PHYSICS
PAPER TWO
SECTION A 25 MARKS
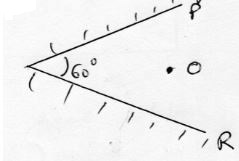
- An object O is placed between two mirrors P and R which are at 60o to each other as shown in the diagram below
Determine the number of images formed (2mks) - State one use of a charged gold leaf electroscope (1mk)
-
- Differentiate between polarization and local action in a simple cell (2mks)
- State the use of manganese (iv) oxide in a dry cell (1mk)
- On the figure below draw magnetic field lines between the poles (1mk)
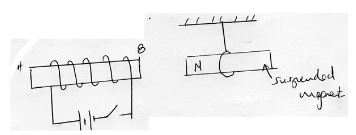
- The figure below shows a soft iron bar AB placed in a coil near a freely suspended magnet
Explain the observation made when the switch is closed (2mks) - A girl standing in front of a cliff blows a whistle and hears the echo after 0.5 second. She then moves 17 metres further away from the cliff and blows the whistle again. She now hears the echo after 0.6 seconds. Determine the speed of sound (3mks)
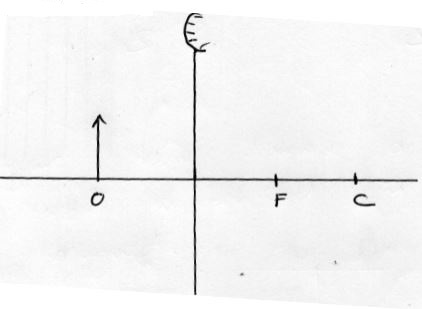
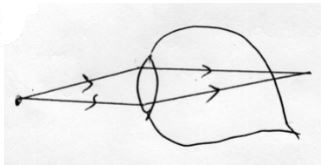
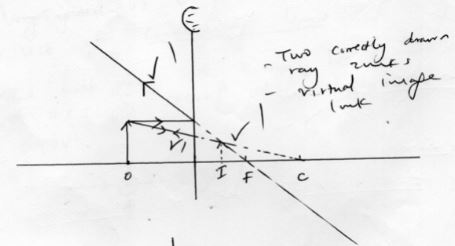
- Copy and complete the ray diagram to locate the position of the image for the object placed at O in front of a convex mirror (3mks)
- Determine the critical angle of a medium of refractive index 1.65 (2mks)
-
- Define the term electromagnetic spectrum (lmk)
- Name one detector of infrared radiation (lmk)
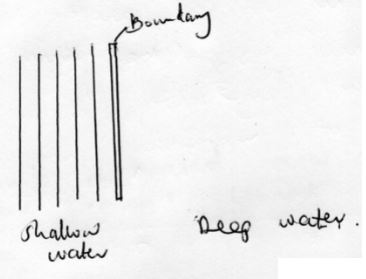
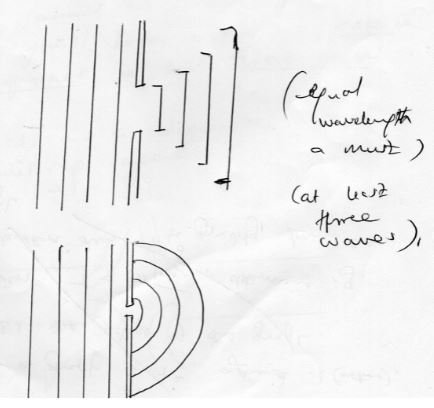
- The diagram below shows plane waves moving from shallow to deep end of a pond
- Complete the diagram to show the waves on the deep end (lmk)
- State what happens at the boundary to the frequency of the waves (lmk)
- The figure below shows a human eye with a certain defect
- Name the defect (lmk)
- State how the defect can be corrected (lmk)
- A bulb is rated 75w, 240v. What does this mean? (lmk)
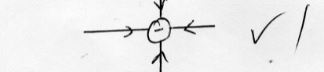
- Draw electric field pattern on the following isolated charge
SECTION B 55 MARKS
Answer all questions in this section
-
- Describe how the focal length of a convex lens can be determined using a screen and a metre rule (3mks)
- An object is placed 8cm from a diverging lens whose radius of curvature is 20cm. Determine the position of the image (3mks)
- An object of height 10cm is placed 30cm from a concave mirror of focal length 18cm.
