Questions
Instructions To The Candidates.
- This paper has two sections A and B.
- Answer ALL questions in section A. in section B answer question 6 and any other TWO questions.
SECTION A
Answer all questions in this section.
-
- Name two types of environment. (2 marks)
- List three main branches under physical geography. (3 marks)
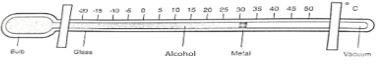
- Use the following weather instrument to answer the questions that follow.
- Name the above instrument. (1 mark)
- Describe how the instrument above works. (4 marks)
-
- Give two types of sedimentary rocks. (2 marks)
- State three characteristics of sedimentary rocks. (3 marks)
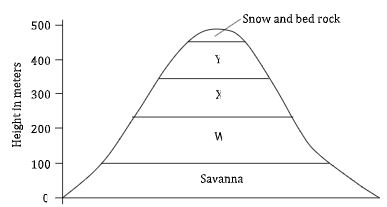
- The diagram below represents zones of natural vegetation on a mountain in Africa. Use it to answer questions A and B.
- Name the vegetation zones marked W, X and Y. (3 marks)
- Give two uses of Savannah vegetation. (2 marks)
-
- What is soil erosion? (2 marks)
- Name three types of soil erosion. (3 marks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other TWO questions in this section.
- Study the map of Nyeri 1:50,000 (sheet 120/4) provided and answer the following questions.
-
- Give the six figure grid reference of the forest Guard Post at grid square 5059. (2 marks)
- What is the magnetic variation of the map? (2 marks)
- What is the general direction of the flow of river Chanya? (1 mark)
-
- Using a vertical scale of 1cm to represents 50m; draw a cross section along Northing 64 from Easting 68 to Easting 78. On it mark and label the following.
- All weather road
- A hill.
- River. (7 marks)
- Calculate the vertical exaggeration of the cross section. (2 marks)
- Determine the intervisibility of the cross section. (1 mark)
- Using a vertical scale of 1cm to represents 50m; draw a cross section along Northing 64 from Easting 68 to Easting 78. On it mark and label the following.
- Citing evidence from the map, identify three social services offered in the area covered by the map. (6 marks)
- Explain two ways relief has influenced the distribution of settlement in the area covered by the map. (4 marks)
-
-
-
- Define the term volcanicity. (2 marks)
- Name two active volcanoes in Kenya. (2 marks)
-
- Differentiate between solfatara and moffete. (2 marks)
- Identify two areas in Kenya where geysers are found. (2 marks)
-
- A part from batholiths, name three features resulting from intrusive vulcanicity. (3 marks)
- With the aid of a diagram describe how a batholith is formed. (6 marks)
- Explain four negative effects of vulcanicity. (8 marks)
-
-
-
- What is weathering? (2 marks)
- Give three factors influencing the rate of weathering (3 marks)
- Name three processes of slow mass wasting. (3 marks)
-
- A part from block disintegration, list four other physical weathering processes. (4 marks)
- Describe how block disintegration occurs. (5 marks)
- Explain four significance of weathering to human activities. (8 marks)
-
-
-
- Define the term ocean (2 marks)
- Name three types of coasts (3 marks)
-
- List three features that result from wave erosion (3 marks)
- Describe the longshore drift. (3 marks)
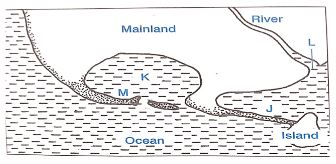
- The diagram below shows coastal features resulting from wave deposition
- Name the features marked J, K and M. (3 marks)
- Describe how the feature marked M is formed (5 marks)
- State three conditions that favor for the growth of coral polyps. (3 marks)
- State three significances of coastal features to human activities. (3 marks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between an ice sheet and an ice berg. (2 marks)
- Name three types of glacial moraines. (3 marks)
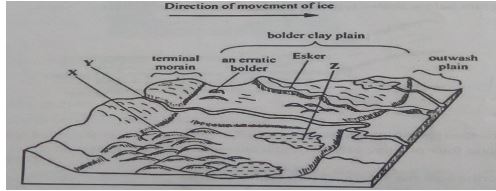
- The diagram below shows features resulting from glaciation in a low land area.
