INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your Name, Index Number and School in the spaces provided above.
- Sign and write the Date of the examination in the spaces above.
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided in the question paper.
- Mathematical tables and silent scientific calculators may be used.
- ALL the working must be clearly shown where necessary.
FOR EXAMINER’S USE ONLY
|
QUESTIONS |
MAX SCORE |
CANDIDATE’S SCORE |
|
1 – 28 |
80 |

QUESTIONS
- The set-up below represents apparatus that may be used to separate a mixture of two miscible liquids “C” and “D” whose boiling points are 80ºC and 100ºC respectively.
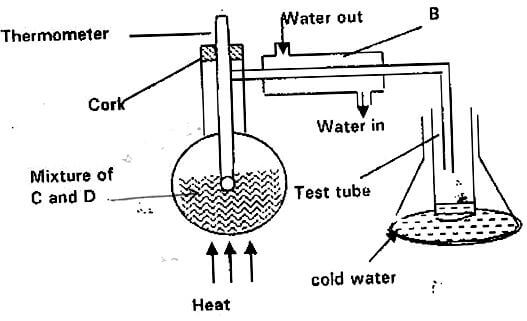
- Name B. (1mk)
- What is the purpose of the thermometer? (1mk)
- Which liquid is collected in the test tube? (1mk)
- The table below gives some properties of gas D and E.
Gas
Density
Effect on H2SO4
Effect on NaOH
D
Lighter than air
React to form salt
Dissolve without reacting
E
Heavier than air
Not affected
Not affected
- Describe how you would obtain a sample of gas E from the mixture of gas D and E. (2mks)
- Suggest a possible identity of gas D. Give reasons for your answer. (2mks)
-
- What is meant by a strong base? (1mk)
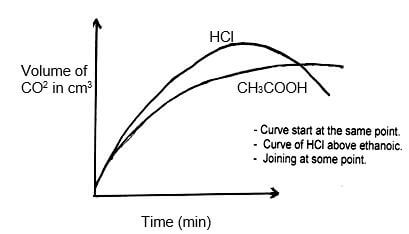
- In an experiment, 20cm3 of 2M hydrochloric acid was reacted with excess sodium carbonate and the volume of carbon (IV) oxide produced recorded with time. In another experiment, the same volume and concentration of ethanoic acid was also reacted with excess sodium carbonate and the volume of carbon (IV) oxide produced recorded with time.
On the grid below, sketch and label the curves if the volumes of carbon (IV) oxide were plotted against time.
(2mks)
- The set-up below was used to obtain a sample of Iron.
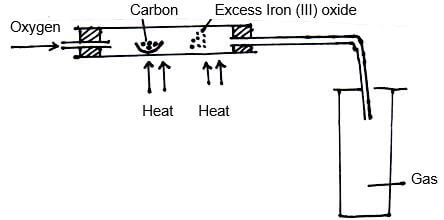
Write two equations for the reactions which occur in the combustion tube. (2mks) - Give the name of the product formed when magnesium reacts with phosphorus. (1mk)
- The table below gives the energy required to remove the outer most electrons from same group.
Arrange the elements in the order of their reactivity starting with the most reactive. (2mks)Elements
I
II
III
IV
Energy kJ / Mole
494
418
519
376
- The electronic structures for elements represented by letters A, B, C and D are:-
A = 2:8:6 B = 2:8:2 C = 2:8:1 D = 2:8:8- Select the element which forms:
- Double charged cation. (1mk)
- A solobule carbonate (1mk)
- Which element has the smallest atomic radius? (1mk)
- Select the element which forms:
- State any two differences between luminous flame and non luminous flame. (2mks)
- The apparatus shown below was used to investigate the effect of carbon (II) oxide on Copper (II) oxide.
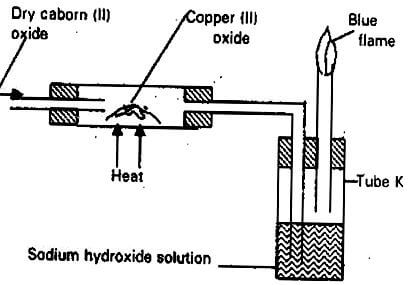
- State the observation that was made in the combustion tube at the end of the experiment. (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction that took place in the combustion tube. (1mk)
- Why is it necessary to burn the gas coming out of tube K? (1mk)
-
- State Graham’s Law of Diffusion. (1mk)
- If it takes 30 seconds for 100cm3 of carbon (IV) oxide to diffuse across a porous plate, how long will it take 150cm3 of nitrogen (IV) oxide to diffuse across the same plate under similar conditions? (C = 12.0, N = 14.0, O = 16.0) (2mks)
-
- Given the IUPAC names of the following compounds:- (2mks)
- CH3(CH2)CH2OH
- CH3CH2CH(CH3)COOH
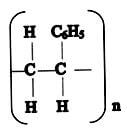
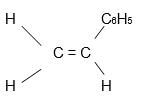
- Given the following polymer, draw the structure of the monomer. (1mk)
- Given the IUPAC names of the following compounds:- (2mks)
- In an experiment, various volumes of 1M sodium iodide solution was added to the same volume of 1M lead (II) nitrate solution. The height of the precipitate were measured and plotted against volume of 1M sodium iodide used. The graph below was obtained.
