- The table below gives elements represented by letters T, U, V, W, X, Y and their atomic numbers. Use the information to answer the questions below. (Letters are not the actual symbols).
Element
T
U
V
W
X
Y
Atomic number
12
13
14
15
16
17
Electron arrangement
- Complete the table by giving electron arrangement of each of the elements. (3mks)
- In which period of the periodic table do these elements belong? Give a reason. (1mk)
-
- How does the atomic radius of V compare with that of X? (1 mk)
- Give the formula of the compound that could be formed between U and X. (1mk)
-
- Arrange the species T, T- and T+ in increasing order of size. (1mk)
- Which of the ions X2+ and X2- is the most stable? Explain. (2mks)
- Give the formula of:
- Any one of the acid anhydride……………………………………… (1mk)
- The chloride of U ……………………………………………………. (1mk)
- The reaction between 0.65g of zinc granules and excess of 0.5M hydrochloric acid was followed by measuring the amount of gas produced. The following results were obtained
Time (sec)
0
30
60
90
120
150
180
210
240
270
Total volume of gas at r.t.p (cm3)
0
80
140
190
220
230
240
240
240
240
- Plot a graph of volume of gas produced against time. (3mks)
-
- Write an equation for the reaction taking place. (1mk)
- How would the gas produced be identified? (1mk)
- Why is an excess of an acid used? (1mk)
- From the graph:
- What is the volume of the gas evolved at 75 seconds? (1mk)
- At what time is the reaction complete? (1mk)
- On the same graph, sketch the curves that you expect if the experiment was repeated under the same conditions but using:
- 4M hydrochloric acid instead of 0.5M hydrochloric acid. Label the graph X. (1mk)
- Zinc powder (same quantity) was used in place of granulated zinc. Label the graph Y. (1mk
- Calculate the volume of the gas that would be produced at r.t.p from 13g of zinc. (Zn = 65.0, molar gas volume at r.t.p. = 24.0dm3) (2mks)
- The table below gives the standard reduction potentials of some elements represented by letters U, V, W, X and Z. (They are not the actual symbols)
Element
Standard electrode potentials (volts)
U
-2.36
V
+0.34
W
+0.79
X
0.00
Z
-0.76
- Identify the strongest reducing agent. Give a reason for your answer. (1 mk)
- Which two half cells would produce the highest e.m.f. Determine the e.m.f that would be produced. (2mks)
- What would element X represent? (1mk)
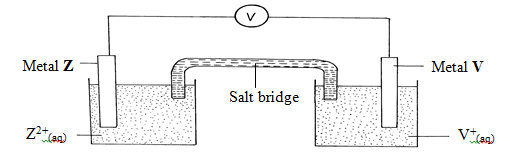
- Elements V and Z were connected to form an electrochemical cell as shown in the diagram below
- Write the equation for the reaction that occurs at:
Metal Z electrode. (1mk)
Metal V electrode. (1mk). - Write the cell representation for the above electrochemical cell. (1mk)
- Determine the e.m.f of the above cell. (1mk)
- Write the overall cell reaction indicating the e.m.f (1mk)
- Give one use of electrochemical cells. (1mk)
- State one use of a salt bridge, and name two salts that can be used in the salt bridge.
Use. (1mk)
Salts (1mk)
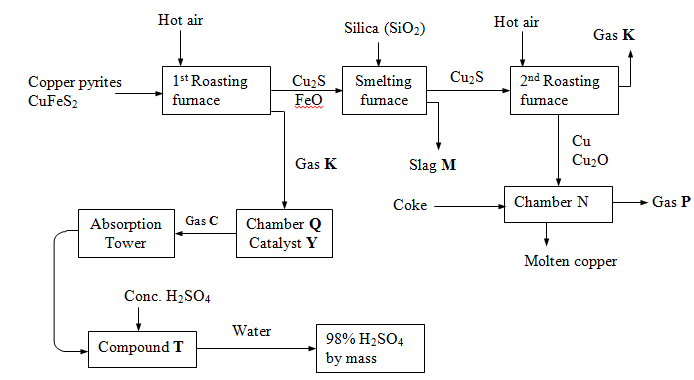
- The flow chart below outlines some of the processes involved during extraction of copper from copper pyrites. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify:
- Gas K………………………………………………………………… (1mk)
- Gas P………………………………………………………………… (1mk)
- Write equations for the reactions that takes place in the
- 1st Roasting furnace (1mk)
- Absorption tower (1mk)
-
- Write the formula of the Cation present in the slag M (1mk)
- What name is given to the reaction that takes place in chamber N? Give a reason for your answer. (1mk)
-
- Name catalyst Y ……………………………………………………….. (1mk)
- State two uses of sulphuric (VI) acid. (1mk)
-
- The copper obtained from chamber N is not pure. Draw a labeled diagram to show the set-up you would use to refine the copper by electrolysis. (2 mks)
- Given that the mass of copper obtained from the above extraction was 210kg, determine the percentage purity of the ore ( copper pyrites), if 810kg of it was fed to the 1st roasting furnace (Cu=63.5, Fe=56.0, S=32.0) (2mks)
- Identify:
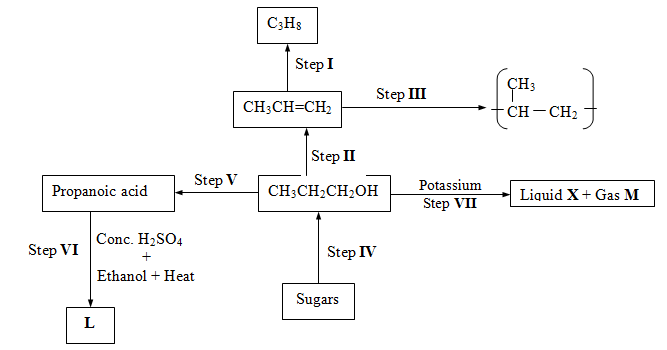
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow:
-
- Name the type of reaction in the following steps
Step III (1mk)
Step IV(1mk) - Name the important reagents and conditions in
Step I (1mk)
Reagent
Condition
Step II (1mk)
Reagent
Condition
Step V (1mk)
Reagent
Condition
- Name the type of reaction in the following steps
-
- Write a balanced equation for the reaction taking place in
Step VI (1mk)
Step VII (1mk) - Give the systematic name of liquid X and substance L.
