INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name, admission number in the space provided
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided
- Mathematical tables and scientific calculators may be used
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary
- Candidates should check the question paper to ascertain that all pages are printed as indicated and that no questions are missing
FOR EXAMINERS USE ONLY
|
QUESTION |
MARKS |
CANDIDATES SCORE |
|
1 |
13 |
|
|
2 |
11 |
|
|
3 |
12 |
|
|
4 |
10 |
|
|
5 |
11 |
|
|
6 |
12 |
|
|
7 |
11 |
|
|
TOTAL |
80 MARKS |

QUESTIONS
- The table below shows some elements in the periodic table Use it to answer the questions that follow The letters are not the actual symbols of the elements
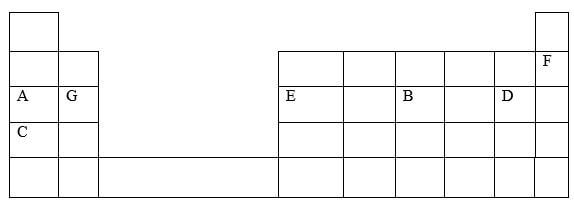
-
- Show the electron arrangement of ions of elements:
A (½mk)
B (½mk) - Using dots (.) and crosses (x) to represent electrons draw a diagram to show how elements C and oxygen combine to form a compound (O = 8) (1mk)
- Show the electron arrangement of ions of elements:
- Show on the grid above an element Y whose ion Y2- has an electron configuration of 288 (1mk)
- Compare the following with explanation
- The reactivity of A and C (2mks)
- Atomic radii of elements A and B (2mks)
- The melting point of the oxide of element G and the oxide of D (2mks)
- Name the type of bond formed when E and D react Explain your answer (2mks)
- The ionic radius of element E is bigger than its atomic radius Explain (2mks)
-
- The following diagram below shows a series of steps followed in the manufacture of sodium carbonate
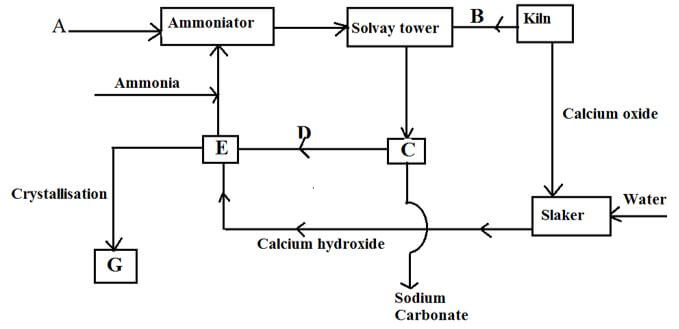
- Name substances A and B (2mks)
A
B - Write equations for the reactions taking place in:
- The solvay tower (2mks)
- Chamber E (1mk)
-
- Identify substance G (1mk)
- State one laboratory use and one industrial use of substance G
- Laboratory use (1mk)
- Industrial use (1mk)
- Name one most important industry where sodium carbonate is used as a raw material (1mk)
- The reaction equation below represents a chemical change that occurs when hydrated sodium carbonate is exposed to the air for 24 hrs
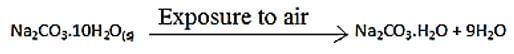
- Give the name of the chemical change represented by the above equation (1mk)
- What observable change is accompanied by the above reaction? (1mk)
- Name substances A and B (2mks)
-
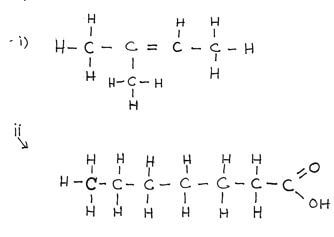
- Draw the structures of the following compounds (2mks)
- 2 – methylbut-2-ene
- heptanoic acid
- Describe a physical test that can be used to distinguish between methanol and hexanol (2mks)
- Use the flow chart below to answer the questions that follow
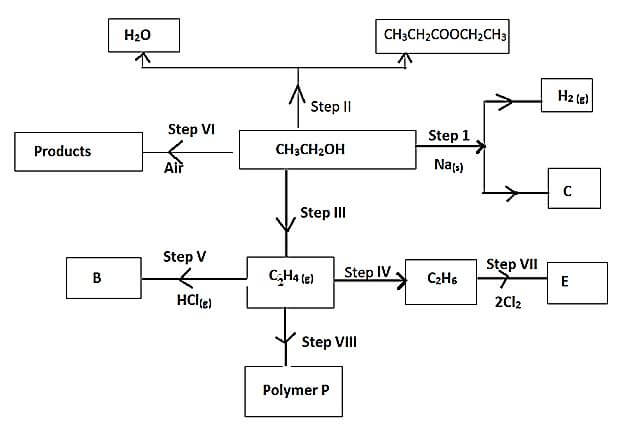
- Name:
- The type of reaction that occurs in step VII (1mk)
- Substance B
- What conditions and reagents are necessary to convert CH3CH2OH to CH3CH2COOCH2CH3 in step II