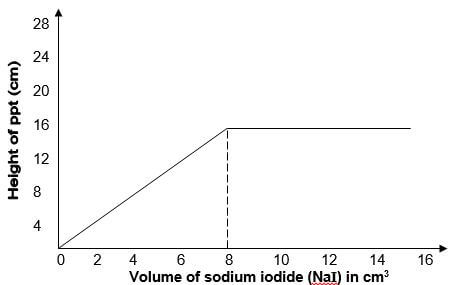
- State the observation made when sodium iodide solution is mixed with lead (II) nitrate solution. (1mk)
- What volume of sodium iodide was required to react completely with lead (II) nitrate? Explain. (1mk)
- Explain the shape of the curve. (1mk)
- When excess zinc powder is added to 30cm3 of solution containing copper (II) ions and the mixture stirred, the temperature is noted to have risen by 150C.
- State the observation made after stirring the mixture. (1mk)
- Calculate the heat change for the reaction (specific heat capacity of H2O = 4.2KJkg-1k-1) (2mks)
- When bismuth (III) chloride is added to water, a reaction occurs and a white precipitate forms as shown below.
BiCl3(aq) + H2O(l) ↔ BiOCl(s) + 2HCl(aq)
What would be the effect on the amount of the precipitate formed if sodium hydroxide solution is added to the equilibrium mixture? Explain your answer. (2mks) - The flow chart below shows some process in extraction of lead metal. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
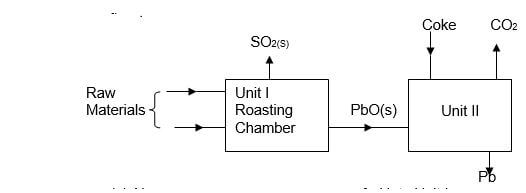
- Name two raw materials that were fed into Unit I. (1mk)
- State one environment hazard associated with the process in Unit I. (1mk)
- What is the function of coke in unit II? (1mk)
-
- Radioactive Polonium – 216 decays as shown below.
216 → 208 + M + nβ
84Po 82Pb
Determine the value of m and n. (2mks) - The table below gives the rate of decay of a radioactive element y.
Calculate the half-life of the radioactive element y. (2mks)Number of days
Mass in g
0
48
270
1.5
- Radioactive Polonium – 216 decays as shown below.
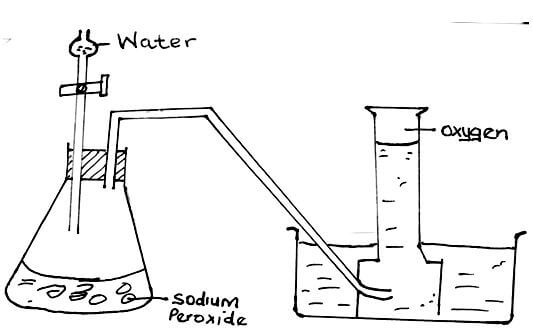
- Water reacts with sodium peroxide forming sodium hydroxide and oxygen gas. Draw a well labelled diagram showing how a sample of oxygen gas can be prepared and collected in the laboratory using the above reagents. (3mks)
- 15g of sodium chloride was dissolved in 120cm3 of distilled water. Calculate the concentration of the resulting solution in moles per litre. (Na = 23, Cl = 35.5) (3mks)
-
- State Boyle’s law. (1mk)
- The volume of a gas at 30ºC and 780mmHg is 400cm3. What will be its volume at 50ºCat 600mmHg. (2mks)
- Sulphur exhibits allotropy.
- What is allotropy? (1mk)
- Name the two allotropes of sulphur. (1mk)
- Sulphur powder was placed in a deflagrating spoon and heated on a Bunsen burner.
