INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES:
- Write your name and index number in the spaces provided above.
- Sign and write the date of examination in the spaces provided above.
- Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided.
- Mathematical tables and silent electronic calculators may be used.
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary.
- Candidates should check the question paper to ascertain that all the pages are printed as indicated and that no questions are missing
- The samples of equal volumes of water were put in 100cm3 conical flasks and heated for 5 minutes on a Bunsen flame. It was observed that sample 1 registered a low temperature than sample II
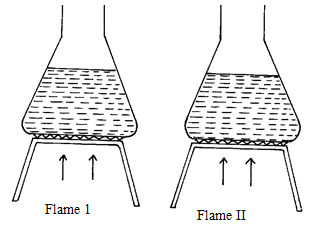
- Name flame I (1mk)
- State one disadvantage of using flame I for heating (1mk)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow.
The diagram shows the method used to separate component of mixture P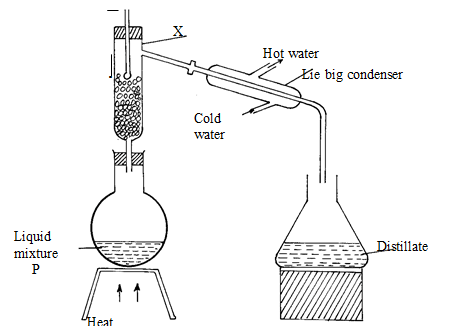
- Name X (1mk)
- What is the name given to the method used in separation of mixture P (½mk)
- What would happen if the inlet and outlet of water were interchanged ( ½mk)
- Which physical property is used to separate mixture P (1mk)
- The table below shows the solubility of three solids P, Q, and R.
How would you obtain pure samples of R,P and Q (2mks)Solid Cold Water Hot Water P soluble soluble Q insoluble insoluble R insoluble soluble - State why a water molecule H2O can combine with H+ ion to form H3O+ ion (1mk)
- The PH values of some solutions are given below
PH 14.0 1.0 8.0 6.5 7.0 Solution M L N P Z - Identify the solution with the lowest concentration of hydrogen ion. Give reason for your answer (1mk)
- Which solution would be used as an anti-acid for treating stomach upset. Give for your answer (1mk)
- The data below gives the electronic configuration of some selected atoms and ions
Atom/ion A2+ B C2- D2+ E F- G+ H Electronic configuration 2 2.4 2.8 2.8.8 2.8 2.8.8 0 2.8.2 - Select an atom that is a noble gas (1mk)
- What is the atomic number of C and A (1mk)
- Select an element that belong to group 2 and period four (1mk)
- Write the formula of the compound formed when D and F react (1mk)
- Helium is used instead of hydrogen in balloons for metrological research. Explain (1mk)
- Zinc metal and hydrochloric acid reacts according to the following equation
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
1.96g of Zinc metal were reacted with 100cm3 of 0.2M hydrochloric acid- Determine the reagent that was in excess (2mks)
Zn=65.2; Molar gas volume at s.t.p 22.4 liters - Calculate the total volume of hydrogen gas that was liberated at s.t.p (1mk)
- Determine the reagent that was in excess (2mks)
- Give the IUPAC names of the following compounds (1mk)
- CH3CH2CH2CH CH3
CH3 ……………………………………………………………………………. - CH3CH=CHCl …………………………………………………………………………… (1mk)
- CH3CH2CH2CH CH3
- 0.9g of potassium chloride and potassium carbonate mixture completely reacted with 25cm3 of 0.2M hydrochloric acid
- Write an equation of the reaction which takes place (1mk)
- Determine the number of moles of the acid used (1mk)
- Calculate the mass of potassium chloride in the mixture (K=39.0; C=12.0; O=16.0) (2mks)
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow
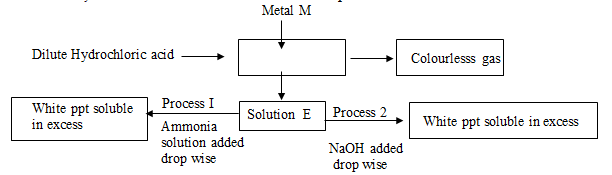
- Identify metal M: ………………………………………………………. (1mk)
- Colourless gas: …………………………………………………………. (1mk)
- Write an equation that leads to the formation of white precipitate in process (1mk)
-
- Define the term dynamic equilibrium (1mk)
- A reaction at equilibrium can be represented as
2CrO2-4[aq] +2H+[aq] Cr2O72[-aq] + H2O{l}
Yellow orange
State and explain the observation made when NaOH is added to the equilibrium mixture (2mks)
- Few drops of hydrochloric acid were added into a test tube containing lead {II} Nitrate solution
- State one observation made (1mk)
- Write an ionic equation of the reaction that occurred in the test tube (1mk)
- A compound of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen contains 57.15% carbon, 4.76% hydrogen and the rest oxy gen. If its relative molecular mass is 126, find its molecular formula. (C = 12, H = 1, O = 16) (3mks)
- Study the information in the table below and answer the questions that follow.
