Instructions to Candidates:
- This paper consists of three sections; A, B and C.
- Answer all the questions in section A and B.
- Answer any two questions in section C.
- All answers should be written in spaces provided in question paper.
SECTION A (30MARKS)
Answer All the questions in this section in the spaces provided
- Name two methods of farming that are considered outdated (1 mark)
- State three symptoms of potassium deficiency in plants (1½ mark)
- State two ways of controlling late blight in tomatoes (1 mark)
- Name three financial documents in farm accounts (1½ mark)
- State four farming practices which can enhance proper light penetration in a crop. (2 marks)
- Give four factors which determine the method of weed control in crop production (2 marks)
- State four causes of seed dormancy (2 marks)
- List four effects of weeds on pastures (2 marks)
- State four qualities to be considered when selecting seeds for planting (2 marks)
- Name four methods of harvesting trees. (2 marks)
- Give two methods of conserving forage. (1 mark)
- State four roles of young farmers clubs in Kenya. (2 marks)
- State three farming practices which may lead to multiplication of pests (1½ mark)
- Give three pieces of information to be found in a master roll (1½ mark)
- State three objectives of land reform (1½ mark)
- Why is it important to weed early in crop production (2 marks)
- State three effects of late defoliation in pasture management (1½ mark)
- Differentiate between undersowing and oversowing as used in forage Production. (2 marks)
SECTION B (20MARKS)
Answer All the questions in this section in the spaces provided
- The diagram F, below illustrates a method of training in crops.
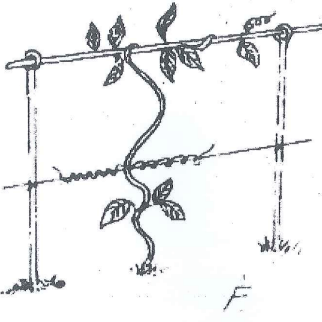
- Identify the method shown in F above. (1 mark)
- Name two other methods used in training in crop production. (1 mark)
- State two advantages of training in crop production. (2 marks)
- List two crops that require training. (1 mark)
- The diagram below illustrates an experiment on soil. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
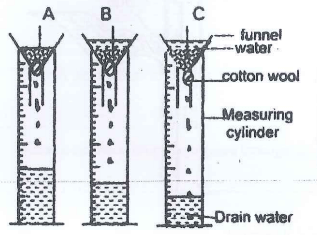
- State the aim of the experiment. (1 mark)
- Cutting
- If the volume of water illustrated in the measuring cylinders was observed after one hour, identify the soil samples labelled A and B. (1 mark)
- State two ways in which the soil structure of the soil sample labeled C above can be improved. (2 marks)
- State the aim of the experiment. (1 mark)
- The diagram below shows a section of a plant from which the planting material illustrated was obtained.
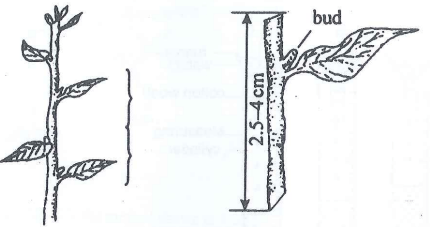
- Identify the planting material illustrated.
- Give two reasons why only the middle part of the plant was used to prepare the planting material. (2 marks)
- Apart from using the middle part of the plant, explain two precautions that should be observed when preparing the illustrated planting material.(2 marks)
- The diagram below illustrate materials, and a method of vegetative propagation. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
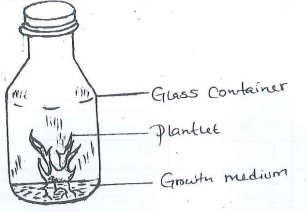
- Identify the method of propagation illustrated above. (1mk)
- Name a common crop propagated through the method. (1mk)
- Give three disadvantages of this method of propagation. (3 mks)
SECTION C (40MARKS)
Answer any two questions from this section in the spaces provided
-
- Describe the production of dry beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) under the following sub-headings:
- Varieties common in Kenya; (2 marks)
- Selection and preparation of planting materials; (3 marks)
- Planting and weeding; (5 marks)
- Describe ten safety precautions that should be taken when using herbicides to control weeds. (5 marks)
- Describe the production of dry beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) under the following sub-headings:
-
- Explain the cultural methods of soil and water conservation (10marks)
- State and explain how various practices carried out in crop production help to control pests (10marks)
- Study the table below showing quantities of fertilizers used and yield of maize obtained over a period of years and answer the questions that follow.