- State the observation made. (1mk)
- The product obtained was dissolved in water. Comment on the PH of the solution formed. (1mk)
-
- A luminous flame has a yellow zone. Explain how the yellow zone is produced. (1mk)
- Explain why a non-luminous flame is preferred for heating substances in a laboratory.(2mks)
-
- State two differences between the terms electrolyte and non-electrolyte. (2mks)
- Graphite is a non-metal yet it conducts electric current. Explain. (1mk)
- 0.318g of an oxide of metal M was completely reduced by hydrogen gas to 0.254g of metal. Calculate empirical formula of the metal oxide. (M = 63.5, O = 16). (3mks)
- In an experiment to electroplate iron with silver, a current of 0.5A was passed through a solution of silver nitrate for 60 minutes.
- Give two reasons why it is necessary to electroplate iron with silver. (1mk)
- Calculate the mass of silver that was deposited on iron. (Ag = 108, 1 Faraday = 96500C).(2mks)
- Given the following reagents: solid sodium carbonate, water, solid lead (II) nitrate. Describe how a sample of lead (II) carbonate can be prepared in the laboratory. (3mks)
- The set-up below was used to prepare a sample of an organic compound X.
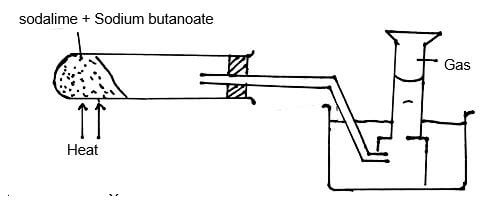
- Identify gas X. (1mk)
- Write the equation for the reaction that produces gas X. (1mk)
- 1 Mole of Chlorine was reacted with gas X in presence of sunlight.
- State one observation made. (½mk)
- Name the major product formed. (½mk)
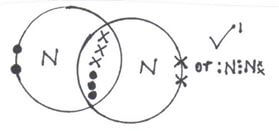
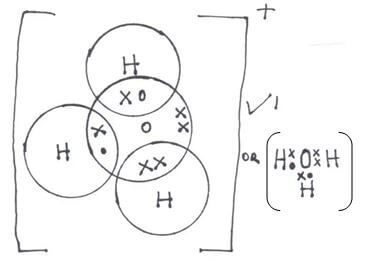
- Draw dot (•) an cross (x) diagram to show bonding in:
- Nitrogen molecule (N2) (1mk)
- Hydroxonium ion. (H3O+) (1mk)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
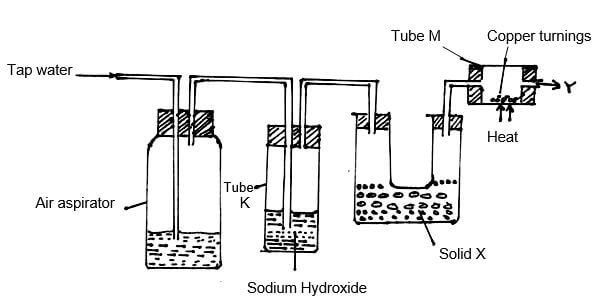
- What is the purpose of passing tap water through the air aspirator? (1mk)
- State and explain the observation that would be made in tube M after sometime. (1mk)
- The sample of nitrogen collected at point Y had greater density than expected. What conclusion could be made about the gas? (1mk)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Liebig’s condenser.
- Determine the point at which one of the liquids in a mixture has evaporated completely. Temperature tends to remain constant when one liquid in a mixture is evaporating.
- Liquid ‘C’ since it is more volatile.
-
- Pass the mixture of gas “D” and “E” through sulphuric acid. Gas “D” will react to form salt – leaving behind gas “E”. Collect gas E by downward delivery / upward displacement of air since it is heavier than air.
OR
Pass a mixture of gas “D” and “E” over sodium hydroxide. Gas “D” will dissolve but gas “E” will not be affected. Collect gas “E” by downward delivery. - Ammonia gas (HN3)
Ammonia is lighter than air. It reacts with acids to form salt since itself is basic. It does react with sodium hydroxide since both are basic but will dissolve in it without any reaction.
- Pass the mixture of gas “D” and “E” through sulphuric acid. Gas “D” will react to form salt – leaving behind gas “E”. Collect gas E by downward delivery / upward displacement of air since it is heavier than air.
-
- A strong base is a substance that dissociate, completely to produce many hydroxide ions.
-
- 2C(s) + O2(g) → 2CO(g)
2CO(s) + Fe2O3(s) → 2Fe(s) + CO2(g) - Magnesium phosphide.
- IV, II, I, III
-
-
- B
- C
- D
-
-
- LUMINOUS NON LUMINOUS
Sooty Flame Non-sooty
Produce more light Less light
Less heat Very hot
Weavy flame Steady flame
(any 2 mentioned @ 1mk)
- LUMINOUS NON LUMINOUS
-
- Colour of solid changed from black to reddish brown.