- Name the features marked X, Y and Z. (3 marks)
- Describe how a terminal moraine is formed. (4 marks)
- Your class carried out a field study on glacial erosional features in a glacial lowland area.
- Give two methods of collecting data you could use. (2 marks)
- State three importance of dividing into groups. (3 marks)
- Explain four economic significance of glaciation in lowland areas. (8 marks)
-
Marking Scheme
-
- Name two types of environment. (2 marks)
- Human environment
- Physical environment
- List three main branches under physical geography. (3 marks)
- Biogeography
- Climatology
- Geomorphology
- Name two types of environment. (2 marks)
- Use the following weather instrument to answer the questions that follow.
- Name the above instrument. (1 mark)
- Minimum thermometer
- Describe how the instrument above works. (4 marks)
- When temperature falls, the alcohol in the glass tube contracts.
- Its meniscus pulls the metal index towards the bulb.
- This goes on until the lowest temperature is reached.
- When the temperature rises, alcohol expands and moves up the glass tube but the metal index remains in the same position when it was pulled to.
- Minimum temperature is obtained by reading the scale at the end of the metal index.
- The reading is recorded on a table.
- The thermometer is then reset.
- Name the above instrument. (1 mark)
-
- Give two types of sedimentary rocks. (2 marks)
- Mechanically formed
- Organically formed
- Chemically formed
- State three characteristics of sedimentary rocks. (3 marks)
- They are non-crystalline
- They are stratified.
- The have bedding planes.
- Some have fossil fuels.
- Give two types of sedimentary rocks. (2 marks)
- The diagram below represents zones of natural vegetation on a mountain in Africa. Use it to answer questions A and B.
- Name the vegetation zones marked W, X and Y. (3 marks)
- W - Rainforest
- X - Bamboo forest
- Y - Heath and moorland
- Give two uses of Savannah vegetation. (2 marks)
- Savanna grassland is used as pasture in ranches
- Savanna grasses are used in thatching the houses.
- Some are used for medicinal value
- Name the vegetation zones marked W, X and Y. (3 marks)
-
- What is soil erosion? (2 marks
- This is a process whereby wind/water removes soil particles causing the soil to deteriorate.
- Name three types of soil erosion. (3 marks)
- Splash erosion
- Rill erosion
- Sheet erosion
- Gully erosion
- What is soil erosion? (2 marks
-
-
- Give the six figure grid reference of the forest Guard Post at grid square 5059. (2 marks)
- What is the magnetic variation of the map? (2 marks)
- 1° 31’
- What is the general direction of the flow of river Chanya? (1 mark)
- Eastwards
-
- Using a vertical scale of 1cm to represents 50m; draw a cross section along Northing 64 from Easting 68 to Easting 78. On it mark and label the following.
- All weather road
- A hill.
- River. (7 marks)
- Calculate the vertical exaggeration of the cross section. (2 marks)
- V.E = V.SH.S
= 15000 ÷ 150000
= 15000 × 500001
= 10
- V.E = V.SH.S
- Determine the intervisibility of the cross section. (1 mark)
- The starting point and ending point are not intervisible
- Using a vertical scale of 1cm to represents 50m; draw a cross section along Northing 64 from Easting 68 to Easting 78. On it mark and label the following.
- Citing evidence from the map, identify three social services offered in the area covered by the map. (6 marks)
Social service Evidence - Educational services - Schools - Health services - Hospitals/dispensaries - Administration services - Chiefs offices/PC/DC - Rehabilitation services - Prison - Security - Police station - Water supply - Pump house - Recreational services - Stadium/golf course - Housing/residential - Built-up areas/huts - Explain two ways relief has influenced the distribution of settlement in the area covered by the map. (4 marks)
- There are many settlements in the South eastern part because the land is gently sloping.
- There are few settlements in Kirurumi because the slope is very steep.
- There are many settlements in the area due to the high altitude shown by contour heights of above 1700m which moderates the temperature of the area.