- On the grid provided draw a ray diagram to locate the position of the image formed (3mks)
- From the diagram in part c (i) determine the
- image height (2mks)
- Image distance (2mks)
-
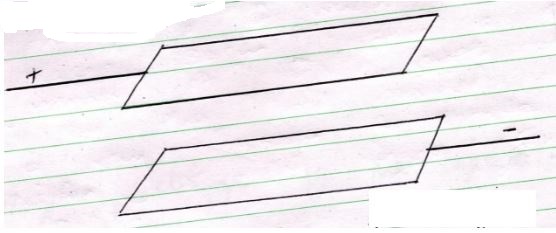
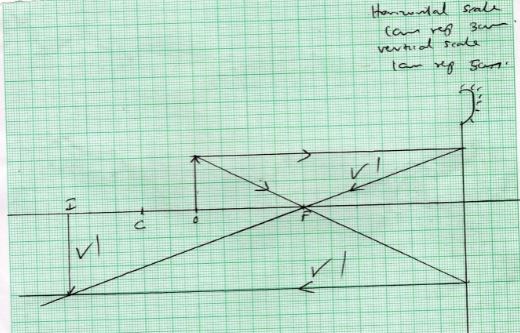
- The figure below shows a pair of parallel plates of a capacitor connected to a battery. The upper plate is displaced to the left.
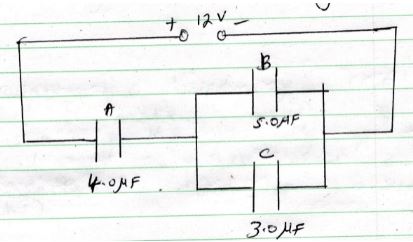
State with reason the effect of this movement to the capacitance (2mks) - the figure below shows an electric circuit with three capacitors A,B and C of capacitance 4.0µf, 5.0µf and 3.0µf respectively connected to a 12v battery
Determine- The combined capacitance of the three capacitors (3mks)
- The charge of the capacitor A (2mks)
- The potential difference across the capacitor B (2mks)
- The figure below shows a pair of parallel plates of a capacitor connected to a battery. The upper plate is displaced to the left.
-
- Define Ohm’s law (lmk)
- State two factors affecting the resistance of a conductor (2mks)
- Calculate the length of a wire required to make a resistor of 0.5Ω if the resistivity of the material is 4.9 x 10-7 Ωm and cross –sectional area is 2.0 x 10-6m2 (3mks)
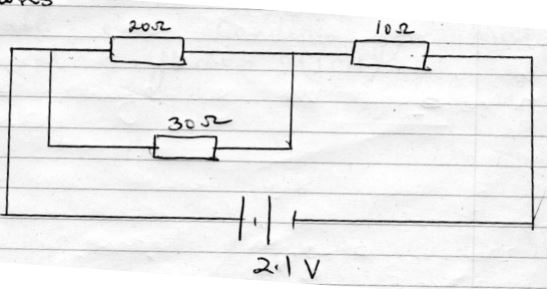
- Study the circuit diagram below and answer the questions
- What is the total resistance in the circuit (2mks)
- Determine the total current in the circuit (2mks)
- Find the voltage across the 10Ω resistor (2mks)
-
- Define critical angle (lmk)
- State one condition for total internal reflection (lmk)
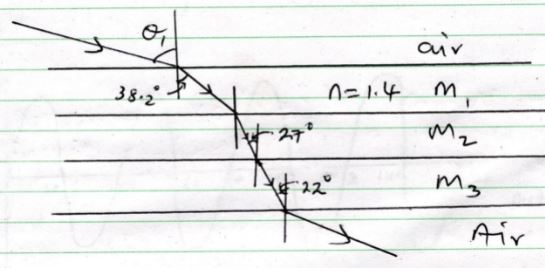
- A ray of light travels from air through a multiple of transparent media m1, m2 and m3 with boundaries that are parallel to each other.
The refractive index of medium 1 is 1.4 and angles are shown on the diagram.
