Questions
Instructions to students
- This paper contains three sections A, B and C
- Answer ALL the questions in section A and B
- Answer any Two questions from section C
- All answer should be written in the spaces provided
- Candidates should answer the questions in English.
SECTION A: 30 MARKS
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided
- State two ways in which agriculture contributes directly to the development of industries. (1 mark)
- State four advantages of shifting cultivation (2 marks)
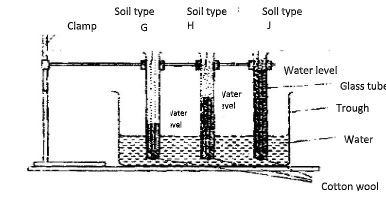
- The diagram below shows an experiment set up using soil types G, H and J and observations made after 24 hours. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
- What is the experiment represented above designed to study? (1/2mark)
- Name the three soil types G, H and J. (1 1/2marks)
- What is the characteristic texture of soil types G and J? (1 marks)
- State two maintenance practices that should be carried out on a wheelbarrow. (1 mark)
- Give four farming practices that may help in achieving minimum tillage. (2 marks)
- The table below shows pH values of different soil samples. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
Soil Sample
S1
S2
S3
S4
S5
S6
S7
S8pH value
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10- Which soil sample has the highest acidity? (1/2mark)
- State two ways in which the pH value of sample S 10 can be lowered. (1 mark)
- Which of the above soil samples is suitable for growing tea? (11/2 mark)
- Calculate the plant population per hectare of a maize crop planted at a spacing of100cm x 50cm. Show your working. (2 marks)
-
- State four advantages of crop rotation. (2 mark)
- State four factors considered when designing a crop rotation programme (2 marks)
-
- State four practices which encourage soil erosion (2 marks)
- Name two forms of gulley erosion (1 mark)
- Give a weed for each case, which has the following effect on cattle:
- Poisoning (1/2mark)
- Tainting milk when eaten before milking (1/2mark)
- State four advantages of land consolidation (2 marks)
- Name five sources of agriculture credit in Kenya (2½ marks)
- List two examples of working capital in crop production. (1 mark)
- State the use of the following in farm accounting: (1 ½ marks)
- Balance sheet
- Inventory
- Cash book
- State four problems that farmers are likely to face when marketing theirproduce. (2marks)
SECTION B (20 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section in the spaces provided
-
- List two sites on which agro forestry trees can be established on a farm (2marks)
- State four benefits of agroforestry to a maize crop. (2 marks)
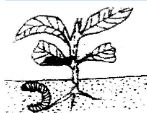
- The diagram labeled D below shows a Kale crop invested by a pest
- Identify the pest. (1 mark)
- What damage does the pest cause to the crop? (1 mark)
- State two methods of controlling the pest (2 marks)
- .A farmer applied a compound fertilizer 10:20:0 on a three hectares piece of land at a rate of 180kg N per hectare.
- Calculate the quantity of the compound fertilizer the farmer applied on the piece of land. (3 marks)
- What do the figures 10 and 20 stand for in the compound fertilizer? (2 marks)
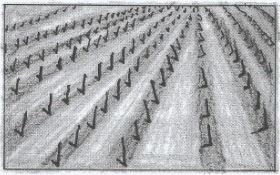
- The diagram below shows crop establishment using a certain method of planting.
- Name the method of planting used for the crop (1mark)
- State three advantages of the plating method used for the crop (3marks)
- Explain three factors that determine the depth of planting (3marks)
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
Answer ANY TWO questions from this section in the spaces provided
- In a maize production enterprise carried over a period of eight years, a farmerused one hectare of land each time and applied different quantities of DAP fertilizer. DAP fertilizer costs Ksh 2500 per 50kg bag and the harvested maize is sold at Ksh 3000 per 90kg bag. The quantities of DAP fertilizer applied and maize harvested are as shown in this table below.