- CuO(s) + CO(g) → Cu(s) + CO2(g)
- CO is poisonous.
-
- Under the same condition of temperature and pressure, the rate of diffusion of gas is inversely proportional to the square root of its density.
-

-
-
- Propan - I – ol
- 2-Methylbutan-I-oic
-
-
-
- A bright yellow precipitate formed.
- 8cm3 – the graph flattens //
- PbNO3 used up. - -Volume lower than 8cm3of NaI, Pb(NO3)2 was in excess.
- At 8cm3 the ratio of moles of Pb2+ ions to Cl- ions was 1:2
- After 8cm3 the I- ions are in excess, all Pb2+ ions are used up.
-
- - Blue solution changes to colourless // pale blue.½
- Brown solid is deposited. ½ - ΔH = MCΔT
= 0.03kg x 4.2kJkg-1k-1 x 15k
= 1.89kJ
= -1.89kJ
- - Blue solution changes to colourless // pale blue.½
- Increased 1
HCl is reduced, thus the rate of forward reaction is favoured. 1
// NaOH neutralizes HCl hence the concentration of HCl is reduced and the reaction proceeds faster in the forward direction to produce more HCl and hence the precipitate. -
- Lead sulphide
Air / Oxygen ( ½ mk each) - SO2 leads to formation of acid rain
SO2 causes respiratory infection. (any mentioned 1mk) - Reduces Lead (II) oxide into lead metal.
- Lead sulphide
-
- 216 = 208 + 4M 84 = 82 + 4 + n
216 – 208 = 4M
4M = 8 84 – 86 = n
M = 2 n = -2 = 2 -

5t ½ = 270
t ½ = 270 = 54 days
5
Or
N1 = No(½) T/t½ 5t ½ = 270
1.5 = 48 (½) 270/t½ t½ = 270
48 5
1 = (½)270/t½ t ½ = 54 days
32
( ½)5 = ( ½)270/t½
- 216 = 208 + 4M 84 = 82 + 4 + n
-
- No. of moles = m
R.f
= 15
58.5
= 0.25641 moles
Molarity = No. of moles
Volume in litres
= 0.25641
0.12
= 2.13675M -
- Boyles law states that the volume V1 of a fixed mass of a gas is inversely proportional to its pressure P1 when temperature is kept constant.
- P1V1 = P2V2
T1 T2
780 x 400 = 600 x V2
303 323
V2 = 323 x 780 x 400
303 x 600
= 554.3234cm3
-
- Allotropy – existence of an element in more than one structural form in the same physical state.
- Rhombic / ½
Monoclini // β½ -
- Blue flame (1mk) // pungent smell
- Acidic (1mk) // low pH
-
- Produced when unburnt carbon glows. 1
- - It is hot.
- Does not produce soot which makes apparatus dirty.
-
- Electrolytes are melts or aqueous solutions which allow electric current to pass through them and are decomposed by it while non-electrolyte are melts or aqueous solutions which do not conduct electric current.
- Electrolytes contain mobile ions while non-electrolytes contain molecules. - Graphite has delocalized electrons in its structure which carry electric current.
- Electrolytes are melts or aqueous solutions which allow electric current to pass through them and are decomposed by it while non-electrolyte are melts or aqueous solutions which do not conduct electric current.
- Ratio M O
Moles 0.254 0.64 ½
63.5 16
0.04 0.04 ½
Ratio 1 : 1 ½
E.F = MO 1 -
- Prevent rusting ½
Improve appearance ½ - Q = 0.5 x 60 x 60 ½
= 1800C
Ag+ + e → Ag ½
96500C → 108g
1800 → 1800 x 108 ½
95600
= 2.0145g ½
- Prevent rusting ½
- - Add water to Lead (II) nitrate to obtain Lead (II) nitrate solution. ½
- Add water to sodium carbonate to obtain sodium carbonate solution. ½
- Mix the two solutions to ppt Lead (II) carbonate. 1
- Filter to obtain Lead (II) carbonate as a residue.½
- Wash the residue and dry between filter papers. ½ -
- Propane.
- CH3CH2CH2COONa + NaOH → Na2CO3 + C3H8 ignore state symbols.
-
- Green – yellow chlorine turns colourless.
- Chloropropane
-
-
-
- Aluminium has more protons than Mg, hence a greater nuclear charge than Mg, resulting in stronger metallic bases in Al than in Mg.
- During the manufacture of nitrogen and oxygen gases. (2mks) -
- To displace the air in the aspirator.
- A black solid (1mk); copper (II) oxide is formed // copper is oxidized to copper (II) oxide.
- Magnesium nitride. (1mk).
-
Download Chemistry P1 Questions and Answers - Mangu High School Trial Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students