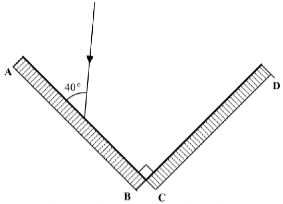
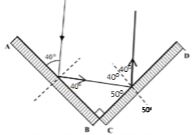
- The mirror AB and CD are at right angles to each other.
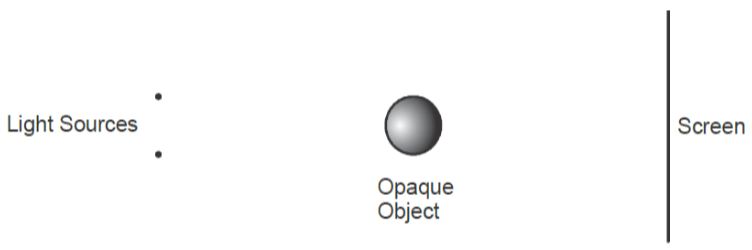
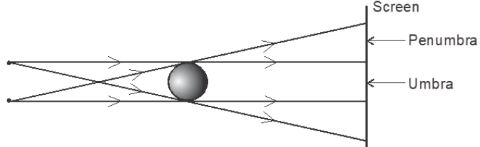
Complete the diagram to show the path taken by the ray PQ after reflection at both mirrors. (2 marks) - The figure below shows two point sources of light with an opaque object placed between them and the screen.
Complete the diagram to show the nature of the shadows formed. Label the shadows. (2 marks) - State the changes that would occur in the size and brightness of the image formed if:
- The object distance is made large (1 mark)
- The length of the camera is made longer (1 mark)
- The single hole is replaced by four pinholes close together (1 mark)
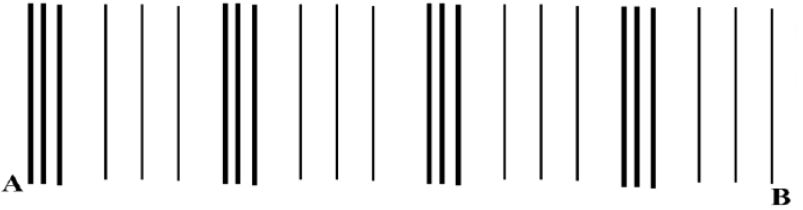
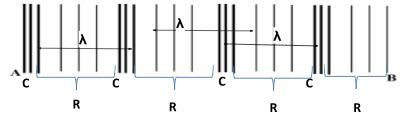
- The diagram below shows sound waves passing through air. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
Label the following (3 marks)- Compression
- Rarefaction
- Wavelength
- The mirror AB and CD are at right angles to each other.
-
- State the functions of carbon brushes in an electric motor. (1 mark)
- Why are carbon brushes and commutators made of graphite in an electric motor? (1 mark)
- The figure below shows a conductor carrying current placed in the magnetic field and moves in the direction shown
Identify the polarity of end X. (1 mark)
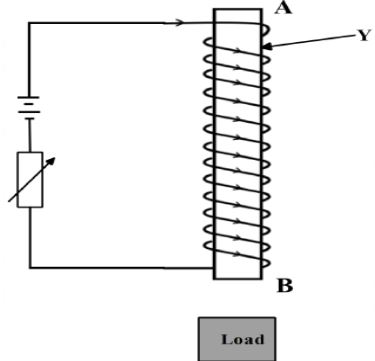
X – - The figure below shows a simple electro magnet for lifting heavier container loads in the kilindini port in Mombasa city in Kenya.
- Which material is Y made from? Explain why it is a preferred choice for its use in the above diagram? (2 marks)
- State the polarity of B (1 mark)
- Explain one way in which the electromagnet can be made more powerful (1 mark)
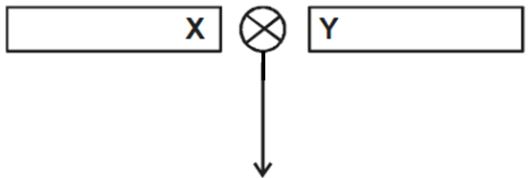
- In an experiment on use of semiconductor diodes, it was noted that bulb X in figure below lights while bulb Y does not. Explain. (1mark)
-
- State the properties of X-rays, which makes it possible to detect cracks in bones. (1mark)
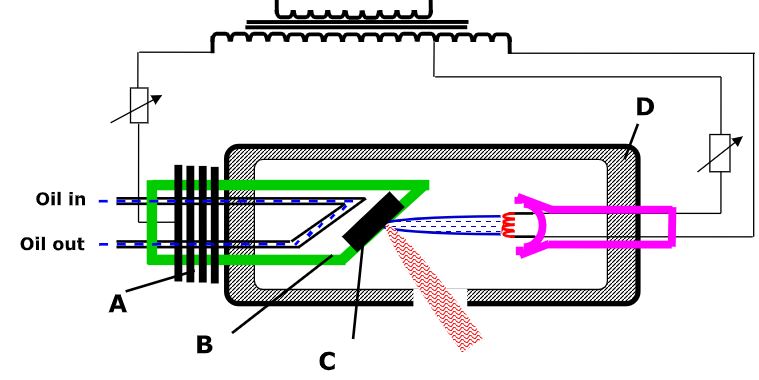
- Figure below shows the features of an X-ray tube.
