- This paper has two sections A and B.
- Answer all questions in section A.
- In section B answer question 6 and any other two questions.
- Candidates should answer the questions in English.
SECTION A
Answer all the questions in this section
-
- What is industrial inertia? (2mks)
- Give three reasons why industrialists prefer locating new industries where old ones exist. (3mks)
-
- What is under population? (2mks)
- State two advantages of a large population in a developed country (2mks)
-
- Name two areas in Kenya where flowers are grown in green houses (2mks)
- Give three reasons why flowers are grown under green houses. (3mks)
-
- Name two types of placer mining (2mks)
- State three negative effects of open cast mining on the environment (3mks)
-
-
- Apart from freshian cows name three other dairy cattle reared in Kenya.(3mks)
- Give two ways in which farming contributes to water pollution. (2mks)
- What is emigration? (1mk)
-
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions in this section.
- Hypothetical figures showing sugar production from various factories in Kenya on ‘000’ tonnes.
Factory Production on tonnes Mumias
Nzoia
Chemilil
Sony sugar
Muhoroni
Total48 200
26 000
36 000
28 000
20 400
158 600-
- Using a pie chart of radius 4cm present the data above (show your calculations) (5mks)
- What percentage of total sugar production was contributed by Mumias? (2mks)
- State three advantages of using pie-charts to present statistical data. (3mks)
- Explain four problems facing sugar cane farming in Kenya. (8mks)
- Describe how sugar is processed in the factory. (4mks)
- Give three government support actions to sugar cane farmers. (3mks)
-
-
- What is energy? (2mks)
- List four examples of renewable types of energy (4mks)
-
- State three limitations of Geothermal energy (3mks)
- Define energy crisis? (2mks)
- Explain four ways Kenya is dealing with energy crisis? (8mks)
-
- Highlight three significance of energy (3mks)
- Give three ways in which atmosphere is heated (3mks)
-
- List four tourist sites in the Coastal countries (4mks)
- Compare national parks and game reserves (5mks)
- Explain four negative effects of tourism (8mks)
-
- Highlight four measures taken by the government of Kenya to promoting tourism (4mks)
- Differentiate between tourism in Kenya and Switzerland. (4mks)
-
-
- What is fishing and fisheries (4mks)
- Explain three physical factors that favour fishing (6mks)
- List three types of fish caught in North East pacific fishing ground. (2mks)
-
- State the significance of fishing industry in Kenya. (3mks)
- Explain four problems facing fishing in Kenya. (8mks)
- State two methods that are used to manage and conserve fish in Kenya (2mks)
-
- Use the map of East Africa to answer questions a(i) and (ii)
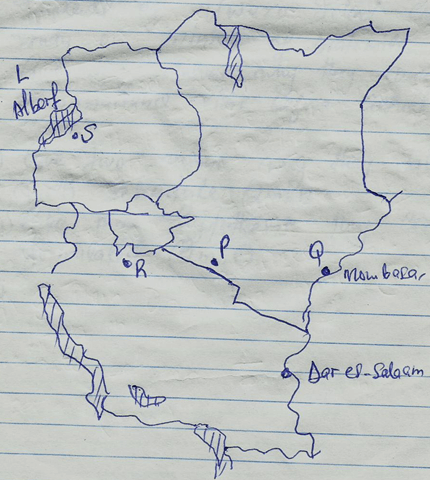
-
- Name the minerals mined at the following marked areas S, P, and Q (3mks)
- State three types of minerals. (3mks)
- Describe how alluvial placer method of mining is carried out. (4mks)
-
- Mention two parts through which some of the minerals mined in East Africa are exported (2mks)
- Explain three ways in which mining derelicts can be reclaimed (6mks)
- Students of Uwezo School carried a field study on mining of Diatomite in Nakuru County.
- Give two reasons why they carried out a reconnaissance visit before actual study. (2mks)
- Give two reasons why they tabulated a work scheduled (2mks)
- Give three hypothesis they could have formulated. (2mks)
-
MARKING SCHEME
SECTION A
Answer all the questions in this section
-
- What is industrial inertia? (2mks)
- Tendency of an industry to maintain its location and activities after factors that attracted it there have ceased to exist.