Land (in ha) DAP fertilizers (in 20kg units) Yield (90kg bags) Marginal production (MP) (in 90kg bags) Average production (AP) (in 90kg bags) 1 0 2 1 1 10 1 2 24 1 3 42 1 4 56 1 5 62 1 6 60 1 7 56 -
- Fill in the marginal and average product columns in the table (4marks)
- Using the graph paper provided draw the production function curve (6marks)
- Show the three zones of production on the graph (3marks)
- State and explain the various land tenure systems practiced in Kenya. (7 marks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A (30MARKS)
Answer All the questions in this section in the spaces provided
- Name two methods of farming that are considered outdated (1 mark)
- Shifting cultivation
- Nomadic pastoralism
- State three symptoms of potassium deficiency in plants (1½ mark)
- Leaf curling
- Stunted growth
- Chlorosis
- Premature leaf fall
- State two ways of controlling late blight in tomatoes (1 mark)
- Use of fungicides
- Crop rotation
- Destruction of affected materials
- Name three financial documents in farm accounts (1½ mark)
- Income
- Purchase order
- Receipt
- Statements
- Delivery notes
- State four farming practices which can enhance proper light penetration in a crop. (2 marks)
- Proper spacing
- Pruning
- Thinning
- Training
- Give four factors which determine the method of weed control in crop production (2 marks)
- Cost
- Size of land
- Spacing
- State four causes of seed dormancy (2 marks)
- Impermeable seed coat
- Premature embryo
- Lack of growth hormones
- Presence of growth inhibitors
- Unsuitable temperature
- Lack of enough water
- Lack of oxygen
- List four effects of weeds on pastures (2 marks)
- Reduce lifespan of pastures
- Compete with forage crops for moisture e.t.c
- Some posion animals
- Some may be interfered with forage fertilization.
- State four qualities to be considered when selecting seeds for planting (2 marks)
- Germination percentage
- Certified seeds
- Lack of physical defects
- Freedom from pests and diseases
- Adaptability
- Healthy
- Name four methods of harvesting trees. (2 marks)
- Pruning.
- Lopping.
- Pollarding.
- Coppicing.
- Thinning.
- Tree falling
- Give two methods of conserving forage. (1 mark)
- Silage
- Hay
- Standing forage
- State four roles of young farmers clubs in Kenya. (2 marks)
- Participation in Agriculture shows.
- Carrying out Agric projects in schools.
- Organize Agriculture field days
- Participate in agricultural exchange program
- State three farming practices which may lead to multiplication of pests (1½ mark)
- Monocropping
- Continuos cropping
- Minimum tillage
- Give three pieces of information to be found in a master roll (1½ mark)
- Names of individual workers
- Days worked
- Amount paid
- State three objectives of land reform
- Ensuring the existing labor is fully utilized
- Encouraging conservation of both soil and water
- Encouraging flexibility in production so as to meet existing market demands
- Easy population pressure
- Promote commercial farming
- Why is it important to weed early in crop production
- Prevent competition
- Destroy weeds before they develop seeds
- State three effects of late defoliation in pasture management
- It has low digestability
- Less palatable
- High dry matter content
- Differentiate between undersowing and oversowing as used in forage Production
- Undersowing - establishing a pasture under an exisiting crop
- Oversowing - Establishment of a pasture legume over an existing pasture grass
SECTION B (20MARKS)
Answer All the questions in this section in the spaces provided
- The diagram F, below illustrates a method of training in crops.

