Instructions to candidates
- This paper has two sections: A and B
- Answer all the questions in section A
- Answer question 6 (compulsory) and any other two questions from section B
QUESTIONS
SECTION A (25 Marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided below each question
-
- Define the term Geomorphology (2 marks)
- Other than being a career subject, state three reasons why it is important for students in secondary school to study geography (3 marks)
- The diagram below shows an instrument used in measuring one of the weather elements Study it and answer the questions that follow
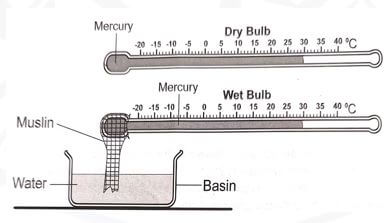
- Identify;
- the instrument shown above (1 mark)
- the weather element measured using the instrument identified in (a) (i) (1 mark)
- State three importance of the weather element identified in (a) (ii) in the atmosphere (3 marks)
- Identify;
-
- Name the temperate grassland found in:
- New Zealand: (1 mark)
- Central Asia: (1 mark)
- State three uses of vegetation (3 marks)
- Name the temperate grassland found in:
-
- Name two output processes in the hydrological cycle (2 marks)
- State three negative influences that rivers have on human environment (3 marks)
-
- Define the term soil (2 marks)
- State three causes of chemical degeneration of soils (3 marks)
SECTION B (75 Marks)
Answer question 6 (compulsory) and any other two questions in this section in the spaces provided after question 10
- Study the map of Nyeri 1:50,000 (Sheet 120/4) provided and answer the questions that follow
-
- Give the longitudinal extent of the area covered by the map (2 marks)
- Name two districts in the area covered by the map (2 marks)
-
- Calculate the area of Nyeri forest Give your answer in kilometres (2 marks)
- What is the magnetic variation of the area covered by the map (1 mark)
- Describe the drainage of the area covered by the map (6 marks)
-
- Using a scale of 1 cm represents 50 metres, draw a cross-section along northing 64 between easting 68 and 74 (4 marks)
- On the cross-section, mark and label the following;
- Hill (1 mark)
- All weather road loose surface (1 mark)
- River (1 mark)
- Calculate the vertical exaggeration of the cross-section (2 marks)
- Citing evidence from the map, identify three social functions of the area covered by the map (3 marks)
-
- Below is a world map showing the distribution of fold mountains Use it to answer question (a)
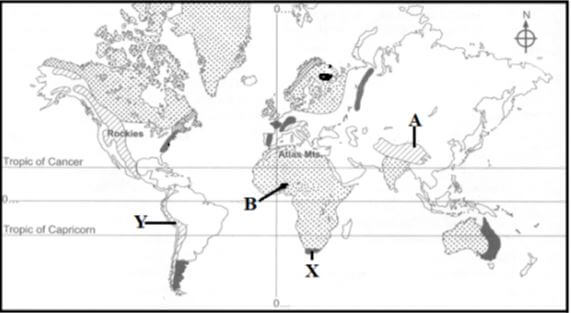
-
- Name the fold mountains marked A and B (2 marks)
- Give the orogenies during which the fold mountains marked X and Y were formed (2 marks)
- With the aid of well labelled diagrams, describe the formation of anticlinorium and synclinorium complex of folds (6 marks)
-
- Give three features resulting from folding other than fold mountains (3 marks)
- Describe how fold mountains were formed according to the proponents of contraction theory (3 marks)
- Explain two positive significance of folding to human activities (4 marks)
- Your class intends to carry out a field study on folding;
- State three ways in which you would prepare for the field study (3 marks)
- Give two methods of data collection you would use during the field study (2 marks)
-
-
-
- Differentiate between a mineral and a rock (2 marks)
- Describe the following characteristics of minerals:
- Tenacity (2 marks)
- Streak (2 marks)
- Describe the process of formation of the following rocks:
- Chemically formed sedimentary rocks (5 marks)
- Volcanic ejecta (4 marks)
- State four characteristics of metamorphic rocks (4 marks)
- Explain three significance of rocks to human activities in Kenya (6 marks)
-
-
-
- What is a piedmont glacier? (2 marks)
- Give three ways through which ice moves (3 marks)
-
- Apart from roche mountonnee, name three other features formed by glacial erosion in lowlands (3 marks)
- Using a well labelled diagram, describe the formation of a roche mountonnee (6 marks)
- Your class is planning to carry out a field study on features formed by glacial erosion in highlands;
- State two objectives you would have for the study (2 marks)
- Give three qualities of a good questionnaire you would prepare for collecting data (3 marks)
- Explain three positive significance of glaciation in lowland areas (6 marks)
-
-
-
- Define the term denudation (2 marks)
- Explain how the following factors influence weathering:
- Mineral composition of the rocks (2 marks)
- Colour of the rocks (2 marks)
- Structure of the rocks (2 marks)
- The diagram below shows a process of mechanical weathering:
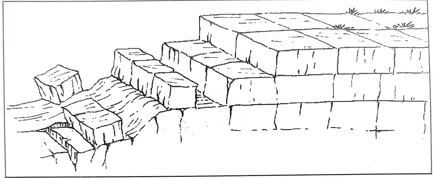
- Identify the process (1 mark)
- Describe how the process occurs (5marks)
- State five evidences of soil creep (5marks)
- Explain three significance of mass wasting on the physical and human environments (6marks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Define the term Geomorphology.
