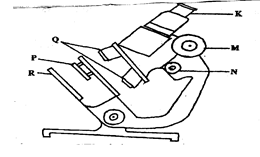
- The diagram below shows some components of a light microscope.
- Name the parts labeled 1mks
K –
M – - State the functions of 2mks
P –
Q – - A student was viewing a prepared slide of a plant cell under high power microscope. The features of the cell were blurred. Which one of the labeled parts of the microscope would the student use to obtain;-
- A sharper outline of the features 1mk
- Give the formula used to calculate magnification in a light microscope 1mk
- A student was preparing a section of a plant cell to be viewed on a light microscope. Give a reason for each of the following steps.
- Cutting a very thin section 1mk
- staining the section 1mk
- Putting the section in water. 1mk
- Name the parts labeled 1mks
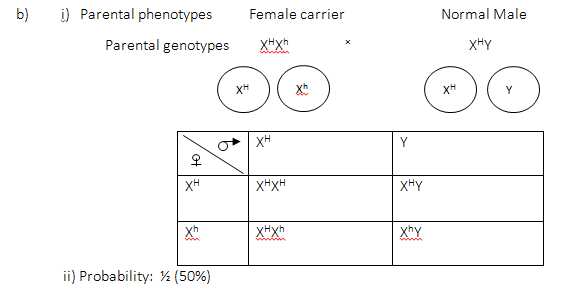
- Haemophilia is a sex linked disorder due to a recessive gene. A carrier woman married a normal man. Let H represent gene for normal condition and h to represent gene for haemophilic condition.
- State the genotypes of
- Man 1mk
- woman 1mk
-
- Using a punnet square, show the genotypes of the children resulting from this marriage 3mks
- State the probability of getting a carrier daughter. 1mk
- Give an explanation why haemophilia is more common in males than in females. 2mks
- State the genotypes of
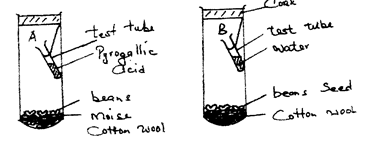
- In an experiment a group of students set up the test tubes as shown below
- What was the aim experiment? 1mk
- Why was pyrogallic acid included in the gas jar. A? 1mk
- What results would you expect in each of the gas jar A and B at the end of experiment? 2mks
- State two artificial ways of breaking seed dormancy. 2mks
- Name two harmones that bring about rapid cell division in plants 2mks
-
-
- Distinguish between single circulatory system and closed circulatory system. 2mks
- Name the blood vessels that transports blood from
- small intestines to the liver 1mk
- Lungs to the heart 1mk
-
- Name one defect of circulatory system in humans. 1mk
- State three functions of blood other than transport. 3mks
-
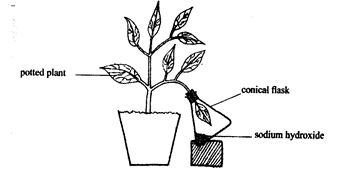
- An experiment was set up to demonstrate the necessity of carbon (IV) oxide for photosynthesis in a certain green plant as shown below. The plant was first kept darkness for 48 hours before the experiment.
- Why was the plant kept in darkness for 48 hours before the start of this experiment. 1mk
- What was the role of sodium hydroxide? 1mk
-
- What happened to the leaf in the flask when it was tested for presence of starch after the set up was exposed to light for a day?. 1mk
- Give reasons for your answer in (c) I above 2mks
- Suggest a control for this experiment. 1mk
- Name other two limiting factors in this experiment. 2mks
SECTION B 40MKS
Answer question 6 (Compulsory) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question 8.
- A certain experiment was performed to demonstrate the effect of sweating on human body temperature. Boiling tubes A and B were filled each with water their initial temperatures recorded. This was repeated after every 5 minutes. The surface of tube A was continuously wiped with a piece of cotton wool which had been soaked in methylated spirit. The results are as shown below
Time (min)
Temperature 0c in tube
A
B
0
80
80
5
54
67
10
40
59
15
29
52
20
21
47
25
18
46
- On the same axis, plot graphs of water temperature against time (min) 8mks
- Find the rate of cooling in A 1mk
- Why was test B included in the set up? 1mk
- Name two ways through which heat is lost in tube B. 2mks
- State the expected results if tube A was insulated. 1mks
- Name the structures in the following organisms that would insulate heat loss.
- Birds 1mk
- Mammals 1mk
- Name any two receptor cells on the skin of man. 2mks
- Describe the response of hair on the skin during cold weather. 3mks
-
- Describe gaseous exchange in alveolus. 8mks
- Describe the process of exhalation in mammals. 8mks
- Discuss the characteristics of gaseous exchange sites in an animal. 4mks
- Discuss the nitrogen cycle. 20mks

MARKING SCHEME
-
- K-eye piece
M -coarse adjustment knob - P- concentrates the light
Q-Brings the image into focus and magnifies it -
- N
- Eye piece magnification × objective lens magnification
-
- for light to pass through easily
- To make the features more clearly and distinguishable.
