INSTRUCTION TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name and index number in the spaces provided above.
- Sign and write the date of Examination in the space provided.
- This paper consists of three sections A, B and C.
- Answer ALL the questions in section A and B.
- Answer TWO questions in section C in the spaces provided.
FOR EXAMINER’S USE ONLY.
|
SECTION |
QUESTIONS |
MAXIMUM SCORE |
CANDIDATES SCORE |
|
A |
1 – 16 |
30 |
|
|
B |
17 – 20 |
20 |
|
|
C |
21 – 23 |
20 20 |
|
|
TOTAL SCORE |
90 |
QUESTIONS
SECTION A(30 MARKS)
Answer ALL questions in this section
- Name four advantages of organic farming (2marks)
- Name four categories of livestock farming (2marks)
- Name three forms of horticulture practiced in Kenya (1½ marks)
- Name the part harvested for each of the following crops
- Onions (½ mark)
- Carrots (½ mark)
- Coffee (½ mark)
- State four disadvantages of broadcasting of seed s during planting (2marks)
- Name four ways in which land reforms can be implemented in Kenya (2marks)
- State four factors that determine the choice of water pipes used in the farm (2marks)
- State four ways in which mulching conserve water (2marks)
- Name four records that should be kept in a poultry farmer (2marks)
- State four reasons for applying phosphatic fertilizers during planting (2marks)
- State four characteristics of a good site of a nursery bed (2marks)
- State four ways in which crop pest can be classified (2marks)
- State four classes of weeds (2marks)
- State four management practices undertaken to improve natural pastures (2marks)
- State four disadvantages of using organic manure on crop production (2marks)
- What is meant by the term preference and choice as used in agricultural economics? (1mark)
SECTION B (20MARKS)
Answer ALL questions in this section
- The diagrams below illustrate some field practices carried out on certain crops
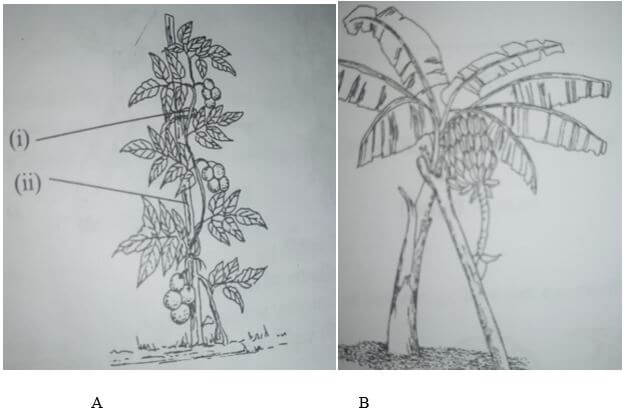
- Identify the practices illustrated in diagram A and B
A (1mark)
B (1mark) - State two problems faced by the farmers who do not carry out practice B (2marks)
- Explain pruning practices of a banana stool (1mark)
- Identify the practices illustrated in diagram A and B
- The diagram below illustrates a soil profile
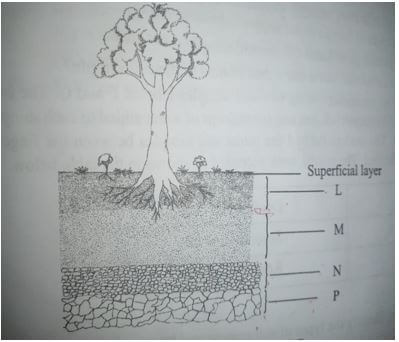
- Identify the layers labelled M,N and P
M.. (1mark)
N.. (1mark)
P .. (1mark) - State one characteristic of the layer labelled L (1mark)
- Name the zone found between two adjoining layers(horizons) (1mark)
- Identify the layers labelled M,N and P
- The diagram illustrates a certain property of different types of soils
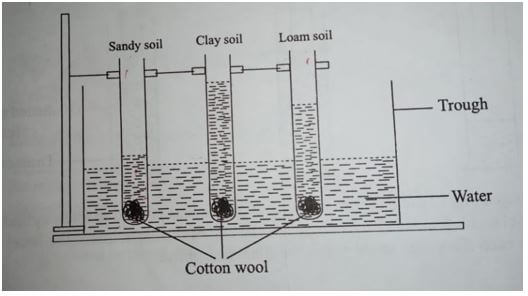
- State the property investigated in the diagram (1mark)
- In which of the three soils would water rise very fast at the beginning of the experiment and the rise stop within hours. (1mark)
- From the diagram what conclusion would be made in regard to the three soil types and the property being investigated? (3marks)
- In a maize production enterprise carried out over a period of eight years, a farmer used one hectare of land each time and applied different quantities of DAP fertilizer.DAP fertilizer costs ksh.2500 per 50kgs bag and the harvested maize is sold at ksh.3000 per 90kg bag. The quantities of DAP fertilizer applied and maize harvested are as shown in thus table below.