DAP fertilizer input in 50 kgs bags Maize yield in 90 kgs bag Total revenue
kshsTotal cost
kshsMarginal revenue
kshsMarginal cost
kshs0
1
2
3
4
5
6
715.0
15.6
52.0
68.5
71.0
71.5
71.5
68.645,000 0
0
0
- Complete the table by determining the values of total revenue, total cost, and marginal revenue and marginal cost (8 marks)
- From the information in your table, how can the farmer determine the level of production at which profit is maximum? (1 mark)
- At the production level that yielded maximum profit, what was the value of each of the following?
- DAP Fertilizers input (1 mark)
- Marginal revenue
- Discuss five importance of budgeting in agricultural production (10 marks)
-
- Explain five methods of harvesting water in a farm (10 marks)
- Outline ten farming activities which may encourage soil erosion. (10 marks)
-
- Describe how the stem cuttings for propagating tea are prepared (9marks)
- Explain six factors that should be considered when selecting seeds for planting (6marks)
- State five advantages of timely planting in crop production (5 marks)
Marking Scheme
- State two ways in which agriculture contributes directly to the development of industries. (1 mark)
- Providing market for industrial goods.
- Providing raw materials that are used in industries.
- State four advantages of shifting cultivation (2 marks)
- Land is allowed to rest and re-gain fertility
- Low incidences of pests and diseases
- Economizes on the use of fertilizers
- No land disputes
- Maintains soil structure
- Low capital requirement
- The diagram below shows an experiment set up using soil types G, H and J and observations made after 24 hours. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
- What is the experiment represented above designed to study? (1/2 mark)
- Capillarity in the three different soil samples.
- Name the three soil types G, H and J. (1 1/2marks)
- G – Sandy soil
- H – Loam soil
- J – Clay soil
- What is the characteristic texture of soil types G and J? (1 marks)
- G – Rough and coarse texture
- J – Fine textured
- What is the experiment represented above designed to study? (1/2 mark)
- State two maintenance practices that should be carried out on a wheelbarrow. (1 mark)
- Tightening loose bolts
- Lubricating movable parts , e.g., axle to prevent wear and tear
- Repairing broken handles
- Give four farming practices that may help in achieving minimum tillage. (2 marks)
- Application of herbicides
- Mulching
- Timing cultivation
- Restricted cultivation to planting areas
- Cover cropping
- Uprooting / slashing
- The table below shows pH values of different soil samples. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Which soil sample has the highest acidity? (1/2mark)
- Sample S1
- State two ways in which the pH value of sample S 10 can be lowered. (1 mark)
- Application of acidic fertilizers: Accept S/A; ASN; DAP; MAP
Rej: Nitrogenous fertilizers - Application of sulphur
- Application of acidic fertilizers: Accept S/A; ASN; DAP; MAP
- Which of the above soil samples is suitable for growing tea? (11/2 mark)
- S1
- S2
- S3
- Which soil sample has the highest acidity? (1/2mark)
- Calculate the plant population per hectare of a maize crop planted at a spacing of100cm x 50cm. Show your working. (2 marks)
- 1 ha= 10,000m2
10,000m2 ÷ (1m x 0.5m)
= 20,000 plants/ha
- 1 ha= 10,000m2
-
- State four advantages of crop rotation. (2 mark)
- Ensure maximum utilization of nutrients
- Control soil – borne pests and diseases
- Control weed
- Add nitrates into the soil
- Control soil erosion
- Improve soil structure
- State four factors considered when designing a crop rotation programme (2 marks)
- Deep rooted crops alternate with shallow rooted ones
- Crop easily weeded are alternated with those difficult to weed
- Crops of the same family should not succeed each other
- Heavy feeders should come first in the cycle
- Include a legume crop
- State four advantages of crop rotation. (2 mark)
-
- State four practices which encourage soil erosion (2 marks)
- Over –cultivation, overstocking/overgrazing.
- Deforestation/planting annual crops on steep slopes.
- Burning of the vegetation.
- Ploughing up and down the slope.
