INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIDATES
- Write your name, admission number in the space provided.
- Answer all the questions in the spaces provided.
- Mathematical tables and scientific calculators may be used.
- All working must be clearly shown where necessary.
- You are not allowed to start working with the apparatus for the first 15 minutes. This time is to enable you read the question paper and make sure you have all the requirements.
- Candidates should check the question paper to ascertain that all pages are printed as indicated and that no questions are missing.
FOR EXAMINERS USE ONLY
|
QUESTION |
MARKS |
CANDIDATES SCORE |
|
1 |
20 |
|
|
2 |
12 |
|
|
3 |
08 |
|
|
TOTAL |
40 MARKS |

QUESTIONS
- You are provided with:
- 1.5 g of solid R
- Solution P which is dilute hydrochloric acid
- Solution Q that was made by dissolving 12g of sodium hydroxide in 500cm³ of water
You are required to:- Calculate the molar enthalpy change for the reaction between solid R and dilute hydrochloric acid.
- Standardize hydrochloric acid solution P using sodium hydroxide solution Q.
PROCEDURE 1
Using a clean burette, transfer 50cm³ of solution P into a clean 100ml plastic beaker. Measure the temperature of solution P for every ½ minute up to 1 minute and record your results in table 1.
At exactly 1½ minutes add all solid R at once stir the mixture carefully with the thermometer. Measure the temperature of the solution after every ½minute up to 5th minute. Record your results in table 1 below. (RETAIN THIS SOLUTION FOR USE IN PROCEDURE II
Table 1 (3mks)
|
Time (min) |
0 |
½ |
1 |
1½ |
2 |
2½ |
3 |
3½ |
4 |
4½ |
5 |
|
Temperature (0c) |
X |
- Draw a graph of temperature against time in the grid provided below (3mks)
- From the graph, calculate the temperature change for the reaction. (1mk)
- Calculate the energy change for the reaction between solid R and dilute hydrochloric acid. (1mk)
(S.H.C= 4.2J/g/k, density = 1g/cm³) - Determine the enthalpy change for the reaction between one mole of solid R and dilute hydrochloric acid solution P. (RFM of solid R=84) (1½mks)
PROCEDURE II
Transfer all the solution formed from procedure I into a clean 250ml beaker. Using a measuring cylinder add 50cm3 of distilled water to the solution and swirl. Label this solution as solution R. Empty the burette and rinse it with distilled water. Fill the burette with solution R. Using pipette filler, pipette 25cm³ of sodium hydroxide solution Q into a clean conical flask. Titrate solution R against solution Q using phenolphthalein indicator. Record your results in table II. Repeat the titration two more times and complete table II below.
Table II
|
Final burette reading cm³ |
I |
II |
III |
|
Initial burette reading cm³ |
|||
|
Volume of solution R used cm³ |
(4mks)
e) Calculate the average volume of solution R used. (1mk)
f) Calculate the concentration of sodium hydroxide solution Q in moles per litre. (Na = 23 O = 16 H=1). (1mk)
g) Calculate the number of moles of:
- Solution Q that reacted with solution R. (1mk)
- Hydrochloric acid in 100cm³ of solution R prepared. (1mk)
- Given that 1 mole of solid R reacts with 1 mole of hydrochloric acid, calculate the number of moles of hydrochloric acid in the original 50cm³ of solution P used. (1½mks)
h) Calculate the molarity of solution P in moles per litre. (1mk)
2. You are provided with solid H. carry out the experiments below, write your observations and inferences in the spaces provided.
a) Place all of the solid H in a boiling tube add 15cm³ of distilled water and shake well.
i) To about 2cm³ of solution formed add sodium hydroxide solution drop wise until excess.
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
(1mk) |
(1mk) |
ii) To about 2cm³ of solution formed add ammonia solution drop wise until excess.
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
(1mk) |
(1mk) |
iii) To about 2cm³ of solution formed add 2 drops of lead (II) nitrate solution.
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
(1mk) |
(2mk) |
iv) To about 2cm³ of solution formed add 2 drops of potassium iodide solution.
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
(1mk) |
(1mk) |
v) To about 2cm³ of solution formed add 2cm³ of sodium hydroxide solutions followed by a small piece of aluminium foil. Warm the mixture and test any gases produced with both blue and red litmus paper.
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
(2mk) |
(1mk) |
3. You are provided with solid G. carry out the tests below. Write your observations and inferences in the spaces provided.
a) Scoop one third of solid G using a spatula. Heat the solid in a non-luminous flame.
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
(1mk) |
(1mk) |
b) Place the rest of solid G in a boiling tube. Add about 10cm³ of distilled water. Filter the mixture.
i) To about 2cm³ of filtrate add 2 drops of acidified potassium manganate (vii) solution.
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
(1mk) |
(1mk) |
b) ii) To about 2cm³ of filtrate add 2 drops bof acidified potassium dichromate (VI) solution.
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
(1mk) |
(1mk) |
iii) Dip a universal paper to the remaining filtrate.
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
(1mk) |
(1mk) |