DAP fertilizer input in 50kg bag
Maize yield in 90kg bags
Total revenue khs
Total cost kshs
Marginal revenue Kshs
Marginal cost kshs
0
15.0
45000
0
0
0
1
35.6
2
52.0
3
68.5
4
71.0
5
71.5
6
71.5
7
68.5
- complete the table by determining the values of total revenue, total cost, marginal revenue and marginal cost (2marks)
- From the information in your table, how can the farmer determine the level of production at which profit is maximum? (1mark)
- At the production level that yield maximum profit, what was the value of each of the following?
- DAP fertilizer input (1mark)
- Marginal revenue (1mark)
SECTION C(40MARKS)
Answer TWO questions from this section
-
- Describe cultural methods of controlling soil erosion (8marks)
- Describe harvesting of tea (7marks)
- Give five reasons for land registration (5marks)
-
- State five ways of improving labour productivity in the farm (5marks)
- State five roles if magnesium in crop production (5marks)
- Describe five reasons why early defoliation is discouraged in pasture utilization. (5marks)
- Describe five harmful effects of crop pest (5marks)
-
- Explain importance of irrigation farming (5marks)
- State five characteristics of variable inputs (5marks)
- Describe the harvesting and marketing of bulb onions (5marks)
- State five disadvantages of communal land tenure system (5marks)
MARKING SCHEME
- Name four advantages of organic farming (2mks)
- Products are free from chemical residues
- It is environmentally friendly
- Livestock and farmer do not risk effects of poisonous chemicals
- Cheap as it uses locally available materials
- It maintain soil structure
- Promotes microbial activities in the soil
- Name four categories of livestock farming (2mks)
- Pastoralism/mammalian livestock farming
- Fish farming/aquaculture/pisci culture
- Apiculture/bee farming
- Poultry rearing
- Name three forms of horticulture practiced in Kenya (1½ mks)
- Floriculture
- Olericulture
- Pomoculture
- Name the part harvested for each of the following crops
- Onions (½ mk)
- bulb/leaves
- Carrots (½ mk)
- roots
- Coffee (½ mk)
- berries/cherries/fruits
- Onions (½ mk)
- State four disadvantages of broadcasting of seed s during planting (2mks)
- Require high seed rate
- Difficulty to carry out crop management practices
- Operations cannot be mechanized
- Difficult to establish plant population
- Uneven crop establishment
- Name four ways in which land reforms can be implemented in Kenya (2mks)
- Land consolidation
- Land adjudication and registration/ issue of title deeds
- Land settlement and resettlement
- Tenancy reforms
- Redistribution of land
- Improved land legislation
- Land subdivision (land sub division)
- State four factors that determine the choice of water pipes used in the farm (2mks)
- Strength of the pipe
- Amount of water to be conveyed
- Cost of the pipe
- Size of the pipe/diameter
- Durability
- Colour of the pipe
- State four ways in which mulching conserve water (2mks)
- Prevent splash erosion/intercept rain drops
- Reduce the speed of surface run off
- Reduces evaporation
- Increases water holding capacity
- Improves water in filtration
- Name four records that should be kept in a poultry farmer (2mks)
- Egg production record
- Labour record
- Feeding records
- Marketing records
- Inventory records
- Health records
- State four reasons for applying phosphatic fertilizers during planting (2mks)
- Less soluble
- Promote root development
- Has slight scorching effects
- Have long residual effect
- Not easily leached
- State four characteristics of a good site of a nursery bed (2mks)
- Near a reliable source of water
- Well drained area with deep fertile soil
- Generally sloping area
- Secure area
- Sheltered place
- Should not have been used fir the same crop species in the previous season
- Should be accessible
- State four ways in which crop pest can be classified (2mks)
- Storage pest
- Field pest
- Biting and chewing mouth parts
- Piercing and sucking mouth parts
- Scientific classification /rodents/insects/mites
- Type of crop attacked
- Stage of crop attacked
- Minor and major pest
- State four classes of weeds (2mks)
- Broad leaved weeds
- Narrow leaved weeds
- Perennial weeds
- Annual weeds
- Biennial weeds
- Monocotyledonous
- dicotyledonous
- terrestrial weeds
- aquatic weeds
- State four management practices undertaken to improve natural pastures (2mks)
- Weed control
- Topping
- Over sowing with leguminous pastures
- Fertilizer application
- Irrigation
- Pest control
- State four disadvantages of using organic manure on crop production (2mks)
