INSTRUCTIONS TO STUDENTS
- Write your name and admission number in the spaces provided
- Answer all questions in this question paper.
- All your answers and working must be written in the spaces provided in this question paper.
- This paper consists of 13 printed pages
- All questions must be answered in English
- SECTION A
A spherical ball bearing of mass 0.0024 kg is held between the anvil and spindle of a micrometer screw gauge. The reading on the gauge when the jaws are closed without anything in between is 0.11mm. Use this information and the position of the scale in the figure below to answer the questions (a) and (b) below: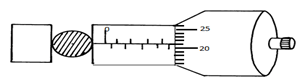
- What is the diameter of the ball bearing? (2 marks)
- Find the density of the ball bearing. (3 marks)
- Figure below shows two identical hollow spheres. Sphere A is completely filled with the liquid while B is partially filled with an identical liquid.
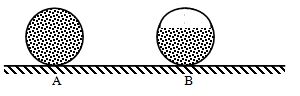
When the two spheres are rolled on a horizontal surface, it is observed that the sphere B stops earlier than sphere A. Explain this observation. (2 marks) - Diffusion in gases is faster than in liquids; state two reasons why this is so. (2 marks)
- A rod consists of glass on one part and copper on the other. The rod is wrapped with a piece of paper and then a flame passed below it. It is observed that the paper on the side with glass is charred while that on the side of copper is not. Explain this observation. (1 mark)
- A needle may float on clean water but sinks when a detergent is added. Explain. (1 mark)
- A body is projected vertically upwards from the top of a building. Assuming that it lands at the base of the building. Sketch the velocity time graph of the motion. (2mks)
- The spiral springs shown in the figure below are identical. Each spring has a constant K = 300N/m.
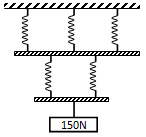
Determine the extension caused by the 150N weight (Ignore weight of springs and connecting rods) (3 marks) - A uniform 120m metal rod is pivoted near one of its ends and kept in equilibrium by a spring balance as shown in figure below.

The reading indicated by the spring balance is 2.0N. Work out the mass of the metal rod. (g = 10N/kg) (3 marks) - Air is trapped in a thin capillary tube by a thread of mercury 5cm long as shown in figure below.
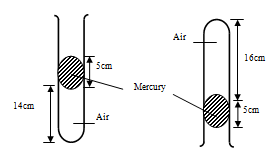
Use the information in figure to calculate the value of the value of the atmospheric pressure in mmHg (3 marks) - State a reason why an air bubble increases in volume as it rises up the surface in a boiler. (1 mark)
- An electric kettle with shiny outer surface is more efficient than one with a dull outer surface, give a reason for this. (1 mark)
- A pipe of radius 3mm is connected to another pipe of radius 9mm. If water flows in the water pipe at a speed of 2ms-1, what is the speed in the narrower pipe (2 marks)
SECTION B -
- The moon goes round the earth at constant speed. Explain why it is true to say that the moon is accelerating. (1 mark)
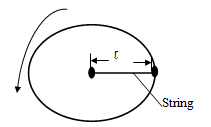
- A string of negligible mass has a bucket tied at the end. The string is 60cm long and the bucket has a mass of 45g. The bucket is swung horizontally making 6 revolutions per second.
Calculate:- The angular velocity. (2 mark)
- The centripetal acceleration. (2 marks)
- The tension on the string. (2 marks)
- The linear velocity. (2 mark)
- Figure below shows of mass m = 200g attached to the centre of a rotating table with a string. The radius of the spring was varied and different values of angular velocity recorded. The mass of the body remained constant throughout the experiment.