- This is the science that studies the earth’s landforms, which result from land forming processes such us vulcanicity, faulting, erosion, mass wasting, weathering, folding, deposition.
- Other than being a career subject, state three reasons why it is important for students in secondary school to study geography.
- Acquisition of skills such as reading, observation, interpretation of maps and calculations.
- Acquire awareness on the management and conservation of the environment and the need to use resources sustainably.
- Geography enhances national unity.
- Geography enhances international awareness, interactions, and co-operation and teaches interdependence among people.
- It also helps us to manage time properly through the study of fieldwork by drawing a working schedule and adhering to it.
- Helps learners acquire positive attitudes and values which enable them to become useful members of the society thus a tool for better citizenship.
- Learn and understand about location, features and characteristics of both the physical and human environments on earth.
- It provides valuable information that can be used in various human activities e.g. space exploration and aviation since it focuses on the physical study of the earth.
- Define the term Geomorphology.
- The diagram below shows an instrument used in measuring one of the weather elements. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
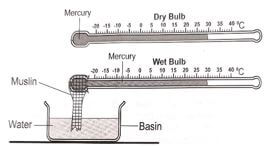
- Identify;
- the instrument shown above. Psychrometer/ Thermohygrometer/ Simple hygrometer
- the weather element measured using the instrument identified in (a) (i).
- Relative humidity
- State three importance of the weather element identified in (a) (ii) in the atmosphere.
- Humidity determines the amount of precipitation that a given area is likely to receive in a given day.
- It absorbs radiation therefore regulating the heat loss from the earth.
- It determines the amount of energy stored in the atmosphere for the development of storms.
- Identify;
-
- Name the temperate grassland found in:
- New Zealand: Downs
- Central Asia: Steppes
- State three uses of vegetation.
- Grasses are used as fodder
- Use for providing fruits/ roots/ vegetables/ food e.g. fruit
- Providing wood fuel/ charcoal wood
- Controlling soil erosion/ protecting catchments areas
- Use for ornamental/ Beauty/ aesthetics
- For cultural / rituals/ worship
- Production of building/ construction materials/ timber
- Name the temperate grassland found in:
-
- Name two output processes in the hydrological cycle.
- Evaporation
- Transpiration
- State three negative influences that rivers have on human environment.
- Flooding of rivers cause loss property and death.
- Wide and deep river valleys between communities make building of transport and communication lines difficult/expensive
- Rivers can be a medium of spreading waterborne diseases such as bilharzia, malaria, amoebiasis etc
- Name two output processes in the hydrological cycle.
-
- Define the term soil.
- The uppermost surface layer of loose (unconsolidated) material which overlies the crustal rocks and on which plant grow.
- State three causes of chemical degeneration of soils.
- Poor land-use practices such as monoculture and over cropping
- Excessive or wrong application of fertilizers
- Environmental causes such as heavy rainfall can lead to leaching
- Excessive drought leading to accumulation of salts in the topsoil
- Define the term soil.
- Study the map of Nyeri 1:50,000 (Sheet 120/4) provided and answer the questions that follow.
-
- Give the longitudinal extent of the area covered by the map.
- 36º45/E – 37º00/E
- Name two districts in the area covered by the map.
- Nyeri District
- Laikipia District
- Give the longitudinal extent of the area covered by the map.
-
- Calculate the area of Nyeri forest. Give your answer in kilometres.
- Number of full squares = 2 = 2km2
Number of ½ squares = 20/2 = 10km2
Area = (2 + 10) km2
= 12km2 ± 0.5 km2
- Number of full squares = 2 = 2km2
- What is the magnetic variation of the area covered by the map.