- Low nutritive value per unit volume
- Likelihood of spread of diseases/pest/weeds
- Bulky/difficult to store/transport/apply
- Looses nutrients if poorly stored
- Difficult to quantify the amount of nutrient per unit volume
- What is meant by the term preference and choice as used in agricultural economics? (2mks)
- It is the act of deciding on how to allocate scarce resources to alternative uses based on the farmers interest
- The diagrams below illustrate some field practices carried out on certain crops
- Identify the practices illustrated in diagram A and B
- A staking (1mk)
- B propping (1mk)
- State two problems faced by the farmers who do not carry out practice B (1mk)
- Production of soiled/dirty fruits
- Plants attacked by diseases such blight
- Difficult to carry out management practices e.g. spraying
- Explain pruning practices of a banana stool (1mk)
- Pruning involves of extra suckers in the stool to leave 3-6 stems per stool. The suckers left in the stool should at different stages of development. Remove the suckers by cutting deeply at the root to stop them from growing again. Remove dry and diseased leaves using a sickle or a panga
- Identify the practices illustrated in diagram A and B
- The diagram below illustrates a soil profile
- Identify the layers labelled M,N and P
- M sub soil/horizon B (1mk)
- N Sub-stratum/weathered rock/horizon C (1mk)
- P Parent rock/horizon D (1mk)
- State one characteristic of the layer labelled L (1mk)
- dark in colour /has high humus content
- its well aerated and drained
- it contain active living micro organisms
- has most of the plant roots
- contain most of the plants nutrients
- Name the zone found between two adjoining layers(horizons) (1mk)
- transitional zone
- Identify the layers labelled M,N and P
- The diagram illustrates a certain property of different types of soils
- State the property investigated in the diagram (1mk)
- capillarity/capillary action
- In which of the three soils would water rise very fast at the beginning of the experiment and the rise stop within hours. (1mk)
- sandy soil. Sandy soil gets wet very fast but due to wide pore spaces the water does not rise very fast.
- From the diagram what conclusion would be made in regard to the three soil types and the property being investigated? (3mks)
- sandy soil has poor/lowest capillary action due to wide pore spaces
- clay soil has the greatest capillarity due to fine pore space hence the great rise in water level
- loamy soil. Have moderate to great capillarity due to their fine spore spaces and high quantity of organic matter which absorbs water very fast
- State the property investigated in the diagram (1mk)
- In a maize production enterprise carried out over a period of eight years, a farmer used one hectare of land each time and applied different quantities of DAP fertilizer.DAP fertilizer costs ksh.2500 per 50kgs bag and the harvested maize is sold at ksh.3000 per 90kg bag. The quantities of DAP fertilizer applied and maize harvested are as shown in thus table below.
DAP fertilizer input in 50kg bag
Maize yield in 90kg bags
Total revenue khs
Total cost kshs
Marginal revenue Kshs
Marginal cost kshs
0
15.0
45000
0
0
0
1
35.6
106800
2500
618700
2500
2
52.0
156000
5000
49200
2500
3
68.5
205500
7500
49500
2500
4
71.0
213000
10000
7500
2500
5
71.5
214500
12500
1500
2500
6
71.5
214500
15000
0
2500
7
68.5
205500
17500
-9000
2500
- complete the table by determining the values of total revenue, total cost, marginal revenue and marginal cost (2mks)
- From the information in your table, how can the farmer determine the level of production at which profit is maximum? (1mk)
- At the stage where marginal revenue is equal or almost equal to marginal cost MR=MC
- At the production level that yield maximum profit, what was the value of each of the following?
- DAP fertilizer input (1mk)
- 5bags/12500/=
- Marginal revenue (1mk)
- kshs. 1500
- DAP fertilizer input (1mk)
-
- Describe cultural methods of controlling soil erosion (8mks)
- Grass/fielder strips-it reduces speed of flowing water/filter soil
- Cover cropping-prevent surface flow/reduce impact of rain drops /prevent evaporation/volatilization/improve soil structure
- Contour farming-creates ridges of soil which hold up water/reduce speed of run off
- Mulching-reduces impact of rain drops/prevent evaporation/surface off/Improve soil structure
- Rotational grazing-allows grass to recover for soil and water conservation
- Crop rotation-maintain soil cover for protection against soil erosion/ improve s soil structure thus improving infiltration.
