QUESTIONS
SECTION A (25MARKS)
Answer all questions in this section.
-
- Name two branches of geography. (2mks)
- Give three reasons why it is importance to study geography. (3mks)
-
- Give three characteristics of nimbostratus clouds. (3mks)
- State three factors that influence atmospheric pressure. (2mks)
-
- Give three causes of earthquakes. (3mks)
- State two major earthquake zones of the world. (2mks)
-
- Identify three features found in the middle stage of a river`s course.(3mks)
- State two factors which influence how a river transport its load. (2mks)
-
- Give two types of soil degeneration. (2mks)
- List three components of soils. (3mks)
SECTION B (75MARKS)
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section.
- Study the map of Nyeri 1:50,000 (sheet 120/4) provided and answer the following questions
-
- Give the longitudinal extend of the area covered by the map (2mks)
- Give two methods that have been used to represent relief in the area covered by the map (2mks)
- What was the magnetic declination of the area covered by the map as at January 1975 (2mks)
-
- Name two administrative divisions found in the area covered by the map (2mks)
- Describe distribution of settlements in the area covered by the map (6mks)
-
- Citing evidence from the map, give three social functions of Nyeri Municipality (3mks)
- Citing evidence from the map, explain four factors favouring beef farming in the area . covered by the map (8mks)
-
-
-
- What is a mineral (2mks)
- Describe the following characteristics of minerals:
- Lustre; (2mks)
- Colour; (2mks)
- Density. (2mks)
-
- Name two examples of extrusive igneous rocks, (2mks)
- Describe three ways in which sedimentary rocks are formed. (6mks)
- Explain the significance of rocks to the economy of Kenya under the following subheadings:
- Tourism (2mks)
- Energy (2mks)
- Water. (2mks)
-
-
-
- What is faulting? (2mks)
- Name four types of faults. (4mks)
- With the aid of well-labelled diagrams, describe how a Rift Valley is formed by Tensional forces. (8mks)
- Apart from the Rift Valley, name other three relief features that may form as a result of faulting. (3mks)
- Explain four ways in which features resulting from faulting are Economic significance. (8mks)
-
-
-
- State the two causes of waves in the oceans (2mks)
- The diagram below shows parts of a wave.
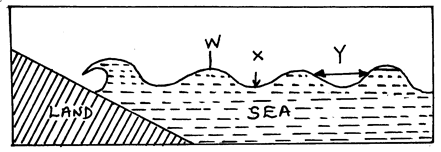
Name the parts marked W, X and Y (3mks)
-
- Name three types of submerged coasts. (3mks)
- Explain the three processes involved in marine erosion (6mks)
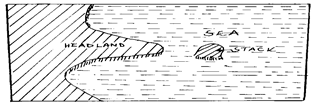
- Using well labeled diagrams, explain how the following coastal features are formed.
- Stacks (4mks)
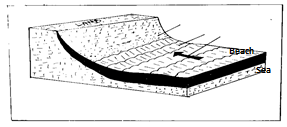
- Beaches (4mks)
- State three ways which Kenya benefits from her coastal features. (3mks)
-
-
-
- Apart from a cirque, name three features found on the upland glaciated areas. (3mks)
- With the aid of a well labelled diagram, describe the process through which a hanging valley is formed (7mks)
- Describe the following glacial erosional processes occur.
- Plucking (4mks)
- Abrasion (3mks)
- Explain four negative effects of glaciated lowland feature. (8mks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Physical geography
Human geography
Practical geography -
- Geography is a career subject it provides a firm foundation for advanced studies in specialized fields like engineering, remote sensing, urban planning etc.
- Study of geography enables one to acquire basic skills and knowledge which contribute to local, regional and national development.
- Through the study of fieldwork, geography teaches one on how to manage time properly by drawing a time schedule and adhering to it.
- Geography focuses on physical study of the earth. We are therefore able to learn and explain the origin of the earth and the solar system.
- Geography enables the learners to understand and appreciate different environmental influences at work on different societies.
- Geography creates awareness in the people on the significance of management and conservation of the environment.
- Physical geography
-
-
- Are dense
- Are dark gray in colour
- Are layered
- Are low clouds
- Bear some rains
- Appear in uniform texture.
