INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- This paper consists of three sections; A, B and C
SECTION A (30 MARKS)
Answer all Questions from this section in the spaces provided.
- Under what condition would a farmer use an ox-cart instead of a tractor drawn trailer? (1 mk)
- State two practices that may require special method of handling of a mature fresian cow. (1 mk)
- State any two physiological conditions of livestock that may be assessed to determine the health status of an animal.
(1 mk) - Give any four precautions taken when harvesting honey. (2 mks)
- Name four exotic pig breeds reared in Kenya. (2marks)
- A cow gives birth to two offspring in a period of three years. One offspring is a male named Zulo and another, female named Kerio. Two years later Zulo is mated to Keroi and another offspring, called Tedi is given birth to
- Identify the specific system of breeding between Zulo and Keroi. (1 mk)
- Give four disadvantages of such a system of breeding. (2 mks)
- List four ways by which an animal may get infected by a disease from another. (2 mks)
- Give one use for each of the following tools and equipment. (2 mks)
- Dibber
- Halter
- Bolus gun
- Shovel
-
- State the purpose of dry cow therapy. ( ½ mk)
- List four factors that affect milk let down process. (2 mks)
- List four observable features in a cow that may indicate that it’s nearing parturition. (2 mks)
-
- Give the meaning of the following terms as used in livestock breeds. (1½ mks)
- Steer
- Capon
- Kindling
- Name the exotic beef breed of cattle with the following characteristics;
- White / cream in colour
- Heavily built
- Originated from France (½ mk)
- Give the meaning of the following terms as used in livestock breeds. (1½ mks)
- State two indicators of prolificacy in pigs. (1 mk)
- Give four reasons for providing high quality ration in the last two weeks to parturition in goats. (2 mks)
- Outline three reasons why calves should be fed on colostrum. (1½ mks)
- State two ways by which each of the following aspects are achieved in a calf pen.
- Proper drainage. (1 mk)
- Freedom from draught (1 mk)
-
- Define Raddling in sheep management. (1 mk)
- State two reasons for raddling. (1 mk)
- Give two reasons why concrete floors are recommended for dairy sheds. (1 mk)
SECTION B (20 MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this question in the spaces provided.
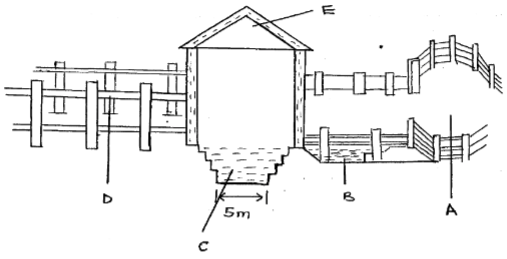
- Below is a farm structure. Study it carefully and answer the questions below.
- What is the use of the above structure? (½ mark)
- State one management practice carried out on livestock before being led into the structure. ( ½ mark)
- State two roles played by the part labeled E. (1 mark)
- Give the role of the parts labeled A and B. (1 mark)
- State four factors to consider when siting the structure in the farm. (2 marks)
-
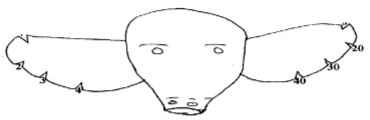
- Study the diagram below illustrating a method of identifying a farm animal.
Using the above illustration draw and mark number 87 (2 mks) - Outline the procedure of castrating a piglet by use of surgical method. (4 mks)
- Study the diagram below illustrating a method of identifying a farm animal.
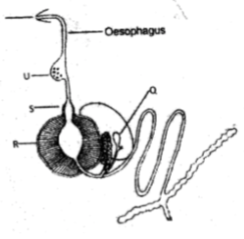
- Study the diagram of chicken digestive system below and answer the question that follow.
