AGRICULTURE
PAPER 2
SECTION A (30 marks)
Answer all the questions in this section in the space provided.
- Explain the meaning of the following terms.
- Raddling. (½mk)
- Farrowing. (½mk)
- Caponisation (½mk)
- Gutting. (½mk)
- What do the figures 3.3.3 in pig production stand for? (1mk)
- Name any two tools in the farm that can be used to sharpen a blunt panga (1mk)
- Name two livestock diseases prevented by use of the vaccine blanthrax. (1mk)
- State any four mechanical methods of controlling ticks. (2mks)
- List any four farm structures a dairy cattle farmer may have in the farm. (2mks)
- State two disadvantages of using a barbed wire fence in sheep rearing. (1mk)
- State four characteristics of an effective acaricide. (2mks)
- State any four factors that affect the digestibility of feeds in an animal. (2mks)
- Distinguish between mothering ability and prolificacy. (1mk)
- State four characteristics of succulent roughage feedstuffs. (2mks)
- State four advantages of inbreeding. (2mks)
- Identify the breed of pig that has the following features.
-Broad and slightly dished snout.
- Has a white skin.
- Has upright ears.
Identity (1mk) - Name two methods used in castration of farm animals. (1mk)
- State four causes of stress in poultry. (2mks)
- List any two construction materials required in the construction of a green house. (1mk)
- Name any two sheep breeds kept for production of meat. (1mk)
- State how the following conditions are achieved in a calf pen.
- Draught free. (½mk)
- Proper lighting (½mk)
- State the functions of the following parts of a plunge dip
- Drying yard. (1mk)
- Foot bath. (1mk)
- State four uses of a crush. (2mks)
SECTION B 20 MARKS
Answer all questions in this section in the spaces provided.
- The diagram below represents an external parasite. Study carefully and use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the parasite above. (1mk)
- State any two harmful effects of the parasite above. (2mks)
- State any two control measures for the parasite above. (2mks)
- The diagram below shows a routine practice being carried out on an animal. Study it and answer the question that follows.
- Identify the practice. (1mk)
- Name the structure in which the practice is being carried out. (1mk)
- State three advantages of using the above structure instead of a plunge dip. (3mks)
- Below is a diagram of a cow suffering from a deficiency disease. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the disease the animal is suffering from. (1mk)
- State the cause of the disease. (1mk)
- List any three symptoms of the above disease. (3mks)
- The diagram below represents farm tools and equipment. Study and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the tools labeled A, and B. (2mks)
A
B - State one use of each of the tools labeled A and B. (2mks)
A:
B: - State one maintenance practice for the tool labeled A. (1mk)
- Identify the tools labeled A, and B. (2mks)
SECTION C (40 MARKS)
Answer any two questions in this section in the spaces provided
-
- Discuss New castle disease under the following sub headings.
- Causal organism. (1mk)
- Animals attacked. (1mk)
- Symptoms of attack. (5mks)
- Control measures. (3mks)
- Outline the characteristics of indigenous cattle breeds. (5mks)
- Describe five microbial activities that take place in the rumen of ruminant animals. (5mks)
- Discuss New castle disease under the following sub headings.
-
- State and explain any five predisposing factors of livestock diseases. (10mks)
- Describe the procedure of constructing a barbed wire fence. (5mks)
- Outline any five general functions of vitamins in livestock. (5mks)
-
- Discuss any five essentials of clean milk production. (10mks)
- Describe the process of egg formation in the reproductive system of a hen. (10mks)
MARKING SCHEME
- Explain the meaning of the following terms.
- Raddling. (½mk)
- This is the practice of fitting the rams with breeding chutes which are painted in different colours during breeding.
- This is the practice of fitting the rams with breeding chutes which are painted in different colours during breeding.
- Farrowing. (½mk)
- The act of giving birth in pigs.
- The act of giving birth in pigs.
- Caponisation (½mk)
- Act of making male birds lose their characteristics/ rendering male birds infertile.
- Act of making male birds lose their characteristics/ rendering male birds infertile.
- Gutting.