Conditions (1mk)
Reagent (1mk) - Give the formula and name of substance C (1mk)
- Give the reagent and conditions necessary for the reaction in step IV (2mks)
-
- Draw and name the structure of polymer P (1mk)
- Name one use of the polymer P (1mk)
- Name:
- Draw the structures of the following compounds (2mks)
-
- Two reagents that can be used to prepare chlorine gas are manganese (IV)oxide and concentrated hydrochloric acid
- Write an equation for the reaction (1mk)
- Give the formula of another reagent that can be reacted with concentrated hydrochloric acid to produce chlorine gas (1mk)
- Describe how the chlorine gas could gas could be dried in the laboratory (1mk)
- In an experiment dry chlorine gas was reacted with aluminum as shown in the diagram below
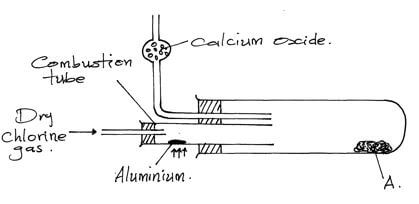
- Name substance A (1mk)
- Write an equation for the reaction that took place in the combustion tube (1mk)
- 084g of aluminium reacted completely with chlorine gas Calculate the volume of chlorine gas used (Molar gas volume is 24dm³ Al = 27) (3mks)
- Give two reasons why calcium oxide is used in the set-up (2mks)
- Two reagents that can be used to prepare chlorine gas are manganese (IV)oxide and concentrated hydrochloric acid
- The combustion of propane can be represented by the following equation:
C3H8 (g) + 5O2 (g) → 3CO2 (g) + 4H2O (l)-
- Define the term ‘molar enthalpy of combustion’ of a compound (1mk)
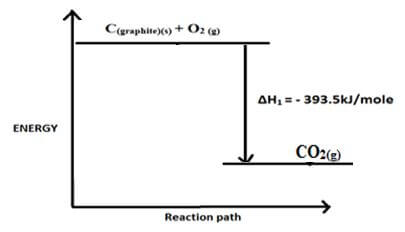
- Use the thermo chemical equations below to answer the questions that follow
- C(graphite)(s) + O2 (g) → CO2 (g) ∆H1 = - 3935kJ/mole
- H2 (g) + ½O2 (g) → H2O (l) ∆H2 = -2858kJ/mole
- 3C(graphite)(s) + 4H2 (g) → C3H8 (g) ∆H3 = - 1037kJ/mole
- Name the type of enthalpy change represented by ∆H3 (1mk)
- Draw an energy level diagram for the reaction represented by equation 1 (3mks)
- Using energy cycle diagram, calculate the molar enthalpy of combustion of propane (3mks)
- The enthalpy of formation of ethanol (CH3CH2OH) is -3239Kj/mole Use the bond energies given below to calculate the bond energy of formation of O-H (3mks)
C-C = -346kJ/mole
C-H = -414kJ/mole
C-O = -360kJ/mole
-
- Equal volumes of dilute sulphuric (vi) acid of various concentrations were placed in five test tubes 026g of zinc granules was used in each experiment and time taken for each experiment to be completed noted The table below shows the results obtained
Acid concentration
0.25M
1.5M
1.6M
2.6M
3.5M
Time in sec
500
250
67.5
40
30
1
time(s-1)-
- Complete the table above by calculating 1/time (2mks)
- Using the grid provided plot a graph of 1/time(s-1) against concentration of the acid (3mks)
- Using the graph determine the rate of reaction when the concentration is 15M (1mk)
- Briefly explain the relationship between the rate of reaction and concentration (2mks)
