Questions
Instructions to Candidates
- This paper consists of TWO sections.
- Answer ALL the questions in sections A and B in the spaces provided.
- ALL working MUST be clearly shown.
- Non-programmable silent electronic calculators and KNEC mathematical tables may be used.
SECTION A (25 MARKS)
Answer questions in the spaces provided
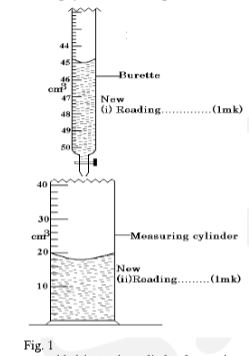
- The figure 1 shows a measuring cylinder containing some water.
Another 3cm3 of water was added in to the cylinder from a burette delivering volumes from 0cm 3 to 50 cm 3 . Record in the spaces provided the new reading indicated on each vessel. (2 marks) - Sketch a Vernier calipers scale reading 3.41 cm. (2 marks)
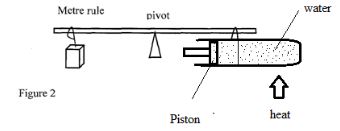
- The system in figure 2 is in equilibrium
When the temperature of the water is raised the system is observed to tilt to the left, explain this observation (2 marks) - The reading on a mercury barometer at a certain town is 760mm. Calculate the pressure at the town.(density of mercury is 1.36x10 4 Kgm -3 ) (3 marks)
- Explain the cause of random motion of smoke particles as observed in Brownian motion experiment using a smoke cell. (1 mark)
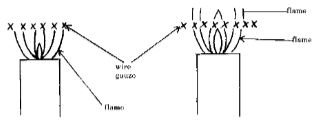
- When a Bunsen burner is lit below a wire gauze, it is noted that the flame initially burns below the gauze as shown in the figure below. After sometime the flame burns below as well as above the gauze.
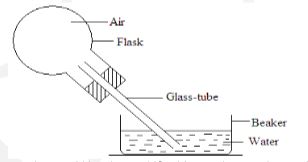
Explain this observation (2 marks) - The diagram below shows a flask fitted with a glass tube dipped into a beaker containing water at room temperature. The cork fixing the glass tube is tight.
State with reason what would be observed if cold water is poured on to the flask. (2marks) - A resultant force F acts on a body of mass ‘m’ causing an acceleration of a1 on the body. When the same force acts on a body of mass 2m, it causes an acceleration of a2 .Expressa 2 in terms of a1 (3 marks)
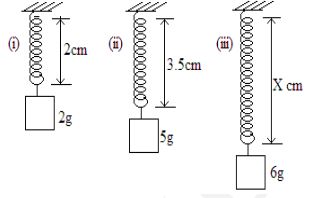
- The diagram below shows three identical springs which obey Hooke’s law.
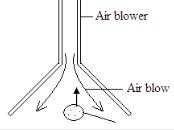
Determine the length X. (3 marks) - The figure below shows a pith ball being lifted in to a funnel end of a blower.
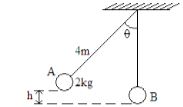
Explain this observation (2 marks) - A metal ball suspended vertically with a wire is displaced through an angle as shown in the diagram below. The body is released from A and swings back to ‘B’.
Given that the maximum velocity at the lowest point B is 2.5 m/s. Find the height h from which the ball is released (g = 10m/s2 )(3 marks)
SECTION B (55 MARKS)
Answer questions in the spaces provided.
-
- Distinguish between solid and liquid states of matter in terms of intermolecular forces (1 mark)
- In an experiment to estimate the diameter of an oil molecule, an oil drop of diameter 0.05 spreads over a circular patch whose diameter is 20cm
Determine- The volume of the oil drop (2 marks)
- The area of the patch covered by the oil (2 marks)
- The diameter of the oil molecule (2 marks)
- State;
- Any assumption made in (b) (iii) above (1 mark)
- Two possible sources of errors in this experiment (2 marks)
-
-
- State what is meant by centripetal acceleration (1 mark)
- A block of mass 200g is placed on a frictionless rotating table while fixed to the centre of the table by a thin thread. The distance from the centre of the table to the block is 15cm. if the maximum tension the thread can withstand is 5.6N. Determine the maximum angular velocity the table can attain before the thread cuts. (4mks)
- Define the term velocity ratio as used in machines (1 mark)
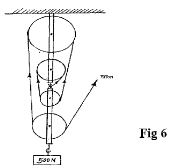
- Figure 6 shows a block and tackle pulley system lifting a load of 500N
- Determine the velocity ratio of the machine (1 mark)
- If an effort of 120N is required to lift the load using the machines determine the efficiency of the pulley system (3 marks)
- In the space provided below, sketch a graph of efficiency against load for the system. (2 marks)
-
- A car of mass 2000kg travelling at 5m/s collides with a minibus of mass 5000kg travelling in the opposite direction at 7m/s, the vehicles stick and move together after collision. If the collision lasts 0.1 seconds
- Determine the velocity of the system after collision to 3 decimal places (3 marks)
- Calculate the impulsive force on the minibus (3 marks)
- Calculate the change in kinetic energy of the system to 5 significant figures (3 marks)
- The graph below shows the force on a tennis ball when served during a game.
Determine the mass of the racket with a velocity of 40ms -1 (assume the ball was stationary before being struck) (3 marks)
-
- Define specific heat capacity. (1 marrk)
- In an experiment to determine the specific latent heat of water, steam at 100 0 C was passed into water contained in a well lagged copper calorimeter.