- Identify the parts labelled Q, R and S. (1½ mks)
- Briefly describe the function of parts Q and R. (2 mks)
- How can a farmer improve on digestion in the structure labelled S. ( ½ mk)
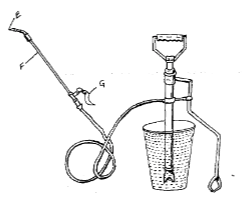
- Below is a diagram of a farm equipment. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the equipment. ( ½ mk)
- State the use of the equipment (1 mk)
- Name the parts labelled G,E and F. (1½mks)
- Identify two draw backs in using this equipment compared to others that may be used for the same purpose.
(2 mks)
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
Answer any two questions from this section in the spaces provided at the end of the section
- Discuss mastitis disease under the following subheading:
- Specific causal organisms (2 mks)
- Predisposing factors (5 mks)
- Symptoms (4 mks)
- Control and treatment (5 mks)
- State four ways by which a farmer can identify an animal suffering from worm infestation. (4 mks)
- Discuss mastitis disease under the following subheading:
-
- Explain the various method of livestock disease control. (10 marks
- Explain the predisposing factors to animal disease. (10 marks)
-
- Discuss the management of layers from one day old to the start of laying in a deep litter system. (l4 mks)
- Explain management practices that would improve fish production. (6 mks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Cannot be used in uneven topography ✔ ½
- require little capital ✔ ½
- Little load to be carried ✔ ½ ( ½ ×2 = 2 mks)
-
- During Inspection ✔ ½
- When Spraying✔ ½
- When Milking ✔ ½
- Treatment / injection / drenching ✔½ (OWITTE) ( ½ ×2 = 2 mks)
-
- Appetite / feeding ✔ ½
- Defecation✔ ½
- Urination ✔½
- Body temperature ✔½
- Respiratory rate ✔½
- Pulse rate✔½
- Production level ✔½ ( ½ × 2 = 2mks)
-
- Avoid excessive smoking of hive✔½
- Do not allow rain water into the hive. ✔½
- Use clean equipment ✔½
- Put on protective clothing to avoid getting stung. ✔½ ( ½ ×2 = 2 mks)
-
- Landrace
- Large white
- Saddleback
- Duroc jersey
-
-
- Close breeding ✔1
Rej. Inbreeding (too general) (1 × 1 = 1 mk
- Close breeding ✔1
-
- Leads to loss of hybrid vigour ✔½
May lead to decline in fertility leading to species extinction ✔½ - Bring reduction in performance. ✔½
- Leads to high rate of pre-natal mortality. ✔½
Poor quantities are easily passed. ✔½ (½ ×4 = 2mks)
- Leads to loss of hybrid vigour ✔½
-
-
- Through Vectors ✔½
- Through the air ✔½ Through contact 1✔½
- Through contaminated water✔½
- Through contaminated food✔½ (½ ×4 = 2 mks)
-
- Dibber- making holes for transplanting
- Halter — control of animals movement especially during animal parades. ✔½
- Bolus gun — shooting solid drugs through the mouth of an animal. ✔½
- Shovel — lifting soil and manure. ✔½ (½ ×4 = 2 mks)
-
- Prevents infection by mastitis. ✔½
-
- Presence of feeds. ✔½
- Presence of a calf ✔½
- Noise related to milking ✔½
Presence of a milkman ✔½ - Stimulation of udder by warm water ✔½ (½ × 5 = 2 mks)
-
- Restlessness. ✔½
- Visible pin bones ✔½
- Loose and slackened pelvic girdle. ✔½
- Swollen vulva ✔½
- Mucus (thick) discharged from the vulva ✔½
- Distended udder ✔½
- Drips of colostrum ✔½
- Water bag appears and burst. ✔½ (½ ×4 = 2 mks)
-
-
- Young male castrated cattle ✔½
- A bird rendered sterile ✔½
- Giving birth in rabbit / young ones of rabbits. ✔½ (½ × 3= 1 ½ mks)
- Charolais. ✔½ (½ mk)
-
-
- Litter size / no of offspring ✔½
- Frequency of farrowing ✔½
- Number of teats ✔½ (½ × 2 = 1 mk)
-
- For maximum foetal growth ✔½
- Build up of energy for parturition ✔½
- Ensure birth of healthy animal ✔½
- Promotes good health of the mother ✔½
- Increase / maintain high milk yield after birth. ✔½ (½ ×4 = 2 mks)
-
- It is highly nutritious.
