QUESTION
SECTION A ( 25 MARKS)
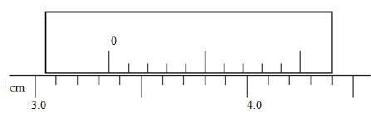
- Determine the reading of the vernier callipers shown in the figure 1.
- Figure 2 shows the apparatus a student uses to investigate the extension of a spring.
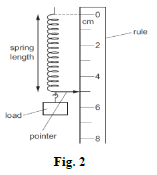
The initial pointer position was at the 2cm mark, when a load of 4N is applied the pointer position is as shown. Find the spring constant of the material of the spring (2mks) - Give a reason why water wets glass. (1mk)
- Figure 3 shows a simple mercury barometer.
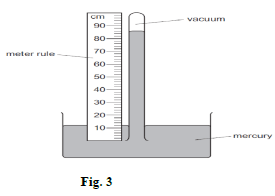
- Determine the value of the atmospheric pressure in pascals.
Take density of mercury =13.6g/cm3 (2mks) - State the reason why mercury is preferred to water as a barometric liquid (1mk)
- Determine the value of the atmospheric pressure in pascals.
- The diagram in figure 4 shows the cross-section of a vacuum flask containing a hot liquid in a cold room. X and Y are points on the inside surfaces of the walls of the flask.
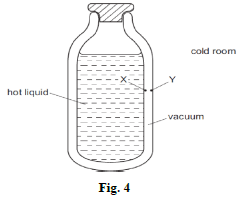
Explain how heat transfer is minimized by the points X and Y (2mk) - A stopwatch is used to time a runner in a race. Figures 5 and 6 show the stopwatch at the start and at the end of a lap of the race in seconds.
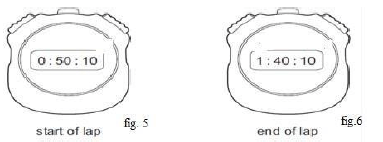
Determine the time runner took to finish the lap of the race. (1mk) - Figure 7 shows a system at equilibrium and pivoted at its geometric center two with identical solids.
Study it and answer the questions that follow: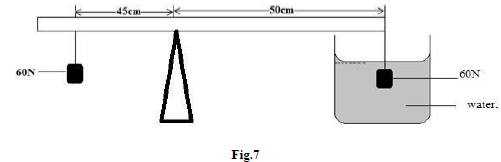
Determine the relative density of solids. (3mks) - 2 kg of iron at 80ºC is placed in a copper can, mass 0.5kg, containing 1kg of water at 20ºC. After stirring, the temperature of the mixture is 30ºC. Find the specific heat capacity of iron.(Take specific
heat capacity of water to be 4200 Jkg-1K-1and Copper 400 Jkg-1). (3mks.) - Explain why a hole in a ship near the bottom is more dangerous than one nearer the surface. (1mk.)
- A student inverted a rounded flask with a glass tube and inserted it into water as shown in figure 8.0 below;
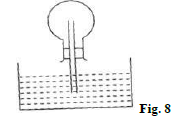
- When the student warmed the flask by rubbing it with his hands he noticed some bubbles escaping from the end of the tube into the water. Explain. (2mks)
- Explain what happens in the glass tube when the student stops rubbing and lets the flask to cool.(1mk)
- The handle of a screw jack shown in figure 9 is 35cm long and the pitch of the screw is 0.5cm.
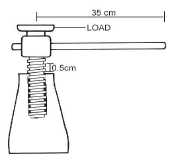
- Determine is the velocity ratio of the system. (2mks.)
- Work out the force that must be applied at the end of the handle when lifting a load of 2,000N if the efficiency of the jack is 40%. (3mks)
SECTION B (55 MARKS)
-
- The mass of a lift cage with its passenger is 500kg and the acceleration of free fall, g, is 10m/s2.
The lift starting from rest moves upwards as follows:
Accelerating uniformly at 1m/s2 for 5s; then travels at a constant speed for the next 10s and finally decelerates uniformly, coming to a stop after a further 5s.- Draw the lift indicating the forces acting on the passenger. (2mks)
- Sketch the velocity-time graph of this motion. (2mks.)
- Determine is the total distance this lift ascends during the 20s. (2mks.)