- Name two forms of gulley erosion (1 mark)
- V- shaped gullies
- U-shaped gullies
- State four practices which encourage soil erosion (2 marks)
- Give a weed for each case, which has the following effect on cattle:
- Poisoning (1/2mark)
- Thorn apple (Datura stramonium)
- Sodom apple (Solanum incanum)
- Tainting milk when eaten before milking (1/2mark)
- Mexican marigold (Tagetes minuta)
- Poisoning (1/2mark)
- State four advantages of land consolidation (2 marks)
- There is proper supervision of the farm.
- Reduces costs on traveling
- Easy to get extension services.
- Allows good farm planning.
- It enhances proper pests, diseases and weed control.
- Encourages long term investments.
- Name five sources of agriculture credit in Kenya (1 ½ marks)
- Crop boards/marketing board/statutory boards.
- Commercial banks
- Cooperative societies
- Agricultural finance corporation (A.F.C)
- Settlement fund trustees
- Private money lenders
- Non –Governmental Organizations (NGOS )
- Insurance companies/
- Hire purchase companies.
- List two examples of working capital in crop production. (1 mark)Fertilizers.
- Seeds.
- Fuel.
- Pesticides.
- State the use of the following in farm accounting: (1 ½ marks)
- Balance sheet
- Balance sheet - showing the financial position of the farm business at a
- particular period of the year/shows values of assets and
- liabilities/shows net worthy/net deficit/shows solvency and insolvency.
- Inventory
- Inventory – recording all the assets owned by the farm business/ helps to detect losses
- Cash book
- Cash book – recording all transactions involving receiving and paying out of cash on the farm business
- Balance sheet
- State four problems that farmers are likely to face when marketing their produce. (2marks)
- Price fluctuations/ low prices
- Lack of transportation.
- Perishability of some products
- Poor storage facilities.
- Competition with substitute products.
- Delayed payments
- Some government policy
-
- List four sites on which agro forestry trees can be established on a farm (2marks)
- Terraces
- River banks/water catchments area
- Steep slopes/slopes
- Within pasture land
- State four benefits of agroforestry to a maize crop. (2 marks)
- Leguminous trees fix nitrogen into the soil;
- Trees act as windbreaks;
- Trees stabilize soil against soil erosion;
- Leaf litter decompose to form humus/recycle nutrients;
- Trees improve and act as water catchment areas/conserve water.
- List four sites on which agro forestry trees can be established on a farm (2marks)
- The diagram labeled D below shows a Kale crop invested by a pest
- Identify the pest. (1 mark)
- Cutworm/Agrotis
- What damage does the pest cause the crop? (1 mark)
- Cuts the stern causing lodging.
- State two methods of controlling the pest (2 marks)
- Use of appropriate insecticide.
- Removing it and killing it.
- Identify the pest. (1 mark)
- A farmer applied a compound fertilizer 10:20:0 on a three hectares piece of land at a rate of 180kg N per hectare.
- Calculate the quantity of the compound fertilizer the farmer applied on the piece of land. (3 marks)
- Nitrogen=10%
Quantity of fertilizer applied
10kg N is in 100 kg of the fertilizer
180 Kg N = 180 x 100
10
=1800 kg x 3 hectares
5400 kg of the fertilizer
- Nitrogen=10%
- What do the figures 10 and 20 stand for in the compound fertilizer? (2 marks)
- 10-Nitrogen percentage
- 20-Phosphorous percentage
- Calculate the quantity of the compound fertilizer the farmer applied on the piece of land. (3 marks)
- The diagram below shows crop establishment using a certain method of planting.
- Name the method of planting used for the crop (1mark)
- Row planting
- State three advantages of the plating method used for the crop (3marks)
- Operations can be mechanized;
- Easy to establish plant population
- Uses less planting materials compared to broadcasting
- Easy to carry out cultural practices
- Explain three factors that determine the depth of planting (3marks)
- soil moisture content wet soils require shallow depth
- Size of the seed; large seeds require greater depth
- Type of germination –epigeal germination requires shallow depth
- Name the method of planting used for the crop (1mark)
- In a maize production enterprise carried over a period of eight years, a farmer used one hectare of land each time and applied different quantities of DAP fertilizer. DAP fertilizer costs Ksh 2500 per 50kg bag and the harvested maize is sold at Ksh 3000 per 90kg bag. The quantities of DAP fertilizer applied and maize harvested are as shown in this table below.