The following measurements were made- Mass of colorimeter = 60g
- Initial mass of water = 80g
- Initial room temperature of water = 15 0 c
- Final temperature of the mixture 45 0 c
- Final mass of water + calorimeter + condensed steam =160g
- Specific heat capacity of water = 4200Jkg -1 k -1 and specific heat capacity of copper = 390Jkg -1 k -1
- Determine
- Mass of condensed steam (1 mark)
- Heat gained by the calorimeter and water. (4 marks)
- Given that Lv is the specific latent heat of evaporation of steam,
- Write an expression for the latent heat of vaporization of steam. (2 marks)
- Determine the value of Lv. (2 marks)
- Determine
-
- State Charles law. (1 mark)
- Describe an experiment to verify Charles law. (5 marks)
- Using kinetic theory explains how temperature affects the volume of a gas. (2 marks)
- The volume of mass of air at temperature 27 0 C is 300cm3 . Find the volume of the air at -73°C. (3 marks)
Marking Scheme
-
- New reading of burette = 48 cm 3 (1 mark)
- New reading of cylinder = 21 cm 3 (1 mark)
- vernier callipers
main sscale= 3.4 cm
Vernier scale 1st division after 0 (2 marks) - water expand on heating causing the COG to shift to the left hence lowering the clockwise moments (3 marks)
- Pressure = ρgh
1.36 x 104 x 10 x 0.760
= 1.0336 x 105N/m2 - Smoke particles are being hit by unseen air molecules moving in a random motion (1 mark)
- Wire gauze is a good conductor of heat and hence conduct heat away from the upper region of the wire gauze the gas reaches its ignition temperature later when the flame starts showing on the upper region. (2 marks)
-
- Water is sucked in to the glass tube
- Air in the flask contracts when cooled.lowering pressure inside (2 marks)
- F = mal1
F= 2mA2
MA1 = 2mA2
a2 = ma₁
2m
a2 = 1/2a₁
[3 marks] - F= Ke
3 = K x 1.5
K= 3/1.5
K= 2g/cm
F=Ke
I = 2 x e
e = 1/2
e= 0.5
x = 0.5 + 3.5
x = 4.0cm
(3 marks) - High velocity air creates a low pressure inside the funnel Air outside push the ball into the low pressure area. (2 marks)
- PE = KE
mgh = 1/2mv2
gh= v2/2
h = v2/2g
h = 2.5 x 2.5
2 x 10
h = 625
20
h = 3.125m -
- In solids the molecules are held in position by intermolecular forces that are very large. In liquids the molecules are able to roll over one another since the forces are smaller
-
- Volume = 4/3πr3
= 4 / 3 πx 0.253
= 6.54x 10-5 cm3 (2mks) - Area = πr2
= πx102
=314cm2 (2mks) - Ax diameter of molecule=volume
314xd=6.54x10-5
Diameter =2.1x10-7cm (3mks)
- Volume = 4/3πr3
-
-
- The oil is assumed to have spread to thickness of one molecule
- The patch is assumed to be a perfect circle
- The drop is spherical
Any one (1mk)
-
- Sources of errors
- Getting the right oil
- Measuring drop diameter
- Measuring diameter of patch
- Getting drop of a right size (any 2x1=2mks)
-
-
-
- Rate of change of velocity towards the centre
- Acceleration directed towards the centre of the motion
- Acceleration towards the center orbit (1mk)
- The ratio of the distance moved by the effort to the distance moved by the load;( 1mk)
-
- V.R=5
- Efficiency =x100%
=83.33%
-
-
- 2000x5+5000x (-7)=v(2000+5000) √1
V= - 25000
7000
=-3.571m/s √1 (3D.P a must) - Ft=m(v-u) √ or
F= m(v - u)
t
5000 (- 3.571)
0.1
=171,450N√ -
- Initial K.E = ½ x 2000x 52 + ½ x 5000x (-7)2
=147,500J√1
Final = ½ x 7000(-3.571)2
=44,632J√1
Change= 44632-147,500 = -102,868J√1
Kinetic energy is converted to heat sound and deformation
- Initial K.E = ½ x 2000x 52 + ½ x 5000x (-7)2
- 2000x5+5000x (-7)=v(2000+5000) √1
-
- Is the heat required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by 1
- Kelvin√ 1mk.
-
-
- Mass of condensed steam= 160 –(80+60)= 20g;√1mk
- Heat gained by calorimeter water√ 1mk
=MWCW + MCCCθ√ 1mk
=0.08 x 4200 x 2 0+ 0.06 x 390 x 20√1mk
=6720+468√ 1mk
=7188J√ 1mk
-
- Lv = Quantity of heat gained
Mass of steam
L=Q/m - Lv = 7188
0.02
=359;400
=3.59x105 J/kg√ 1mk
- Lv = Quantity of heat gained
-
- Is the heat required to raise the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by 1
-
- The volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature provided pressure is kept constant
- Drawing and labeling of diagram
Method / procedure (5 Marks)- Put some concentrated sulphuric acid in the capillary tube to trap some air.
- attach the tube, thermometer and meter rule using a rubber band as shown
- record the room temperature and height h of air column in the tube
- heat gently the water bath and record the temperature and corresponding heights of air column as suitable temperature intervals
- plot a graph of volume h (which is proportional to the height against temperature reading
- as the temperature rises the height (volume) also increases. The graph is a straight line passing through the origin of the absolute scale.
Conclusion - This shows that at constant pressure the volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature. This is the charle’s law of gases
- heated molecular have higher kinetic energy and higher velocity (V) since pressure is constant the volume of the gas increases with temperature increase
- T1 = 27 + 273 = 300k
T2 = -73 + 273 = 200k
V1 = 300cm3
V2 = ?
V₂ = V₁
T₂ T₁
V₂ = 300 x 200 = 200cm3
300
Download Physics Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Bondo Joint Mocks Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students