- State what the passenger experiences as the lift accelerates upwards. (1mk.)
- Determine for the entire motion:
- the potential energy. (2mks)
- the kinetic energy gained of the lift. (2mks)
- the power developed by the lift during the of the motion. (2mks)
- The mass of a lift cage with its passenger is 500kg and the acceleration of free fall, g, is 10m/s2.
-
- State Archimedes principle (1mk)
- A solid displaces 8.5 cm3 of liquid when floating on a certain liquid and 11.5 cm3 when fully submerged in the liquid. The density of the solid is 0.8 gcm3 .
Determine:- The upthrust on the solid when floating. (3mk)
- The density of liquid. (3mk)
- The upthrust on the solid when fully submerged (3mk)
- Write the statement of the law that relates the volume of a gas to its temperature. (1mk)
- State two assumptions made for ideal gases. (2mks.)
-
- Figure 10 shows an experiment set-up that may be used to investigate one of the gas laws. The glass tube has a uniform bore and it is graduated in millimetres.
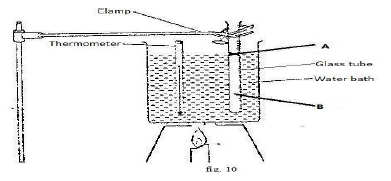
- Name the parts labelled A : .............................................. (1mk)
Describe how the set-up would be used to verify the law under investigation. (4mks) - Sketch a suitable graph for the expected results for an ideal gas. (2mks)
- A mass of oxygen gas occupies a volume of 1200 cm3 at 273ºC and a pressure of 1.2 atmospheres. It is compressed until its volume is 600 cm3 and its pressure is 3.0 atmospheres. Determine the temperature of the gas after compression. (2mks)
- Name the parts labelled A : .............................................. (1mk)
- Distinguish between latent heat of fusion and specific latent of fusion. (1mark)
- Figure 11 shows a block of ice. A thin copper wire with two heavy weights hanging from its ends-passes over the block. The copper wire is observed to pass through the block of ice without cutting it.
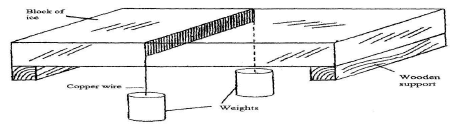
- Explain this observation, (3mks)
- State and explain the effect of replacing the copper wire with a cotton thread. (2mks)
- Figure 12. shows one method of measuring the specific latent heat of fusion of ice. Two funnels A and B, contain crushed ice at 0°C.
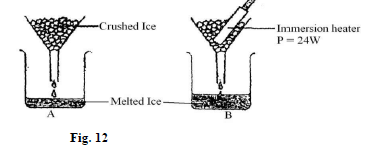
The mass of melted ice from each funnel is measured after 11 minutes. The results are shown below.
Mass of melted ice in A = 24g Mass of melted ice in B = 63g- Give the reason for setting up experiment A (1mk)
- Determine the:
- Quantity of heat supplied by the heater. (2mks)
- mass of ice melted by the heater. (1mk)
- specific latent heat of fusion of ice. (2mks)
- Figure 10 shows an experiment set-up that may be used to investigate one of the gas laws. The glass tube has a uniform bore and it is graduated in millimetres.
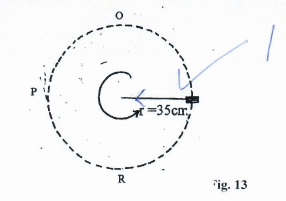
- Figure 13 below shows a mass of 500g moving in a vertical circle having a radius of 35cm at a constant velocity. It makes 2 revolutions in one second.