- Complete the table by determining the values of total revenue, total cost, and marginal revenue and marginal cost (8 marks)
DAP Fertilizer input in 50 kgs bags) Maize yield in 90kg bags Total revenue kshs total cost kshs marginal revenue (kshs) Marginal cost (kshs) 0 15.0 45 000 0 0 0 1 35.6 106 800 2 500 61 800 2 500 2 52.0 156 000 5 000 49 200 2 500 3 68.5 205 500 7 500 49 500 2 500 4 71.0 213 000 10 000 7 500 2 500 5 71.5 214 500 12 500 1 500 2 500 6 71.5 214 500 15 000 0 2 500 7 68.5 205 550 17 500 -8950 2 500 - From the information in your table, how can the farmer determine the level of production at which profit is maximum? (1 mark)
- At 5 bags of fertilizer
- At the production level that yielded maximum profit, what was the value of each of the following?
- DAP Fertilizers input (1 mark)
- ksh. 12500
- Marginal revenue
- kshs 1500
- DAP Fertilizers input (1 mark)
- Discuss five importance of budgeting in agricultural production (10 marks)
- Assists the farmer in estimation of the required production resources
- Help to reduce uncertainty in farming process
- Helps predict future returns
- Helps farmers to avoid incurring losses
- Helps in securing loans
- For periodic analysis of farm business
- Used in decision making
- Determines efficiency or weekiness in farm operations
- Acts a record which can be used for future reference
- Complete the table by determining the values of total revenue, total cost, and marginal revenue and marginal cost (8 marks)
-
- Explain five methods of harvesting water in a farm (10 marks)
- Ponds
- Dams
- weirs
- Roof catchments
- Rock catchments
- Retention ditches
- Wells
- Outline ten farming activities which may encourage soil erosion. (10 marks)
- Continuous cropping without giving the land a rest
- Burning of vegetation
- Ploughing along the slopes/ farming on step land
- Deforestation
- Ploughing along river banks
- Cultivating when the soil is too dry or wet
- Overgrazing/ overstocking
- Flooding/ application of a large amount of water at high rate
- Over cultivating the land to fine tilth/ pulverizing the soil
- Explain five methods of harvesting water in a farm (10 marks)
-
- Describe how the stem cuttings for propagating tea are prepared (9marks)
- To test them for purity to prevent entry of noxious / foreign weeds into the country
- To test them for purity to prevent entry/ spread of pests and diseases into the country
- Select shoots from mother plants that are highly yielding / healthy
- Select healthy and vigorous growing shoots
- That have grown unchecked for 6 months
- Obtain cuttings from the middle part of the shoots
- Make a cut close to the axial bud/leaf
- Using a sharp knife make a cut
- The cut should face away from the bud
- Put the cuttings in water before planting to prevent dehydration
- The cutting should have a single leaf/bud
- Make a slanting cut
- The cuttings should be 2.5-4cm long
- Explain six factors that should be considered when selecting seeds for planting (6marks)
- Adaptability: should be adapted to local ecological condition.
- Physical deformities/damages: should be free from physical deformities/damages.
- Health - should be free from pests/disease.
- Viability/germination percentage: - should have high viability/germination percentage.
- Parent plant - should be from high yielding/healthy parents/high quality/early maturing
- Purity - should be clean / free from impurities.
- Maturity - should be of correct maturity stage.
- Age/storage period: - seeds stored for long periods have low viability/germination percentage hence should not be selected
- Size of seeds should be the correct size
- State five advantages of timely planting in crop production (5 marks)
- Crop matures early when market prices are high/high demand.
- Disease and pest control;
- Benefit from nitrogen flash;
- Weed control;
- Maximises rainfall utilization by the crop;
- Describe how the stem cuttings for propagating tea are prepared (9marks)
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Kijiset Revision Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students