- he removal of the gut and intestines after opening the fish.
- he removal of the gut and intestines after opening the fish.
- Raddling. (½mk)
- What do the figures 3.3.3 in pig production stand for?
- 3months, 3 weeks ,3 days which is the gestation period of a sow.
- 3months, 3 weeks ,3 days which is the gestation period of a sow.
- Name any two tools in the farm that can be used to sharpen a blunt panga.. (1mk)
- File
- Oil stone.
- Name two livestock diseases prevented by use of the vaccine blanthrax. (1mk)
- Anthrax
- Black quarter/ Black leg.
- State any four mechanical methods of controlling ticks. (2mks)
- Burning the infested pastures.
- Interfering with or altering the ticks environment.
- Fencing off pasture land and farm.
- Starving the ticks to death.
- Handpicking the ticks from livestock and killing them.
- List any four farm structures a dairy cattle farmer may have in the farm. Crush.
- Plunge dip.
- Spray race.
- Zero grazing unit.
- Calf pen.
- State two disadvantages of using a barbed wire fence in sheep rearing. (1mk)
- Tears off the fleece / wool lowering its quality.
- Causes injury to the animal.
- State four characteristics of an effective acaricide. (2mks)
- Have ability to kill ticks.
- Harmless to both human& livestock.
- Be stableShould remain effective after having been fouled with dung, mud or hair
- State any four factors that affect the digestibility of feeds in an animal. (2mks)Chemical composition of the feed.
- Form in which the feed is offered to the animal.
- Species of the animal.
- Ratio of energy to protein
- Quantity of feed already present in the digestive system of the animal.
- Distinguish between mothering ability and prolificacy. (1mk)
- Mothering ability is the ability to take good care of the young ones/ natural instinct toward the young ones while prolificacy is the ability of the animal to give birth to many offspring at a time /large litter
- Mothering ability is the ability to take good care of the young ones/ natural instinct toward the young ones while prolificacy is the ability of the animal to give birth to many offspring at a time /large litter
- State four characteristics of succulent roughage feedstuffs. (2mks)
- High fibre content.
- High moisture content.
- Low protein content.
- High carbohydrate content.
- State four advantages of inbreeding. (2mks)
- Increases genetic uniformity in the herd.
- Fixes the required phenotypic uniformity.
- Used to get proven sires.
- Used to test prepotency in animals ie ability to pass desirable characteristics to the off springs.
- Identify the breed of pig that has the following features.
- Broad and slightly dished snout.
- Has a white skin.
- Has upright ears.
- Identity large white. (1mk)
- Name two methods used in castration of farm animals. (1mk)
- Open castration.
- Closed castration.
- State four causes of stress in poultry. (2mks)
- Sudden change such as change of feed.
- Strangers and predators like mangoose.
- Handling of birds e.g during vaccination.
- Sudden change of weather for instance from warm to cold weather.
- Sudden noise e.g a passing tractor.
- List any two construction materials required in the construction of a green house. (1mk)
- Metal or wooden frames.
- Translucent materials e.g polythene sheets.
- Name any two sheep breeds kept for production of meat. (1mk)
- Dorper.
- Blackhead Persian.
- Red maasai.
- State how the following conditions are achieved in a calf pen.
- Draught free.
- The windward side wall should be completely solid from bottom to top to prevent cold winds from entering the pen.
- Proper lighting. (1mk)
- Front wall of the calf pen should be constructed solid 60 to 90cm high while the rest of the space is covered with wire mesh.
- Front wall of the calf pen should be constructed solid 60 to 90cm high while the rest of the space is covered with wire mesh.
- Draught free.
- State the functions of the following parts of a plunge dip. (2mks)
- Drying yard. (1mk)
- The animals are held for a while to prevent pasture contamination as well as to allow all the animals to be released at the same time.
- Foot bath. (1mk)
- To wash the animals feet to remove mud and also contain chemicals which controls foot rot.
- To wash the animals feet to remove mud and also contain chemicals which controls foot rot.
