INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name, admission number, date and school in the spaces provided
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary
- Scientific calculators may be used
FOR EXAMINERS’ USE ONLY
|
Questions |
Maximum Score |
Candidate’s Score |
|
1 |
10 |
|
|
2 |
12 |
|
|
3 |
10 |
|
|
4 |
12 |
|
|
5 |
13 |
|
|
6 |
12 |
|
|
7 |
11 |
|
|
TOTAL |
80 |

QUESTIONS
-
- In an experiment to determine the percentage of oxygen in air, the apparatus below were set up Study the set up and the information provided to answer the
questions that follow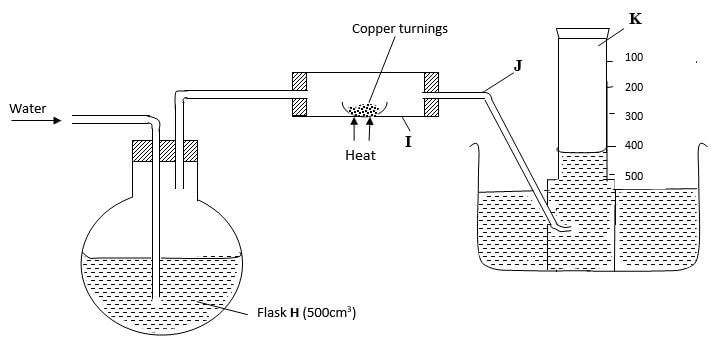
A 500cm3 measuring cylinder K was filled with water and assembled for gas collection Copper turnings were heated red hot and water was slowly passed into 500cm3 flask H until it reached the 500cm3 mark A colourless gas was collected in K- What was the purpose of passing water into flask H? (1 mark)
- What observations were made in the tube I? (1 mark)
- Name one of the gases that is likely to be found in J (1 mark)
- What was the volume of the gas collected in the measuring cylinder at the end of the experiment? (1 mark)
- Calculate the percentage of oxygen in air using the above results (2 marks)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow
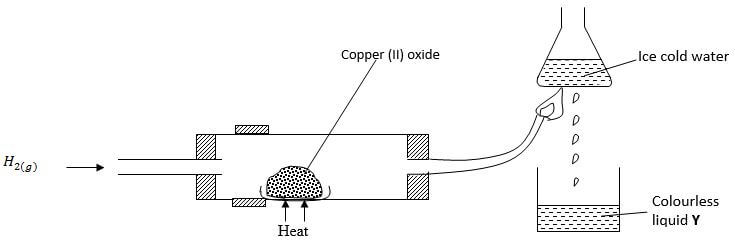
- Give one observation made in the combustion tube after some time (1 mark)
- Write an equation for the formation of the colourless liquid Y (1 mark)
- What was the aim of the above experiment as demonstrated in the combustion tube? Explain (2 marks)
- In an experiment to determine the percentage of oxygen in air, the apparatus below were set up Study the set up and the information provided to answer the
- Use the information below to answer the questions that follow The letters are not the actual symbols of the elements
Element
Atomic No
MP0C
BP0C
Ionic radius (nm)
P
11
98
890
0095
Q
12
650
1110
0065
R
13
660
2470
0050
S
14
1410
2360
0041
T
15
442 & 590
280
0034
U
16
113 & 119
445
0184
V
17
-101
-35
0181
W
18
-189
-186
-
-
- Write the electronic configuration of the atoms represented by letters T and W (1 mark)
- State the nature of the oxides of the elements represented by Q and U (2 marks)
- Why does the elements represented by the letters T and U have two values of melting points? (1 mark)
- Explain the following observations in terms of structure and bonding
- There is an increase in boiling point from P to R (2 marks)
- Element S has a high boiling point (2 marks)
- There is a decrease in boiling points from U to W (2 marks)
-
- Compare the atomic radius of U and V (1 mark)
- Why is there no ionic radius for W reported in the table(1 mark)
-
-
- The solubilities of potassium nitrate and potassium bromide at different temperatures was determined. the following data was obtained
Temperature 0C
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
Solubility g/100g H2O
KNO3
5
15
26
43
61
83
105
135
165
KBr
50
55
60
65
70
77
85
90
95
- Draw solubility curves for both salts on the same axis (3 marks)
- What was the solubility of each salt at 65ºC? (1 mark)
- 100g of a saturated solution of potassium nitrate at 70ºC was cooled to 20ºC What mass of the crystals will be crystallized? (2 marks)
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow
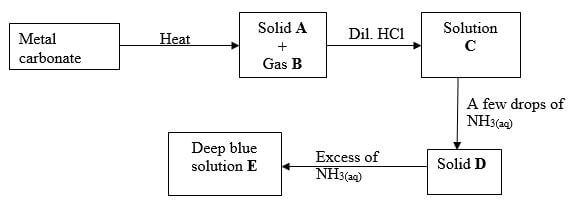
- Write an equation for the formation of solid A and gas B (1 mark)
- Name;
Solution C - (1 mark)
Solid D - (1 mark)
- Write the formula of the complex ion in solution E (1 mark)
- The solubilities of potassium nitrate and potassium bromide at different temperatures was determined. the following data was obtained
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow
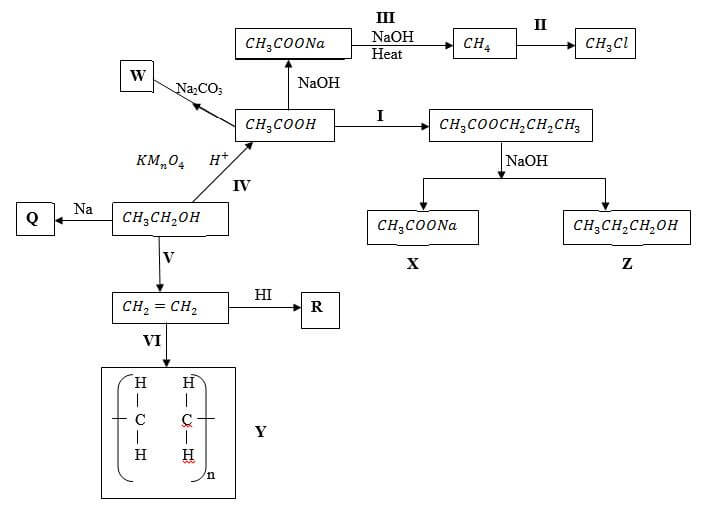
- Name substance (3 marks)
X -
Q -
R - - Write down an equation for the reaction represented by step III (1 mark)
- What are the conditions and reagent required for steps?
- I (2 marks)
Reagent -
Condition - - IV (2 marks)
Reagent -
Condition -
- I (2 marks)
- Name the process represented by: (4 marks)
I -
II -
IV -
V -
- Name substance (3 marks)
-
- Study the scheme below and answer the questions that follow
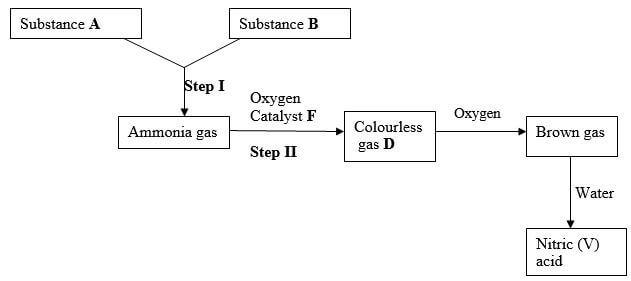
- Identify substances (3 marks)
A -
B -
D - - State the catalyst necessary for; (2 marks)
Step I -
Step II - - Write an equation for the reaction taking place in step II (1 mark)
- Write two balanced chemical equations for the reaction between chlorine gas and;
- Hot and concentrated sodium hydroxide (1 mark)
- Dilute and cold sodium hydroxide (1 mark)
- Identify substances (3 marks)
- The diagram below shows an experiment in which the Lead (II) nitrate crystals are heated
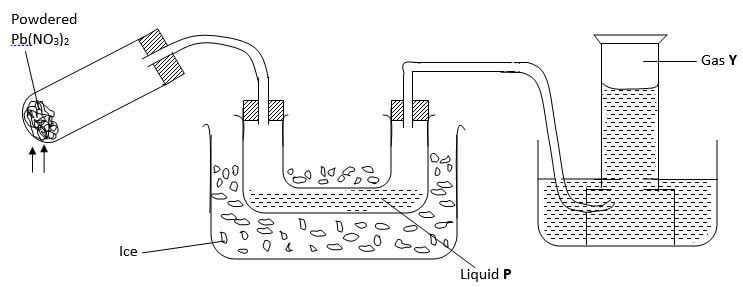
- Name; (2 marks)
- Liquid P -
- Gas Y -
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the decomposition of Lead (II) nitrate (1 mark)
- Explain how you can distinguish between nitrogen (II) oxide and nitrogen (I) oxide (2 marks)
- Name; (2 marks)
- Study the scheme below and answer the questions that follow
-
- Study the standard electrode potentials given below and answer the questions that follow
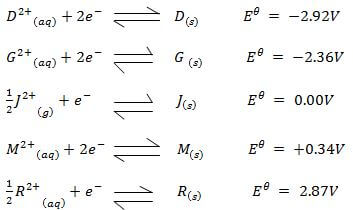
- Identify the strongest:
- Reducing agent (1 mark)
- Oxidizing agent (1 mark)
- Calculate the emf of a cell made of G and M (2 marks)
- Write the cell representation for the above cell in (b) (1 mark)
- Draw a cell diagram for the cell in (b) above (2 marks)
- Write the cell reaction for the drawn cell diagram in (d) above (1 mark)
- Identify the strongest:
- Electrolysis of aqueous solution of metal M resulted in the deposition of 107g of metal upon passage of a current of 132 amperes for 75 minutes
(M = 52, 1F = 96500C)- Calculate the quantity of electricity passed through the cell (1 mark)
- Calculate the charge on the metal ion (3 marks)
- Study the standard electrode potentials given below and answer the questions that follow
- Extraction of iron involves two main processes, smelting and refining Below is the blast furnace which is used to smelt iron from its ore
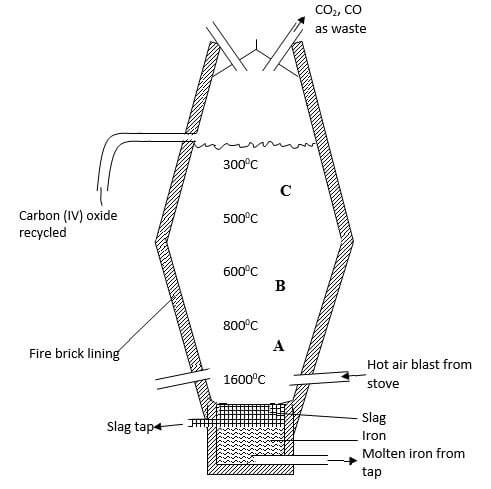
-
- What does the word smelt mean? (1 mark)
- Name the reducing agent in the process (1 mark)
- What is the role of the hot air blast in the process? (2 marks)
- Write equations for the reactions that take place at the region marked A, B and C (3 marks)
A -
B -
C - - What is the purpose of limestone in the extraction process? (1 mark)
- Write equations to show how impurities are removed from the ore (3 marks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
-
