- This paper consists of section A and B.
- Answer ALL questions in section A and B.
- All your workings must be clearly shown as must be awarded for correct working even if the answer is wrong.
- Non programmable silent scientific calculators and KNEC mathematical tables may be used.
SECTION A (25MARKS)
Answer all the questions in this section
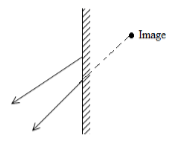
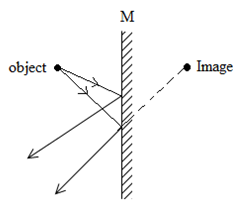
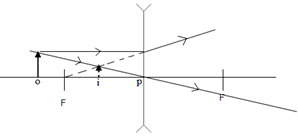
- Figure (1) below shows two rays of light from an object reflected on a plane mirror
Fig 1.
Using proper ray construction, show the object position (2marks) - The fig 2 below shows a ray of light incident on a glass prism
Fig2
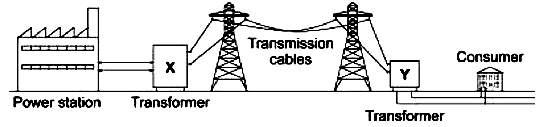
Given that the critical angle for the grass is 39°, sketch on the diagram the path of the ray through the prism. (2 marks) - The diagram on figure 3 shows the National Grid system.
Fig3.
What type of transformer is;- X………………………………………… (1mark)
- Y…………………………………………. (1mark)
- State one advantages of using circuit breakers in the consumer unit than using fuse wire. (1marks)
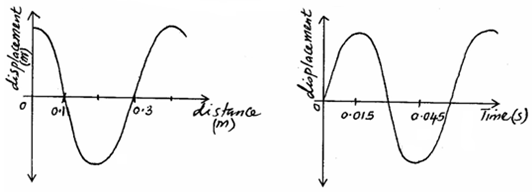
- The figures below shows two waveforms representing the same wave motion.
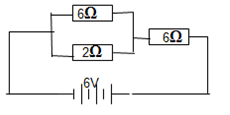
Determine the velocity of the wave. (3mks) - Figure 4. Below shows a 6V battery connected to an arrangement of resistors. Determine the current flowing through the 2Ω resistor. (3marks)
- The figure 7 below shows the electromagnetic spectrum.
Fig 7.Radio waves Infrared rays A Ultra - violet rays B Gamma rays - Identify A (1 mark)
- State one industrial use of B (1 mark)
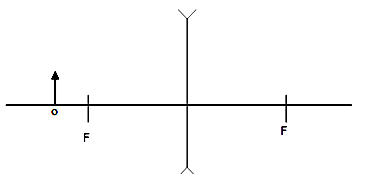
- The diagram (Fig 8) shows a positively charged acetate strip and a negatively charged polythene strip that are freely suspended.
Fig8.
Two rods X and Y are brought up in turn to these two strips. Rod X attracts the acetate strip but repels the polythene strip. Rod Y does not repel either the acetate strip or the polythene strip.
State the type of charge is on each rod. (2mks)- X……………………………………………………………………………………….
- Y………………………………………………………………………………………
- State two advantages of an alkaline accumulator over lead acid accumulator. (2mks)
- Figure 9 below show a concave lens and object.
Fig 9.
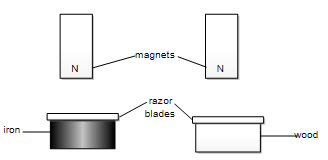
Sketch the rays to show the image formed. (2marks) - Two similar razor blades were placed on a wooden block and the other on an iron block as in figure 10.
Fig 10.
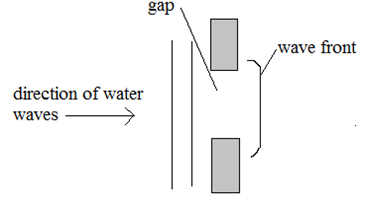
It was observed that the razor blade on the wooden block is attracted by the magnet while that on the iron block was not.Explain. (2 marks) - The figure 11 below shows water waves about to pass through a gap. One wave front is shown after it has passed through the gap.
Fig 11- On the diagram, draw two more wave fronts that have passed through the gap. (1mark)
- State two changes which would each make the wave fronts become more curved after passing through the gap.
(1 mark)
SECTION B (55MARKS)
ANSWER ALL THE QUESTIONS IN THIS SECTION.