- Drying yard. (1mk)
- State four uses of a crush. (2mks)
- Spraying against external parasites.
- Identifying animals by use of methods such as branding.
- Vaccination.
- Administering prophylactic drugs to the animals.
- Treating sick animals.
- Dehorning
- Pregnancy test
- Artificial insemination.
- Taking body temperatures.
- Hoof trimming
- Milking
- Any two. 2x1 = 2mks.
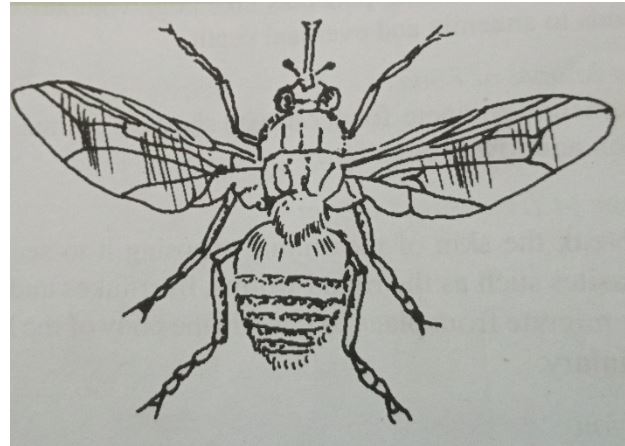
- The diagram below represents an external parasite. Study carefully and use it to answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the parasite above. (1mk)
- Tsetsefly.
- Tsetsefly.
- State any two harmful effects of the parasite above. (2mks)
- Transmits trypanosomiasis.
- Sucks out large volumes of blood leading to an anemia.
- Bites causing damage on skin and hides and make wounds which act as routes for secondary infection.
- State any two control measures for the parasite above. (2mks)
- Use of fly traps with impregnated nets.
- Use of sterilizing agents.
- Bush clearing in order to destroy the breeding places of the flies.
- Spraying their breeding places with suitable insecticides regularly will also kill the adult flies.
- Any two points 2x1 – 2mks.
- Identify the parasite above. (1mk)
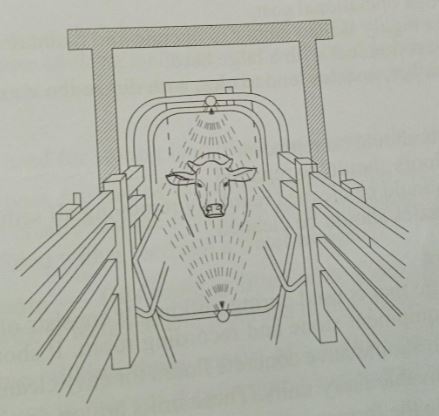
- The diagram below shows a routine practice being carried out on an animal. Study it and answer the question that follows.
- Identify the practice. (1mk)
- Spraying.
- Spraying.
- Name the structure in which the practice is being carried out. (1mk)
- Spray race.
- Spray race.
- State three advantages of using the above structure instead of a plunge dip. (3mks)
- Suitable for pregnant and sick animals.
- Acaricide wash is not wasted since it is recycled in the process.
- Animals cannot swallow the acaricide wash.
- Spraying is faster.
- Less labour is required.
- Any three points 3x1 = 3mks.
- Identify the practice. (1mk)
- Below is a diagram of a cow suffering from a deficiency disease. Study it and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the disease the animal is suffering from. (1mk)
- Milk fever./Parturient paresis. (1mk)
- Milk fever./Parturient paresis. (1mk)
- State the cause of the disease. (1mk)
- Lack of calcium in lactating cows. (1mk)
- Lack of calcium in lactating cows. (1mk)
- List any three symptoms of the above disease. (3mks)
- Dullness.
- Muscular twitching causing the animal to tremble.
- Staggering as the animal moves.
- Animal falls down and becomes unconscious.
- The animals lie down on its side and the whole body stiffens.
- Body functions such as urination, defecation & milk secretion stops.
- Sudden death.
- Stomach contents are drawn into the mouth which later causes lung fever when breathing in.
