QUESTIONS
SECTION A
Answer all questions in this section
-
- What is a derelict land? (2 mks)
- State three causes of land dereliction. (3 mks)
-
- State three problems facing coffee in Kenya. (3 mks)
- Outline two benefits of coffee farming in Brazil. (2mks)
-
- Name two exotic breeds of dairy cattle reared in Kenya. (2mks)
- State three physical conditions that favor dairy farming in Denmark. (3mks)
- The table below shows petroleum production in thousand barrels per day for countries in the Middle East in April 2006. Use it to answer question (a)
Country Production in ‘000” Barrels Iran
Kuwait
Qatar
Saudi Arabia
United Arab Emirates
Iraq3800
2550
800
9600
2500
1900-
- What is the difference in production between the highest and the lowest producer (1mk)
- What is the total amount of petroleum produced in April 2006 in the region? (1mk)
- State three conditions that are necessary for the formation of petroleum. (3mks)
-
-
- State two reasons why some industries are located near the sources of raw materials. (2mks)
- Give three characteristics of the cottage industry in India. (3mks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other Two questions from this section
- The table below shows four principal crops produced in Kenya in the years 2000 - 2001. Use it to answer question(a) and (b).
Source: Central Bureau of statisticsCROP AMOUNT IN METRIC TONS 2000 2001 Wheat 70,000 130,000 Maize 200,000 370,000 Coffee 98,000 55,000 Tea 240,000 295,000 -
- Using a scale of 1 cm to represent 50,000 metric tons, draw a simple comparative bar graph based on the data above. (8mks)
- State two advantages of using comparative bar graphs (2mks)
- Calculate the percentage increase in wheat production between the years 2000 and 2001. (2mks)
- State five physical conditions required for the growing of tea in Kenya. (5mks)
- Explain four problems experienced in small scale tea farming in Kenya. (8mks)
-
-
-
- What is forestry? (2mks)
- Explain three factors that favor the growth of natural forests on the slopes of Mt. Kenya. (6mks)
- State five factors that have led to the reduction of the area under forest on the slopes of Mt Kenya. (5mks)
- Explain four measures that the government of Kenya is taking to conserve forests in the country. (8mks)
- Give the differences in the exploitation of softwood forests in Kenya and Canada under the following sub-headings;
- Period of harvesting; (2mks)
- Transportation (2mks)
-
- The map below shows some major fishing grounds in the world. Use it to answer question (a)
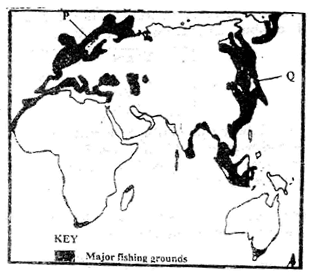
-
- Name the countries marked P and Q. (2mks)
- Explain four conditions that favor fishing in the shaded coastal waters. (8mks)
- The diagrams below represent some fishing methods
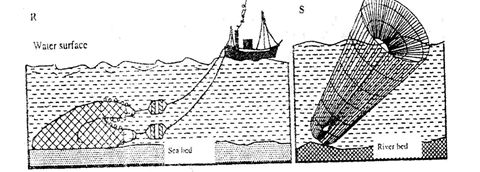
- Name the methods R and S. (2mks)
- Describe how each of the two methods is used in fishing. (7mks)
- Explain three measures used to conserve fish in Kenya. (6mks)
-
-
-
- Define the term tourism. (1mk)
- Name two tourist attraction found in the Rift valley province of Kenya. (2mks)
- Explain four factors which hindered the development of domestic tourism in Kenya. (8mks)
- Explain three problems experienced by the Kenya government in its effort to conserve wildlife. (6mks)
- Explain four factors which have made Switzerland a major tourist destination in Europe. (8mks)
-
-
-
- Name two non – renewable sources of energy. (2mks)
- Explain four physical factors that influence the location of a hydroelectric power station. (8mks)
- A part from generating H.E.), give three other benefits that have resulted from the construction of Masinga Dam. (3mks)
- Explain three benefits that would result from rural electrification in Kenya. (6mks)
- In what three ways did the power shortages resulting from the drought of the years 1999 and 2000 affect the industrial sector in Kenya. (6mks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
-
- This is land that has been abandoned because it is damaged, has no vegetation and is depleted of minerals.
