Instructions to candidates
- Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided.
- Candidates MUST answer all questions in English.
- KNEC mathematical tables and silent non-programmable electronic calculators may be used.
QUESTIONS
- The relationship between the pressure and volume of a fixed mass of gas was studied at 25ºC. The data was recorded as shown in the table below.
Volume (m3)
1
2
4
6
Pressure (Pa) x 105
12
6
3
2
Product of volume and pressure
- Complete the table by calculating the product of the volume and pressure. (2 marks)
- Using the data, state the law governing the relationship between volume and pressure of a fixed mass of a gas. (1 mark)
- The volume of nitrogen gas at 27ºC and a pressure of 1 x 105 pa is 8m3. Calculate its volume at 128ºC and a pressure of 3.2 x 105pa (2 marks)
- The set up below was used to study the properties of dry ice. Study it and answer the questions that follow:
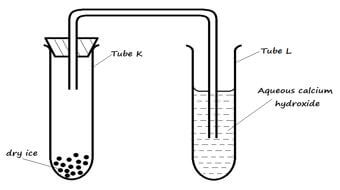
- State the observation(s) that was made in tubes K and L after some time. (2 marks)
- Tube K
- Tube L
- Name two processes that took place in tube K. (2 marks)
- State the observation(s) that was made in tubes K and L after some time. (2 marks)
- The relationship between the pressure and volume of a fixed mass of gas was studied at 25ºC. The data was recorded as shown in the table below.
-
- Give the names of the following compounds.
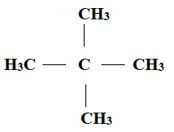
- CH3C Ξ C CH2 CH3
- Describe a chemical test that can be carried out to distinguish between the compounds: (2 marks)

- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow
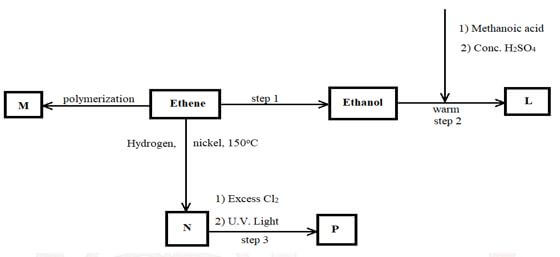
- Name the compounds (2 marks)
- L:
- N:
- Draw the structural formula of compound M showing three repeating units. (1 mark)
- Give the reagent and condition used in step 1 (2 marks)
- State the type of reaction that takes place in: (2 marks)
- Step 2:
- Step 3:
- The molecular formular of compound P is C2H2Cl4. Draw the two structural formulae of compound P (2 marks)
- Name the compounds (2 marks)
- Give the names of the following compounds.
-
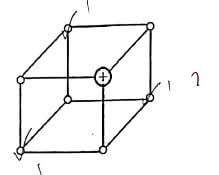
- The diagram below represents part of the structure of a sodium chloride crystal. The position of one of the sodium ions in the crystal is shown as +.
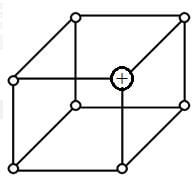
- On the diagram, mark the positions of the other three sodium ions (3 marks)
- The melting and boiling points of sodium chloride are 801ºC and 1413ºC respectively. Explain why sodium chloride does not conduct electricity at 25oC but does at temperatures between 801ºC and 1413ºC. (2 marks)
- Give a reason why ammonia gas is highly soluble in water (1 mark)
- The structure of an ammonium ion is shown below.
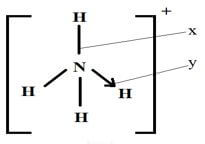
Name the types of bonds represented by the letters X and Y (1 mark)
X
Y - Carbon exists in different crystalline forms. Some of these forms were recently discovered in soot and are called fullerenes.
- What name is given to different crystalline forms of the same elements (1 mark)
- Fullerenes dissolve in methylbenzene while other forms of carbon do not. Given that soot is a mixture of fullerenes and other solid forms of carbon, describe how crystals of fullerenes can be obtained from soot. (3 marks)
- The relative molecular mass of one of the fullerenes is 720. What is the Molecular formula of this fullerene? (C = 12.0) (1 mark)
- The diagram below represents part of the structure of a sodium chloride crystal. The position of one of the sodium ions in the crystal is shown as +.
- The set up below was used by a student to investigate the product formed when aqueous Copper (II) chloride was electrolysed using platinum electrodes.