- Complete loss of appetite that is the animal does not eat at all.
- Any three points 3x1 = 3mks.
- Identify the disease the animal is suffering from. (1mk)
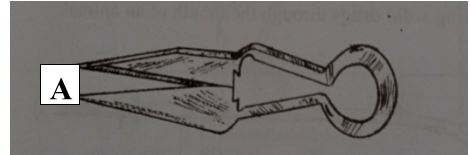
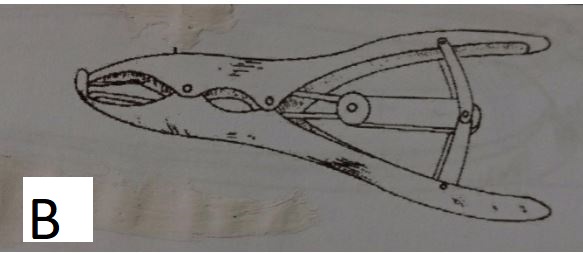
- The diagram below represents farm tools and equipment. Study and answer the questions that follow.
- Identify the tools labeled A, and B. (2mks)
- A – Wool shears.
- B – Elastrator.
- State one use of each of the tools labeled A and B. (2mks)
- A- Used for clipping or shearing fleece/ wool from sheep.
- B- used for expanding the rubber ring while castrating, docking or dehorning animals. (1mk)
- State one maintenance practice for the tool labeled A. (1mk)
- Clean after use.
- Sharpen the blunt cutting edges.
- Any one point 1x1 = 1mk.
- Identify the tools labeled A, and B. (2mks)
-
- Discuss New castle disease under the following sub headings.
- Causal organism. (1mk
- Virus.
- Virus.
- Animals attacked. (1mk)
- Poultry.
- Poultry.
- Symptoms of attack. (5mks)
- Birds have difficulties inbreathing / produce a harsh grating rasping sound when breathing.
- The beaks remain wide open and necks are strained.
- Birds loose appetite.
- Nasal discharge which force the birds to slake the heads to clear it.
- Birds walk with staggering motion since the nervous system is affected. Paralysis of wings and legs may occur.
- Often the birds have their beaks and wings down.
- Birds produce watery greenish diarrhea.
- Eggs laid have soft shells.
- Any 5 points 5x1=5mks.
- Control measures. (3mks)
- Quarantine.
- Vaccination should be done during the first weeks and then two to three months later.
- Kill all the attacked birds and burn them.
- Clean and disinfect the house before bringing in new stock.
- Any 3 points 3x1 = 3mks.
- Causal organism. (1mk
- Outline the characteristics of indigenous cattle breeds. (5mks)
- They have humps that store fat which is broken down to energy and water in times of starvation.
- They are fairly tolerant to high temperatures due to the presence of dewlap and thick hides.
- They have high tolerance to tropical diseases such as trypanosomiasis.
- They have a slow growth rate leading to late maturity.
- They have low production of both meat and milk due to inheritance of poor characteristics.
- They can walk for long distances in search of food and water.
- They can stay for long periods without food and water without seriously affecting their performance and body condition.
- They have long calving intervals of more than one year.
- Any 5 points 5x1=5mks.
- Describe five microbial activities that take place in the rumen of ruminant animals. (5mks)
- Fermentation of food.
- Synthesis of vitamin B complex.
- Synthesis of amino acids from ammonia gas.
- Breakdown of proteins to peptides, amino acids and ammonia.Breakdown of carbohydrates and cellulose to carbon (iv)
- oxide and volatile fatty acids.
- Any 5 points 5x1=5mks.
- Discuss New castle disease under the following sub headings.
-
- State and explain any five predisposing factors of livestock diseases. (10mks)
- The species of the animal – there are diseases that attack specific species of animals and not any other species e.g swine fever affects only pigs.
- The breed of the animal – There are diseases that will affect a particular breed of animal e.g Cancer of the eye will affect only Hereford breed of cattle.
- The age of the animal – There are certain diseases which are associated with animals of a certain age group e.g piglet anemia fro piglets.
