QUESTIONS
SECTION A (30 MARKS)
Answer ALL Questions in this section.
- State two economic effects of HIV/Aids on agriculture.
- State three guidelines used in coming up with a crop rotation programme.
- Give four factors to consider when planning a farm.
- Outline four functions of trees in soil conservation.
- List three factors that affect the selectivity and effectiveness of herbicides.
- Distinguish between the terms below as used in pasture utilization.
- carrying capacity
- stocking rate
- Why is it not advisable to use manure in carrot production
- State two methods of frame formation in tea.
- Give two reasons why processing of raw materials is important.
- State two ways in which agriculture contributes to the development of industries.
- State three biological factors that influence the weathering process.
- Give three qualities of trees used in agro forestry.
- List three common risks and uncertainties in most farms.
- Give two financial statements a farmer may prepare on a well organized farm.
- List two liming elements in agriculture.
- State three causes of fragmentation and land sub-division.
- Give two disadvantages of feeding livestock on lush pasture.
- Give two examples of working capital in a poultry enterprise.
-
- Give three advantages of drip irrigation
- State two surface water sources on the farm
- State two ways of increasing labour efficiency in the farm.
SECTION B (20 MARKS)
Answer ALL questions in this section
- The diagram below shows an illustration of a method of crop propagation. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
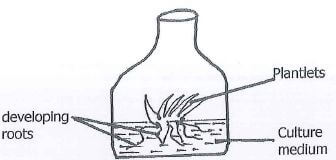
- Identify the method
- Name two ways of inducing the rooting in plantlets.
- Outline two disadvantages of the method shown above.
- The diagram below shows a method of silage preparation. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
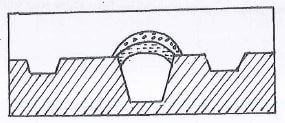
- Identify the structure.
- State one way of improving the palatability of silage.
- What is the importance of chopping silage material before ensiling.
- Give two ensiling losses in silage making,
- Study the illustration below and answer the questions that follow.
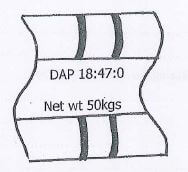
- What do the figures labeled on the diagram stand for.
- A farmer was advised to apply 20kg of N, 30kg of phosphorus and 10kg of potassium. The fertilizers available are CAN (20%N), SSP (10%P2O5) and KCI (20%K2O). Calculate the amount of each fertilizer the farmer needs to apply on his farm. Show your working.
- The diagram below is of a tea cutting. Study it carefully and answer the questions that follow.
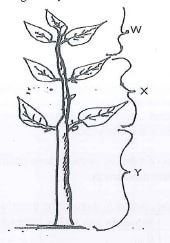
- Which part of the branch is the most appropriate for raising a new seedling.
- Give reasons for your answer in (a) above.
- Give four reasons why farmers are advised to raise tea in polythene sleeves.
- State two factors that promote rooting in cuttings.
- What is the name given to a stem cutting used to propagate sugarcane.
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
Answer any TWO questions from this section in the spaces provided after the question.
-
- Discuss the production of Napier grass (pennisetum perpureum) under the following headings.
- Ecological requirement (3mks)
- Land preparation (3mks)
- Establishment and management. (3mks)
- Utilization (2mks)
-
- Explain the benefits of a mixed grass-legume pasture over pure grass pasture.(5mks)
- State four effects of late defoliation (4mks)
- Discuss the production of Napier grass (pennisetum perpureum) under the following headings.
- Use the data from the table below to answer the questions that follow.
Unit of labour input Maize in kgs yield Marginal product Average product 0 0 1 600 2 1800 3 3000 4 3600 5 3700 6 3600 7 3400 - Calculate and fill the columns for:
- Marginal product. (7mks)
- Average product. (7mks)
- Assume the cost of labour in (i) above is Kshs.200 per day and the price of maize to be Kshs.20 per unit
- Calculate the value of the maize yield produced against the corresponding units of labour inputs. (2mks)
- Calculate the cost of labour for producing various quantities of maize given in the table. (2mks)
- Determine from (b) above the most profitable level of production. (2mks)
- Calculate and fill the columns for:
-
- Discuss the factors that determine the spacing of crops.