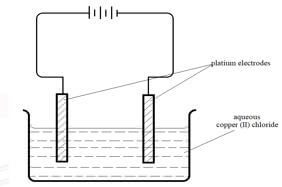
-
- Write the equation for the reaction taking place at the cathode. (1 mark)
- Name and describe a chemical test for the product initially formed at the anode when a highly concentrated solution of Copper (II) chloride is electrolysed. (3 marks)
- How would the mass of the anode change if the platinum anode was replaced with copper metal? Explain. (2 marks)
- 0.6g of metal X were deposited when a current of 0.45A was passed through an electrolyte for 1 hour and 12 minutes. Determine the charge on the ion of metal X. (RAM of X = 59 1 Faraday = 96500 C) (3 marks)
- The electrode potentials for cadmium and zinc are given below
Cd2+(aq) + 2e- ⇌ Cd(s) E0 +-0.40v
Zn2+(aq) + 2e- ⇌ Zn(s) E0 = -0.76v
Explain why it is not advisable to store a solution of cadmium nitrate in a container made of zinc. (2 marks)
-
-
-
- what is meant by the term Enthalpy of formation? (1 mark)
- The enthalpies of Carbon, methane and hydrogen are indicated below: -
C (s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) ; ∆H = -393KJmol-1
H2 (g) + 1/2 O2 (g) → H2O (g) ∆H =-286KJmol-1
Enthalpy of combustion of CH4 = -890KJmol-1- Draw an energy cycle diagram that links the enthalpy of formation of methane to enthalpies of combustion of carbon, hydrogen, and methane. (2 marks)
- Determine the enthalpy of formation of methane. (2 marks)
- An experiment was carried out where different volumes of dilute nitric (V) acid and aqueous potassium hydroxide both at 25ºC were mixed and stirred with a thermometer. The highest temperature reached by each mixture was recorded in the table below.
Volume of nitric acid (cm3)
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
Volume of Potassium hydroxide (cm3)
45
40
35
30
25
20
15
10
5
Highest temperature of mixture (oC)
27.2
29.4
31.6
33.8
33.6
31.8
30.0
28.4
26.6
- On the grid provided, plot a graph of highest temperature (vertical axis) against volume of nitric (V) acid. (3 marks)
- Using your graph, determine the:
- Highest temperature reached (1 mark)
- Volume of acid and base reacting when highest temperature is reached. (1 mark)
- Calculate the amount of heat liberated during the neutralization process. (Specific heat capacity is 4.2Jg-1K-1 and density of solution is 1.0gcm-3). (2 marks)
- On the grid provided, plot a graph of highest temperature (vertical axis) against volume of nitric (V) acid. (3 marks)
- The molar enthalpy of neutralisation between nitric (V) acid and ammonia solution was found to be -52.2KJmol-1, while that of nitric (V) acid and potassium hydroxide was – 57.1 KJmol-1. Explain the difference in these values. (2 marks)
-
- The scheme below shows the preparation of a certain salt. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
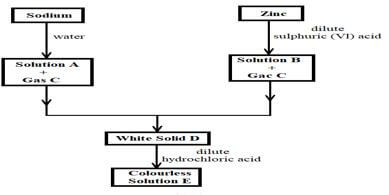
- Identify the following substances: (2 marks)
Solution A
Solution B
Gas C:
Solid D -
- Write an ionic equation for the formation of solid D. (1 mark)
- Write an equation for the formation of colourless solution E. (1 mark)
-
- Describe how the identity of gas C can be confirmed (2 marks)
- Name the catalyst that can be used in the reaction between zinc and dilute sulphuric (VI) acid. (1 mark)
- Explain any two observations made when sodium reacts with water. (2 marks)
- Describe how you can obtain from solution E:
- A hydrated salt (1 mark)
- Anhydrous salt (1 mark)
- Identify the following substances: (2 marks)
- A student set up the following arrangement to prepare and react gases V and W. Use it to answer the questions that follow. (S =32, H =1, Cl =35.5).
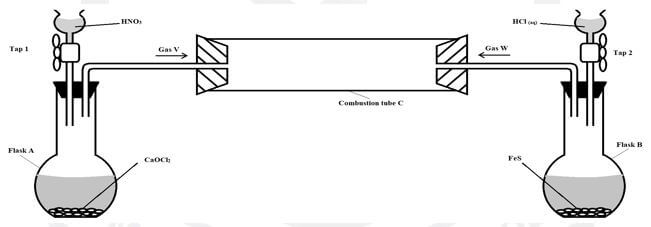
Taps 1 and 2 were opened at the same time.- Write an equation for the reaction that took place in flask A. (1 mark)
- State and explain the observations that were made in: (2 marks)
- Flask B
- Combustion tube (2 marks)
- Mark on the diagram the approximate position where reaction occurred in the combustion tube. Explain your answer. (2 marks)
- State one possible objective of the experiment apart from testing whether gas W reacts with gas V. (1 mark)
- Giving a reason, state one precaution that should be taken when carrying out this experiment. (2 marks)
MARKING SCHEME
-
- The relationship between the pressure and volume of a fixed mass of gas was studied at 25ºC. The data was recorded as shown in the table below.