-
- Overgrazing and overstocking.
- Mining
- Deforestation
- Poor farming methods like monocropping.
-
-
- Attack by pests like leave miner –coffee leaves
- diseases such as coffee berry disease
- fluctuation of coffee prices which discourage farmers
- inadequate capital for buying farm inputs and paying labour
- mismanagement of coffee cooperative societies.
-
- employment opportunities –industries,farms,etc
- earnings from coffee export –developing sectors such as education,health,etc
- provision of coffee bevearage
-
-
- Fresian / Hoisten
Ayshire
Guernsey
Jersey
Alderney
Brown Swiss / Swiss Brown. (2mks) -
- The landscape is gently sloping which is suitable for grazing
- The climate has warm / sunny summer / moderate temperature (10º – 17ºC) that allow out door grazing.
- There is cool climate suitable for pasture growing
- The moderate rainfall (500 – 1000mm) that supports growth of grass / fodder crops
- Boulder clay soil are fertile support high pasture
NB if one writes moderate rainfall of 11000mm – its wrong. (3mks)
- Fresian / Hoisten
-
-
- 8,800 , 000 barrels (1mk)
- 634,500,000 barrels (2.55 x108) (1mk)
- Deposition / presence of flora and fauna over a long period of time / fossils presence of presence of porous rocks / presence of non porous underneath in the deposits of the flora and fauna.
Deposition of other layers of rocks / non porous / over the remains of flora and fauna Compression of the remains of flora and fauna due to folding of the layers of rocks.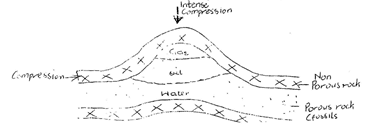
-
-
-
- The raw materials may be too bulky and thus expensive to transport
- Some raw materials are perishable so they have to be processed before transportation
- Processing reduces transport costs ( any 2 x 1 = 2 mks)
-
- They rely on simple equipment/ machines
- They are labour intensive
- They are owned by families
- They use locally available raw materials
- They produce mainly for local markets
- They are widespread in the country (Any 3 x 1 = 3 mks)
- They allow ease in comparison interpretation.
-
-
- They give clear visual impression
They are easy to read
They easily show the trend of the given data.
Easy to draw / construct (Any 2x1 = 2mks) - 130,000
- 70,000 60,000 x 100 = 85.7 / 85 (2mks)
60,000 70,000 -
- Cool / warm climate / condition. 10oc to 28oc throughout the year
- High rainfall/ 1000 – 2000 mm per year.
- Well distributed rainfall through the year.
- Areas the are frost – free
- Deep light and well drained soils
- Gently sloping / undulating land
- Acidic / Volcanic soils / ph of 4 – 6
- High altitude / 100 m – 2300m a.s.l (Any 5 x 1 (5mks)
-
- Delayed payments / low payments that lowers the morale of the farmers mismanagement / Embezzlement of funds thus farmers are discouraged
- Poor feeder roads in the tea growing areas lead to delays in collection / delivery of the green leaf hence wastage.
- Adverse weather conditions such as long droughts / hale storms lead to destruction of the crop / lower production.
- Fluctuation of prices in the world market makes it difficult for the farmer to plan ahead/ lower morale/ discourages farmers
- High production costs due to high prices of farm inputs leads to lower yields since most farmers cannot afford to buy them
- Pests/ Fungal diseases destroy crops. Reduce yields ( pests e.g. red spider-mites, weevils and beetles), termites, nematodes.
- Inadequate/ unreliable transport facilities delays the collection/ delivery of green leaf reducing the quality.
- Labour shortage/ expensive labour leads to low products/quality.. (8mks)
- They give clear visual impression
-
-
- It is the science of planting, caring and using trees/ forests and their resources
It is the practice of managing and using trees/ forests associated resources -
- The area receives high rainfall 1000- 22000 mm throughout the year which encourages continuous growth of trees.