- Identify any other condition if carried would increase the rate of reaction between Zinc and Dilute suplhuric (vi) acid (1mk)
- What volume of hydrogen gas is evolved when all the zinc is reacted with excess dilute sulphuric (vi) acid (Zn = 654, molar gas volume = 224 litres) (3mks)
-
- Study the scheme below and answer the questions that follow
p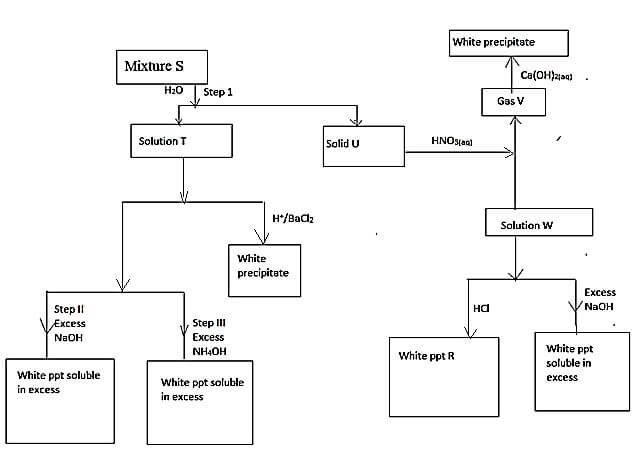
- What property of mixture S is shown in step 1 (1mk)
- Name the following (1mk)
- Solid U
- Solid V
- Write the formula of precipitate R (1mk)
- Identify the ions present in solution T (1mk)
- Write an ionic equation for the reaction between solution T and Barium chloride solution (1mk)
- Identify mixture S (1mk)
-
- Write a chemical equation for the reaction in which the white precipitate dissolves in excess reagent in Step II (1mk)
- Name the complex ion formed in Step III (1mk)
- Starting with lead (II) oxide, describe how a pure sample of lead (II) sulphate can be prepared in the laboratory (3mks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
-
- A- 2.8
B – 2.8.8 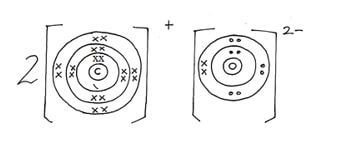
- A- 2.8
- Shown on the grid between (B and D)
-
- A is less reactive√1 than C, C has a larger atomic radius√1 hence loses its outermost electrons more easily.
- B has a smaller√1 atomic radius than A since B has stronger nucleus√1 charge.
- Oxide of G has a higher melting point than oxide of D √1 since G oxide is ionic and has strong ionic bonds√½ whereas oxide of D has a molecular structure with weak vanderwaal forces√½ between molecules.
- Covalent bond√1
E and D share valence electrons√1 to form covalent bond. - E forms ion by gaining electrons √1. There exist repulsive forces √1 between the incoming electron and the existing electrons in E making the outer energy level bulge outward.
-
-
- A – Brine/ concentrated sodium chloride. Reject sodium chloride
B – Carbon (iv) oxide -
- NH3(g) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) → NH4HCO3(aq) √1
NH4HCO3(aq) + NaCl(aq) → NH4Cl(aq) + NaHCO3(s) √1 - Ca(OH)2(s) + 2NH4Cl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + 2H2O(l) + 2NH3(aq) √1
(award ½mk for correct equation without symbols)
- NH3(g) + H2O(l) + CO2(g) → NH4HCO3(aq) √1
-
- Calcium chloride√1
- I- Drying agent for gases/ as a drying agent√1 in the desiccators
II – In extraction of sodium from molten sodium chloride√½. It lowers the melting point√½ of NaCl from 8010c to above 6000c
-
- Glass manufacturing industry
- Paper industry
-
- Efflorescence√1
- –Decrease in mass√½
- Loss of crystalline nature√½
- A – Brine/ concentrated sodium chloride. Reject sodium chloride
-
- Heat the two substances separate and determine their boiling point√1. Hexanol has a higher boiling point than methanol. √1
-
- I – Substitution
II – Chloroethane - Condition