- In an experiment to determine the percentage of oxygen in air, the apparatus below were set up Study the set up and the information provided to answer the
questions that follow
A 500cm3 measuring cylinder K was filled with water and assembled for gas collection Copper turnings were heated red hot and water was slowly passed into 500cm3 flask H until it reached the 500cm3 mark A colourless gas was collected in K- What was the purpose of passing water into flask H? (1 mark)
To displace air in flask H over the hot copper turnings. - What observations were made in the tube I? (1 mark)
The brown solid changes to black - Name one of the gases that is likely to be found in J (1 mark)
Nitrogen, carbon (IV) oxide, argon, (Xeron, neon) (Any one) - What was the volume of the gas collected in the measuring cylinder at the end of the experiment? (1 mark)
410cm3 - Calculate the percentage of oxygen in air using the above results (2 marks)
(500 x 410) x 100 = 90 x 100 = 18%
500 500
- What was the purpose of passing water into flask H? (1 mark)
- Study the diagram below and answer the questions that follow

- Give one observation made in the combustion tube after some time (1 mark)
Black CuO turns to red-brown Cu.
- Write an equation for the formation of the colourless liquid Y (1 mark)
2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H2O(l) - What was the aim of the above experiment as demonstrated in the combustion tube? Explain (2 marks)
To determine the reducing property of hydrogen. Hydrogen is above Cu in the reactivityseries, thus it reduces the oxygen from CuO.
- Give one observation made in the combustion tube after some time (1 mark)
- In an experiment to determine the percentage of oxygen in air, the apparatus below were set up Study the set up and the information provided to answer the
- Use the information below to answer the questions that follow The letters are not the actual symbols of the elements
Element
Atomic No
MP0C
BP0C
Ionic radius (nm)
P
11
98
890
0095
Q
12
650
1110
0065
R
13
660
2470
0050
S
14
1410
2360
0041
T
15
442 & 590
280
0034
U
16
113 & 119
445
0184
V
17
-101
-35
0181
W
18
-189
-186
-
-
- Write the electronic configuration of the atoms represented by letters T and W (1 mark)
T - 2.8.5
W - 2.8.8 - State the nature of the oxides of the elements represented by Q and U (2 marks)
Q - Basic Oxide
U - Acidic oxide
- Write the electronic configuration of the atoms represented by letters T and W (1 mark)
- Why does the elements represented by the letters T and U have two values of melting points? (1 mark)
The two elements exhibit allotropy. - Explain the following observations in terms of structure and bonding
- There is an increase in boiling point from P to R (2 marks)
There is gradual increase in the strength of the metallic bonds due to the increase in the number of delocalized (valence) electrons in the element - Element S has a high boiling point (2 marks)
The atomic radius of V is smaller than that of U. V has more protons therefore has a stronger nuclear attraction hence the smaller atomic radius. - There is a decrease in boiling points from U to W (2 marks)
Elements U, V and W have simple molecular structures in which the molecules are held by weak Van der waals forces. The Van der waals forces weaken from U to W.