- Identify the method shown in F above. (1 mark)
- Trellising
- Name two other methods used in training in crop production. (1 mark)
- Staking
- Propping
- State two advantages of training in crop production. (2 marks)
- Facilitates better light penetration
- Lowers incidences of soil borne diseases
- Easy to carry out field operations like spraying
- List two crops that require training. (1 mark)
- Passion fruits
- Cucumbers
- Tomatoes
- Bananas
- Watermelons
- Pumpkins
- Identify the method shown in F above. (1 mark)
- The diagram below illustrates an experiment on soil. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.

- State the aim of the experiment. (1 mark)
- To compare the porosity and water holding capacities of sandy, loam and clay soils
- If the volume of water illustrated in the measuring cylinders was observed after one hour, identify the soil samples labelled A and B. (1 mark)
- A - Sandy soil
- B - Loam soil
- State two ways in which the soil structure of the soil sample labeled C above can be improved. (2 marks)
- Addition of organic matter
- Addition of lime
- State the aim of the experiment. (1 mark)
- The diagram below shows a section of a plant from which the planting material illustrated was obtained.

- Identify the planting material illustrated.
- Cutting
- Give two reasons why only the middle part of the plant was used to prepare the planting material. (2 marks)
- The brown hard bottom part takes long to root
- The soft upper part rots when planted.
- Apart from using the middle part of the plant, explain two precautions that should be observed when preparing the illustrated planting material.(2 marks)
- A sharp knife should be used to make slanting cuts
- Each cutting should be placed in water to avoid dehydration
- Leaf of the cutting should not touch the soil to avoid rotting.
- Identify the planting material illustrated.
- The diagram below illustrate materials, and a method of vegetative propagation. Study it and answer the questions that follow.

- Identify the method of propagation illustrated above. (1mk)
- Tissue culture
- Name a common crop propagated through the method. (1mk)
- Banana
- Pineapples
- Give three disadvantages of this method of propagation. (3 mks)
- Expensive
- Requires skilled labor
- Requires a special working environment
- Identify the method of propagation illustrated above. (1mk)
SECTION C (40MARKS)
Answer any two questions from this section in the spaces provided
-
- Describe the production of dry beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) under the following sub-headings:
- Varieties common in Kenya; (2 marks)
- Rose cocoa,
- Mwezi moja /GLP1004
- Canadian Wonder/GLP24
- K74
- Wairimu/Red haircot
- Mexican 142
- Mwitemania
- Rose cocoa,
- Selection and preparation of planting materials; (3 marks)
- Select varieties suited to the local ecological conditons
- Select dry and mature seeds
- Select sound seeds that are free from physical damage and wrinkles
- Dress seeds against soil borne pests and diseases
- Obtain seeds from a reputable source/certified seeds
- Inoculate seeds with the right strain of bacteria
- Select varieties suited to the local ecological conditons
- Planting and weeding; (5 marks)
- Plant at the beginning of rains/timely planting
- Make shallow farrows /holes at a depth of 3-5 cm using appropriate tools
- Apply phosphatic fertilizer /DSP/SSP/DAP/MAP/manure during planting
- Place 2-4 seeds per hole and cover it up.with the soil/seed rate 50-60kg/ba.
- Spacing is 30-50cm by 10-1 5cm depending on variety.
- Shallow weeding is done to avoid root damage.
- Avoid weeding during flowering to prevent knocking off the flowers.
- Weed when the field is dry to avoid spread of diseases.
- Keep the field weed free in the early stages of growth.
- Plant at the beginning of rains/timely planting
- Varieties common in Kenya; (2 marks)
- Describe ten safety precautions that should be taken when using herbicides to control weeds. (5 marks)
- Wear protective clothing
- Avoid inhaling the herbicide/spray along the direction of wind
- Read and follow the manufacturer’s manual
- Avoid sucking or blowing blocked nozzles
- Was thoroughly after handling the chemical
- Store herbicides in a safe place away from children .