- Contain vitamins for growth.
- It has antibodies- enable calves to resist infections.
- Has laxative effects.
- Is highly palatable.
- Is highly digestible.
-
-
- Slatted floor ✔½
- Raised floor ✔½ (½ ×2 = 1 mk)
-
- Windward side wall is completely solid / covered ✔½
- Placed in a sheltered place. ✔½ (½ ×2 = 1 mk)
-
-
- Is the practice of fitting the rams with breeding chutes on the underside which are painted with colours during breeding / mating. (1 mk)
-
- Used to identify rams which have mated. ✔½
- Helps to identify ewes that have been mated. ✔½
- Helps to identify fertile rams. ✔½ (½ ×2 = 1mk)
-
- Easy to clean ✔½
- Fast /good drainage ✔½
- Eradicate predisposing factors. ✔½ (½ ×2 = 1 mk)
-
- Controlling external / ectoparasites✔½
- Watering / provide drinking water. ✔½ (1 × ½ = ½ mk)
-
- Prevent evaporation
- Prevent dilution of chemicals by rain water (2× ½ = 1 mk)
- A - Assembling animals
B - Cleaning animal hoofs. (2× ½ = 1 mk) -
- Source of water
- Drainage
- Wind direction
- Accessibility (4 × ½ = 2 mks)
-
-
-
- Restrain animal / piglet properly
- Using one hand to pull the testis slightly
- Using the other hand make a cut at the base of scrotum
- Squeeze out the testis until spermatic cord is extended and exposed
- Make zig-zag scratch to cut spermatic cord (RJ cutting only)
- Remove the testis
- Disinfect the cut
- Apply healing oil / appropriate drug
- Repeat the procedure on the second testis
NB: mark in this order / procedure
(8 × ½ = 4mks)
-
-
-
- Q-crop ✔½
- R-proventriculus/ true stomach ✔½
- S-gizzard ✔½
-
- Q-temporary storage of food ✔½
- moistening of food ✔½
- R-production of pepsin. ✔½
- S-provide grit / sand in the diet. ✔½
-
-
- Stir-up pump. ✔½
- Spraying livestock ✔½
-
- G - Trigger ✔½
- E - Nozzle ✔½
- F - (Brass) lance. ✔½ ( 1 ½ mk)
-
- Need two people to operate. ✔1
- Not easy to carry about during operation. . ✔1 (1× 2 = 2 mks)
-
-
-
- Streptococcus agalactiae ✔1
- Staphylococcal mastitis ✔1
-
- age ✔1
- Stage of lactation period ✔1
- Udder attachment ✔1
- Incomplete milking ✔1
- Mechanical injuries ✔1
- Poor sanitation ✔1
- Poor milking technique. ✔1
-
- Pus, blood, thick clots in milk or watery milk ✔1
- Pain when milking / udders / teats are swollen ✔1
- Death of infected quarter.✔1
- Salty taste in milk, fine clots or flakes in fore milk ✔1 (1 x 4 = 4 mks)
-
- Empty the affected quarter of udder and instill antibiotic ✔1
- Use teat dip on each teat after every milking. ✔1
- Use the right milking technique.✔1
- Strict cleanliness and use of disinfectant during milking.
- Dry cow therapy./ infusing a long acting antibiotics into the teat canal when drying off the cow. ✔1
- Use a strip cup to test for mastitis, infected animals should be milked last.
- Use separate udder clothes ✔1
- Remove sharp objects from grazing and milking areas to prevent teat injury ✔1
- Open wound on the teats should be treated immediately. ✔ ½ (1 x 5 =5 mks)
-
-
- Check on the following areas.