- Intercropping-provide adequate cover on the soil to prevent splash erosion /surface runoff/evaporation.
- Grass/vegetated waterways-slow the speed of water/trap eroded soils
- Afforestation/reforestation-act as water catchment/stabilizes soil/canopy intercepts raindrops/act as water catchment/windbreak.
- Use of manure/fertilizers-promotes vegetative growth which covers soil against evaporation and erosion/improve soil structure
- Correct spacing of crops-ensure adequate soil cover to prevent splash erosion/surface runoff/evaporation.
- Minimum tillage –to maintain soil structure/have seed seedbed with rough surface
- Describe harvesting of tea (7mks)
- leaves are plucked selectively for highest quality
- pluck top two leaves and a bud for fine plucking and top three leaves and a bud for coarse plucking
- use plucking stick to maintain the plucking table
- pluck at 5-7days interval at rainy season and 10-14days in dry period
- put plucked leaves in woven baskets to facilitate air circulation/prevent fermentation
- do not compress the leaves in the basket to prevent heating up/browning
- put plucked tea in cool and shaded place
- deliver to the factory in the same date
- Give five reasons for land registration (5mks)
- it can be used to secure credit facilities
- it minimizes land disputes
- security of tenure encourage long term investment projects/ensure s investment of land
- it enables occupant to lease or sell part of the land
- encourages soil conservation measures
- Describe cultural methods of controlling soil erosion (8mks)
-
- State five ways of improving labour productivity in the farm (5mks)
- Training
- Giving incentives/improving terms and condition of service
- Farm mechanization
- Labour supervision
- Proper remuneration/payment
- Assigning tasks according to skills
- State five roles if magnesium in crop production (5mks) important in chlorophyll formation
- promote formation of fats and oils e.g. soya beans
- aid in absorption and translocation of phosphorous
- enhances nitrogen fixation
- activates enzymes
- activates the synthesis and translocation of carbohydrates and proteins in plants
- Describe five reasons why early defoliation is discouraged in pasture utilization. (5mks)
- high moisture content
- low dry matter content
- low crude protein yield
- low digestible nutrients
- leads to gradual weakening of the stand
- Describe five harmful effects of crop pest (5mks)
- transmit crop diseases
- feed on whole or part of the plant
- some unearth planted seeds
- deprive the plant of food by sucking the sap
- lowers quality of flowers/fruits and berries
- eat growing points of the plant causing retarded growth
- feed on whole or part of the seeds and lower germination percentage
- lowers the yields expected
- cause wilting of plants by feeding on the roots
- reduce surface area for photosynthesis by feeding on the leaves
- chemical pest control measures affect the environment
- State five ways of improving labour productivity in the farm (5mks)
-
- Explain importance of irrigation farming (5mks)
- increases crop yields
- ensures steady supply of food throughout the year
- maximimizes utilization of resources e.g. in places where the soil is infertile but the water is inadequate
- important for reclamation of arid and semi arid lands
- provide regular, reliable and adequate supply of water in areas with little or no rain
- source of employment in areas in areas where it is used extensively.
- Promote production of crops for export market and therefore contribute to country’s revenue
- Allows production of paddy rice
- Allows growing of crops in greenhouses
- Facilitate fertigation in crop production
- State five characteristics of variable inputs (5mks)
- quantity required varies with the level of production in a given time
- are added to fixed inputs for production
- cost value depend on the quantity used
- they are allocated to specific enterprises
- their cost value is used to calculate the gross margin of the enterprises
- Describe the harvesting and marketing of bulb onions (5mks)
- harvested after 4-5months /when leaves start to dry
- bent the tops at the neck
- dig up the bulbs
- put the bulbs under shade to dry
- turn the bulbs to ensure uniform drying
- grade the bulbs according to size
- put bulbs in slatted boxes
- sell in net bags
- sell to suitable markets
- State five disadvantages of communal land tenure system (5mks)
- lacks incentives for land development
- low yields due to overstocking
- poor stock breeding programme
- difficult to control pest/parasites and diseases
- soil erosion is common
- lowers the carrying capacity of the land
- Explain importance of irrigation farming (5mks)
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Londiani Joint Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