- Equipment used should not be washed in water sources to prevent pollution
- Empty containers and left overs should be properly disposed to avoid danger to humans, livestock and environment
- Avoid chemical spillage to unintended places/where it may cause danger to human and livestock
- Thoroughly wash the equipment to avoid damage là crops/livestock in subsequent operations
- Avoid eating or handling food before washing to prevent contamination/poisoning.
- Wear protective clothing
- Describe the production of dry beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) under the following sub-headings:
-
- Explain the cultural methods of soil and water conservation (10marks)
- Grass strips/filter strips; These are narrow uncultivated strips along the contour left between cultivated strips.
- Cover cropping; The establishment of a crop that spreads out over the surface of the soil to provide it with a cover.
- Contour farming; Carrying out all land operations along the contour.
- Mulching; Covering of the soil with either organic or synthetic materials.
- Crop rotation that involves the use of cover crops
- Correct spacing to ensure adequate soil cover
- Inter-cropping ensures the soil is adequately covered -
- Ridging/f furrowing to prevent surface runoffs and accumulate water
- Controlled grazing; Proper stocking rate, rotational grazing to ensure soil cover is not depleted.
- Strip cropping; Growing crops which give little ground cover in alternate strips with crops such as beans which have a good ground cover.
- Afforestation growing of trees where non-existed.
- Re-afforestation - growing of trees where they have been cut down.
- Agroforestry - land use that involves the growing of trees in combination with crops and astures on the same piece of land.
- Grass strips/filter strips; These are narrow uncultivated strips along the contour left between cultivated strips.
- State and explain how various practices carried out in crop production help to control pests (10marks)
- Consider disease potential when selecting planting sites, dates, and seeding rates.
- Use disease-free and weed-free seed to prevent diseases and weeds from being introduced.
- Control alternate host plants of insects and diseases.
- Minimize moisture conditions optimum for disease development by carefully managing irrigation water applications.
- Use weed-free feed to prevent the spread of weeds by livestock.
- Control reinfestation sources of weeds on adjacent property such as fencerows, ditch banks and roadways. (Take care to avoid damage to non-target organisms and threatened or endangered species.)
- Use good sanitation practices to remove soil, crop residues, weed seeds, and weed parts from equipment before moving to other fields.
- Consider disease potential when selecting planting sites, dates, and seeding rates.
- Explain the cultural methods of soil and water conservation (10marks)
- Study the table below showing quantities of fertilizers used and yield of maize obtained over a period of years and answer the questions that follow.
Land (in ha) DAP fertilizers (in 20kg units) Yield (90kg bags) Marginal production (MP) (in 90kg bags) Average production (AP) (in 90kg bags) 1 0 2 0 0 1 1 10 8 10 1 2 24 14 14 1 3 42 18 14 1 4 56 14 14 1 5 62 6 12.4 1 6 60 −2 10 1 7 56 −4 8 -
- Fill in the marginal and average product columns in the table (4marks)
- Using the graph paper provided draw the production function curve (6marks)
- Show the three zones of production on the graph (3marks)
- State and explain the various land tenure systems practiced in Kenya. (7 marks)
- Leasehold/landlordism/tenancy: This gives legal rights to an individual to own and use land at a payment for a specific period of time.
- Company/concession/plantation: This is where company and government enter into an agreement on the use of land for a specific period of time.
- Communal land tenure: This is where the whole community has the light to the use of land/each individual member of that community has equal rights to the use of the land.
- Individual ownership/individual owner operator/freehold: This is where the land is owned by the individual (farmer who either operates it or leases it to another person to operate.
- State ownership: Here the government (state) controls land use. capital. enterprise. labour and marketing.
- Co-operative land tenure: Here land is owned by a group of members who run it on co-operative basis
- Leasehold/landlordism/tenancy: This gives legal rights to an individual to own and use land at a payment for a specific period of time.
-
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Alliance Mock Examinations 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