The results obtained for angular velocity and radius were used to plot the following graph.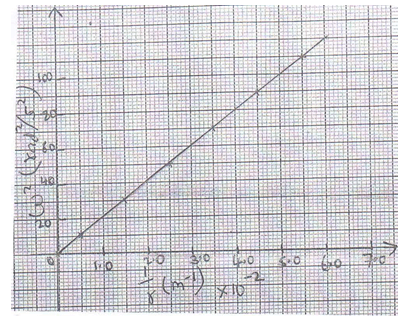
From the graph above;- Calculate the value of the slope. (3 marks)
- If ω2 and 1/r are related by the equation; ω2= p/r x 1/m, find the value of P. (2 marks)
- State the significance of P. (1 mark)
-
- State the Law of floatation. (1 mark)
- A block of length 50cm, cross-sectional area of 5cm2 and density 1.4g/cm3 is completely immersed in a liquid of density 1.08g/cm3 find;
- the mass of the block (2 marks)
- the weight of the block in the liquid. (3 marks)
-
- Define the term heat capacity (1mark)
- A block of metal of mass 150g at 100ºC is dropped into a logged calorimeter of heat capacity 40Jk-1 containing 100g of water at 25ºC. The temperature of the resulting mixture is 34ºC. (Specific heat capacity of water = 4200J/Kg/K)
Determine: -- Heat gained by calorimeter (2marks)
- Heat gained by water (2 marks)
- Heat lost by the metal block (1mark)
- Specific heat capacity of the metal block (3marks)
-
-
- Define velocity ratio of a machine. (1 mark)
- Draw a labeled diagram of a pulley system with a velocity ratio of 5. (2 marks)
- Suggest any two possible reasons why the efficiency does not reach the 100% mark. (2 marks)
- The effort piston of a hydraulic machine is of radius 2.8 cm, while that of the load piston is of radius 14cm. The machine raises a load of 120 kg at a constant velocity through 2.5m. If the machine has an efficiency of 80%, find:-
- the velocity ratio of the hydraulic machine. (2 mark)
- The mechanical advantage of the hydraulic machine. (2 marks)
- The effort needed to raise the load. (2 marks)
-
-
-
- State Newton’s second law of motion. (1 mark)
- A striker kicks a ball of mass 250g initially at rest with a force of 75N. if the foot was in contact with the ball for 0.10sec. Calculate the take off velocity of the ball. (2 marks)
- A bullet of mass 20g moving at 400 m/s strikes a block of wood of mass 3.5kg initially at rest. The bullet sticks into the block and the two move off together on a horizontal surface.
- Determine the initial common velocity of bullet and wooden block. (2 marks)
- What is the deceleration given the retarding force is 4 N? (3 marks)
-
-
-
- State what is meant by an ideal gas (1mk)
- The pressure acting in a gas in a container was changed steadily while the temperature of the gas was maintained constant. The value of volume V of the gas measured various values of pressure. The graph in the figure A shows the relation between the pressure. P1 and the reciprocal of volume 1/V
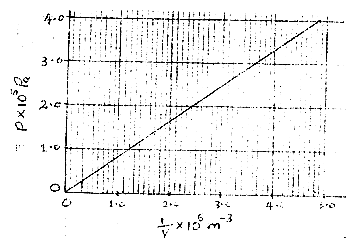
Given that the relation between the pressure P1 and the value, V1 of the gas is given by PV = k Where k is a constant, use the graph to determine the value k (3marks)
- A gas occupies a volume of 4000 litres temperature of 37°C and normal atmosphere pressure. Determine the new volume of the gas if it is heated at constant pressure to a temperature of 67°C (normal atmosphere pressure P = 1.01 x 105pa) (3marks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
-
- 5.50 mm + 0.21 mm = 5.71 mm
5.71 mm – 0.11 mm = 5.60 mm - ϱ = m/v
v = 4/3 πr3 = 4/3 x 3.142 x 0.283 = 0.09196 cm3
ϱ = 2.4 g / 0.09196 cm3 = 26.098 g/ cm3
- 5.50 mm + 0.21 mm = 5.71 mm
- In A the C.O.G stays at the same place throughout while in B, C.O.G changes hence resisting motion.