-
- State what is meant by refractive index of a material. (1 mark)
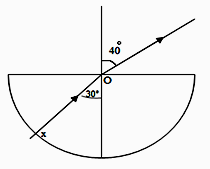
- Figure 12 represents a ray of light falling normally on the curved surface of a semi-circular plastic block at X, meeting the opposite face at an angle of incidence of 300 and emerging into the air at an angle of 400.
Fig 12- State and explain what happens to the ray as it moves from:
- Air to glass at X. (1marks)
- From glass to air at O. (1marks)
- Calculate refractive index of the plastic. (3marks)
- State the conditions to be satisfied for total internal reflection to occur. (2marks)
- Describe how the apparatus above could be used to find the critical angle experimentally. (3marks)
- Calculate the critical angle for this plastic. (2marks)
- State and explain what happens to the ray as it moves from:
-
- State what is meant by the term capacitance. (1marks)
- Distinguish between a paper capacitor and an electrolyte capacitor. (1marks)
- State two factors that determine capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor (2mks)
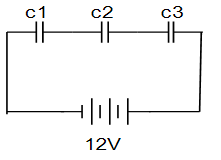
- Figure 10 below shows a network of capacitors in series.
Fig 10.- Derive an expression for their effective capacitance CE from first principles. (3marks)
- Given that C1=10.5µF, C2 =2µF and C3= 3µF.
Calculate effective capacitance CEin (2) above and hence
Determine the charge stored on each capacitor. (3marks)
- State two applications of capacitors. (2marks).
-
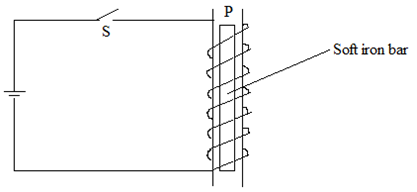
- Use the figure 11 below to answer the questions that follows.
Fig.11- Show the direction of the current on the turns when the switch S is closed. (1marks)
- State the polarity at P (1marks)
- Explain using domain theory what happens on the soft iron bar. (1marks)
- If steel bar was used instead, what could be the difference? (2marks)
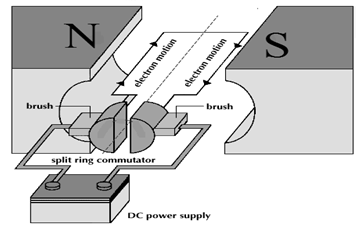
- The following diagram (figure 12), shows a part of an electric d.c motor.
Fig 12.- On the diagram above show the direction of rotation of the coil. (1marks)
- State the effect of increasing the number of turns of the rotating coil of an electric motor. (1marks)
- Sketch the magnetic field pattern around the conductor carrying current on figures 13 and 14 shown below. (2marks)
Fig 13. Fig 14
- Use the figure 11 below to answer the questions that follows.
-
- Distinguish between real image and a virtual image. (2mks)
- The distance between an objectand itsupright image produced by a curved mirror is 40cm. the image is 3 times as tall as the object
- State the type of mirror used. (1mk)
- Determine the object distance (2mks)
- Determine the radius of curvature of the mirror (3 mks)
- State one application of the mirror as used in (b) above (1mk)
-
- State Ohm’s Law. (1mk)
- Explain why a 12V car battery is able to start the motor car engine while eight dry cells of 1.5 v each connected in series will not. (2mks)
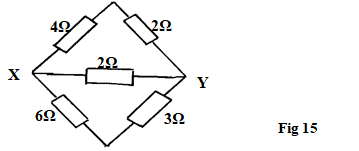
- In figure 15 the current in the circuit is 1.80A
- Find the effective resistance between X and Y. (3mks)
- The p.d of the source. (2mks)
- Current through the 3Ω resistor (2mks)
- Give two differences between a primary and a secondary cell (2mks)
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
-
- for correct rays with arrows 1 mark
- distance OM = MI 1 mark
-
- X-step-up transformer√1mark, Y-step-down transformer√1mark
-
- circuit breakers do not require replacement. √1mark
- circuit breakers response is instantaneous. √1mark
- λ = 0.4m✓1mark
T = 0.06m ✓1mark
V = λ f = 0.4 × 0.06
=0.024ms-1 √1mark - RT = 6×2 + 6 =7.5Ω√1mark
6+2
IT = V/ RT = 6 = 0.8A
7.5
Current across 2Ω = 1.2 = 0.6A √1mark
2 -
- A-Visible light√1mark ,
- X-rays- Used to get the correct thickness of materials e.g. papers √1mark
- X-negative. √1mark, Y-neutral/no charge. √1mark
-
- Alkaline produces higher current
- Lasts longer
- It is portable
- Less maintenance and care
-
√1mark for correct rays and √1mark for correct image position and size - The magnet induces magnetism into the razor√1mark which in turn Induces the iron block√1mark hence the razor remains attracted to the iron block.