- There is an increase in boiling point from P to R (2 marks)
-
- Compare the atomic radius of U and V (1 mark)
The atomic radius of V is smaller than that of U. - Why is there no ionic radius for W reported in the table(1 mark)
It has a stable electron configuration hence does not ionize.
- Compare the atomic radius of U and V (1 mark)
-
-
- The solubilities of potassium nitrate and potassium bromide at different temperatures was determined. the following data was obtained
Temperature 0C
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
Solubility g/100g H2O
KNO3
5
15
26
43
61
83
105
135
165
KBr
50
55
60
65
70
77
85
90
95
- Draw solubility curves for both salts on the same axis (3 marks)
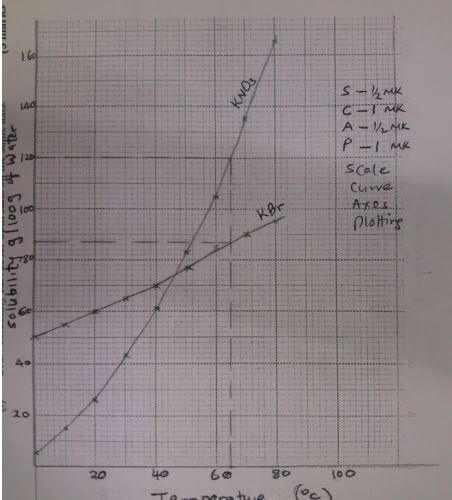
KBr - 87g/100g of water ± 1 - What was the solubility of each salt at 65ºC? (1 mark)
At 700C solubility = 135g/100g of water
If 235g contain 135g of salt
100g contain 135g
100 x 135 = 57.4468g
235At 200C solubility = 26g/100g of water
If 126g contain 26g of salt
100g contain ?
100 x 26 = 20.6349g
126
Mass which will crystallized
57.4468 – 20.6349
= 36.8119g - 100g of a saturated solution of potassium nitrate at 70ºC was cooled to 20ºC What mass of the crystals will be crystallized? (2 marks)
- Draw solubility curves for both salts on the same axis (3 marks)
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow

- Write an equation for the formation of solid A and gas B (1 mark)
CuCo3(g) heat → CuO(s) + CO2(g) - Name;
Solution C - Copper (II) chloride (1 mark)
Solid D - Copper (II) hydroxide (1 mark)
- Write an equation for the formation of solid A and gas B (1 mark)
- Write the formula of the complex ion in solution E (1 mark)
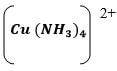
- The solubilities of potassium nitrate and potassium bromide at different temperatures was determined. the following data was obtained
- Study the flow chart below and answer the questions that follow

- Name substance (3 marks)
X - Sodium ethonoate
Q - Sodium ethoxide
R - Iodoethane - Write down an equation for the reaction represented by step III (1 mark)
CH3COONa(s) + NaOH(aq) → CH4(g) + Na2CO3(s) - What are the conditions and reagent required for steps?
- I (2 marks)
Reagent - Propan-l-ol
Condition - Conc. H2SO4 - IV (2 marks)
Reagent - Conc. H2SO4
Condition - Temp 160 – 1800C
- I (2 marks)
- Name the process represented by: (4 marks)
I - Esterification
II - Substitution
IV - Oxidation
V - Dehydration
- Name substance (3 marks)
-
- Study the scheme below and answer the questions that follow

- Identify substances (3 marks)
A - Hydrogen
B - Nitrogen
D - NO - State the catalyst necessary for; (2 marks)
Step I - Iron finely divided / iron
Step II - Platinum – rhodium catalyst - Write an equation for the reaction taking place in step II (1 mark)
4NH(3) + SO2 → 2NO(g) + 6H2O - Write two balanced chemical equations for the reaction between chlorine gas and;
- Hot and concentrated sodium hydroxide (1 mark)
6NaOH(aq) + 3Cl2(g) → NaClO3(aq) + 5NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) - Dilute and cold sodium hydroxide (1 mark)
2NaOH(aq) + Cl2 → NaOCl + NaCl + H2O
- Hot and concentrated sodium hydroxide (1 mark)
- Identify substances (3 marks)
- The diagram below shows an experiment in which the Lead (II) nitrate crystals are heated

- Name; (2 marks)
- Liquid P - dinitrogen tetra oxide
- Gas Y - oxygen
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the decomposition of Lead (II) nitrate (1 mark)
2Pb(NO3)2 → 2PbO(s) + 4NO2(s) + O2(g) - Explain how you can distinguish between nitrogen (II) oxide and nitrogen (I) oxide (2 marks)
• Nitrogen (V) oxide relights a glowing splint while nitrogen (II) oxide does not.