- For cells to remain turgid
- K-eye piece
-
-
- XHY
- XHXh
-
- Parental phenotypes Female carrier Normal Male
- Probability: ½ (50%)
- Parental phenotypes Female carrier Normal Male
- Males have only one X chromosome which if it carries the single recessive allele, it will express itself fully; females can only express the gene in homozygous state; thus reducing their chances.
-
-
- To show that oxygen is necessary for germination
- To absorb oxygen present in air.
- A- No germination
B- Germination occurred - Scarification, soaking in gibberellic acid, boiling seeds, appropriate temperatures (mark the first two)
- Gibbberellins; auxins;
-
-
- Single circulation is where the blood passes through the heart once to make a complete circulation while closed the blood passes through the heart twice to make a complete circulation.
- Hepatic portal vein
- pulmonary vein
- Thrombosis; varicose vein; arteriolosclerosis; hypertension ( mark the first one)
- -Regulation of the body temperature;
-Regulation of the PH of body fliud;
-Defense against diseases- disease causing microorganisms;
- Prevent excessive bleeding by enhancing clotting; ( mark first three)
-
-
- To destarch the leaf
- To absorb carbon(IV) oxide
-
- Starch absent
- It lacked carbon(IV) oxide; therefore photosynthesis could not take place;
- A leaf is enclosed in a flask but instead of sodium hydroxide, water is used or leaf that was enclosed in the flask is tested for starch.
-
- Light intensity
- Chlorophyll
- Temperature
-
- As shown on the graph
- (80-18) /25
62/25 = 2.48oC - Control experiment.
- –Convention
- Radiation - Less heat loss
-
- Feather
- Fur and hair; (tied)
- -Skin thermoreceptors
-Hypothalamus - Erector pili muscle contract; hair stands upright trapping air; air being a bad conductor of heat prevents heat loss;
-
- Lungs have numerous alveoli to increase S.A for diffusion of gases; alveoli have thin membrane which minimizes resistance against gases; blood flowing in the capillaries contains less oxygen and more C02 since it is from the body tissue; alveoli are supplied with air through bronchioles which link them to the trachea; alveoli are supplied with many capillaries containing blood to transport gases; air in the alveoli contain more oxygen and combine with haemoglobin, forming oxyhaemoglobin; C02 diffuses out of the blood into the alveoli ;from where it is exhaled; (8mrks)
- Internal intercostal muscles contracts and external intercostal muscles relax; The ribcage moves downwards and inwards; diaphragm muscles relax; diaphragm assumes its dome-shaped; volume in the thoracic cavity decreases; resulting in increase in lung volume, pressure in the lung increases; air is then forced out of the lungs; (8marks)
- Thin membrane and epithelial lining for easy diffusion of respiratory gases;
Highly folded surfaces to provide large surface area for efficient diffusion of gases;
Moist surfaces for dissolving the gases before they diffuse;
Highly vascularized surface for efficient transport of gases to maintain high concentration gradient (4 marks)
- Nitrogen fixation; is the process of converting Nitrogen to Nitrates; and is done through three means. During thunderstorm/ lightning energy combines, atmospheric Nitrogen gas with oxygen to form oxides of nitrogen; which dissolve in water to form nitric acid and nitrous acid; acid combines with chemical compounds to form nitrates which are absorbed by plants; Symbiotic bacteria such as Rhizobium; which are found in root nodules of leguminous plants; fix free nitrogen to nitrates; Free living bacteria e.g clostridium, Azotobacter, fix nitrogen; and also non-bacteria fixers e.g Nostac algae / chlorella/ anabaena, fix nitrogen to ammonia; Nitrification; is the process of oxidizing ammonium compounds or nitrites to nitrates; Ammonia is oxidized into nitrites by nitrifying bacteria e.g nitrosomonas and nitrococcus; Nitrites are converted into nitrates b nitrifying bacteria e.g nitrobacter; Absorption and assimilation; Nitrates is then absorbed by the plants; plants use nitrates to form plant proteins; animals feed on plants and convert plant protein into animal protein; Death and decomposition; plants and animals die and are decomposed by saprophytic bacteria and fungi; Decomposition release ammonia which is converted to nitrites the to nitrates; Denitrification; Process in which nitrates are reduced into nitrites or atmospheric Nitrogen; This is done by denitrifying bacteria such as pseudomonas denitrificans and Thiobacillus denitrificans; they utilize oxygen released to carry out respiration ;
Total marks 26
Max 20
Download BIOLOGY PAPER 2 - KCSE 2019 NYANDARUA PRE MOCK EXAMINATION.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students