- Give three reasons why industrialists prefer locating new industries where old ones exist. (3mks)
- Presence of raw material from other industries
- Well-developed transport facilities
- A market that is already established
- A skilled labour force with industrial skills.
- What is industrial inertia? (2mks)
-
- What is under population? (2mks)
- Condition in which an area has such few people that it is not able to utilize and exploit the resources available.
- State two advantages of a large population in a developed country (2mks)
- A large local market for goods thus further industrial development
- A source of labour for use in the various sectors of the economy
- What is under population? (2mks)
-
- Name two areas in Kenya where flowers are grown in green houses (2mks)
- Naivasha
- TimauMeru
- Give three reasons why flowers are grown under green houses. (3mks)
- Control moisture requirement therefore grow with minimum moisture
- Control their temperature conditions thus grow them in any climate zone.
- Bring pests and diseases under control by limit their spread lead to deep growth
- Name two areas in Kenya where flowers are grown in green houses (2mks)
-
- Name two types of placer mining (2mks)
- Panning
- Hydraulic mining
- Dredging
- State three negative effects of open cast mining on the environment (3mks)
- Leaves huge ugly sears that interfere with beauty of landscape
- It leads to dereliction of land
- It causes pollution
- Name two types of placer mining (2mks)
-
-
- Apart from freshian cows name three other dairy cattle reared in Kenya.(3mks)
- Guernsey
- Ayrshire
- Sahiwal
- Jersey
- Channel island
- Give twoways in which farming contributes to water pollution. (2mks)
- Use of chemicals eg nitrogen and phosphorus fertilizers
- Increased use of farm sprays as herbicides
- Poor cultivation techniques and overgrazing increased the rate of soil erosion.
- Apart from freshian cows name three other dairy cattle reared in Kenya.(3mks)
- What is emigration? (1mk)
- Movement of people out of a place
-
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions in this section.
- Hypothetical figures showing sugar production from various factories in Kenya on ‘000’tonnes.
Factory Production on tonnes Mumias
Nzoia
Chemilil
Sony sugar
Muhoroni
Total48 200
26 000
36 000
28 000
20 400
158 600-
- Using a pie chart of radius 4cm present the data above (show your calculations) (5mks)
- Mumias
48200 × 360° = 109.4°
158600 - Chemilili
36000 × 360° = 81.7°
158600 - Muhoroni
20400 × 360° = 46.3°
158600 - Nzoia
26000 × 360° = 59.0°
158600 - Sony sugar
28000 × 360° = 63.5°
158600
- Mumias
- What percentage of total sugar production was contributed by Mumias? (2mks)
48200 × 100=30.3%
158600 - State three advantages of using pie-charts to present statistical data. (3mks)
- Gives a god impression of individual components
- Can represent a wide range f data
- Easy to read and interpret
- Can be used for comparison of a set of data
- Using a pie chart of radius 4cm present the data above (show your calculations) (5mks)
- Explain four problems facing sugar cane farming in Kenya. (8mks)
- Pests eg white, scale, white grubs, termites and diseases egratoon stunting, smut, mosaic reduce production hence reduced income to farmers.
- Frequent fires caused by arsonists or accidental fires reduce quality of cane or completely destroy hence reduce income to farmers.
- Local sugar cane faces stiff competition from imported sugar leading to reduced market hence low earnings.
- Over production causes farmers to incur losses as local factories are unable to process their sugarcane on time.
- Mismanagement in local sugar factories has led to the closure of some.
- Delayed payment reduces farmers morale hence reduce production.
- Describe how sugar is processed in the factory. (4mks)
- At factory sugar cane is weighed and washed
- Passed in a machine that cuts into small pieces
- The pieces are then passed between rollers which crush the cane and squeeze out the juice.
- Juice then put into a cleanlier
- The juice is put into boilers and boiled with lime and allow to crystallize to, form raw or brown sugar.
- The raw sugar is then refined to give brown and while sugar of different grades.
- Give three government support actions to sugar cane farmers. (3mks)
- Co-operatives – loans to farmers and inputs
- Extension offices for advice
- Improve and upgrade roads
- Electricity in factories.
-
-
- What is energy? (2mks)
- Power to do work.