- Write a balanced equation for the reaction taking place in
- State one chemical test used to differentiate between C3H8 and C3H (1mk)
-
- If the relative molecular mass of compound formed in step III is 42,000, determine the value of n in compound (C=12.0, H=1.0) (1mk)
- State one disadvantage of the continued use of items made from the compound formed in (d) (i) above. (1mk)
-
-
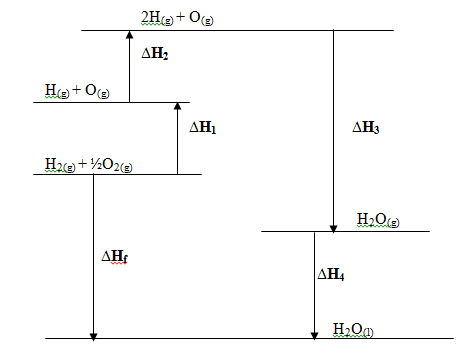
- Below is the energy level diagram for the formation of water.
- Which ∆H values will have a positive sign? (1mk)
- What change is represented heat change ∆H1 is involved? (1mk)
- What is the process taking place where ∆H4 is involved? (1mk)…
- What is ∆Hf in terms of ∆H1, ∆H3 and ∆H4 for the reaction? (1mk)
- Explain whether the reaction in (iv) above is exothermic or endothermic. (1mk)
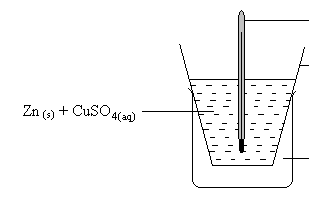
- The apparatus below were used to determine the molar heat of displacement of copper.
1.0g of zinc powder was added to 50cm3 of 0.2M copper(II) Sulphate solution and the mixture stirred gently. The temperature of bthe mixture rose from 200C to 270C.- Explain why polystyrene cup was used instead of a glass beaker. (1mk)
- Calculate the number of moles of copper (II) Sulphate in the solution. (1mk)
- Calculate the molar heat of displacement of copper. (Specific heat capacity of solution = 4.2kJ/Kg/K density of solution = 1gcm-3) (1mk)
- Why is the molar heat of displacement obtained in (iv) above lower that the actual value? (1mk)
- Draw an energy level diagram fo the reaction above. (2mks)
- Below is the energy level diagram for the formation of water.
-
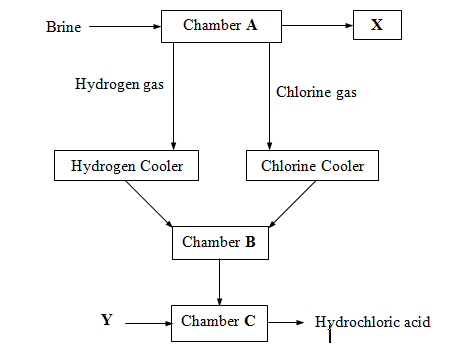
- The flow chart below shows major steps in industrial manufacture of hydrochloric acid.
- Identify substance X and Y. (2 mks)
- Name the process that takes place in chambers A and B (2 mks)
- Write equations of the reactions that lead to the formation of hydrogen and chlorine gases in chamber A. (2mks)
- State one safety precaution taken in chamber B. (1mk)
- State one use of hydrochloric acid (1mk)
-
- State one effect of chlorofluorocarbons (CFC(s)) on the environment. (1mk)
- Suggest any measure that should be taken to minimize the effect stated in (i) above (1mk)
- The flow chart below shows major steps in industrial manufacture of hydrochloric acid.
Download CHEMISTRY PAPER 2 - KCSE 2019 JOINT PRE MOCK EXAMINATION NAMBALE.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students