- Presence of eggs in animal faeces/ dropping✔1
- Swollen stomach / distended stomach✔1
- Staring coat / hair ✔1
- Unhealthy status / condition ✔1
- Loss of appetite ✔1
(1 x 4 = 4mks)
-
-
- A Various methods of disease control
- Proper feeding and nutrition.
Proper feeding not only avoid deficiency diseases but also make animals strong and hence able to resist disease attack. Livestock should be given balanced rations diets which must be adequate in quantity and quality. - Proper breeding and selection
Healthy animals should be selected for bleeding such animals should be free from disease or be resistant to prevalent diseases. - Proper housing and hygiene
Animals houses should be constructed such that they meet the necessary requirement for particular animals and that should be well ventilated, leak proof, proper drainage and easy to clean. - Isolation of Sick animals
It’s preventive measures taken when an animal is suspected to have contracted a disease any animal slowing clinical symptoms of ill health should be isolated to avoid further speed. Its usually applied against highly infections and contagious diseases. - Imposition of quarantine
This is the restriction of movement of animals and their production from and into the infected areas in the event of an outbreak of a notable disease. - Carrying out regular vaccinations.
This is an article way of giving animal some immunity against a particular disease. Vaccines are preparation meant to stimulate the production of antibodies in an animal
(Stating 1 x Explaining 1 mk)
5 x 2 = 10 marks)
- Proper feeding and nutrition.
- Explain the predisposing factors to animal disease
- The species of the animal
This determines the type of disease that is likely to affect that species and not any other e.g. swine fever only affects pigs - The breed of the animal
This will influence the kind of disease that will affect a particular bleed of animal for example piglet anemia affect only piglet lamb dysentery affects only lambs - The sex of the animals
There are certain disease which are associated with the sex of the animal. This is due to the different structure of various organs in the two sexes. For example orchitis will affect male animals viginitis will affect the female animals. - The colour of the animals.
Animals which are black in colour are likely to suffer from heat stress. On the other hand animals with light pigmented skin may suffer from disorder such as photosensition was exposed to high light intensity
(Stating 1 x = Explain (1mk)
5 X 2 = 10 marks)
- The species of the animal
- A Various methods of disease control
-
-
- Disinfect the brooder 2 — 3 days before the day old chicks are brought in.
- Spread newspaper over the litter to prevent chicks from eating litter. ✔1
- Spread some food on the newspaper so that chicks can learn to eat.
- Remove the newspaper when the chicks have learnt to eat from feeders
- Feed on chick mash up to 8th week. ✔1
- Gradually introduce growers mash from week 7 ✔1
- Debeak (on the 10th day) ✔1
- Keep chicks in the brooder for 6—8 weeks. ✔1
- Provide and maintain source of heat as necessary. ✔1
- Provide adequate clean water ✔1
- Vaccinate against common diseases especially new castle. ✔1
- Control external parasites ✔1
- Insulate sick chicks ✔1
- Treat sick chicks. ✔1
- Introduce roosts for perching (on 6th week) ✔1
- Introduce grit / sand to help in digestion. ✔1
- Hang green vegetable to keep them busy. ✔1
- Feed on grower’s marsh to 18th – 20th week. ✔1
- Gradually replace by layers mash from 18th week.✔1
- A specific day/week must be indicated to award mark.
(1 ×14 = 14 mks)
-
- Ensure correct and adequate supply of food for fish through regular pond fertilization.
- Control stocky rate to avoid overpopulation
- Control water pollution by removing debris
- Lime the fishpond regular.
- Maintain a steady supply of flowing water. This ensures that there is sufficient oxygen in the water
- Maintain appropriate level of water in the pond by regulating the flow of water in and out of the pond.
- Harvest the fish at the right stage of maturity.
- Control predators by facing off the pond
- Remove weed or grass that grows on the pond lining.
(6×1 = 6 mks)
-
Download Agriculture Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Joint Pre-Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students