- Name the parts marked with letters A and B (1mark)
- State and explain which material is suitable for part C. (1mark)
- State the reason why the machine should be surrounded by D. (1mark)
- State one way in which cooling is achieved in this X-ray machine. (1mark)
- The figure below shows the trace on the screen of an a.c signal connected to the y-plates of C.R.O with time base on.
Given that the time control is 5ms/div, and the y-again is at 100V/div, determine:- The frequency of the a.c signal. (2marks)
- The peak voltage of the input signal (2marks)
-
-
- Name one type of electromagnetic radiation whose frequency is greater than that of visible light but less than that of gamma rays. (1mark)
- Arrange the following in order of increasing frequencies: Red, Green, Yellow, Blue. (1mark)
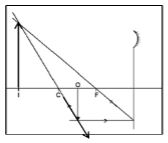
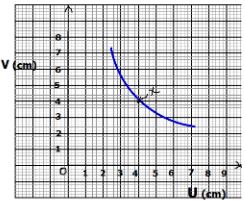
- The figure below shows an object placed in front of a convex lens.
- On the same figure indicate a point X where the object distance is equal to the image distance of the lens. (1 mark)
Use the point X in (a) above to determine; - The radius of curvature (2 marks
- Focal length of the lens (1 mark)
- Calculate the magnification of the mirror at point X from the graph (1 mark)
- On the same figure indicate a point X where the object distance is equal to the image distance of the lens. (1 mark)
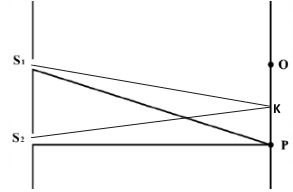
- The figure below shows the waves starting from two coherent sources S1 and S2
What would be observed at K if the waves are;- light waves. (1 mark)
- Sound waves. (1 mark)
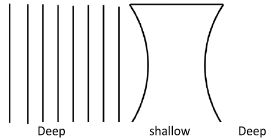
- Co mplete how the wave fronts emerge from the concave lens below. (1 mark)
-
-
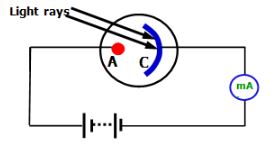
- The figure below shows a circuit diagram for a photocell.
- Name the part labeled A (1mark)
- Why is the milliammeter showing a deflection when ultraviolet light is shown on the photocell? (1mark)
- State how the milliameter reading is affected when the intensity of light is increased. (1mark)
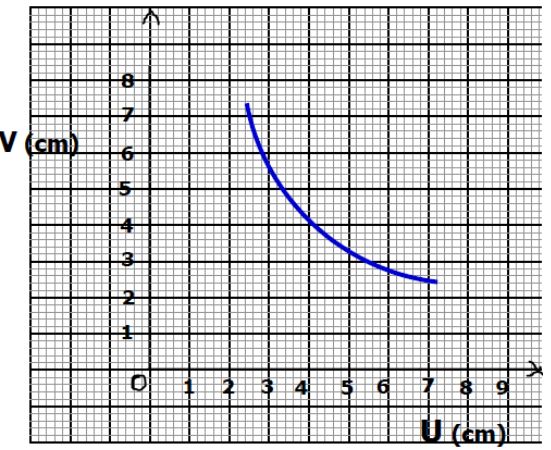
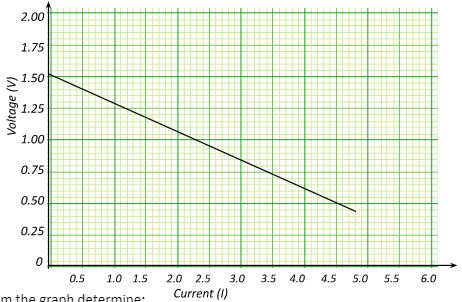
- The graph below shows the relationship between the emf (E) and the current I flowing through a cell of internal resistance, r.