- List four examples of renewable types of energy (4mks)
- Solar energy
- Wind
- Tidal
- Wave
- Hydroelectric power draught animals
- Biomas
- Charcoal
- Fuel wood
-
- State three limitations of Geothermal energy (3mks)
- Require advanced technology to produce which is expensive
- Area where steam is extracted is prone to collapsing due to withdrawal of underground water.
- It reduces dangerous gases as hydrogen sulphide.
- Define energy crisis? (2mks)
- Situation whereby the demand for oil is higher than the amount being supplied and this leads to high oil prices due to uncertainties on supply.
- Explain four ways Kenya is dealing with energy crisis? (8mks)
- Educate the public through mass media on the need to conserve energy.
- Improve public transport in order to encourage more people to use it. This would result in a lot of energy being saved.
- The government is controlling the importation of vehicles with high engine capacity through importation of high import duties on such vehicles.
- Government encouraging the use of alternative sources of energy eg solar energy, biomas and wind.
- State three limitations of Geothermal energy (3mks)
-
- Highlight three significance of energy (3mks)
- Energy is used for domestic purposes eg heating, lighting, ironing, running TV and refrigerators.
- A lot of energy is used in industries to run industrial machines.
- Energy is used in transport sector and petroleum is used to run many vehicles.
- Energy is used as agriculture to our agriculture machines eg factories used for plouging, planting and harvesting
- Energy used to run windmills which pump underground water to the surface for use by animals and human beings, diesel, petrol and electrical pumps are also used.
- Modern mechanical equipment such as x-rays and scanning machines run using electricity thus equipment is used for diagnosis and treatment of ailments.
- Give three ways in which atmosphere is heated (3mks)
- Radiation
- Convection
- Conduction
- Highlight three significance of energy (3mks)
- What is energy? (2mks)
-
- List four tourist sites in the Coastal countries (4mks)
- Modern beach hotels
- Marine wildlife
- Sandy beaches
- Historical like fort Jesus and Vasco da Gama pillar
- Coastal culture
- Compare national parks and game reserves (5mks)
National park Game reserves Has a fence boundary
Has no human activity only tourism
Set aside for preservation of scenery
Has no fence boundary
has no fence boundaryhas limited activities eg grazingset a aside for conservation of historical sites eg wildlife - Explain four negative effects of tourism (8mks)
- Increase of sexual immorality
- Drug trafficking and abuse
- Spread of foreign ideologies
- School drop outs
- Culture degradation iedress almost naked.
-
- Highlight four measures taken by the government of Kenya to promoting tourism (4mks)
- Improved infrastructure
- Encouraging of domestic tourism
- Opening up of other tourists sites
- Improvement of security
- Marketing country mas a major destination abroad.
- Differentiate between tourism in Kenya and Switzerland. (4mks)
Kenya Switzerland Four seasons in Kenya
Variety of tourist attracting features eg Rivers, lakes, craters
Marine attractions
Lacks winter sports
Seasonal fluctuations as number of visitors
Roads not well developed
Unpronounced domestic tourists
Animals kept on home parkTwo seasons Few only alps as main attractionLacks marine ieDorminantInflux high throughout the yearEfficient and elaboratePronouncedKept in zoos
- Highlight four measures taken by the government of Kenya to promoting tourism (4mks)
- List four tourist sites in the Coastal countries (4mks)
-
-
- What is fishing and fisheries (4mks)
- Fishing is an activity of catching aquatic animals in seas and other water bodies.
- Fisheries are areas where fish is caught (grounds)
- Explain three physical factors that favour fishing (6mks)
- Fish thrive us shallow waters through environment provides conditions suitable for the thriving of plankton which is fish food.
- Indented coastlines with sheltered in lets provide ideal sites for filling villages, purp and fish breeding
- The convergence of cold and warm ocean current provides ideal conditions for the survival of fish as the temperature of the water is regulated. The convergence improves the circulation of oxygen and dispersal of nutrients for fish.
- Planktons require cool temperatures of about 200C to grow. This is why fish is abundant in the temperature latitudes.