• N2O has xtic sweet smell, while. NO2 is odourless.
- Name; (2 marks)
- Study the scheme below and answer the questions that follow
-
- Study the standard electrode potentials given below and answer the questions that follow
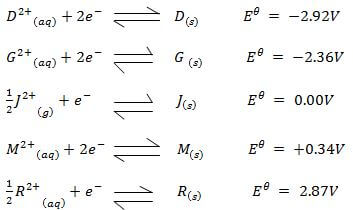
- Identify the strongest:
- Reducing agent (1 mark) D
- Oxidizing agent (1 mark) R2+
- Calculate the emf of a cell made of G and M (2 marks)
e.m.f = EθR - EθO
= +0.34 - -2.36
= +2.70V - Write the cell representation for the above cell in (b) (1 mark)
G(s) / G2+(aq) // M2+(aq) / M(s) ;E= +2.70V Penalize for lack of states and E value - Draw a cell diagram for the cell in (b) above (2 marks)
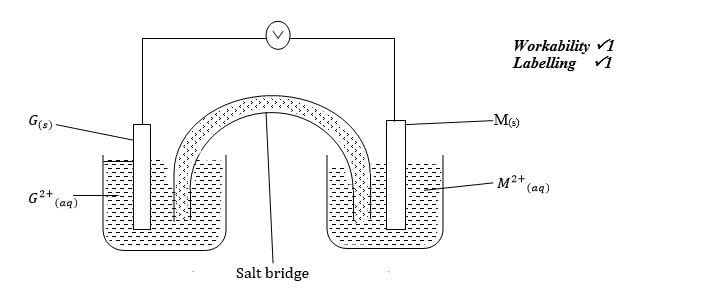
- Write the cell reaction for the drawn cell diagram in (d) above (1 mark)
G(s) + M2+(aq) → G2+(aq) + M(s); E = +2.70V
- Identify the strongest:
- Electrolysis of aqueous solution of metal M resulted in the deposition of 107g of metal upon passage of a current of 132 amperes for 75 minutes
(M = 52, 1F = 96500C)- Calculate the quantity of electricity passed through the cell (1 mark)
Q = 1t
=1.32 x 75 x 60
= 5940C - Calculate the charge on the metal ion (3 marks)
If 1.07g is departed by 5940C
52g “ “
(52×5940)=288,672.8972C
1.07
If 1F is 96500C
? “ 288672.8972C
(1×288,672.8972)
96500
= 2.994 ± 3
- Calculate the quantity of electricity passed through the cell (1 mark)
- Study the standard electrode potentials given below and answer the questions that follow
- Extraction of iron involves two main processes, smelting and refining Below is the blast furnace which is used to smelt iron from its ore

-
- What does the word smelt mean? (1 mark)
Extraction of a metal from its ore using a reducing agent and heat.
- Name the reducing agent in the process (1 mark)
Carbon ( in form of coke) - What is the role of the hot air blast in the process? (2 marks)
Hot air reacts with coke to form carbon (IV) oxide producing a lot of heat which melts the iron formed in the blast furnace.
- What does the word smelt mean? (1 mark)
- Write equations for the reactions that take place at the region marked A, B and C (3 marks)
A - C(s) + O(2) → CO2(g)
B - CO2(g) + C(s) → 2CO(g)
C - 2Fe2O3 + 3C → 4Fe(s) + 2CO2(g) - What is the purpose of limestone in the extraction process? (1 mark)
To remove silica impurities in the ore. - Write equations to show how impurities are removed from the ore (3 marks)
CaCO3(s) heat → CO2(g)
CaO(s) + SiO2(s) → CaSiO3(s)
Al2O3 + CaO(s) → CaAl2O4(s)
slag
-
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - KCSE 2022 Kapsabet Highschool Trial 1 Pre-Mock Examination.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