- The area has deep fertile volcanic soils that allow the roots to penetrate deep into the ground to support the trees
- The area has well drained soil thus there is no water logging which can choke plants and interfere with their growth
- The area has moderate cool condition/ climate are ideal for the growth of a variety of trees.
- The area is a gazeted forest reserve/ settlement and cultivation are prohibited hence allowing forests to grow without interference
- The steep slopes discourages human activities thus enabling forests to thrive well
-
- The illegal encroachment of human activities
- The illegal cultivation has led to clearing of parts of the forest
- Prolonged droughts have caused drying of some forests
- Plant disease/ pests destroy some trees in the forest
- Outbreak of forest fires/ charcoal burning destroy some trees in the forest
- Over exploitation of certain species of trees. (5mks)
- It is the science of planting, caring and using trees/ forests and their resources
-
- Registering/ recognizing the efforts of NGOs like the green Belt Movement which have mounted campaigns on planting of trees
- Gazeting forested areas to reduce encroachment of the public
- Creating public awareness through mass media/ public bazaars on the importance of conserving forest resources
- Enacting laws to prohibit the cutting of trees without a license/ protecting indigeous tree species
- Establishing NEMA/ ministry of environment and natural resources to coordinate environmental management and conservation activities
- Setting aside national tree planting day to encourage people to plant more trees
- Advising people to practice agro- forestry so as to avoid cutting trees from the forests
- Employing forest guards to protect forests form fires/ other illegal human activities
- Encouraging recycling of paers/ wood based products/ use of other sources of energy to reduce demand of trees
- Carrying out research through KEFRI and ICRAF in order to come up with ways of controlling diseases/ pests/ develop species suitable for different ecological regions. (8mks)
- Period of harvesting
Transportation
Kenya Canada
Period of harvesting is done throughout the year Harvesting is in winter and Early spring (2mks)
Transportation mainly road transport Mainly water transport (2mks)
-
-
-
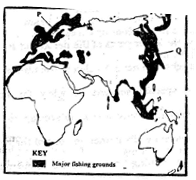
P- Norway Q- Japan. (2mks)-
- The areas have shallow continental shelves which allow light to penetrate to the sea below encouraging the growth of micro- organisms used as food by fish
- The areas experience convergence of warm and cool currents which result in upwelling of ocean waters thus bringing minerals for fish and plankton from the sea bed to the surface
- Most of the coast are indented/ have numerous sheltered bays which provide secure breeding grounds for fish.
- The shelters bays provide suitable sites for building fishing ports/ fish landing sites
- The large population in these area limits agricultural activities thus people turn to fishing as an alternative economic activity/ cold climate also limit agriculture
- Cold climate provides natural preservation of fish. (8mks)
-
-
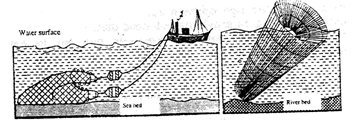
- R – Trawling S – Basket fishing. (2mks)
- Basket fishing
- The basket funnel shaped to allow easy entry for fish
- At the mouth there is a non- return valve which restricts the outward/ escape movement of fish once inside the basket it is held in position with tropes/ stones/ sticks to prevent it from being swept downstream
- The basket is left in that position for sometime/ overnight then removed for landing the fish (3mks)
Trawling - A bag – shaped net is attracted to a ship – trawler
- The nets mouth is kept open by otter boards/ head beam
- The upper part of the net is kept a float by corks/ floats
- Weights are used to keep the lower parts of the net at the seabed
- The trawler drags along the net
- After sufficient fish is caught, the net is hauled to the trawler. (4mks)
- The size if the nets used in fishing are standardized to ensure that fingerlings are not caught
- Licenses are issued to prospective fishermen to control their number and to ensure that there is no over fishing
- The law of the sea restricts fishing in the exclusive economic zones/ this ensure the protection of marines fisheries from external exploitation
- Fish farming is being encouraged to ensure that there is sufficient supply of fish from other sources other than the natural fisheries
- There is restriction of the water remain artificial fertilization is carried out is special hatcheries to sustain the supply of fish/ restocking of over fished waters. (6mks)
-
-
-
-
- Tourism is the visiting of places of interest for e recreational purposes
- The varied relief features.
