INSTRUCTIONS:
Answer all the questions in the spaces provided
- Name the part of a flower that develops into:
- Seed [1mk]
- Fruit [1mk]
- State two ways in which floating leaves of aquatic plants are adapted to gaseous exchange. [2mk]
- The diagram below represents a stage during cell division
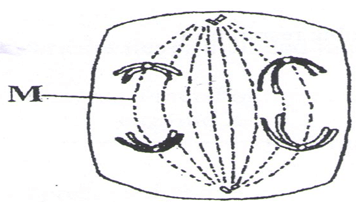
-
- Identify the stage of cell division [1mk]
- Give two reasons for your answer in [a] [i] above [2mk]
- Name the structures labeled M [1mk]
- Name the class to which millipede belongs [1mk]
-
-
- Distinguish between the terms [2mk]
Homodont and heterodont - what is the function of the carnassial teeth [2mk]
- Distinguish between the terms [2mk]
- An A blood group patient involved in a road accident required an urgent blood transfusion. His relatives were invited to donate blood.
- Name the possible relative who would not donate blood to him [2mk]
- State why the others would not be in a position to donate blood to him [2mk]
- The flow chart shows a part of a food relationship in an ecosystem
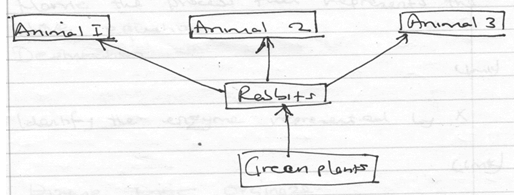
-
- Name the food relationship shown [1mk]
- How many trophic levels are shown in the diagram [1mk]
- What is the main source of energy in the ecosystem [1mk]
-
- Name the only epidermal cell in plants that contain chloroplast [1mk]
- The equation below represents a metabolic process that occurs in the mammalian lives
Amino Acids Enzyme x organic compound- Name the process that represents the above equation [1mk]
- Identify the enzyme represented by x [1mk]
- What is the importance of the process to the mammal [1mk]
-
- Name the carbohydrate that is stored in mammalian muscle [1mk]
- What name is used to describe removal of indigestible and undigested food material from the alimentary canal [1mk]
- Carl Linnaeus developed the taxonomic units of classification
- What is taxonomy [1mk]
- Why was the system of classification by carl linneaus described as natural system of classification [2mk]
- Phagocytes also called granulocytes or polymorphs are cells found in the blood whose they ingest pathogens and cell debris
- why are they called polymorphs. [1mk]
- Name the cell organelle most abundant in phagocytes to enable them function effectively [1mk]
- Name the:
- Material that strengthens xylem tissue [1mk]
- Tissue that is removed when the part of a plant is ringed [1mk]
- The diagram below represents a cell organelle.
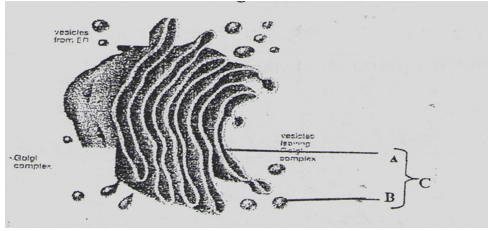
- State the function of this organelle [1mk]
- Name each of the parts A and B
- [1mk]
- [1mk]
- In which two ways do guard cells differ from other epidermal cells [2mk]
-
- Through cellular respiration, the chemical energy stored in glucose molecule is converted into which specific molecule [3mk]
- Name the substance that speed up chemical reaction without being used up in those reactions [1mk]
- During germination and early growth, the dry weight of endosperm decreases while that of embryo increase explain [2mk]
- The diagrams below show changes in the life cycle of flowering plants
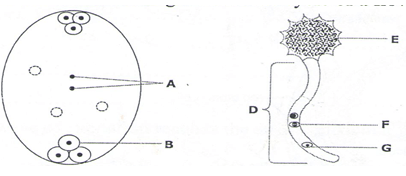
Complete the table below by choosing the letters from the diagram which refers to each of the stages given [4mk]
[1mk]STAGE OF LIFE CYCLE LETTER Male gametophyte Tube nucleus Female gamete Male gamete - State 2 characteristics of kingdom Monera that are not found in other kingdoms [2mk]
- State three ways by which plants compensate for lack of the ability to move from one place to another [3mk]
- State three physiological processes that are involved in movements of substances across the cell membrane [3mk]
- If the human pancrease is not functional:
- Name the hormone which will be deficient [1mk]
- Name the disease the human is likely to suffer from [1mk]
- The oxidation state of a certain food is represented below by a chemical equation
2C3H2O2N + 6O2(NH4)2CO2 + 5CO2 + 5H2O- Calculate the respiratory quotients[RQ] of the food substance [2mk]
- Identify the food substrate [1mk]
- The diagram below shows an apparatus used during collection of specimen
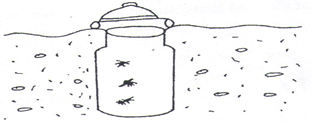
- Identify the apparatus [1mk]
- What is the use of the apparatus named above [1mk]
- State two factors in an ecosystem that affect the distribution of organisms [2mks]
- A DNA strand has the following base sequence G C C T A G A T C A C
What is the sequence of the- Complementary DNA strand [1mk]
- M-RNA strand copied from this DNA strand [1mk]
- State three limitations of fossil records as evidence of organic evolution [3mk]
- How does nutrition as a characteristic of living organism differ in plants and animals [2mk]
- State the function of the following parts of a light microscope .