- There are few settlements at Gathaini because the land is rugged.
-
-
-
- Define the term volcanicity. (2 marks)
- Volcanicity is a process by which solid, liquid and gaseous materials are forced out of the interior of the earth.
- Name two active volcanoes in Kenya. (2 marks)
- teleki
- `likaiyu.
- Define the term volcanicity. (2 marks)
-
- Differentiate between solfatara and moffete. (2 marks)
- Solfatara is a hole on the earth emitting sulphurous compounds while moffette is a hole on the earth emitting carbon (iv) oxide.
- Identify two areas in Kenya where geysers are found. (2 marks)
- Around lake Bogoria.
- Lake magadi.
- Lake turkana.
- Differentiate between solfatara and moffete. (2 marks)
-
- A part from batholiths, name three features resulting from intrusive vulcanicity. (3 marks)
- Sill
- Dyke
- Lacolith
- Lopolith
- Phacolith.
- With the aid of a diagram describe how a batholith is formed. (6 marks)
- It consist of a plutonic mass of magma which intruded the country rocks.
- The magma gets out of the interior of the earth is hot so it metamorphose the country rocks on its path.
- A part from batholiths, name three features resulting from intrusive vulcanicity. (3 marks)
- Explain four negative effects of vulcanicity. (8 marks)
- Volcanic eruption can results in the loss of lives.
- Volcanic eruption can lead to destruction of properties.
- Weathered volcanic material like ashes and granite can results in infertile soils.
- Some features resulting from volcanicity create barriers making construction of communication lines difficult eg in Yatta plateau.
- Rugged nature of some volcanic landscape often discourages economic activities.
- Volcanic mountain ranges create rain shadow effect on the lee ward side causing aridity.
-
-
-
- What is weathering? (2 marks)
- This is the breakdown and decomposition of rocks at or near the earth’s surface due to physical, chemical and biological processes.
- Give three factors influencing the rate of weathering (3 marks)
- Nature of rocks
- Topography/gradient of slope
- Temperature variations
- Rainfall amounts
- Living organisms
- Human activities
- Time duration
- What is weathering? (2 marks)
- Name three processes of slow mass wasting. (3 marks)
- Soil creep
- Talus/scree creep
- Solifluction
- Rock creep
-
- A part from block disintegration, list four other physical weathering processes. (4 marks)
- Granular disintegration
- Crystal growth/crystallization
- Slaking/Rain water action
- Frost shattering/frost action/free thaw action
- Unloading/pressure release
- Describe how block disintegration occurs. (5 marks)
- Occurs in hot/arid areas having a wide/high decimal temperature ranges.
- Occurs in rocks having single/homogenous minerals.
- During the day, high temperature heat the rocks reaching the expansion and during the night, low temperature causes rocks to cool and contract.
- Repeated expansion and contraction lead to development of stress in the rock making the rock cracks to widen.
- Eventually the rock breaks along the cracks into small angular blocks this is called block disintegration/separation.
- A part from block disintegration, list four other physical weathering processes. (4 marks)
- Explain four significance of weathering to human activities. (8 marks)
- Weathering lead to formation of deep and fertile soils supporting agricultural production.
- Weathering may expose valuable minerals in some rocks which are exploited/mined.
- Weathering process may make some rocks to have unique scenery attracting tourists.
-
-
-
- Define the term ocean (2 marks)
- An ocean is an extensive mass of saline water occupying a large basin between continents
- Name three types of coasts (3 marks)
- Emerged coast
- Submerged coast
- Coral coast
- Define the term ocean (2 marks)
-
- List three features that result from wave erosion (3 marks)
- Cliff
- Blow-holes
- Geos
- Wave-cut platform
- Caves
- Bays
- Headlands
- Arches
- Stacks
- Stumps
- Describe the longshore drift. (3 marks)
- The waves break obliquely to the shore, the swash moves the material obliquely up the shore.
- The backwash rushes them back at right angles down the shore.
- The zigzag movement of material along the shore by the waves is referred to as long shore drift.