- 1º 31/
- Calculate the area of Nyeri forest. Give your answer in kilometres.
- Describe the drainage of the area covered by the map.
- The area is drained by many permanet rivers e.g. River Amboni, Muiga
- Most rivers flow from the western to the eastern parts of the area covered by the map.
- Most rivers form dentritic drainage pattern wit their tributeris e.g. R. Chanya
- Aberdare forest is the main cathment area for riversa
- The area is also drained by many man-made lakes along rivers e.g. GR 6962
- Other drainage features include water holes e.g. GR 6961
-
- Using a scale of 1 cm represents 50 metres, draw across-section along northing 64 between easting 68 and 74.
- On the cross-section, mark and label the following;
- Hill.
- All weather road loose surface.
- River.
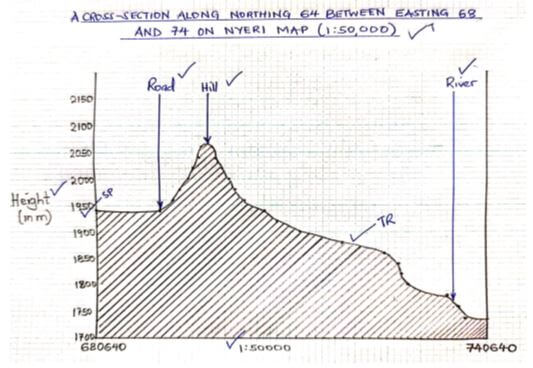
- Calculate the vertical exaggeration of the cross-section.
- Vertical exaggeration = Vertical Scale/Horizontal scale
= 1/50
1/50,000
=1/50 x 500/1
=10 times
- Vertical exaggeration = Vertical Scale/Horizontal scale
- Citing evidence from the map, identify three social functions of the area covered by the map.
- Recreation – Stadium GR6663, Youth club, Show ground
- Education – Schools e.g. Kaindu sch, Kagumo college
- Heath care provision – Hospitals
- Security – Police post
- Administration – Chiefs centre, Admin offices
- Water provision – Irrigation canals
- Residential services – Nyeri town, settlements
-
- Below is a world map showing the distribution of fold mountains. Use it to answer question (a).
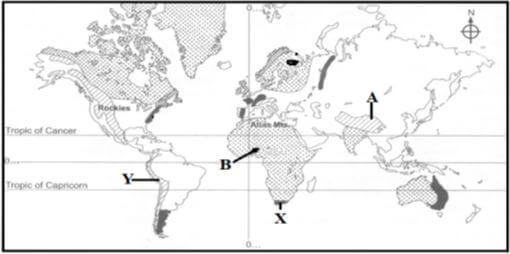
-
- Name the fold mountains marked A and B.
- A – Himalayas
- B – Akwapim Hills
- Give the orogenies during which the fold mountains marked X and Y were formed.
- X – Hercynian orogeny
- Y – Alpine orogeny
- Name the fold mountains marked A and B.
- With the aid of well labelled diagrams, describe the formation of anticlinorium and synclinorium complex of folds.
- Initially, the crustal rocks may be subjected to minor folding resulting in the formation of minor folds on the surface.
- Later, the same rocks could be subjected to greater compressional forces which cause the already folded rocks to fold further into bigger folds, leading to anticlinorium and synclinorium complex landscape.
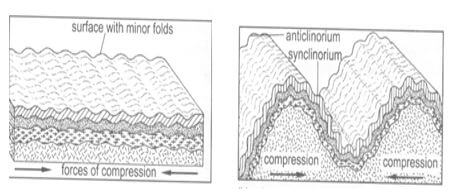
-
- Give three features resulting from folding other than fold mountains.
- Rolling plains
- Ridge and valley landscape
- Escarpments
- Depressions
- Intermontane plateaus and intermontane basins
- Describe how fold mountains were formed according to the proponents of contraction theory.
- During the formation of the earth, the outer part of the earth cooled, contracted and hardened faster than the interior part.
- Cooling of the interior causes the surface rocks to wrinkle in order to fit on the contracting interior.
- The wrinkles formed the fold mountains.
- Give three features resulting from folding other than fold mountains.
- Explain two positive significance of folding to human activities.
- Resultant features of folding such as fold mountains, intermontane plateaus, etc. attract tourists thus earning foreign exchange to the country.
- Fold mountains receive high rainfall on their windward slopes which supports dense forest. These forests are a source of valuable timber for making furniture, building and construction. Forests also act as water catchment areas and prevent soil erosion.