- Body tube [1mk]
- Diaphragm [1mk]
- State three characteristics of gaseous exchange surfaces [3mk]
- State two sources of variations [2mk]

MARKING SCHEME.
-
- Ovule
- Ovary
- Aerenchyma tissue with large air spaces to store air.
Large stomata found on the upper surface of the leaf -
- Prokaryotic
- Cell not made of cellulose
- Few organelles
- Diplopoda
- Prokaryotic
-
-
- Homodont –teeth of the same size and shape
- Heterodont –teeth of different size and shape
- Special pre-molars with smooth sides and sharp edges to slice through flesh and crush bones
-
-
-
- B
- AB’
- O –Universal donor since they have no antigens
A – Same blood group hence agglutination
-
-
-
- Food web
- Three
- Sun
-
- Guard cells
-
- Deamination
- Enzyme orginaze
- Removal of the excess amino acids which cannot be stored in the body
-
- Glycogen
- Egestion
-
- Science of classification
- Uses evolutionary relationship between specimen and their ancestor
-
- They have lobed nuclei
- Lysosomes
-
- Ligin
- Phloem
-
-
- Packing and transport in venicles of material such as enzyme
- Secretion of synthesized proteins, carbohydrates
- Process of cisternae
- Involved in lysosome formation
-
- Golgi bodies
- Golgi vesicles
-
-
- Guard cells have chloroplast hence photosynthesis
- Have thicker inner walls and thin outer walls for differential expansion to facilitate opening and closing of the stomata.
- Are bean shaped
-
- ATP-Adenosine triphosphate
CO2-Carbon [IV] oxide
H2O-Water - Catalyst [enzyme]
- ATP-Adenosine triphosphate
- Food stored in the endosperm was oxidized to form energy for the process and also form new material for growth in the embryo.
-
STAGE OF LIFE CYCLE LETTER Male gametophyte D Tube nucleus G Female gamete B Male gamete F -
-
- Anaphase
- Homologous chromosome separate at the equator
- Chromosomes start migrating to opposite poles
- Spindle fibres
-
-
- Plants are able to synthesize their own food.
- Plants are able to use pollination rather than moving to seek mating partners.
- Plants use seed and fruits dispersed to colonize new habitats.
-
- Diffusion
- Osmosis
- Active transport
-
- Insulin
- Diabetes mellitus
-
- RQ = volume of carbon[iv] oxide produced
Volume of oxygen consumed
5/6 =0.83 - Proteins
- RQ = volume of carbon[iv] oxide produced
-
- Pitfall trap
- For catching crawing animals
-
- Temperature
- Light
-
- CGGATCTAGTG
- CGGAUCUAGUG
-
- Several missing links
- Most organisms especially soft-bodied ones do not form fossils
- Exposed fossils are usually destroyed by physical and chemical weathering
- Most animals are preyed upon.
- Plants make their own food from carbon[iv] oxide and water while animals depend on already manufactured food from plants directly or indirectly
-
- Holds the eyepiece and the revolving nosepiece
- An aperture that regulates the amount of light passing through the condenser to illuminate the specimen.
-
- Thin walled
- Highly vascularized
- Has a large surface area
-
- Mutation
- Crossing over during prophase of meiosis
- Sexual reproduction [fertilization]
- Independent assortment of chromosomes during metaphase of meiosis 1
Download Biology Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Mwakican Joint Pre Mock Examination 2021.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