A mixture containing 35g of CuSO4 and 78g of Pb(NO3)2 in 100g of water at 60°C was cooled to 40°C.Salt Solubility g/100g of water At 40°C At 60°C CuSO4 28 38 Pb(NO3)2 79 98 - Which salt crystallized out? Give a reason. (2 marks)
- Calculate the mass of the salt that crystallized out. (1 mark)
-
- Distinguish between strong and concentrated acid ( 1mk)
- A solution of ammonia in methylbenzene has no effects on red litmus paper while a solution of ammonia in water turns red litmus paper blue. Explain (2mks)
- Name the process which takes place when
- Iodine changes directly from solid to gas (1mk)
- Fe2+( aq) changes to Fe3+(aq) (1mk)
- White sugar changes to black when mixed with concentrated sulphuric (VI) acid (1mk)
- In the last stage of the solvay process, a mixture of sodium hydrogen carbonate and ammonium chloride is formed
- State the method of separation used (1mk)
- Write an equation showing how lime is slaked (1mk)
- Name the by- product recycled in the above process (1mk)
- The diagram below is a section of a model of the structure of element K
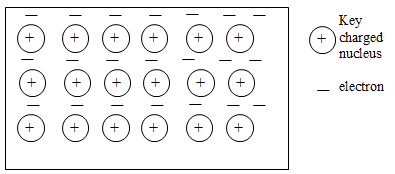
- State the type of bonding that exist in K (1mk)
- In which group of the periodic table does element K belong. Give a reason (2mks)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow
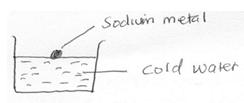
- State two observations made in the above experiment when sodium react with water (2 mks)
- Write a chemical equation for the reaction that takes place (1mk)
-
- Explain why permanent hardness in water cannot be removed by boiling (2mks)
- Name two methods that can be used to remove permanent hardness from water (1mk)
- Write an equation to show the effect of heat on the nitrate of: - (2mks)
- Potassium
- Silver
- Study the diagram below and use it to answer the questions that follow.
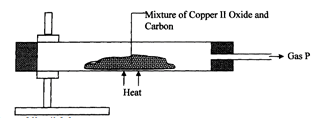
- State the observation made in the combustion tube. (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction that took place in the combustion tube. (1mk)
- Name gas P
- Sulphur exists in two crystalline forms.
- Name one crystalline form of Sulphur. (1mk)
- State two uses of Sulphur. (2mks)
- Bond energies for some bonds are tabulated below: -
Use the bond energies to estimate the enthalpy for the reaction. (3mks)BOND BOND ENERGY KJ/mol H-H 436 C=C 610 C-H 410 C-C 345
C2H4(g) + H2(g) → C2H6(g) - Study the set up below and answer the questions that flows
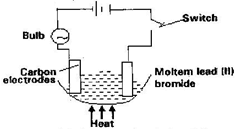
State all the observations that would be made when the circuit is completed (3mks) - Describe how solid samples of salts can be obtained from a mixture of lead (II) chloride, sodium chloride and ammonium chloride. (3mks)
- The diagram below represents a set-up used to prepare oxygen gas.
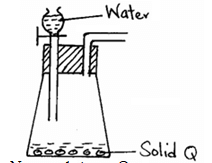
- Name substance Q. (1mk)
- Complete the set-up to show how oxygen gas is collected. (1mk)
- Write the equation for the reaction that occur. (1mk)
- Two reagents that can be used to prepare chlorine gas are potassium manganate (VII) and hydrochloric acid.
- Write an equation for the reaction. (1mk)
- Give the formula of another reagent that can be used instead of potassium manganate (VII). (1mk)
- Using an equation illustrate how chlorine bleach coloured substances. (2mks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Luminous flame 1mk
- Produces less heat
or
Blackens the conical flask/ sooty 1mk
-
- Fractionating column ½ mk
- Fractional distillation ½ mk
- Condensation would not occur 1 mk
- Differences in boiling points 1mk
-
- Dissolve the mixture in hot water ½ mk
- Filter the solution to remove insoluble solid Q as a residue ½ mk
- Cool the filtrate. R crystallizes and is removed by filtration ½ mk
- Evaporate the latter filtrate to obtain P ½ mk
- H2O has lone pairs of electrons which can be shared with H+ ion 1mk
-
- Solution P ½ Weak acid ½ mk
- Solution N ½ Weak base ½ mk
-
- E 1 mk
- C=8 ½ mk
A=4 ½ mk
- Helium is inert (unreactive) ½ while hydrogen is reactive ½ mk
-
- Moles of zinc=1.96 =0.03 ½ mk
63.5 - Moles of HCL 100 x 0.2 =0.02 ½ mk
1000 - Moles of zinc reacted 0.02 =0.01 ½ mk
2
Zinc is in excess ½ mk - Mole ratio of HCL: H2 2:1
Moles of H2 (g) produced = 0.02 = 0.01 moles ½ mk
2 - Volume of H2 g at S.T.P= 0.01x22.4
= 0.224 dm3
or 224cm3 ½ mk
- Moles of zinc=1.96 =0.03 ½ mk
-
- 2, methyl pentane 1 mk
- 1- chloro propene 1 mk
- To prevent oxidation of magnesium ribbon 1 mk
To generate steam 1 mk - Mgs + H2O(l) → MgO(s) + H2(g) 1 mk
Should be balanced with state symbols
- To prevent oxidation of magnesium ribbon 1 mk
-
- K2 CO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → 2KCl(aq) + CO2(g)+ H2O(l) 1 mk
Should be balanced with state symbols - Moles of acid 25x0.2
1000
=0.005 moles ½ mk
Moles of K2 CO3 = 0.005
2
=0.0025 moles ½ mk - RFM of K2CO3 = 138 ½ mk
Mass of K2CO3 in the mixture
138 x 0.0025= 0.345g ½ mk
Mass of KCL in the mixture
0.9-0.345
= 0.555g ½ mk
- K2 CO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → 2KCl(aq) + CO2(g)+ H2O(l) 1 mk
-
- Zinc 1 mk
- Hydrogen 1mk
- Zn2+ + 2OH-(aq) → Zn(OH)2(s) 1mk
-
- Dynamic equilibrium is attained when the rate of the forward reaction is equal to that of the reverse reaction 1mk
- The intensity of the yellow colour in the equilibrium mixture increased 1mk.