- Folding can result in rock metamorphism by subjecting the rocks to great pressure which can lead to the formation of valuable minerals such as coal and petroleum, promoting mining.
- Folding can also expose deeply seated minerals (Gold, tin) making their mining easy.
- Rivers originating from fold mountains are a source of water for domestic, irrigation and industrial purposes.
- Your class intends to carry out a field study on folding;
- State three ways in which you would prepare for the field study.
- Obtaining permission from relevant authorities
- Conducting a reconnaissance
- Revision of stated objectives and formulated hypotheses
- Selecting appropriate data collection methods
- Assembling relevant tools and equipment
- Preparing a working schedule
- Dividing into workable groups
- Give two methods of data collection you would use during the field study
- Administering questionnaires to respondents
- Observation the features of folding under study
- Interviewing respondents in the area
- Reading about folding from secondary sources
- Conducting simple experiments in the field
- Taking photographs/photographing
- Collecting samples of rocks for analysis.
- State three ways in which you would prepare for the field study.
-
-
-
- Differentiate between a mineral and a rock. (2 marks)
- A mineral is an inorganic substance which occur naturally at or beneath the surface of the earth while a rock is an aggregation of mineral particles that form the solid part of the earth.
- Describe the following characteristics of minerals:
- Tenacity.
This is the ability of a mineral to withstand tearing, crushing, breaking or bending. Different minerals are said to be elastic, flexible, ductile or brittle. - Streak.
This is the colour that a mineral leaves behind when it is rubbed against a hard surface. Different minerals have different streaks.
- Tenacity.
- Differentiate between a mineral and a rock. (2 marks)
- Describe the process of formation of the following rocks:
- Chemically formed sedimentary rocks.
- Rivers and surface runoff flow through rocks
- Soluble minerals dissolve in water and then carried away in solution
- The solution is deposited in lakes or seas
- The chemicals in the minerals mix and coagulate
- Coagulated mass increases in weight and settles in the lake
- With time it accumulates in layers and the lower layers are compressed by the overlying materials
- They harden to form rocks
- Volcanic ejecta.
- During volcanic eruptions, solid ash and semi-liquid materials are thrown out from the earth’s interior
- These materials cool as they fall onto the earth’s surface
- These materials settle on the ground to form spongy rocks (e.g. pumice)
- Lower layers are compressed and consolidated into (mechanically formed sedimentary) rocks (e.g.tuff)
- Chemically formed sedimentary rocks.
- State four characteristics of metamorphic rocks.
- Have different texture from the original rocks
- Are formed from pre-existing rocks
- Minerals in the rocks recrystallize
- Are harder than their original rocks
- The rocks contain compounds and minerals of great economic importance
- Explain three significance of rocks to human activities in Kenya.
- Some rocks form spectacular features that are tourist attractions e.g. the crying stone of Kakamega thus earning foreign exchange
- Some rock types act as water reservoirs storing underground water that can be harnessed for domestic and industrial uses e.g. Mzima springs that provide water to Mombasa county
- Some rocks provide parent materials that are weathered to produce fertile soils that are used for crop cultivation
- Some rocks such as limestone provide raw materials that are used in building and construction e.g. cement manufactured at Bamburi in Mombasa county
- Some rocks such as coal provide fuel used in homes and industries
- Some rocks contain valuable minerals which are extracted and sold to earn income used to improve living standards
-
-
-
- What is a piedmont glacier?
- It is a large glacier formed by coalescing/convergence of two cirque glaciers.
- Give three ways through which ice moves.
- Plastic flowage
- Basal slip
- Extrusion flow
- What is a piedmont glacier?
-
- Apart from roche mountonnee, name three other features formed by glacial erosion in lowlands.
- Depressions
- Crag and tail
- Ice-eroded plains
- Using a well labelled diagram, describe the formation of a roche mountonnee.
- As ice sheet erode a low lying area, it comes across a resistant rock outcrop
- The surrounding area is eroded at a much faster rate than the resistant rock outcrop
- The ice erodes the upstream side of the outcrop rock through abrasion to form a smooth gentle slope
- The downstream side of the outcrop rock is eroded by plucking leading to a rugged steep slope
- When the ice melts or retreats, it exposes a resistant rock with a smooth upstream and a rugged leeward side known as a roche mountonnee.
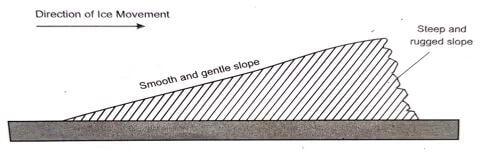
- Apart from roche mountonnee, name three other features formed by glacial erosion in lowlands.
