QUESTIONS
SECTION A (40 MARKS)
Answer All questions in this section
-
- Explain why people with sickle cefftrait have an advantage of surviving malarial attack than those with normal red blood cells (2mks)
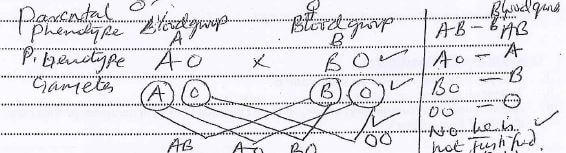
- Mr. Mwasimba accuses his wife of infidelity after the birth of a child. He is heterozygous of blood group A and his wife is heterozygous for blood group B. If the child is blood group o, is Mr. Mwasimba justified in his accusation? Show your working. (4mks)
- State two advantages of polyploidy in plants (2mks)
- A form 1 student placed a red blood cell in a solution and made an observation as follows. Start of experiment/ end of experiment
-
- In what solution was the red blood cell paced? (1 mark)
- Explain the observation above. (2 marks)
- If the red blood cell was replaced by a plant cell what would be the observation. (2 marks)
- Why don't the red blood cell undergo the same changes as above while in the body. (3 marks)
-
- The graph below shows the growth pattern of an organism.
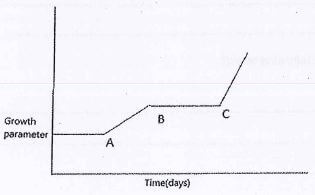
- Name the type of growth curve shown above.
- Name the phylum where organisms shows the above curve
- ame the hormones that influences the growth above.
- Give reasons for the shape of the graph between:
- A and B
- B and C
-
- What is meant by the following terms?
- Adaptive radiation
- Vestigial structures
- Evolution is an ongoing process. State two pieces of evidence which suggest that evolution is still taking place.
- Explain how the following factors influence natural selection.
- Predators (2mks)
- Diseases (2mks)
- What is meant by the following terms?
- The diagram below represents the nitrogen cycle.
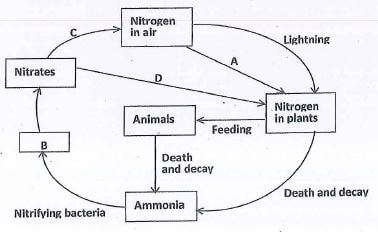
- Identify the processes labelled A and D. (2 marks)
- Name the compound represented by B. (1 mark)
-
- Name the group of organisms labelled C. (1 mark)
- Name the group of plants that promote process A. (1 mark)
- In which part of the plant does process A take place? (1 mark)
- How would excess pesticides in the soil interfere with process A? (2 marks)
Section B
Answer question 6/compulsory) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question 8
- The table below shows how the quantities of urine and sweat vary with external temperature
External temperature (ºC) Urine (cm3/hr) Sweat (cm3/hr) 0 100 5 5 90 6 10 80 10 15 70 20 20 60 30 25 50 60 30 40 120 35 30 200 - On the grid provided, plot the quantities of urine and sweat produced against external temperature (7 marks)
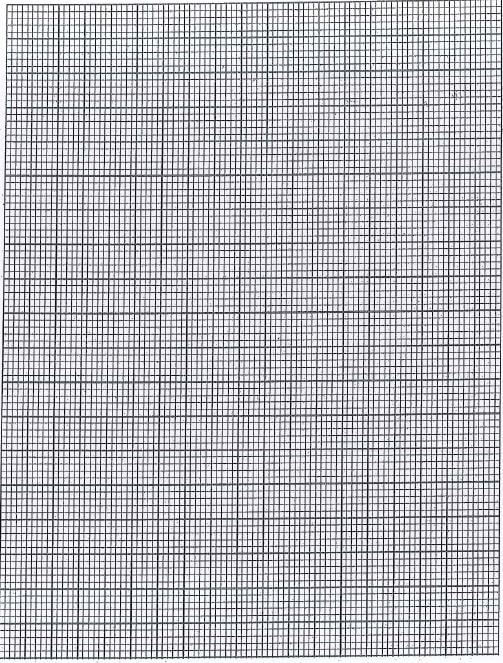
- At what temperature is the amount of sweat and urine produced equal? (1 mark)
- What happens to the amount of sweat produced as the temperature rises? Explain your observation (3 marks)
- Explain the observation made on the amount of urine produced. (3 marks)
- How are the following parts of the mammalian skin adapted for temperature regulation during cold weather? (6 marks)
Hair:
Sweat glands
Blood vessels
- On the grid provided, plot the quantities of urine and sweat produced against external temperature (7 marks)
- Describe how mammalian eye is adapted to its functions. (20mks)
-
- state four characteristics of gaseous exchange surfaces. (4mks)
- Discuss various mechanisms of opening and closing of stomata. (16mks)
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A (40 MARKS)
Answer All questions in this section
-
- Explain why people with sickle cefftrait have an advantage of surviving malarial attack than those with normal red blood cells (2mks)
sicle cell-shaped red blood cells have less surface area to carry the malaria parasite ; hence they cannot carry the parasite that causes the maria disease - Mr. Mwasimba accuses his wife of infidelity after the birth of a child. He is heterozygous of blood group A and his wife is heterozygous for blood group B. If the child is blood group o, is Mr. Mwasimba justified in his accusation? Show your working. (4mks)
- State two advantages of polyploidy in plants (2mks)
leads to increased yields
early maturity
resistant to drought/pests/diseases
- Explain why people with sickle cefftrait have an advantage of surviving malarial attack than those with normal red blood cells (2mks)
- A form 1 student placed a red blood cell in a solution and made an observation as follows. Start of experiment/ end of experiment

-
- In what solution was the red blood cell paced? (1 mark)
hypotonic solution - Explain the observation above. (2 marks)