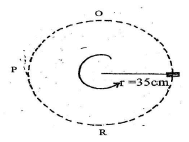
- Indicate on the diagram the direction of centripetal force. (1mk)
- Determine:
- the linear velocity of the mass. (3mks)
- the centripetal acceleration of the object (2mks)
- centripetal force. (3mks)

MARKING SCHEME
- 3.35cm
- e = 5.0 - 2.0 = 3.0cm
F = Ke
K = F/e
= 4/0.03
133.333N/m - Water has stronger adhesion than cohesion
-
- h = 86 - 11 = 75cm
= 75/100 x 13600 x 10 = 102,000N/m2 - It has a shorter barometric height due to its higher density
- h = 86 - 11 = 75cm
- The double silvered wall is shiny/polished
This minimizes heat loss through radiation - 100.10seconds
- 60 x 45 = 50 x x
x = 60 x 45
50
= 54N
Upthrust = weight - apparent weight
= 60 - 54 = 6N
Density = weight
upthrust
= 60/6.0 = 10 - Heat lost = heat gained
2 x CFe x (80-30) = (1 x 4200 x 10) + (400 x 0.5 x 10)
= (400 x 0.5 x 10) + 42000
100
242Jkg-1k-1 - Water can sip into the ship more easily and increase its weight thereby sinking the ship
-
- Rubbing produces heat which made air in the flask to expand and escape as bubbles
- Level of water in the tube rose to occupy space created by condensed air
-
- V.R = circumference
pitch
= 2 x 3.142 x 35
0.5
= 439.88 - η = M.A/V.R x 100
40 = M.N/439.88 x 100
M.A = 175.952
M.A = L/E
175.952 = 2000/E
E = 11.366N
- V.R = circumference
-
-
-
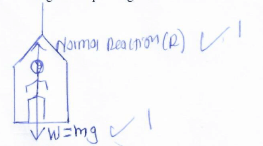
-
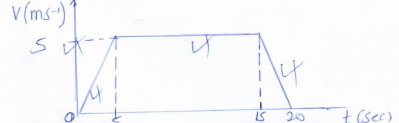
- S = Area under graph
= ½(a + b)h
=½(20+10)5
= 75m - Experience more weight
-
-
- P.E = mgh
500 x 10 x 75 = 375,000J - K.E = ½mv2
=½ x 500 x 25
= 6250J - Power = Energy
time
S = ut + ½at2
500 x 10 x 12.5
5
= 12,500J/s
- P.E = mgh
-
-
- When an object is wholly or partially immersed in a fluid it experiences and upthrust force which is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced
-
- 0.8 x 11.5
= 9.2g
w = 9.2/1000 x 10
= 0.092N - 0.092 = 5 x 8.5 x 10
1000000
= 0.092 x 1000000
10 x 8.5
= 1082.35kg/m3 - = 1082.35 x 11.5 x 10
1000000
= 0.12447N
- 0.8 x 11.5
-
- The volume of a fixed mass of a gas is directly proportional to the temperature at constant pressure
- Size of molecules are negligible
Intermolecular forces are negligible -
- Index
-
- Heat the water bath
- Record the value of temperature and corresponding length of air
- Repeat for several values of temperature and pressure
- Plot a graph of the length of air column against temperature
-

- V1 = 1200
T1 = 273
P1 = 1.2
V2 = 600
T2 = ?
P2 = 3
P1V1 = P2V2
T1 T2
1200 x 1.2 = 3.0 x 600
273 T2
T2 = 30 x 600 x 273
1200 x 1.2
= 341.25K
-
- Latent heat of fusion - heat energy required to change a mass from solid to liquid without change in temperature. Specific latent heat of fusion:Amount of heat energy required to change a unit mass of a solid to liquid without change in temperature
-
- Hanging weight exerts pressure on the ice making it melt at a temperature loer than its melting point. Water formed flows over the wire and solidifies since its no longer under pressure
Latent heat of fusion is released and conducted by the copper wire to melt the ice below - It will not cut through the ice block
Cotton thread is a poor conductor of heat
- Hanging weight exerts pressure on the ice making it melt at a temperature loer than its melting point. Water formed flows over the wire and solidifies since its no longer under pressure
-
- To get the mass of the ice that melted due to room temperature
-
- 24 x (11 x 60)
= 15840J - 63 - 24 = 39g
- Heat supplied
mass
= 15840 = 406.15Jkg-1
0.039
- 24 x (11 x 60)
-
-
-
- w = 2πf
= 2 x 3.142 x 2
= 12.568
v = wr
= 12.568 x 0.35
= 4.3988ms-1 - 12.5682 x 0.35
= 55.2841 rads-2 - Fc = mw2r
= 500 x 55.2841
1000
= 27.642N
- w = 2πf
-
Join our whatsapp group for latest updates
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Download Physics Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Mumias West Pre Mocks 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