Volume (m3)
1
2
4
6
Pressure (Pa) x 105
12
6
3
2
Product of volume and pressure
12 12 12 12 x 106 x 106 x 106 x 106 - Complete the table by calculating the product of the volume and pressure. (2 marks)
- Using the data, state the law governing the relationship between volume and pressure of a fixed mass of a gas. (1 mark)
volume of a fixed mass of a gasis inversely proportional to its pressurre at sonstant temperature
- The volume of nitrogen gas at 27ºC and a pressure of 1 x 105 pa is 8m3. Calculate its volume at 128ºC and a pressure of 3.2 x 105pa (2 marks)
p1v1 = p2v2
T1 T2
1 x 105 x 8 = 3.2 x 105 x 2
300 401
v2 = 3.342m3 -
-
- tube k sublimes
tube l white precipitatae / solid/ suspension
- tube k sublimes
- sublimation and difussion
-
- The relationship between the pressure and volume of a fixed mass of gas was studied at 25ºC. The data was recorded as shown in the table below.
-
-
- 2,2- dimethylpropene
- pent-3-ene
- ignite each 2,2 dimethypropane burns with non-sooty flame
white pent-2-yne burns with sooty flame
pass each through H+/KMnO4.1 does not decolorise
H+/KMnO4 while 2 decolorises H+/KMnO4
use bromine water in the dark
-
-
-
- L ethymethanacate
N ethane 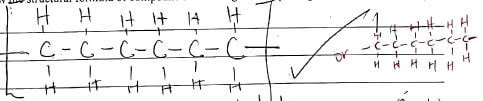
- Hydrolysis
reagent - water
condition - concentrated H2SO4
Hydration
Reagent - steam
Condition - H3PO4
Temp of 300º / heat 2 for at least
pressure (60 - 70) - step 2: esterification
step 3; substitution 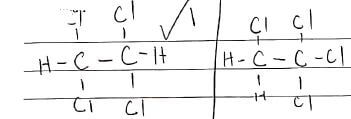
- L ethymethanacate
-
-
-
- At 25ºc the ions are at fixed position while above 801º the ions are mobile
- it is polar due to hydrogen bondity
- x - covalent
y - coordinate / dative -
- allotropes
- add methyl/benzene and stir to dissolve fullerones - filter to obtain a solution of fullerene in methy/benzene
leave the solution in the soln for methylbenzene to evaporate(rej: evaporate the sln) - n = 720 = 60
12
-
-
-
- Cu2+(aq) + 2e- → Cu(s)
- chlorine . lower dump/wet blue litmus paper into the gas. The paper changes to red then white bleaches
rej colourise - decreases. Cu anode is oxidised (dissolves)
or (Cu(s) -> Cu2+(s) + 2e)
- charge = R.A.M x Q
IF x mass deposited
59 x (0.45 x 72 x 60)
96500 x 0.6
=2 +
rej ±2 - Eθ = Ered - Eox
= -0.40 - - 0.76 = + 0.36
reaction is feasible
-
-
-
- enthalpy charge that occurs when one mole of a compound is formed from its constituent elements. (heat produced/heat evolved)
-
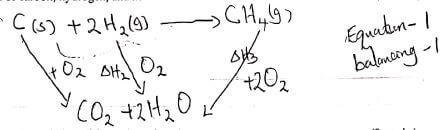
- ΔHf = ΔH - ΔH3
but ΔH2 = -393 + -(2 x 286) = -965
= -965 + 890 = -75 KJ/mol
-
-
- showing 1/2 reading 1/2
- showing 1/2 reading 1/2
volume of acid 1/2 alkali 1/2
- ΔH = mcΔT
= 50 x 4.2 x ΔT
= correct ans
- ammonia solution dissociates / ionizes partially hence some heat is used to ionize it completely while KOH is a strong ............ therefore dissociates fully
-
-
- solution A - sodium hydroxide / NaOH
solution B - zinc sulphatae / ZnSO4
Gas C - hydrogen / H2
Solid D zinc hydroxide / Zn(OH)2 -
- Zn2+(aq) + 2OH-(aq) -> Zn(OH)2(s)
- Zn(OH)2(s) + 2HCl(aq) -> ZnCl2(aq) + 2H2O(l)
-
- lower a burning wooden splint "pop" sound produced // or the splint extinguishes/goes off/put off with a pop sound
- copper (II) sulphate crystals
- darts on the surface of water since it is less dense than water /dalting propelled by H2(g) produced
hissing/fizzing sound - production of the gas
melts into silvery ball - reaction is exothermic -
- heat the solution to saturation , allow to cool and form crystals
- heat the solution to dryness
- solution A - sodium hydroxide / NaOH
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Maranda Mock Examinations 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