Calculate the following- Angle θ1 (3mks)
- Refractive index of m2 (3mks)
- Speed of light in m1 given speed of light in air is 3.0 x 108 m/s. (2mks)
-
- Define period (lmk)
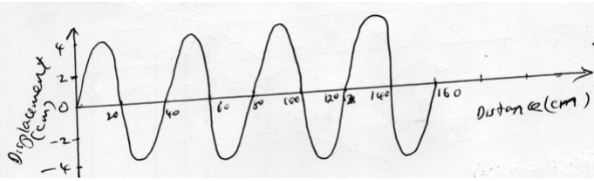
- The figure below shows waves in a spring travelling along it from one end
- Determine
- Wavelength of the wave (lmk)
- Amplitude of the wave (lmk)
- If the velocity of the wave is 3.2m/s determine the
- Frequency of the wave (3mks)
- Period of the wave (2mks)
- Determine
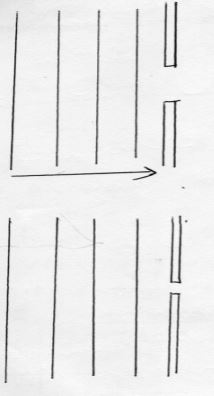
- Waves in a ripple tank are incident on slits as shown below, complete the diagram to show the diffracted waves (2mks)
MARKING SCHEME
- No. of images = 360 - 1
θ
360 - 1 = 5 images
θ -
- Used to test insulation properties
- Used to test sign of charges (Any one)
-
- Polarization a production of hydrogen gas around the copper plate (positive plate) Local action is presence of impurities in the zinc plate .
- Acts as a depolariser or oxidizing agent
-
- Repulsion like pole repel and end B attains north pole (Accept n on the diagram if explanation is not there)
- V= 2s/t
2 x 17/0.1 = 340m/s -
- = 1/’sin c sin c = 1/1.65
C=37.31º -
- Arrangement of electromagnetic waves in order of increasing or decreasing wavelength or frequency
-
- Skin
- Blackened bulb thermometer
-
-
- Frequency remains constant
-
-
- long-sightedness
- Use of converging lens
- The bulb gives out energy at a rate of 75J per second when operated at 240v
-
-
-
- Using a lens focus on distance object into the screen
- Adjust the distance between the lens and screen to obtain a sharp image
- Measure the distance between the screen and the lens using a metre rule – this is the focal length of the lens
- u= 8cm
r= 20
f = 10cm
r= ?
1/f = 1/r + 1/u
-1/10 = 1/v + 1/8
1/v = -1/10 - 1/8
1/v = 4 - 5/40 = -9/40
v=4.44cm -
-
-
- HI = 3x 5 = 15cm + 2cm
- R= 14.8 x3 = 44.4cm + 0.5cm
-
-
-
- Capacitance decreases due to decrease in area of overlap
-
- 5+ 3 = 8µf
C₁ = C₁ C₂ = 8 x 4 = 32 = 2.667µf
C₁ +C₂ 8+4 12 - Q= CV 2.667 x 12 = 32.004µc
- V= 4/c = 32.000/4 = 8.001v
12-8.001 = 3.999v
- 5+ 3 = 8µf
-
- the current flowing through a conductor is directly proportional to potential difference provided temperature and other physical condition are kept constant
-
- Temperature
- Cross sectional area
- Length of conductor (Any two)
- L= RA/e
L= 0.5 x 2.0 x10¯⁶
4.9 x 10 -7
L= 2.0408M -
- 20 x 30 = 600 = 12µ
CT = C₁ + C₂ = 12 +10 = 22µ - V= IR I = V/R = 2.1/22 = 0.095A
- 0.095 x 10 = 0.95
- 20 x 30 = 600 = 12µ
-
- Angle of incidence is denser medium of which angle of refraction is less dense medium is 90o.
-
-
- Ray must be from denser medium to less dense medium.
- Angle of incidence is denser medium must be greater than critical angle
- ∫ sin i
Sin r
1.4 = sinθ1 sinθ1= 1.4sin 38.2
sin 38.2
θ= 59.97º
∫= 2.67 - ∫= C/V
1.4 = 3.0 x 108
V
V= 3.0 x 108 = 2.143 x 108m/s.
-
-
- Time taken to complete one oscillation
-
-
- 40cm or 0.4m
- 4cm
-
- V= f/π = 3.2/0.4 = 8Hz
- T = 1/f = 1/8 = 0.125 second
-
-
Download Physics Paper 2 Questions and Answers - MECS Cluster Joint Pre Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students