From the graph determine;- Emf of the cell (1 mark)
- the internal resistance r of the cell (2 marks)
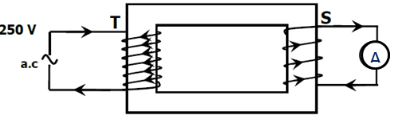
- Two coils T and S are wound on a soft iron core as shown. T has 1000 turns while S has 600 turns and resistance of 100Ω
Calculate the maximum current measured by the ammeter. (2marks)
- The figure below shows a circuit diagram for a photocell.
Marking Scheme
- Angle of incidence = angle of reflection =00
√ 1mark -
- Contact method
- If the rod is brought closer, the negative charges will be induced at the cap while the positive charge will be repelled to the plate. If the rod now touches the cap, it neutralizes the negatives charges ,
- If it is withdrawn, the positive charge will be more in the electroscope hence charged positively
√ 1mark
- E=V +Ir
- When the bulb is at the Centre of curvature, it produces a stronger parallel beam that travels longer distance.
- Q=It, Q= 2A x 2.5 x 60=300 C
Number of electrons=300C/1.6 x10 -19C
=1.875 x 1025electrons -
- It penetrates deepest
- It is easily reflected even by tiny grains
- Angle 42°(must be measured directly from the diagram)
n=1/Sin θ
n=1/Sin 42=1.4945 -
- Image that cannot be focused on the screen
-
- Q=CV
Cr = 40 x 20 = 13.33 μF
40 + 20
Q = 13.33 x 24 = 320 μC
V = 320 x 10¯⁶ = 16V
20 x 10-6 - P
It takes a smaller current to achieve magnetic saturation as compared to Q OR P is easily magnetized than Q - Provide an inert atmosphere to prevent the oxidation of the filament
- Thermionic emission is the process of emission of electrons through heat energy while photoelectric effect is the process of emission of electrons when radiation of sufficient energy/frequency is irradiated on a metal surface
- a=234, b=82
-
- a thin wire has got more resistance to the flow of current as compared to the copper leads hence produces a higher heating effect than copper leads
-
- Electrical energy to heat energy and Light Energy
-
- Resistance of the conductor
- Quantity of current flowing
- Time of heating
- being made of material of high melting point, it withstand the high temperature inside the filament bulb
-
- V= IR
I = V/R = 240/950 = 0.2526A
P = VI = 240 x 0.2526 = 60.624W
or use P = V2/R = 60.63W - E = Pr = 60.624 x 2 x 3600 = 436492.8J
- V= IR
-
-
-
-
- The image will appear smaller
- The image will appear larger
- Each pinhole will form its image resulting into brighter but blurred image
-
-
- Presses lightly against the commutators so that the coil rotates freely and easily.
- Graphite is a good conductor of electricity
It serves as a lubricant since it is slippery -
- X - North Pole
Y - South pole
- X - North Pole
-
- Soft iron since it and easily magnetized and demagnetized
- South pole
-
- by increasing the strength of current
- By increasing the number of turns per unit length
- By replacing the core with a U shaped one
- X is connected to a forward biased diode which makes the junction to become smaller while Y is connected to a Reverse biased diode. Diodes conduct only in forward bias
- .
- X-rays have high penetrating power.
-
-
- A. Cooling fins
B. Copper anode.
- A. Cooling fins
- Tungsten or molybdenum. It is made of high melting point to withstand high temperatures.
- To absorb the stray x-ray radiations which would otherwise affect the x-ray tube operators.
-
- By efficient cooling fins on the outside of the tube.
- By circulating oil through the channels in the copper anode.
-
-
- f = 1/T = 1 = 50Hz
20 x 10-3 - Vpeak = 3 div x 100Vdiv = 300v
- f = 1/T = 1 = 50Hz
-
-
- Ultra violet, X-rays
- Red, Yellow, Green, Blue
-
- Indicated on the diagram
- When V=U=4cm,then,Radius of curvature ,r , =4cm(object and Image is also at C
- Since f=?/2 =4??/2 =2??
- M=?/? −1, ?=4/2 −1=1 OR m=v/u=4/4=1
- Indicated on the diagram
-
- A bright fringe/band formed –at constructive interference
- loud sound
-
-
-
- Anode
- When UV is illuminated on photocell, photoelectrons are emitted. Emitted photoelectrons are attracted toward plate A, completing the circuit, photocurrent flows hence deflection on the milliammeter.
- Milliammeter reading increases/Deflection on milliammeter increases
-
- Emf is the voltage intercept=1.50V
- slope =-r
Points,(0,1.5), (4.5,0.5), slope =1/-4.5 r=0.22Ω
Ns/Np = Vs/Vp = 1s x R/Vp
Is = 600/1000 x 2.5 = 1.5A
-
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Physics Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Mathioya Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students