- Explain the importance of the following practices in crop production.
- Chitting
- Seed dressing
- Seed innoculation
- Earthing up
- Rogueing
- State reasons for raising seedlings in a nursery.
MARKING SCHEME
-
- Shortage of farm labour.
- Increase cost of living of Aids patients and their relatives.
- Low food supply and poverty in general
- Resources that could be used in agriculture are used in treatment.
-
- Crop root depth
- Crop nutrient requirements
- Weed control
- Pest and disease control
- Soil fertility
- Soil structure
-
- Size of the farm.
- Climatic conditions
- Security
- Government policy
- Communication and transport facilities
- Available resources.
- Expected returns
- Farmer's objectives and performance.
-
- They intercept the raindrops therefore reducing splash erosion
- They reduce the surface evaporation by providing shade.
- They reduce wind speed thereby minimizing wind erosion.
- The trees bind soil particles together.
- They slow down theerosive of forces water hence reducing erosion.
-
- Stage of plant growth.
- Plant morphology and Anatomy
- Herbicide characteristics.
- Environmental factors
- Carrying capacity - This is the ability of the forage stand to maintain a particular number of livestock units per unit area.
Stocking rate - This is the number of animals maintained per unit area of land. -
- It leads to forking
- It leads to bursting
-
- Formative pruning
- Pegging
-
- Increase shelf life of a commodity.
- Transforms commodities into utilizable forms.
- Reduces bulkness and therefore eases storage.
- Makes commodities easy to handle.
- Improves flavour of a commodity.
-
- Agriculture supplies raw materials to the industries.
- Agriculture provides market for industrial goods.
- Agriculture provides capital which is used to start industries.
-
- Large animals
- Soil organisms and micro-organisms
- Human activities
- Plant roots.
-
- Fast growth
- Deep rooted
- Nitrogen fixing
- Good in by products.
- Have appropriate canopy (should not shade the other crops)
- Should be nutritious and palatable.
- Should not be allelopathic to crops
-
- Weather changes
- Theft of crops/livestock/machines
- Outbreak of pests and diseases
- Health of the farmer
- Accidents to employees/employer
- Fire
- Price fluctuation
-
- Balance sheet
- Profit and loss account
- Cash analysis
-
- Sulphur
- Magnesium
- Calcium
-
- Shifting cultivation
- Buying several pieces of land scattered
- Farmer sub-dividing land to his heirs.
- Accumulation of land holdings by money lenders.
- Land offered to pay debts.
-
- High moisture content which depresses DM intake
- Low total digestible nutrients
- Less laxative effects
- Bloat
-
- Casual labour
- Fuel
- Feeds
- Drugs
-
- Little amount water used.
- Water under low pressure can be used.
- Discourages fungal diseases such as blight
- Discourages the growth of weeds between the rows
-
- Training
- Supervision
- Mechanization
- Giving incentives e.g. promotions and rewards
- Provide welfare services for workers e.g. medical, housing etc.
- Assigning specific duties
-
- Tissue culture.
-
- Use of culture medium with correct nutrients
- Use of growth regulators e.g. hormones.
- Introducing correct light intensity.
- Providing correct temperature and relative humidity.
-
- Can only be done under specific structures e.g. green houses and laboratories.
- Requires high level of sanitation.
- Requires high skills and careful handling.
-
- Trench silo
- Adding feed addictives.
- For easy compaction.
- Through seepage
Evaporation
-
- 18%N, 47% P2O5, 0% K20
- Amount of CAN
100% kg of CAN contain 20 kg N
What about 20kg N.
100 - 20N
?-20
20x100 = 100kgCAN
20
Amount of Phosphorus
100kg DSP-10% Phosphorus
100x30 = 300kg SSP
10
Amount of Potassium required 10kg
100 - 20
? - 10
10x100 = 50kg Muriateofpotash
20
-
- X
- Not too succulent/soft or too mature because when it is too succulent/soft it can rot faster or too much mature, cannot rot easily.
-
- For easy transplanting
- Roof system is not disturbed during transplanting.