Warming√½
Concentrated sulphuric (vi) acid√
Reagent
Propanoic acid √1 - CH3CH2ONa√½ – Sodium Ethoxide√½
- Hydrogen √1
Nickel catalyst√½
Temperature 1500c – 2500c√½ - I
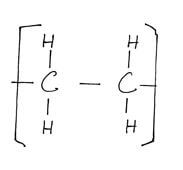 √½
√½
Polyethene√½
II – Polythene bags√1
- I – Substitution
-
-
- MnO2(s) + 4HCl(l) → MnCl2 + Cl2(g) + 2H2O(l)
- KMnO4(s)/PbO2(s)
- By passing it through concentrated sulphuric (vi) acid. √1
-
- Aluminium chloride √1
- 2Al(s) + 3Cl2(g) → 2AlCl3(s)
- 2Al(s) + 3Cl(g) →2AlCl3(s)
0.84g = 0.03111 moles
27
Cl2(g) volumeused = 0.03111 x 3 = 0.09333 moles
Volume of chlorine = 0.09333 x 24000√1
= 2240cm³ -
- Calcium oxide prevents any moisture from outside since the AlCl3 is deliquescent hence keeps combustion tube dry. √1
- Calcium oxide reacts with moisture forms calcium hydroxide that prevents chlorine from escaping to the atmosphere. √1
-
-
-
- Energy or enthalpy change that occurs when a compound reacts completely with oxygen at standard conditions. √1
-
- - Molar enthalpy of formation of propane. √1
- –
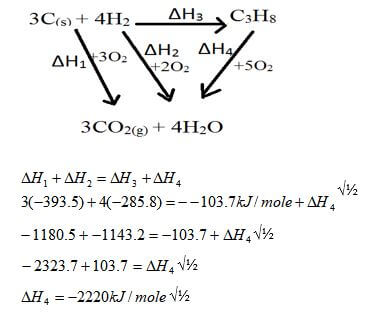
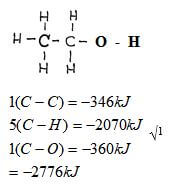
1 x -346kJ
5x -414 = - 2070kJ
1 x -360 = - 360Kj
- 2776kJ + (O – H) = -3239 √1
O – H = -463kJ √1
-
-
-
Acid concentration
0.25M
1.5M
1.6M
2.6M
3.5M
Time in sec
500
250
67.5
40
30
1/time(s-1)
0.002
0.004
0.015
0.025
0.033
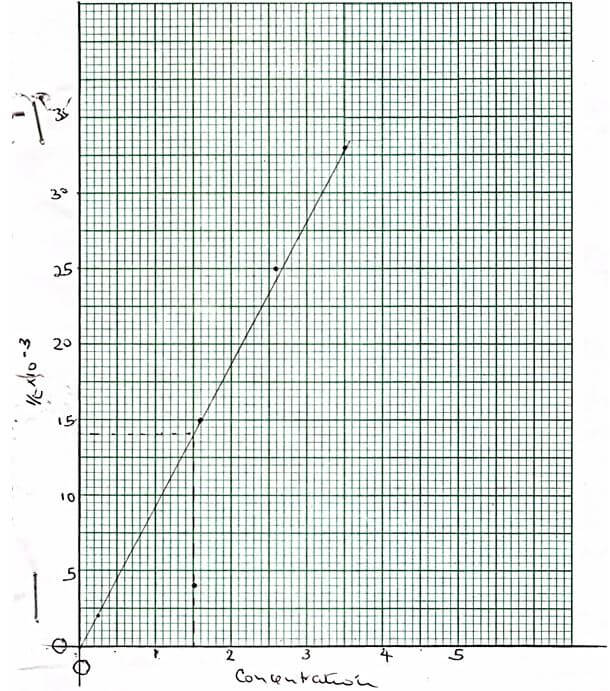
- Labelling – √½
- Scale – √½
- Plots – √1
- Line -√1
NB: Straight line passing through the origin.- 0.014√ correct showing √½
Correct reading √½ - The rate of reaction increases with increase in concentration √1/ increased concentration increases the number of reacting particles and number of effective collisions√1.
- – Increased temperature (warm the mixture) √1
- Presence of a catalyst/ add crystals of CuSO4 √½ - Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g)
1: 1 1: 1√½
65.4g of Zinc produce 22400cm³ of H2 at STP√½
0.26G of Zinc produces cm³ of H2 at STP
= 0.26g x 22400cm3 √1
65.45
= 89.05cm3√½
-
-
- Mixture of soluble and insoluble salt
-
- Lead carbonate (Reject formula)
- Carbon (iv) oxide (Reject formula)
- PbCl2
- Zn2+, SO2-4 (Reject names)
- (Penalise ½for wrong state symbol)
- PbCO3 and ZnSO4 (accept names tied to the two for 1mk)
-
- Zn(OH)2(s) + 2OH-(aq) → [Zn(OH)4]2- (aq)
(Reject fully if not balanced, penalise ½mk for wrong state symbols) - Tetramine Zinc (ii) ions
- Zn(OH)2(s) + 2OH-(aq) → [Zn(OH)4]2- (aq)
- Add excess lead (ii) oxide to dilute nitric (v) acid√½.
Filter√½ the unreacted lead (ii) oxide;
Add sodium sulphate√½/ K2SO4/ H2SO4 to the filtrate
Filter√½ to obtain lead (ii) sulphate as the residue
Wash the residue√½ with distilled water
Dry the residue between filter paper√½
Download Chemistry Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Cekenas Pre Mocks 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