-
- Attitude
- Temperature\
- Earth rotation 2 @ 1=2mks.
-
-
-
- Underground nuclear test.
- Movement of trains.
- Use of explosives.
- Construction of large reservoirs.
-
- Ring of fire (circum-pacific belt)
- Along boundaries of thectonic plates
- Southern Europe and southern asia
-
-
-
- Meanders/Bends.
- Concave banks.
- Bluffs.
- Convex banks.
- Open V-Shaped valley.
- River – braids.
- Alluvial fans
-
- Size of individual rock particles.
- Gradient of the river channel.
- Amount of water in the stream/stream volume.
- Amount of load.
-
-
-
- Physical degeneration
- Chemical degeneration
- Biological degeneration
-
- Soil organic matter
- Soil inorganic matter
- Soil water/moisture
- Soil air/gases
-
-
-
- 36º 45’’ E TO 37º 00’’ E
-
- By use of contours
- By use of trigonometrical stations
- By use of spot height
- 1º 31’
-
- District
Province -
- There are no settlements in the forest
- There are few settlements in the North Eastern part of the area covered by the map
- There are linear settlements along the roads e.g. all weather road bound surface B5
- There are many/ dense settlements in the southern/ south eastern part of the area covered in the map
- There are clustered settlements to southern part of the area covered by the map
- There are linear settlements along some rivers
- There are no settlements within the woodland
- District
-
-
- It is a residential centre as evidence by the presence of settlement
- It is administrative centre as evidenced by the presence of PC/DC/DO/Admin offices
- It is a health centre as evidenced by the presence of hospitals
- It is a recreational centre as evidenced by the presence of hotel, golf, clubs, show grounds
- It is a religious centre as evidenced by the presence of churches
- It is an educational centre as evidenced by the presence of schools, institutes
- It is a rehabilitation centre as evidenced by the presence of prisons
- It is a communication centre as evidenced by the presence of post office
-
- Availability of large tract of land which favours the location of Monte Carlo Ranch
- Presence of scrub which is used for grazing beef cattle
- Presence of permanent rivers which provide water for beef cattle
- Availability of transport as evidenced by presence of roads which are used for transportation of livestock and livestock products to the markets
- Dense population to the southern part of the area covered by the map which provide market for livestock and livestock products
-
-
-
-
- Mineral is an organic substance with a definite chemical composition at/beneath the surface of the earth
-
- Lustre; (2 marks)
Minerals differ in their brightness depending on nature of their reflective surfaces. (smooth surfaces are dull.) - Colour; (2 marks)
Different minerals display different colours. Minerals that have iron/Magnesium have dark colours. - Density. (2 marks)
Minerals have different weight per unit volume of water.
- Lustre; (2 marks)
-
-
- Basalt - rhyolite
- Pumice - obsidian
- Tuff - andesite
-
- Mechanically formed sedimentary rocks – rock fragments are transported by wind/water/ice. they are deposited in layers. Over a long period of time, they are compacted into a hard rock
- Organically formed sedimentary rocks – dissolved minerals are transported in layers. Over a long period of time, the remains are compacted forming a hard rock.
- Chemically formed sedimentary rocks- dissolved minerals are transported into water bodies. They are then precipitated/evaporated over a long period of time. The precipitates/evaporates are then compacted. To form hard a rock
-
-
- Tourism (2 marks)
Some rocks form unique features that attract tourists earning the country foreign exchange. - Energy (2 marks)
Some sedimentary rocks contain fossil fuels which are sources of energy for domestic/industrial use. - Water. (2 marks)
Some rocks act as storage for water which can be supplied for domestic/industrial/agricultural
- Tourism (2 marks)
-
-
-
- A process through which britle crustal rock fracture (break) due to tectonic forces (tensional / compression) (2mks)
-
- Normal fault
- Reverse fault
- Tears fault
- Shear /slip fault
- Thrust fault (4x1=4mks)
- The layer of crustal rode is subjected to tensional forces line of weakness occurs this leads to the development of the adjacent normal faults. The central block eventually sinks or subside as the central bloke are pulled apart
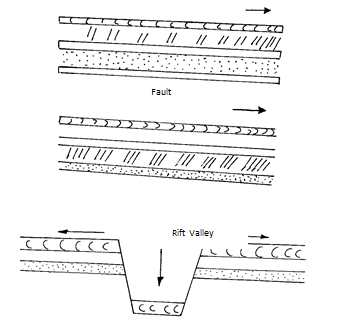
-
- Fault scarp / escarpment
- Fault steps
- Fault blocks
- Tilt blocks
-
- Faults may expose mineral on the surface for easy extraction.