- Density of gases is lower than in liquids -Intermolecular forces in gasesare weaker than in liquids. - Kinetic energy of gas particles is higher than that of liquids
- Copper being a better conductor of heat compared to glass, conducts away heat faster than glass
- The surface tension of water holds the needle making it to float. Detergent lowers the surface tension of water making the needle to break it hence sinking
- Correct diagram
- F= Ke
e= f/k
e= 150/300 = 0.5m
For 3 parallel e = 0.5/3 = 0.1667
For 2 springs parallel in e = 0.5/2 = 0.25m
Total extension 0.1667 + 0.25 = 0.4167m - Clockwise moment = Anticlockwise moment
0.48 x = 0.34 x 2.0
w =0.34 x 2= 1.4167
0.48
m = w/g=1.4167 x 1000
10
= 141.67g - P1 = (PA + 5) cmHg
P2 = (PA – 5) cmHg
V1 = 14cm
V2 = 16cm
P1V1 = P2V2
(PA + 5) (14) = (PA-5)16
⇒14PA + 70 = 16PA – 80
2PA= 150
PA = 75cmHg - As it rises the pressure decreases hence volume increases.
- Shinny surface reduce heat loss through radiation since they are emitters of heat.
- Smaller area A1 = πr2
= 3.14 x 3 x 3
= 28.26mm2
Wider area A2 = πr2
= 3.14 x 9 x 9
= 254.34m2
A1V1 = A2V2
28.26 x V1 = 254.34 x 2
V1 =254.34 x 2
28.28
= 18m/s
SECTION B -
- The direction of velocity of the moon keeps on changing due to the changes in direction moon as it revolves around the earth.
-
- ω = 2πf 1mk = 2 x 3.142 x 6 = 37.704 rad/s 1mk
- a = v 2 = rω2 1mk = 37.7042 x 0.6 = 852.955m/s2 1mk
r - T = Fc = mrw2 1mk
= 0.045 x 0.6 x (37.704)2 = 38.38N 1mk - v = wr = 0.6 x 37.704 1mk = 22.62m/s
-
- Slope = ∆Y= 90-30 1mk= 60 = 2000N/kg 1mk
∆X (4.5-1.5)x10-2 3 x 10-2 - P/m=Slope=P=m x 2000 1mk
= 0.2 x 2000 = 400N 1mk - Centripetal force 1mk
- Slope = ∆Y= 90-30 1mk= 60 = 2000N/kg 1mk
-
- A floating object displaces its own weight of the fluid in which it is floating
- m = ϱv
V = Ah = 5 x 50 = 250 cm3
m = 1.4 x 250 = 350 g - apparent weight = weight in air – upthrust
Weight in air W = mg = 0.35 x 10 = 3.5 N 1mk
Upthrust = ϱvg = (250 x 10-6) x 1080 x 10 = 2.7 N 1mk
Apparent weight = 3.5 – 2.7 = 0.8 N 1mk
-
- quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of a given mass of a material by one degree or one Kelvin
-
- Q = Cϴ
Q = 40 x 9 = 360 J/kg/K - Q = mcϴ
Q = 0.1 x 4200 x 9 = 3780 J/kg/K - Q = mcϴ
Q = 0.51 x 66 x c
Q = 9.9c - Heat gained = heat lost
360 + 3780 = 9.9c
c = 418.181 J/kg/K
- Q = Cϴ
-
-
- ratio of DE to DL
- correct diagram
-
- Some energy is used to overcome friction
- Some energy is used to lift/move parts of the machine
-
- VR = R2/r2 = 142/2.82
VR = 25 - n = (MA/VR) x 100%
80 = (MA/25) x 100 %
MA = 20 - MA = L/E
20 = 1200/E
E = 60 N
- VR = R2/r2 = 142/2.82
-
-
-
- The rate of change of momentum of a body is directly proportional to the resultant external force producing the change and takes place in the direction of the force
- MV = Ft
0.25V = 75 x 0.1
V = 30 m/s
-
- m1u1 + m2u2 = (m1 + m2) v
(0.02 X 400) + 0 = (0.02 + 3.5) v
v = 2.2727 m/s - F = ma
4 = (0.02 + 3.5) a
a = 11.364 m/s
- m1u1 + m2u2 = (m1 + m2) v
-
-
- Gas that obey gas law 1
- 2.0 x 105 - 10 x 10 5 = 1 x 10-1
2.4 x 106 x 1.2 x 106 12
= 0.0833pa m3 (Extract value from graph) - V1 = V2
T1 T2
4000 = V2
310 340
V2=4387.097litres
Download Physics Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Kangundo Subcounty Pre Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