MARKING SCHEME
- Table 1
Award three marks distributed as follows:- Complete table (1mk)
- Complete table with 8 readings (1mk)
- Incomplete table with 7/6 readings (½mk)
- Incomplete table with less than 6 readings (0mk)
- Decimal place (½mk)
- Award half mark for consistently used whole numbers or 1 decimal point for temperature readings otherwise penalise FULLY.
- Accuracy (½mk)
- Award half mark for temperature readings at time 0 if it is of the school value.
- Trend (1mk)
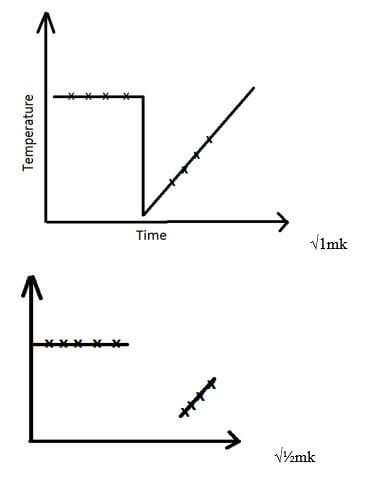
- Award 1mk for constants up to 1 minute followed by a decrease in temperature then a rise in temperature readings.
Or constants upto 1min, a drop, constants, continuous rise. - Penalise ½mk if reading at time 5 minutes is above the initial temperature at T= 0 MIN
- Award 1mk for constants up to 1 minute followed by a decrease in temperature then a rise in temperature readings.
- Complete table (1mk)
- Labelling of axes ½mk
- Scale (consistent and covering more than ½page) ½mk
- Plotting (1mk)
- Lines (1mk) (with extrapolation)
84
CORRECTANSWER(c)
0.0179
- Complete table (1mk)
- Decimal place (1mk)
- Accuracy (1mk)
- Principles of averaging (1mk)
- Final accuracy (1mk)
500
(Penalise ½mk for wrong formula)
1000
100 x 0,015 √½
answer(e) AV
50
QUESTION 2
a) i)
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
White ppt√½ Soluble in excess√½ |
Pb2+, Zn2+ , Al3+ 3√1mk 2√½mk 1- 0mk |
ii)
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
White ppt√½ Insoluble in excess√½ |
Pb2+√½, Al3+√½ |
iii)
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
No white ppt√1 |
Each ion ½mk to maximum of 2mks Penalise ½mk for each contradicting ion up to a maximum of 2mks |
iv)
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
Yellow ppt√1 |
Pb2+ √1mk Penalise fully for any contradicting ion |
v)
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
- Effervescence√½ - Colourless gas with pungent smell√½ - Red litmus changes to blue√½ - Blue litmus remains blue √½ |
√1 Penalise fully for any contradictory ion |
Question 3
a)
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
- Melts√½ - Burns with a yellow sooty flame√½ |
√1 Or long chain organic substance or high ratio of C:H |
b)i)
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
- purple colour acidified potassium manganate (vii) persists √1 |
√½ And R-OH Absent√½ |
ii)
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
- Orange colour of acidified potassium dichromate (vi) persists√1 |
R-OH absent√1 |
iii)
|
Observations |
Inferences |
|
- PH = 4/5 √1 |
Weakly acidic√1 |

CONFIDENTIAL
In addition to the laboratory fittings each candidate requires the following:
- About 60cm³ of solution P
- About 80cm³ of solution Q
- Accurately weighed 1.5g of solid R in a stoppered container.
- Solid H- about 0.5g in a stoppered container
- Solid G – about 0.5g in a stoppered container
- A burette
- A pipette and pipette filler
- Two conical flasks
- A 100ml plastic beaker
- A 250ml beaker
- Thermometer
- One stop watch
- 5 test-tubes
- One boiling tube
- 100ml measuring cylinder
- A small piece of aluminium foil
- A spatula
- Red and blue litmus paper
- Universal indicator paper and PH chart
- Test tube holder
- Filter paper
- Filter funnel
Access to
- 2M sodium hydroxide solution
- 2M ammonia solution
- Distilled water
- Phenolphthalein indicator
- Source of heat
- Acidified potassium dichromate (vi)
- Acidified potassium manganate (vii)
- Lead (ii) nitrate solution
- Potassium iodide solution
Preparations
- Solution P is 2M dilute hydrochloric acid
- Solution Q is 0.6M sodium hydroxide solution
- Solid R is accurately weighed 1.5g of sodium hydrogen carbonate solid
- Solid H is lead (ii) nitrate solid
- Solid G benzoic acid
Download Chemistry Paper 3 Questions, Answers and Confidential - Cekenas Pre Mocks 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