- Your class is planning to carry out a field study on features formed by glacial erosion in highlands;
- State two objectives you would have for the study.
- To identify the features formed by glacial erosion in highlands
- To investigate how the features were formed through erosion
- To find out how the features influence human activities
- To identify the characteristics of the features
- Give three qualities of a good questionnaire you would prepare for collecting data.
- The questions should be simple and clear
- The questions should be few
- The questions should be arranged in a logical order from simple to complex
- The questions should strictly be related to the topic of study
- The questions should be free of bias
- The questions should obey privacy of respondents
- State two objectives you would have for the study.
- Explain three positive significance of glaciation in lowland areas. (6 marks)
- During summer, glaciated lowlands have good pasture for grazing livestock
- Features such as outwash plains and glacial till have fertile soils for crop farming
- Glaciated lowlands generally have gentle slopes due to erosion and deposition. Such areas are ideal for construction of buildings and transport lines
- Glacial lakes can be exploited for economic uses such as fishing, transportation and tourist attractions
- Fiords provide deep natural harbours and rich fishing grounds
- Sand for building and construction has been excavated from outwash plains, eskers and kames.
-
-
-
- Define the term denudation.
- This is the destruction, wastage and removal of parts of the earth’s surface
- Explain how the following factors influence weathering:
- Mineral composition of the rocks.
- Minerals that constitute a rock expand at different rates when subjected to heat. This causes internal strain in the rocks which eventually disintegrates.
- Other minerals are very soluble in water which encourages chemical weathering
- Colour of the minerals.
- Dark coloured minerals absorb more heat compared to light coloured minerals. The rocks with dark coloured minerals therefore absorb heat faster causing internal stress in the rocks which eventually breaks them up faster than the light coloured ones.
- Structure of the rocks.
- Weathering largely depend on lines of weakness of the rocks such as jonts, cracks and bedding planes. Rocks are easily weathered along such joints.
- Rocks with air spaces allow water to enter and pass through them therefore encouraging chemical weathering.
- Mineral composition of the rocks.
- Define the term denudation.
- The diagram below shows a process of mechanical weathering:
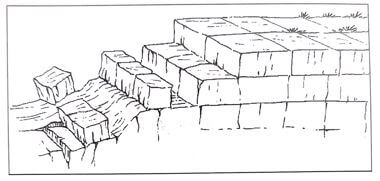
- Identify the process.
- Block disintegration/block separation
- Describe how the process occurs.
- It is caused by large diurnal ranges of temperature in some regions such as deserts
- Very high temperatures are experienced during the day in such areas due to intense solar insolation since the skies are always clear. The high temperatures cause the rocks to heat up intensely causing them to expand.
- At night when the temperatures drop, rapid cooling occurs considerably which causes the rocks to contract.
- The process of expansion and contraction is repeated daily over a long period of time.
- Stress develops within the rocks along the joints and cracks causing blocks of rocks to eventually separate along these lines of weakness.
- Identify the process.
- State five evidences of soil creep.
- Accumulation of soil particles at the base of a slope which results to deep soils at the base of the slope
- Inclined fence posts and telegraph poles from their original positions
- Destroyed stone walls built across the slope as a result of pressure from creeping soil
- Bare and exposed upper slopes as a result of downhill movement of soil particles
- Retreated slopes which become gentler than before
- Accumulated soil on roadsides and railway lines which may eventually block them
- Stepped soil patterns on a slope/formation of terracettes
- The ends of rock outcrops may arch downhill when the soil lies on them during creeping.
- Explain three significance of mass wasting on the physical and human environments.
- Materials from landslides may create a barrier across a river valley thus leading to formation of lake which can provide water for domestic and industrial uses
- Mass movement may create sceneries which may become tourist attractions thus earning the country foreign exchange
- Fertile soils shift positions and is accumulated at the lower areas where it is used for crop cultivation
- Some forms of mass movement such as rock fall may lead to loss of lives when people and animals are buried under large quantities of rock waste
- Landslides cause damage to properties when rock materials cover structures such as roads, farms and houses
- Landslides may cause rivers to change their courses thus reducing the volume of water downstream
- Movement of materials overt the land facilitates loosening of top soil thus increasing soil erosion
- Mass wasting leads to formation of derelict land or scars which spoil the beauty of the land
- Fertile soils are moved from upper slopes to lower slopes thus discouraging agriculture and settlement on the upper slopes.
-
Download Geography Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Maranda Mock Examinations 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