- Wild animals
- Birds / flamingos
- Hot springs / Geysers / Fumaroles /Geothermal
- Vegetation
- People culture
- Pre- historic sites /Historical sites e.g. Kapenguria
- Mining sites
- Sports tourism e.g. fishing (2mks)
-
- Inadequate local comparing and advertisement of tourist attractions/ special packages leads to low public awareness.
- Familiarity with the tourist attraction among the local people makes them fail to appreciate their beauty and value
- Negative attitude towards local tourism limits the number of people who engage in tourism.
- Insecurity from gangsters/ poachers in national parks and game reserves scare people away from visiting them.
- The high cost of accommodation in the game lodges discourages local tourism / the high cost of hiring tourism vehicles discourages people from touring / low income. (8mks)
-
- Overstocking of some wild animals leads to destruction of natural environment through over-grazing.
- Frequent drought experienced in some of the nation parks and reserves leads to loss of animals through starvation and death.
- Staying wild animals from the parks to settlement leads to destruction / high cost of fencing.
- Inadequate capital limits government conservation efforts / over reliance on foreign donor.
- Rapid human population growth leads to the encroachment of games parks and reserve.
- Pollution of the environment leads to death of wild animals.
- Fire outbreaks destroy wildlife. (6mks)
-
- The varied scenery consisting of snow – capped mountains, cascading waterfall and glaciated landscape provides varied tourist attraction which are lacking in other parts of Europe make the country easily accessible from the other European countries.
- Political neutrality of Switzerland removes any travel restrictions to the country as a tourist destination.
- Diversity of languages spoken in Switzerland makes it possible for tourist to communicate and move around the area.
- Well- developed transport network tourist sites provide easy accessibility.
- Advanced training in tourist industry enables Switzerland to provide the necessary services to tourist thus attracting more to the country / package tours services offered e.g. hotels.
- Availability of health resorts.
- Inherent hospitality of Swiss people encourage tourist to visit Switzerland.
- Well-developed financial institutions (Banks) have promoted easy transaction, hence encouraging tourist to Switzerland.
- Switzerland is HQ of several international agencies; this has lead to the influx of delegates to the country later turn to tourist. (8mks)
-
-
-
-
- Petroleum /oil
- Natural gas
- Uranium
- Coal/peat (2mks)
-
- Presence of large volume of water from a river /Lake / large catchments area to provide water to drive the turbines
- Regular / constant supply of water to ensure continuous generation of power
- Hard basement rock to provide a firm foundation for the construction of a dam
- Provide space for reservoir
- Non-porous rock to prevent seepage. (8mks)
-
-
- It filters silt to save the other dams which are down stream
- It provides a fishing ground for the local communities
- It provides water for domestic use.
- It is a tourist attraction/reaction
- The dam provides a link role river Tana.
- Water for irrigation
- Provides employment
- Non-exhaustible/ renewable.
- Lean to use / non-pollutant
- Relatively heap
- Easy to use
- Adjustable to any fraction of energy using transformers
- Convenient to use in a variety of ways. (3mks)
-
- It would encourage setting up of industries in the rural areas thus stimulating decentralization of industries.
- It would reduce the cutting down of trees and electricity would be available for domestic use
- It would attract/improve social amenities in rural areas reducing the need for people to move to urban areas.
- Most people would invest in the rural areas, which would lead to higher standards of living.
- It would encourage development of horticultural farming / to have ideal storage of perishable of products. (6mks)
-
- It leads to closure of some industries
- It led to unemployment /redundancy/early retirement of workers.
- It led to an increase in the cost of electricity / purchase and use of generators
- It led to power rationing. Which slowed down rate of production. (2X3=6mks)
-
Download Geography Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Londiani Joint Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