- Can be carried over a long distance
- Seeds can easily be stored before transplanting.
-
- Temperature
- Oxygen amount
- Chemical treatment
- Relative humidity
- Leaf area
- Light
- Sett
-
-
- Ecological requirements
- Attitude range 0 -2100 above sea level
- Rainfall of atleast 750mm per annum
- Temperature range of 24°C -29°C.
- Soil pH of 6.5
- Fertile soil with free drainage.
- Land preparations
- Should be done during the dry season.
- Clear the vegetation and remove stumps.
- Carry out primary cultivation.
- Harrow/carry out secondary cultivation.
- Harrow the land to medium tilth.
- Make furrows/holes at spacing of 90 - 100 x 50cm
- Crop establishment and management
- Apply manure i.e. 7-10 tonnes of well rotten organic manure per hectare.
- Use stem cutting or splits of selected varieties. Stem cuttings to have 2-3 nodes.
- Plant the materials at the onset of rains.
- Apply NPK fertilizer at the rate of 200kg/ha at planting time.
- Plant the cuttings at a slanting manner and at appropriate depth.
- Cover the furrows/holes adequately i.e. 2 nodes to be underground and a node above the soil surface.
- Control weeds early by inter-row cultivation and uprooting.
- Top dress using nitrogen fertilizers at the rate of 200kg/ha.
- Defoliation is done from 6-8 weeks after planting depending on rainfall availability.
- Utilisation
- When ready, Napier grass is cut and fed to livestock. (i.e. when 3-5 months old)
- Excess Napier grass is conserved as silage for future use.
- Can be cut, dried and used as mulching material.
- Ecological requirements
-
-
- Makes maximum use of soil nutrients because of different nutrient requirements.
- Reduces soil erosion because of good coverage.
- Increases soil fertility, due to Nitrogen fixation.
- There is better distribution of growth e.g. a mixture of early and late maturing varieties.
- There is economical use of fertilizers in mixed pasture.
- Has better weed control effect. - Yields are higher per unit area of land than pure grass alone.
- It is more nutritious than pure grass i.e. more palatable.
- Ensures security against total loss due to attack by pests, diseases, bad weather etc (hence a way of diversification)
-
-
-
-
Unit of labour input Maize in kgs yield Marginal product Average Product - - 600 600 1200 900 1200 1000 600 900 100 740 -100 600 200 500 -
- value of maize produced
Mark as a whole if any unit is missing candidate loses the 2mksunits of labour value of maize 0 0 1 600 x 20 = 12000 2 1800 x 20 = 36000 3 3000 x 20 = 60000 4 3600 x 20 = 72000 5 3700 x 20 = 74000 6 3600 x 20 = 72000 7 3400 x 20 = 6800 - cost of labour
Mark as a whole if any unit is missing candidate loses the 2mksunits of labour value of maize 0 0 1 200 2 400 3 600 4 800 5 1000 6 1200 7 1400
- value of maize produced
- The level of 5 units of labour when the value of maize is Kshs.74000 against Kshs. 1000 for labour.
-
-
-
- Growth habit of the crop
- Type of machinery to be used.
- Fertility of the soil
- The size of the plant.
- Moisture availability
- Use of the crop
- Pests and disease control
-
- Chitting
- Ensures faster establishment
- Ensure uniform germination
- Maximum use of the rains
- Seed dressing
- Seeds are dressed with appropriate chemicals to control soil borne pests and diseases.
- Seed inoculation - Application of appropriate Rhizobia on legume seeds to promote nitrogen fixation.
- Earthing up
- heaping soil around the roof zone of the crop.
- Preserve moisture
- Support/prevent lodging
- Easier harvesting of tuber crops
- Easier of enlargement of tubers
- Brings nutrients closer to the crop roots.
- To control soil erosion.
- Roguing
- uprooting and destroying of infected crops.
- Helps in preventing further spread of diseases and pests to health crops
- Chitting
-
- Easy to carry out routine management practices.
- Easy to select health and vigorous growing seedlings
- Favours germination of tiny seeds
- Excess seedlings can be sold
- Enhances fasters maturity in the main seed bed.
-
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Mangu High School Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