- The sex of the animal – There are certain diseases which are associated with the sex of the animal e.g orchitis will affect male animals as it is a disease of the testes.
- The colour of the animal – Animals which are black in colour are likely to suffer from heat stress. Animals with light pigmented skins may suffer from disorders such as photosensitization when exposed to high light intensity.
- Stating 1 mk.
- Explanation 1mk
- 5 points x 2 = 10 mks.
- Describe the procedure of constructing a barbed wire fence. (5mks)
- Clear the fence line – should be 2m wide.
- Measure and mark points on the fence line when holes are to be dug.
- Dig holes to a depth of 60 cm for the main fence and 75cm to 90cm for eth corner and gate posts.
- Place treated posts in the holes in an upright position.
- Mix concrete of 1:3:5 ratio and place it in the hole/ put soil and stones in the hole and ram to firm the base.
- Nail barbed wire onto the posts with fencing staples while stretching using a wire strainer.
- Fix the lower to fix the next up to the required number.
- Fix the lower strand of wire first and use it as a guide to fix the next up to the required number.
- Being a procedural question ensure the steps are followed. (5mks)
- Outline any five general functions of vitamins in livestock. (5mks)
- Promote growth.
- Help in blood formation.
- Help in muscular activity.
- Prevent diseases in animals.
- Act as organic catalyst in various metabolic and physiological reactions.
- Any 5 points 5x1=5mks.
- State and explain any five predisposing factors of livestock diseases. (10mks)
-
- Discuss any five essentials of clean milk production.
- Healthy milking herd - The animals with milk borne diseases such as tuberculosis and brucellosis should be removed immediately from the herd and treated.
- Clean milking cows – The flanks, underline and whose udder should be washed and dried thoroughly before milking. The long hair on the udder and flanks should be clipped off regularly to avoid milk contamination.
- Healthy and clean milkman. – The milkman should be physically clean and preferably wear white overalls when milking and handling milk. The milkman should also keep the finger nails short and the hair covered.
- Clean milking shed – The milking shed should be kept clean, free from dust or odours. It should be built away from roads, poultry houses, piggeries and lavatories to avid dust and bad smells.
- Milk filtration, cooling and storage – Mil should be filtered and cooled down to 50c immediately after milking to slow down bacteria multiplication thereby improving its keeping quality.
- Clean milking utensils - The milking utensils and equipment should be seamless, smooth with joints filled to facilitate easy and thorough cleaning.
- Avoid flavours in milk – foodstuffs which cause bad flavor in milk should be fed to cows after and not before or during milking such food stuffs include Mexican marigold, onions, pineapples fruit wastes and silage.
- Any 5 points 5x2=10 mks.
- Describe the process of egg formation in the reproductive system of a hen.
- Ovary - A hen has two ovaries but only left one is functional.
- Eggs (ova) are formed in the ovary and upon maturation they are released from the ovary by the rapture of the follicle.
- The funnel (Infudibulum)
- Fertilization takes place here.
- Chalaza is added to hold the yolk.
- The ovum stays here for about ¼ an hour.
- Magnum
- Thick albumen is added.
- The yolk stays here for 3 hours.
- Isthmus.
- Shell membranes are added which determine the shape of the egg.
- Water, mineral salts and vitamins are added.
- The egg takes ¼ an hour here.
- Uterus (Shell gland)The shell is added round the egg.
- Shell pigments are added.
- Addition of albumen is completed here.
- Egg stays here for 18 – 22 hours.
- Vagina.
- The egg is temporarily stored here.
- The egg is turned so that it can be laid with the broad side first to avoid breakage.
- Cloaca.
- Extends out as the egg is laid to prevent the egg from breaking.
- Retracts back after the egg has been laid.
- Explanation of what takes place at each part must be correct and if time is indicated must be correct.
- The parts should not be inter changed. (10mks)
- Ovary - A hen has two ovaries but only left one is functional.
- Discuss any five essentials of clean milk production.
Download Agriculture Paper 2 Questions and Answers - MECS Cluster Joint Pre Mock Exams 2021/2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students