INSTRUCTIONS
- Write your name class, and index number in the spaces provided above.
- Answer ALL the questions in the spaces provided.
- Answer all questions in Section A.
- In section B answer question 6 (compulsory) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question 8.
- Students should check the question paper to ascertain that all the pages are printed as indicated and that no questions are missing.

QUESTIONS
-
- Digestive enzymes are made by different organs in the digestive system. Complete the table below by putting a tick (√) or a cross (X) in the boxes. The first has been done. (2mks)
Enzyme
Salivary glands
Stomach
Pancrease
Ileum
Amylase
√
X
√
√
lipase
Protease
- Name the features that increase the surface area of small intestines. (2mks)
- Name the vitamin which is associated with citrus fruits and green vegetables. (1mk)
- What food nutrient would be found in the villi of ileum few hours after a meal of boiled rice? (1mk)
- Caecum is poorly developed in humans. Name the group of mammals in which its well developed and outline its role. (2mk)
- Digestive enzymes are made by different organs in the digestive system. Complete the table below by putting a tick (√) or a cross (X) in the boxes. The first has been done. (2mks)
- The diagram below shows the structure of a chromosome.
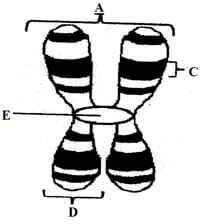
- Identify the parts labelled D and E. (2mks)
D
E - Name:
- Two organelles in an animal cell where DNA is found. (1mk)
- The process whereby DNA makes an identical copy of itself. (1mk)
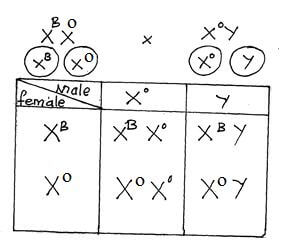
- Coat colour in cats is determined by a sex linked gene with two alleles, black and orange. When black cats are mated with orange cats, the female offspring are always tortoise shell, their coats show black and orange patches of various sizes, while the male offspring have the same coat colour as their mothers. Using symbols (B) for black and (O) for orange, draw a punnet square to account for a cross of tortoise shell female with an orange male. (4mks)
- Identify the parts labelled D and E. (2mks)
- A form 2 student wanted to investigate the effect of temperatures on the rate of carbon (IV) oxide production by yeast. He set up the apparatus as shown below.

- The student varied the temperatures of the water bath between 15ºc – 65ºc. He measured the rate of carbon (IV) oxide production by counting the number of bubbles per minute.
- Sketch the shape of the graph that the student would obtain on the axes below. (3mks)

- Account for the shape of the graph. (1mk)
- Sketch the shape of the graph that the student would obtain on the axes below. (3mks)
- Give two variables that the student would need to keep at constant in his experiment. (2mks)
-
- Yeast is used in production of beer. Write the equation for the respiration of yeast that occurs during production of beer. (1mk)
- Suggest why lactic acid produced in the body is not highly excreted out of the body. (1mk)
- The student varied the temperatures of the water bath between 15ºc – 65ºc. He measured the rate of carbon (IV) oxide production by counting the number of bubbles per minute.
- The diagram below represents the relationship between the blood system of the foetus and that of the mother. The arrows indicate the direction of blood flow in the blood vessels
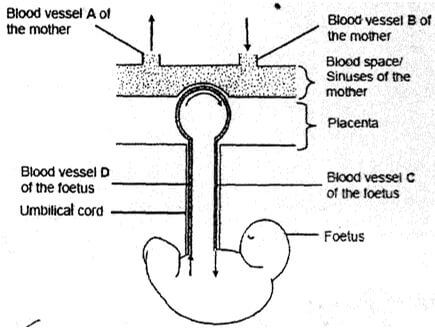
- Apart from diffusion of substances from the mother’s blood to the foetus blood and vice versa, state two other functions of the placenta. (2mks)
-
- Name the blood vessels C and D. (2mks)
C
D - State two differences between the composition of blood found in blood vessel C and blood found in blood vessel D. (2mks)
C
D
- Name the blood vessels C and D. (2mks)
- Explain one consequence for the foetus if blood vessel D becomes blocked preventing blood flow. (2mks)
- The diagram below is of a mammalian nephron and associated structures.
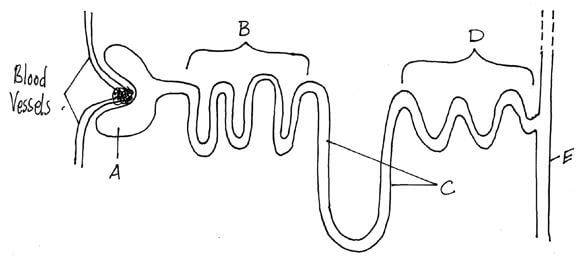
-
- Identify the parts labelled D and E. (2mks)
D
E - Reabsorbtion of substances takes place along the regions labelled B-E. Which two letters correspond to the regions in which most water is reabsorbed? (1mk)
- Identify the parts labelled D and E. (2mks)
- The table below summarizes differences in the concentration of some substances in the blood plasma and the renal filtrate at the end of the proximal convoluted tubule.