- List three features that result from wave erosion (3 marks)
- The diagram below shows coastal features resulting from wave deposition
- Name the features marked J, K and M. (3 marks)
- J - Tombolo
- K - Bay
- M - Spit
- Describe how the feature marked M is formed (5 marks)
- It is formed at a point where the coastline abruptly changes its direction towards the land.
- The movement of material by long shore drift is halted.
- The materials are then deposited in the water.
- This continues until they bulge out with the accumulation growing towards the sea.
- The end of the hook is usually curved into a hook by minor waves which swing around the end of the spit.
- These waves carry some sand to the inner end of the spit creating a hook-like feature.
- This leads to formation of a low-lying narrow ridge of sand, shingles or pebbles with one end attached to the coast and the other end projecting into the sea.
- State three conditions that favor for the growth of coral polyps. (3 marks)
- Optimum water temperature range should be between 25 ̊c and 29 ̊c.
- The polyps must be submerged but they may be exposed during low tide but only for a short period of time.
- The waters must be shallow. Most polyps thrive within a depth of less than 10m but some species can grow to depth of up to 60m.
- The water must be clear and salty.
- Name the features marked J, K and M. (3 marks)
- State three significances of coastal features to human activities. (3 marks)
- The sheltered waters of the fiords provide favorable breeding grounds for fish, the fjords of British Columbia in Canada and those of Norway in North- west Europe. The shallow waters of the continental shelf encourage the growth of the fish food called planktons, like in the south west coast of Africa and East China Sea thus encouraging fishing.
- A variety of coastal features like fjords, sand beaches, cliffs , stacks and caves , form tourist attractions which encourage tourism
- Raised coral reefs are a source of coral limestone which is used for manufacturing of cement thus encouraging construction and industry e.g. cement manufacturing at Bamburi in Mombasa.
- Coastal features like lagoons, fjords, coral reefs, mudflats, and continental shelf provide suitable grounds for marine life breeding, especially in shallow sea-inlet. (tourism)They also support the growth of mangrove forests which provide strong building poles leading to building and construction.
- Some submerged coasts favor the development of deep, well sheltered harbours which are key for water transport
-
-
-
- Differentiate between an ice sheet and an ice berg. (2 marks)
- An ice sheet is a massive glacier ice cover over a terrain while as ice berg is a broken glacial mass that floats on water/ the ocean
- Ice sheets are usually on land ans when thety extend over water bodies, they are nown as ice shelves while ice bergs are found in water bodies, usually the ocean
- Name three types of glacial moraines. (3 marks)
- lateral morraines
- teminal morraines
- medial morraines
- superglacial morraines
- Differentiate between an ice sheet and an ice berg. (2 marks)
- The diagram below shows features resulting from glaciation in a low land area.
- Name the features marked X, Y and Z. (3 marks)
- X - Drumlines
- Y - River/meet water
- Z - Kettle lake/lake
- Describe how a terminal moraine is formed. (4 marks)
- Formed in a lowland glaciated area when moving ice carrying solid materials stagnates and the ice meet at the snout.
- The meeting ice releases its load such that gradually the load piles up into a ridge. Over time, the ridge forms block of solid materials called terminal moraine.
- Name the features marked X, Y and Z. (3 marks)
- Your class carried out a field study on glacial erosional features in a glacial lowland area.
- Give two methods of collecting data you could use. (2 marks) - Observation method
- Taking photographs
- Taking videos/videoing
- State three importance of dividing into groups. (3 marks)
- To ensure there is organization
- To ensure all relevant areas are covered
- For proper time management
- To remain within the slope of study
- Give two methods of collecting data you could use. (2 marks) - Observation method
- Explain four economic significance of glaciation in lowland areas. (8 marks)
- Glacial till provide fertile soils suitable for arable farming.
- Ice sheet may cover the landscape exposing valuable minerals for easy mining .
- Outwash plain may contain gravel and sand materials for building and construction.
- Glacial lake in lowlands may form ideal fishing grounds/transportation routes.
- Glaciated features such as ……, Eskers are unique sceneries for tourism.
- Glaciated lowlands are generally gentle ideal for establishment for human settlements.
-
Download Geography Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Mokasa II Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students