-
-
√1mark
-
- Make the gap smaller. √1mark
- Reduce the frequency of the source producing the wave/make wavelength longer. √1mark
-
SECTION B
-
- The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of retraction for a material. √1mark
-
-
- the ray enters the plastic block at right angle at X. it travels undeflected at X. √1mark
- At O the ray strikes the boundary at an angle of 300 and is refracted away from the normal since it moves from a optically denser medium to (air) a less dense medium through 400 √1mark
- Refractive index of a material
n = sin 40° √1mark
sin30°
= 1.286√1mark -
- Light must travel from optically denser medium to optically less dense medium.√1mark
- Angle of incidence in the denser medium must be greater than critical angle in the less dense medium.√1mark
-
- Draw round the semicircular block on a sheet of a paper and by measurement draw a normal at the midpoint of a straight side direct a ray of light through the plastic to be internally reflected exactly at the mid-point of the straight side. √1mark
- Move the ray box round until the critical condition is found.
- Remove the block and draw in the rays’ measure the angle between the incident ray and reflected ray with a protractor. √1mark
- This angle is twice the critical angle since the angle reflection equals the critical angle of incidence. This half this angle gives the critical angle c. √1mark
- sin c = 1/n where c = critical angle √1mark
= sin c = 1 √1mark
1.286
= c = sin-1 1 √ 1mark
1.286
c = 51°
-
-
-
- the ability of capacitor to store charge √1mark OR
- the charge per unit volt
- In a paper capacitor the dielectric is thin strips of paper between long strips of metal foil. In an electrolytic capacitor the dielectric is a suitable electrolyte ( mostly aluminum borate)
-
- Dielectric constant√1mark,
- distance of separation, √1mark
- Area of plates
-
- In series
Q₁ = Q₂ = Q₂ = Q√1mark
Q₁ = C₁ V₁ , Q₂ = C₂V₂ , Q₃ = C₃V₃
Q= CV
V= V₁ + V₂ + V₃
Q = Q₁ + Q2 + Q3 √1mark
C C₁ C2 C3
= Q (1 ) = Q ( 1 + 1 + 1 )
C C1 C2 C3
1 = ( 1 + 1 + 1 ) √1mark
C C1 C2 C3 - 1 = 1 + 1 + 1 √1mark
CE C1 C2 C3
1 = 1 + 1 + 1 √1mark
CE 1.5 2 3
= 0.67µF√1mark
Q1= Q2 = Q3 = Q = CEV
Q = 0.67 x 10-6 x 12
= 8.0 x 105C √1mark
- In series
-
- used in delay circuit.
- Used in camera flash.
- Used in tuning circuits
- used in smoothing circuits.√2marks
-
-
-
√1mark
- P is South Pole. √1mark
- Dipoles in the domain are aligned in the process of magnetism. √1mark
-
- Steel retains magnetism than soft bar
- Steel will also take longer to be magnetized. √1mark
-
-
√1mark
- Increase the power of the electric motor. √1mark
-
-
√1mark
√1mark
-
-
-
- Real image is formed on the screen while virtual image cannot be formed on the screen.√1mark
- Real image is formed by actual intersection of ray while virtual image is formed by imaginary rays.√1mark
-
- Concave mirror
- U + V = 40
V = 40 – U
M= v/u
3= 40 – U
U
4U = 40
U = 10cm - 1/f = 1/u + 1/v
1/f = 1/10 – 1/30
1/f = 3 − 1
30
1/f = 2/30
f = 30/2
= 15 cm
R = 2f
= 2 x 15
= 30cm -
- Used as a shaving mirror
- Used by a dentist
-
-
- The current through a conductor is directly proportional to the potential difference across it provided there is no change in the physical conditions and temperature. ✓
- 12V car battery has a very low internal resistance compared to high resistance (internal) of the ✓ eight dry cell. The car battery produces large currents which is able to start a car engine whereas 8 dry cell produce small currents which cannot start the engine. ✓
-
- Series connection 4 + 2 = 6Ω
6 + 3 = 9Ω
Parallel connection 1 = 1 + 1 + 1 = 14✓
R 6 9 2 18
R = 18 = 1.286Ω - V = 1.8 x 1.286✓
= 2.315v ✓ - I = V ✓
R
= 2.315✓
3
= 0.772 A ✓ -
- primary cells cannot be recharged whereas secondary cells can be recharged
- large current can be drawn from primary cells whereas high current can be drawn from secondary cells.
- Series connection 4 + 2 = 6Ω
Download Physics Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Momaliche Joint Pre Mock Exams 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students