the red blood cell absorbed water molecules by osmosis; & bursts; swells and bursts
- In what solution was the red blood cell paced? (1 mark)
- If the red blood cell was replaced by a plant cell what would be the observation. (2 marks)
a plant cell will absorb water by osmosis; and become turgid - Why don't the red blood cell undergo the same changes as above while in the body. (3 marks)
red blood cells lack rigid cellulose cell wall; that prevent the plant cells from bursting; when they absorb water hence they burst
-
- The graph below shows the growth pattern of an organism.

- Name the type of growth curve shown above.
intermittent / discontinuous curve - Name the phylum where organisms shows the above curve
arthropoda - ame the hormones that influences the growth above.
juvenile hormone; edysone hormone - Give reasons for the shape of the graph between:
- A and B
rapid growth; due to the shadding off of the exoskeleton initiated by secretion of ecdysone - B and C
constant growth ; due to accumulation of exoskeleton intiated by juvenile hormone
- A and B
- Name the type of growth curve shown above.
-
- What is meant by the following terms?
- Adaptive radiation
- Vestigial structures
- Evolution is an ongoing process. State two pieces of evidence which suggest that evolution is still taking place.
natural selection in action; resistance to drugs; (pesticides and antibiotics) - Explain how the following factors influence natural selection.
- Predators (2mks)
- Diseases (2mks)
- What is meant by the following terms?
- The diagram below represents the nitrogen cycle.

- Identify the processes labelled A and D. (2 marks)
A - fixation
D - absorption - Name the compound represented by B. (1 mark)
nitrite -
- Name the group of organisms labelled C. (1 mark)
- Name the group of plants that promote process A. (1 mark)
- In which part of the plant does process A take place? (1 mark)
root nodule
- Name the group of organisms labelled C. (1 mark)
- How would excess pesticides in the soil interfere with process A? (2 marks)
it bills the rhizobium/bacteria hence no fixation
- Identify the processes labelled A and D. (2 marks)
Section B
Answer question 6/compulsory) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question 8
- The table below shows how the quantities of urine and sweat vary with external temperature
External temperature (ºC) Urine (cm3/hr) Sweat (cm3/hr) 0 100 5 5 90 6 10 80 10 15 70 20 20 60 30 25 50 60 30 40 120 35 30 200 - On the grid provided, plot the quantities of urine and sweat produced against external temperature (7 marks)

- At what temperature is the amount of sweat and urine produced equal? (1 mark)
24ºC ± 0.5 - What happens to the amount of sweat produced as the temperature rises? Explain your observation (3 marks)
sweat production increases with increase in temp; high temp increases the evaporation rate and hence more sweat converted to vapour. This loses latent heat of vapourisation from the body hence cooling; - Explain the observation made on the amount of urine produced. (3 marks)
an increase in temp decreases the amount of urine produced; this is due to sweating that raises the osmotic pressure of blood alot of water is then reabsorbed into the blood from the kidney tubules resulting in production of little concentrated urine - How are the following parts of the mammalian skin adapted for temperature regulation during cold weather? (6 marks)
Hair: when erectapili muscles contract; causes hair to stand erect and trap air which act an insulator against heat loss;
Sweat glands: when cold sweat gland releases less sweat; hence less evaporation leading to less heat loss;
Blood vessels: when cold blood vessels constrict ; less blood flows near skin surface reducing heat loss by radiation
- On the grid provided, plot the quantities of urine and sweat produced against external temperature (7 marks)
- Describe how mammalian eye is adapted to its functions. (20mks)
