Instructions to candidates:
- You are required to spend the first 15 minutes of the 1¾ hours allowed for this paper reading the whole paper carefully.
QUESTIONS
- You are provided with Specimen K .Carefully cut a transverse section through specimen K using a scalpel provided.
-
- By observing one of the two halves of specimen K, Give two reasons to prove that specimen K has axile placentation (2marks)
- Squeeze some juice from specimen K into 100ml beaker provided and label it as juice K. Using a portion of juice K, carry out the food test using the reagents provided and complete the table below. (NB preserve the remaining portion of juice K for use in question 2 ) (8marks)
Food substance
Procedure
Observation
Conclusion
- Name the deficiency disease that results from lack of the food substance present in juice K. (1mark)
- Highlight two symptoms of the disease named in (a) (iii) above (2marks)
- Put 2cm3 of liquid labeled C into a test tube. Draw some of the juice from specimen K into a dropper. Add 4 drops of the juice into the test tube with solution C and shake.
- State your observation. (1mark)
- State the part of the human body where the process demonstrated above occurs and the enzyme that carries out the process.
Part of body... (1mark)
Enzyme... (1mark) - Which gland produces the enzyme stated in (a) (ii) above? (1mark)
-
-
- Take a small amount of substance B provided and add to it 2cm3 of sodium hydrogen carbonate solution.
- State your observations (1mark)
- Which process in the body is illustrated above? (1mark)
- State the part of the body where the above process takes place (1mark)
- State two functions of substance B in the body (2marks)
- Name two diseases of the circulatory system caused by excess cholesterol in food. (2marks)
- Study the photographs below depicting plants growing in different habitats. Use them to answer the questions that follow.

- Identify the habitats in which they are found (2marks)
Y
Z - State the significance of the following structures found in the specimens shown above. (2marks)
R
S
- Identify the habitats in which they are found (2marks)
- Take a small amount of substance B provided and add to it 2cm3 of sodium hydrogen carbonate solution.
-
- Below are photographs of Venus flytrap (an insectivorous plant). Study them and answer the questions that follow.

- Name one major nutrient that is deficient in the soil where the above plant grows. (1mark)
- Name the type of response shown by photograph C (1mark)
- Describe how the above plant traps the insect (4marks)
- The photographs below are of the same mammalian vertebra showing two views of the same bone. Examine them carefully.
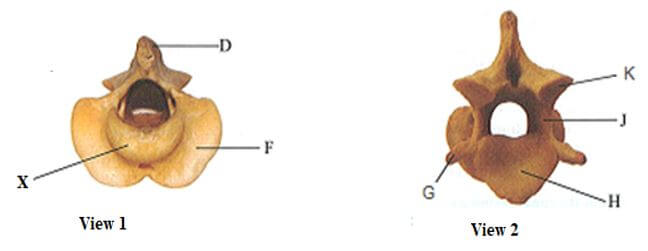
- Identify the vertebra.. (1mark)
- Name the region from which the vertebra is obtained. (1mark)
- Name the part marked X (1mark)
- State the function of part X (1mark)
- State the functional difference between a tendon and a ligament (1mark)
- Name the bone that articulate with this vertebra at the distal end (1mark)
- Below are photographs of Venus flytrap (an insectivorous plant). Study them and answer the questions that follow.
MARKING SCHEME
-
-
-
- Edges of the carpels fuse together to form a central placenta;
- Ovary wall divides into multiple loculi/chambers;
-
Food substance
procedure
observation
conclusion
Starch;
-To a little amount of juice K in a test tube add two drops of iodine solution;
-Brown color of iodine solution remains/persist;
Starch absent;
Vitamin C;
-To a little amount of DCPIP in a test tube, add juice K drop wise as you shake;
-DCPIP decolorizes;
Vitamin C present;
- scurvy;
-
- bleeding gums;
- poor healing of wounds
- anaemia
- swelling of skin
- reduced resistance to infections
-
-
- liquid C forms a solid particles /liquid C curdles;
- body part-stomach
Enzyme-rennin rej.renin - gastric gland
-
-
-
- broken down into small droplets;
- emulsification;
- duodenum;
- oxidized to release energy;
shock absobers on vital organs
storage form of food;
source of metabolic water - artheriosclerosis;
thrombosis;
-
- Y-aquatic/fresh water
Z- teresterial - R-minimizes rate of water loss / defense against browsers;
S-store air for buoyancy;
- Y-aquatic/fresh water
-
-
-
- nitrogen
- thigmo tropism /haptonasty;
- when the sensitive hairs on the leaves are touched (by the landing insect);the midrib loses turgidity rapidly; this makes the trap to spring inwards; hence closing the leaf; with the spines interlocking.
-
- axis;
- cervical/neck;
- odontoid process;
- articulate with the atlas vertebra to permits nodding of the head;
- tendon-attaches bone to muscles
ligament- attaches bone to bone - atlas vertebra
-
CONFIDENTIAL
Each candidate should be provided with the following:
- Specimen K (Orange fruit)
- About 3cm3 of substance B (olive oil)
- About 3cm3 of liquid C (fresh cow milk)
- About 2cm3 of 0.01% DCPIP (supplied with a dropper)
- About 2cm3 of Iodine solution
- About 2cm3 NaHC03 solution (supplied with a dropper)
- 6 test tubes in a test tube rack
- Distilled water in a wash bottle
- Scalpel
- Two 10ml measuring cylinder
- One 100ml beaker
- 2 Labels
- Two droppers
Download Biology Paper 3 Questions, Answers and Confidential - Maranda Mock Examinations 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