Explain the results. (3mks)Substances
Concentration in blood plasma
Concentration in filtrate at the end of PCT
Proteins
12
0
Glucose
0.15
0
Urea
0.04
0.09
- In mammals there is a strong positive correlation between the length of the loop of henle and the degree of aridity (dryness) of the environment that a mammal such as the desert rat inhabits. Explain this relationship. (2mks)
-
SECTION B (40marks)
Answer question 6 (compulsory) and either question 7 or 8 in the spaces provided after question 8
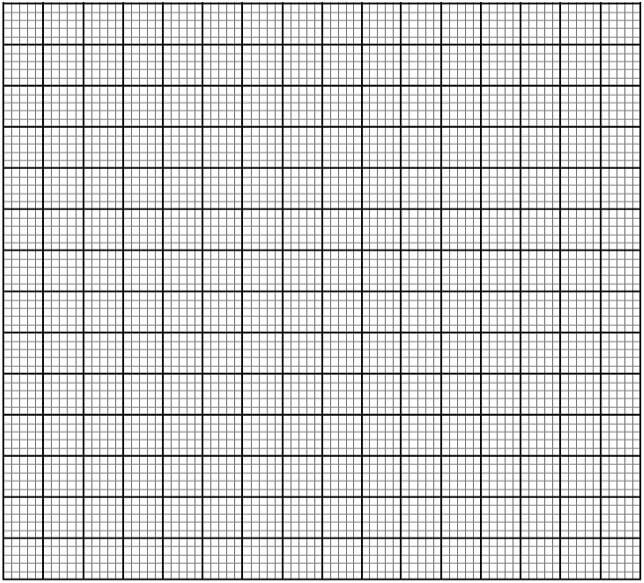
- The table below contains information on changes that occur in a river, downstream from sewage outflow.
Distance downstream from point of sewage entry (m) Concentration dissolved oxygen (%) Number of organisms (arbitrary units)
Distance downstream from point of sewage entry (m)
Concentration dissolved oxygen (%)
Number of organisms (arbitrary units)
Bacteria
Algae
Fish
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
800
900
1000
95
30
20
28
42
58
70
80
89
95
100
88
78
74
60
50
48
44
42
38
36
34
20
8
6
20
40
70
84
90
84
68
54
20
6
2
0
0
0
0
0
0
4
20
- Plot a graph of number of organisms against distance downstream. (7mks)
- Describe the changes in the concentration of oxygen dissolved in the water downstream from the point of sewage entry. (2mks)
- Account for the changes in the numbers or each of the following organisms downstream.
- Bacteria (3mks)
- Algae (3mks)
- Fish (3mks)
- State two ways in which the degree of water pollution covered by sewage can be reduced. (2mks)
- Plot a graph of number of organisms against distance downstream. (7mks)
- Describe the evidences of organic evolution. (20mks)
-
- Describe the process of fertilisation in a flowering plant. (15mks)
- State the changes that take place in a flower after fertilization. (5mks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
-
Salivary glands
Stomach
Pancrease
Ileum
Enzyme lipase
X
X
ü
ü
Protease
X
ü
ü
ü
- Long
Coiled - Vitamin C
- Glucose
- Herbivores; contains bacteria that secrete enzyme (cellulose) that digest cellulose to simple sugars;
-
-
- D – Chromatid
E – Centromere -
- Nucleus and mitochondria; (both to be given to earn the mark)
- (DNA) replication
- D – Chromatid
-
-
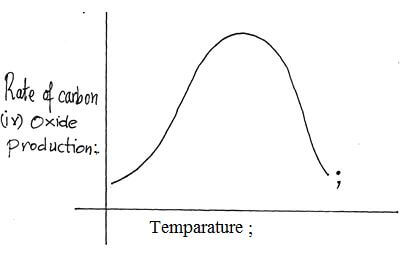
- At temperatures below optimum, the rate of CO2 production increases with increase in temperature as enzymes are activated/ at optimum temperatures the rate of CO2 production is at its maximum/ at temperatures above the optimum the rate of CO2 production decreases as enzymes are denatured.
-
- Amount of glucose
- Volume/ number of yeast cells
- pH of solution
-
- Glucose → ethanol + carbon (iv) oxide + energy
- Lactic acid has unutilized energy
-
-
-
- It act as a micro-filter/ prevents harmful substances from reaching foetus
- It secretes progesterone/ oestrogen during pregnancy
- Immunity is transferred from the mother to the foetus;
-
- Vessel C – umbilical vein
Vessel D – umblical artery
Blood vessel C
Blood vessel D
- High concentration of nutrients/ example of nutrient
- Low concentration of waste products/ example of waste product.
- High concentration of oxygen
- Low concentration of CO2
- Low concentration of nutrients/ example of nutrients
-High concentration of waste products/ example of products
- Low concentration of oxygen
- High concentration of CO2
- Vessel C – umbilical vein
- Waste products/ nitrogenous wastes/ CO2 will accumulate in the foetus body causing the death of the foetus.