Sclera/sclerotic layer; white fibrous layer; made up of thick connective tissue, protects the eye; maintains shape of eyeball; Cornea; transparent; disc-shaped layer; that allows light to enter the eye; refracts light towards the retina; Conjunctiva; delicate membrane; lining the inside of the eyelid; protects the cornea/eye; Eyelids and eye lashes; thin muscle with hairs; protects the cornea/eye from mechanical/chemical damage/protects the eye from entry of foreign particles protects retina from bright light; Choroid; dark pigmented and membranous layer; that prevents light reflection within the eye/absorbs light; to prevent distortion of the image; has blood vessels; that nourish eye/retina/supply oxygen/remove carbon (IV) oxide and wastes; extends to form the ciliary body and iris; Ciliary muscles have elastic muscles that contract and relax; to alter shape/curvature of lens curing accommodation; Ciliary body; thickened front edge of the choroids layer; that produces aqueous humour; Suspensory ligaments; made up of elastic connective tissue whose contraction and relaxation helps to adjust the shape of lens during accommodation/holds lens in position; Lens; transparent; biconvex; balloon-like; it refracts light rays/focus light onto the retina; Vitreous humour; nourishes cornea/lens; refraction of light; maintains eyeball shape; Iris; thin circular ring; with circular and radial muscles; it gives eye colour/absorbs light; controls the amount of light entering the eye/adjusts size of pupil; Pupil; an aperture through which light enters the eye; Retina; has photoreceptor cells/roc's/cones for image formation; generates impulses to the brain for interpretation; Fovea/Yellow spot; with only cones; for high visual acuity/most sensitive part of the retina Blind spot; point where nerve fibres emerge from the optic nerve/where optic nerve leaves eye/point where nerve fibres and blood vessels enter the eye; Optic nerve; transmits impulses to the brain; Muscles; inferior and superior oblique muscles; move eye from left to right; superior and inferior rectus muscles; move the eye up and down; external and internal rectus muscles steady the eye in its up and down movement; Tear/Lachrymal glands, secrete a watery and saline fluid containing lysozymes/lytic enzymes/is antiseptic (tears); that moisten the conjunctiva and cornea; washes away d ist and other foreign objects; kills microorganisms entering the eye; Max. 20 mks -
- state four characteristics of gaseous exchange surfaces. (4mks)
- Discuss various mechanisms of opening and closing of stomata. (16mks)
Moist; Highly vascularized; Thin walled; Large surface area; Well ventilated. 4mks) Discuss the various mechanisms of opening and closing of stomata Photosynthetic theory; during the day, guard cells carry out photosynthesis manufacturing glucose; This increases the osmotic pressure of the sap vacuole; which becomes higher than that of the neighbouring epidermal cells; guard cells therefore take in water by osmosis; and become turgid; the outer thin wall stretches easily; pulling the thicker inner wall outwards; thus the stomata opens; At night, there is no light hence no photosynthesis takes place; plant cells respire using up more glucose; the osmotic pressure of the sap vacuole of the guard cells reduces; becoming lower than the neighboring epidermal cells; the guard cells lose water by osmosis; to adjacent epidermal cells; they then become flaccid; pulling together the thick inne walls, and stomata closes; Enzymatic interconversion between starch and glucose/sugar; At day time, plants continuously use carbon (IV) oxide for photosynthesis; leading to an increase in the pH of the guard cells; this causes tarch to be converted to sugar/glucose; the glucose increases the osmotic pressure of the guard cells; hence water is taken in by osmosis; the cells become turgid and bulge outwards; causing the stomata to open; At night, no photosynthesis occurs but respiration takes place; carbon (IV) oxide accumulates in guard cells; lowering the pH; the low pH favors conversion of glucose into starch; starch is osmotically inactive; this lowers the osmotic pressure of guard cells; guard cells therefore lose water by osmosis to the adjacent epidermal cells; beco'ne flaccid; pulling together the thick inner walls; and the stomata closes; Active ion exudation; during the day, there's an accumulation of potassium and sodium ions; as a result of active pumping of the ions by the ATP formed through photosynthesis; carbon (IV) oxide fixation occurs in the guard cells; the guard cells become turgid; and stomata open; At night, before the stomata close, the ions diffuse out of the guard cells into epidermal cells; the osmotic pressure of guard cells is lowered; they lose water to epidermal cells by osmosis; and become flaccid; thereby closing the stomata; Max. 16 mks
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Mangu High School Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