- Features resulting from faulting eg rift valleys, hotsprings, etc attract tourist.
- Vertical faulting across a river may cause a water fall which may be used to generate H.E.P
- Rift valley lakes are used for fishing and mining e.g soda ash
- Fault Mountains are catchments areas and sources of rivers which are used for irrigation and domestic use.
- Fault scarp slopes may expose underground water result ground water result in the formation of clean water encouraging settlements.
-
-
-
- Wind
Earthquakes - W – Wavecrest
X – Trough
Y – Wavelength
- Wind
-
- Ria
Flord
Longitudinal - Abrasion(corrasion)
- Wave erode through hurling water containing pebbles, rock fragments or sand on the coast. It leads to cliff undercutting
Hydraulic action - Is direct wave force
- The water from a breaker splaster on the cliff eroding it
- Cliffs that have cavities / cracks / caves are subjected to great compression of air. Once the wave reatreats , the air explodes causing rock breakup
Solution (corrosion) - Rain water / waves dissolves limestone rocks
Attrition - Is where the materials carried in the wave [pebbles, sand and hingle] hit / knock against each other reducing in size
- Wave erode through hurling water containing pebbles, rock fragments or sand on the coast. It leads to cliff undercutting
- Ria
- Stacks
- Is a rock pillar rising steeply from the sea which has been isolated by the erosive work of waves
- Formed by the collapse of an arch leaving a stack isolated from the headlands
- Visible during the high and low tide levels
Beaches - Are accumulation of sand, pebbles and shingles between the low tides and the high tides [upper limits of the wave action]
- Concave in profile
- Formed by wave deposition in a process called longshore drift
- Waves bring materials to a gentle coast. The swash being greater than the backwash deposits shingle, sand and pebbles which over time accumulate to form a beach.
- Tourists attraction – foreign exchange
- Fishing (oceans)
- Transport and communication (sea transport)
- Limestone – building and construction
- Tidal / wave energy can be harnersed from waves.
- Sand – building and construction.
- Harbours are built on headlands promoting trade and anchoring of ships
- Forestry – mangrove trees which provides timber
- Lagoons and mudflats can be irrigated for rice production.
-
-
-
- Arête, Pyramidal peak, U-shaped valley/ glacial trough, Hanging valleys, Rocks basins.
-
- Pre-existing main valleys and tributary are occupied by ice.
- Erosion by plucking and abrasion takes place on both main and tributary valleys.
- More erosion is experienced in the main valley than tributary valley because the main valley contains more ice.
- Eventually the main valley is deepened and widened leading to formation of broad u-shaped steep sided valley called glacial trough.
- When ice melts, the tributary valley is left suspended/raised at a higher level
- The tributary valley left raised/suspended obove the main river valley is kwon as a hanging valley.
- Plucking (4 marks)
- Occur in well pointed rocks such that the melt water will enter into the rock cracks
- Temperature slightly reduces / falls and the melt water freezes in the rock cracks.
- There is repeated action of freezing and thawing.
- This enlarges the rock cracks and eventually causes part of the rock to fall off, and is pulled and carried away by moving glacier.
Abrasion (3 marks) - Occurs when the rock debris at the base and sides of the glacier is used as an erosive tool to scratch and polish the rock surfaces where glacier moves over.
- The underlying rocks will be smothered when the debris are dragged along the rock as glacier moves.
-
- Boulder clay deposits have poor drainage and so cannot promote farming.
- Infertile sand deposited in many outwash plains makes the land unsuitable for agriculture.
- Moraine deposits result in the formation of numerous lakes which reduce the land available for use by people.
- Glaciations results in rugged landscapes that discourage the settlement or putting up transport and communication line.
- Presence of erratic drumlins and settle lakes makes the landscape rugged discouraging construction of transport and communication line.
- Some minerals may be buried deep underneath the moraine making it difficult expensive to mine
-
Download Geography Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Londiani Joint Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