-
- Harmful substances/ bacteria may pass from the mother’s blood to the foetus;
- The blood types/ proteins of the mother and foetus may not be compatible.
-
-
-
- D –Distal convoluted tubule;
E – collecting tubule - C & D
- D –Distal convoluted tubule;
-
- Proteins absent at end of PCT since they are too large to be ultra filtered;
- Glucose absent at end of PCT, all was reabsorbed;
- Urea concentration increased since some of the water was reabsorbed;
- The longer the loop of henle the more the water is reabsorbed; necessary to conserve water;
-
-

- The concentration of dissolved oxygen was high; after the point of entry up to 300m downstream and then increases further downstream; aerobic bacteria uses dissolved oxygen to break down organic matter in sewage; as amount of organic matter in sewage decreases downstream so does the amount of oxygen needed for breakdown;
-
- Initially the bacteria population increases; sewage contains a lot of bacteria and organic matter;
Bacteria breakdown organic matter and reproduce rapidly; population then decreases downstream as the amount of organic matter decrease downstream. - Decreases immediately after sewage discharge; organic matter in sewage reduces light penetration hence reduced photosynthesis and growth of algae, increases downstream; organic matter in sewage broken down providing excess nutrients leading to eutrophication; later decreases as the algae die due to excess competition leading to death of algae;
- Drops sharply and all die within 300m from point of discharge; decrease in concentration of oxygen leads to death of fish by suffocation. Organic matter in sewage clogs gills of fish leading to their death; sewage have toxic chemicals which directly kill fish; fish reappears after 800m from point of sewage discharge and thereafter increases; amount of organic matter in sewage has decreased hence increasing oxygen concentration; less solid matter to clog fish gills;
- Initially the bacteria population increases; sewage contains a lot of bacteria and organic matter;
-
- Proper sanitation
- Sewage must be purified before it enters the river;
- Education; to make people aware of proper waste disposal measures.
- Research; more efficient ways of treating sewage
-
- Fossil records; fossils are preserved remains of ancestral forms of organisms; fossil records give evidence of the type of organisms that existed at a certain geological time; shows the increase in complexity of different organisms by comparing the fossils of different organisms, it’s possible to draw the phylogenetic/ evolutionary relationship between organisms; the age of the organisms is determined by carbon-dating;
- Geographical distribution of organisms; supposes that the present day continents were one single landmass which later broke up into parts which drifted apart; closely related organisms were separated and isolated; from one another thus evolving differently; with time leading to formation of different species; each group of organisms adapted to different set of environmental conditions; e.g.
- Comparative embryology; embryology is the study of formation and development of an embryo; comparative embryology is the study comparing formation and development of different embryos; embryos that show similar morphological features during their early stages of development indicate a common ancestry/ closer phylogenetic relationship.
- Comparative anatomy; anatomy is the study of structures of living organisms; comparative anatomy is comparison of internal structures of various organisms; some show basic structural similarities, this suggests that the organisms have a common/related ancestry, homologous structures; but are modified to perform different functions; they have gone through different divergent evolution; e.g. pentadactyl links in mammals. Other structures show basic structural difference since they have different embryonic origin but have gone through convergent evolution and modified to perform similar functions, analogous structures; e.g. wings of insects and birds;
- Vestigial structures; are structures in course of time have ceased to be functional hence reduced in size; this indicates that they were present in their ancestral forms which have since evolved; e.g. cocoyx in humans.
- Comparative serology; serology is the study of blood/serum proteins; comparative serology is comparison of different blood proteins in different organisms; organisms that are closely related/ have a common ancestry have similar blood proteins; this is tested using antigen-antibody reaction; the greater the precipitate the closer the phylogenetic relationship;
- Cell biology; study of cells making up living organisms; similarities in structures and pigments (such as ATP, haemoglobin) point to a common ancestry. The differences in cells of different organisms show they separated and evolved differently;
-
- Once the pollen grain lands on the stigma; it is stimulated to germinate into a pollen tube by chemical substance produced by the stigma. The pollen tube grows down the style to the ovary obtaining its nourishment from the cells lining the style. The tube nucleus leads the way and generative nucleus follows closely. As pollen tube grows downwards, the generative nucleus divides by mitosis to form two male nuclei. The pollen tube breaks through the ovary wall and enters the ovule through the micropyle tube nucleus disintegrates leaving clear way for the two male nuclei. The male nuclei enter the embryo sac. One of the male nuclei fuses with egg cells to form zygote where as the other male nucleus fuses with two polar nuclei to form a primary triploid endosperm nucleus in a process called double fertilization.
-
- Ovule developed to seed.
- Ovule integuments becomes seed coat/testa
- Zygote develops into embryo
- Primary triploid endosperm nucleus forms endosperm
- Ovary becomes the fruit enclosing the seed
- Ovary wall becomes pericarp/fruit wall
- Stamen/ corolla – wither and die
Download Biology Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Cekena Pre Mocks 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