- What is fishing and fisheries (4mks)
- List three types of fish caught in North East pacific fishing ground. (2mks)
- Hakey, Alaska Pollack, Salmon, Tuna, Sardine and henth
-
- State the significance of fishing industry in Kenya. (3mks)
- It’s a source of income
- It’s a source of employment
- It’s a tourist attraction
- It’s a source of food
- Has led to development of related industries eg net making
- It a source of medicine and cooking fat
- It has led to the development of fishing ports
- Feeder roads in fishing areas have been improved to facilitate fishing and fish marketing
- Explain four problems facing fishing in Kenya. (8mks)
- Overfishing in some fresh water lakes leading to the near extinction of some species
- Some industries release untreated waste into rivers and lakes resulting in the fish being killed
- Most fishermen in Kenya lack adequate capital to purchase modern fishing gear and thus luggage in small scale fishing.
- Most roads in the fishing areas are in very poor condition and this hinders the marketing of fish.
- Fishing in some lakes such as L. Vitoria is hampered by the presence of weeds eg hyacinth which make fishing difficult
- There is low demand for fish in the country as most communities have not adapted on fish eating culture.
- Due to shortage of capital the fishermen use poor refrigerators facilities hence fish going bad is frequent phenomena.
- Fishermen from Asia and Europe fish on Kenyan territorial waters using sophisticated equipment this reduces the amount of fish in the Kenyan waters of Indian Ocean.
- State the significance of fishing industry in Kenya. (3mks)
- State two methods that are used to manage and conserve fish in Kenya (2mks)
- Banning fishing in overfished areas
- Licensing to fishermen in order to monitor their activities
- Banning the use of poor fishing methods like use of nets with small nets
- Introduce new fish species that are fast breeding and maturing in some of the water bodies
- Encouraging fish farming
- Controlling the foreign fishermen through patrolling Kenyan waters of the Indian Ocean to discourage entry of foreign fishermen.
-
- Use the map of East Africa to answer questions a(i) and (ii)
-
- Name the minerals mined at the following marked areas S, P, and Q (3mks)
- S – oil Uganda
- P – trona Kenya
- Q – limestone Kenya
- State three types of minerals. (3mks)
- Metallic
- Non metallic
- Energy minerals/fossil fuels
- Name the minerals mined at the following marked areas S, P, and Q (3mks)
- Describe how alluvial placer method of mining is carried out. (4mks)
- Mix alluvial deposit with water in a container
- The mixture is rotated to separate light presides eg sand mud and small stones leaving only mineral particles eg gold, platinum and diamonds
- Circular pan used by swirling around where lighter materials are washed away leaving heavy mineral deposit
- Minerals are picked for storage
-
- Mention two parts through which some of the minerals mined in East Africa are exported (2mks)
- Mombasa
- Dar el salaam
- Explain three ways in which mining derelicts can be reclaimed (6mks)
- Planting of trees to pave way for better micro-climate
- Filling in depressions by earthier materials (refill)
- Creating of parks with animals likes reptiles hence local and foreign tourists attracted
- Can be used for agricultural activities
- Introduce aqua culture
- Mention two parts through which some of the minerals mined in East Africa are exported (2mks)
- Students of Uwezo School carried a field study on mining of Diatomite in NakuruCounty.
- Give two reasons why they carried out a reconnaissance visit before actual study. (2mks)
- Gather general information and relevant documents from officials
- Helps one to decide on the appropriate equipment methods of data collection.
- Helps in identifying the appropriate method of data collection
- Helps in identifying the appropriate equipment or instruments to be used during the study.
- To familiarize with the area and save time during the actual study.
- Determine appropriate routes to be taken
- Access suitability
- Identify problems
- Help in general planning and prepare work schedule.
- Give two reasons why they tabulated a work scheduled (2mks)
- Ensure proper time management and reduce tendency waste time
- Ensure no area will be inadequately covered or forgotten
- Ensure those involved don’t deviate into irrelevant areas
- It’s a pointer as to how much time will be required for the study.
- Give three hypothesis they could have formulated. (2mks)
- There is a lot of diatomite resources enough for Kenya
- The diatomite in Kenya is mined and exported
- The diatomite mines have attracted labour force.
- Give two reasons why they carried out a reconnaissance visit before actual study. (2mks)
-
Download Geography Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Asumbi Girls Highschool Pre-Mock Exams May-June 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