Additional of NaOH reduces the concentration ofH+ ions hence equilibrium shifts to the left 1mk
-
- White precipitate was formed 1mk
- Pb2+[aq] + 2Cl- [aq] → PbCl2[s] 1mk
-
Empirical formula= C2H2O√ ½Element C H O % Composition 57.15 4.76 38.09 r.a.m 12 1 16 %
R.A.M4.7625 4.76 2.380625 Moles Ratio 4.7625 = 2.004 = 2
2.3806254.76 = 2.00
2.3806252.380625 = 1
2.380625
n = 126 = 3 √ ½
42
Molecular formula = (C2H2O)3 = C6H6O3√ ½ -
- Copper(II) sulphate;√ 1 at 40ºC ONLY 28gm is soluble leaving the rest undissolved. √ 1
At 40ºC, all lead nitrate dissolves. - 35-28√ ½=7g√ ½
- Copper(II) sulphate;√ 1 at 40ºC ONLY 28gm is soluble leaving the rest undissolved. √ 1
-
- Strong acid ionizes completely in solution while concentrated acid contain high number of acid molecules per given volume. 1mk
- Ammonia in water dissociate to produce hydroxide ion √ 1while in methybenze it remain in molecular form. √ 1
-
- Sublimation √ 1
- Oxidation √ 1
- Dehydration √ 1
-
- Filteration√ 1
- Ca(OH)(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq) √ 1
- Carbon(IV) oxide// Ammonia√ 1
-
- Metallic bond√ 1
- Group I√ 1; Has one delocalized electron from each atom√ 1
-
- Melts into a silvery ball√ 1/darts on the surface of water√ 1/Floats on the surface of water/hissing sound ( any two)
- 2Na(s)+ H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g) √ 1
-
- Permanent hardness is caused by the presence of MgSO4/ CaSO4/CaCl2 √ 1which do not decompose on heating√ 1
- Addition of Sodium Carbonate√ ½/ammonium hydroxide√ ½/ Ion exchange (any two)
-
- 2KNO3(s) 2KNO2(s) + O2(g)
- 2AgNO3(s) 2Ag(s) + 2NO2(g) + O2(g)
-
- A brown solid is formed
- CuO(s) + C(s) Cu(s) + CO(g)
- Carbon (II) Oxide.
-
- Rhombic or monoclinic Sulphur.
-
- For hardening rubber
- Manufacture of sulphuric acid (Any two correct)
- As a fungicide
- In making calcium hydrogen sulphite used in bleaching.
- Bond breaking
4 C-H - 4x410 = 1640
C=C - 1x610 = 610
H-H - 1x436 = 436
+2686
ΔH = +2686 - 2805
= -119kJ/Mol
Bond formation
6C - H 6x410
=2460
C-C- 3 45
-2805 -
- The bulb lights √ 1
- Grey solid deposits at the cathode √ 1
- Brown gas bubbles produced at the anode √ 1
-
- Heat to sublime NH4Cl. ½
- Add water ½ to dissolve NaCl. ½
- Filter ½ the residue is PbCl2 ½
- Evaporate ½ the filtrate (NaCl solution) to obtain NaCl solid
-
- Sodium peroxide
-
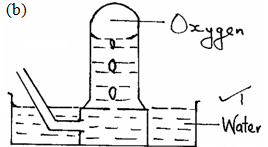
- 2Na2O2(S) + 2H2O(l) → 4NaOH(aq) + O2(g)
-
- 2KMnO4(S) + 16HCl(aq) → 2KCl(aq) + 2MnCl2(aq) + 8H2O(l) + 5Cl2(g)
- MnO2
- Cl2(g) + dye + H2O(l) → 2HCl(aq) + (dye – O)
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Chemistry Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Kapsabet Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

