QUESTIONS
SECTION A
Answer ALL questions in this section.
-
- What is a weather station? (2 marks)
- Give three factors that influence wind direction. (3 marks)
-
- Name two types of tectonic plate boundaries. (2 marks)
- Give three effects of the movement of tectonic plates. (3 marks)
- State four causes of the decline of the areas under forests in Kenya. (4 marks)
- The diagram below shows a section of a river. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
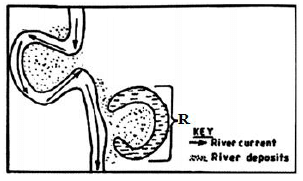
- Identify the stage of development of the section of the river. (1 mark)
- A part from feature marked R, give two other features formed at this stage. (2 marks)
- State three conditions necessary for the formation of the feature marked R. (3 marks)
-
- Differentiate between an aquifer and a water table. (2 marks)
- Give three problems associated with artesian wells. (3 marks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other two questions from this section
- Study the map of Nyeri 1:50,000 (sheet 120/4) provided and answer the following questions.
-
- Give the longitudinal extent of the area covered by the map. (2 marks)
- Give the six figure grid reference of the trigonometric station at Nyeri Hill forest. (2 marks)
- Calculate the area of Nyeri forest. Give your answer in square kilometres. (2 marks)
-
- What is the bearing of The Ark Lodge from the trigonometric station 120 UT 16. (2 marks)
- Identify three man-made features in grid square 7263. (3 marks)
- Give three drainage features found in the area covered by the map. (3 marks)
- Describe the relief of the area covered by the map. (5 marks)
- Citing evidence from the map, identify three social services offered in Nyeri Township. (6 marks)
-
-
-
- What is a mineral? (2 marks)
- Describe the following characteristics of minerals:
- Lustre (2 marks)
- Colour (2 marks)
- Cleavage (2 marks)
- Describe three ways in which sedimentary rocks are formed. (9 marks)
- Explain four significance of rocks to the economy of Kenya. (8 marks)
-
-
-
- State three causes of faulting. (3 marks)
- Differentiate between a normal fault and a reverse fault. (4 marks)
-
- A part from rift valley, give three other relief features formed due to faulting. (3 marks)
- With the aid of diagrams, describe how compressional forces can lead to formation of a rift valley. (8 marks)
- Students from your class are planning to carry out a field study on an area affected by faulting.
- State four reasons why it is important to have a pre-visit to the area. (4 marks)
- Give three reasons why it would be inappropriate to use observation to collect data during the field study. (3 marks)
-
-
-
- What are ocean tides? (2 marks)
- Name two ocean currents along the western coast of Africa. (2 marks)
- State three factors that determine the rate of coastal erosion. (3 marks)
- With the aid of labeled diagrams, describe the formation of the following coastal features:
- Fringing reef (5 marks)
- Spit (5 marks)
- Explain the significance of oceans to human activities. (8 marks)
-
-
- Name three components of soil. (3 marks)
- Explain how the following factors influence the formation of soil:
- Climate (4 marks)
- Topography (4 marks)
- Describe how laterization occurs. (6 marks)
- Explain four ways in which human activities contribute to soil erosion. (8 marks)

MARKING SCHEME
-
- What is a weather station?
a place that is set aside for the purpose of observing, measuring and recording weather elements.
1×2=2 marks - Give three factors that influence wind direction.
- the pressure gradient
- Coriolis force
- centrifugal force
- friction with the earth’s surface
3×1=3 marks
- What is a weather station?
-
- Name two types of tectonic plate boundaries.
- divergence/extension/constructive
- convergence/compressional/destructive
- transform/conservative
2×1=2 marks
- Give three effects of the movement of tectonic plates.
- they cause earthquakes
- can lead to formation of fold mountains
- can lead to formation of new oceanic crust
- can lead to formation of submarine islands/volcanic islands
3×1=3 marks
- Name two types of tectonic plate boundaries.
- State four causes of the decline of the areas under forests in Kenya.
- forests are destroyed by accidental or intended fires
- pests attack planted forests making them to dry up
- human activities/settlement/charcoal burning/logging have destroyed many forests
- overexploitation depletes some tree species
- prolonged droughts lead to degeneration of forests
- government policy of degazetting some forests
4×1=4 marks
-
- The diagram below shows a section of a river. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
Identify the stage of development of the section of the river.
old/lower stage
1×1= 1 mark - A part from feature marked R, give two other features formed at this stage.
- meanders
- braided channel
- flood plain
- deltas
- bluffs
- deferred tributaries
2×1=2 marks
- State three conditions necessary for the formation of the feature marked R.
- presence of pronounced meanders in the flood plain
- heavy load being carried by the river
- a reduction in the river gradient/energy/low velocity
- presence of obstacles in the river channel
- lateral erosion on the outer side of the river banks
- deposition on the inner side of the river banks
- The diagram below shows a section of a river. Use it to answer the questions that follow.
-
- Differentiate between an aquifer and a water table.
an aquifer is a mass of permeable rock which can hold water in its air spaces and can allow it pass through while a water table is the level of ground water below which all available air spaces are saturated with water.
1×2=2 marks - Give three problems associated with artesian wells.
- saline water in the wells
- overexploitation of the wells
- pollution of ground water
- prolonged drought leading to the wells drying up
3×1=3 marks
- Differentiate between an aquifer and a water table.
-
-
- Give the longitudinal extent of the area covered by the map.
36º45’E to 37º00’E
1×2=2 marks - Give the six figure grid reference of the trigonometric station at Nyeri Hill forest.
665548
1×2=2 marks - Calculate the area of Nyeri forest. Give your answer in square kilometres.
2 +19/2 = 11.5 km2
1×2=2 marks
- Give the longitudinal extent of the area covered by the map.
-
- What is the bearing of The Ark Lodge from the trigonometric station 120 UT 16.
317º±1º or N43ºW
1×2=2 marks - Identify three man-made features in grid square 7263.
- road D449
- other track/footpath
- settlement/houses
- Nderitu farm
3×1=3 marks
- Give three drainage features found in the area covered by the map.
- rivers
- dams/reservoirs
- water holes
- water tank
- ditch
3×1=3 marks
- What is the bearing of The Ark Lodge from the trigonometric station 120 UT 16.
- Describe the relief of the area covered by the map.
- there are several river valleys
- there is a hill in grid square 6963
- north eastern and western area has gentle slopes
- there are steep slopes in the north western and southern parts
- there are ridges in the south western part
- the highest point is 2820m and lowest point is 1680m
- the area generally slopes downwards from west to east
5×1=5 marks
- Citing evidence from the map, identify three social services offered in Nyeri Township.
- administration services – PC/DC/Admin offices
- religion – church
- recreation – golf course/club/show ground/hotel
- rehabilitation – prison
- education – school
- security – police station
3×2=6 marks
-
-
- What is a mineral?
a mineral is an inorganic substance with a definite chemical composition found at or beneath the surface of the earth. - Describe the following characteristics of minerals:
- Lustre - minerals differ in their brightness depending on the nature of their reflective surfaces (dull/shiny).
- Colour – different minerals display different colours
- Cleavage – minerals have patterns in which they split/divide/break into thin layers or along layers or shapes
- Describe three ways in which igneous rocks are formed.
- mechanically formed sedimentary rocks; rock fragments are transported by wind/water/ice are deposited in layers. Over a long period they are compacted in hard rocks.
- organically formed sedimentary rocks; remains of plants or animals are deposited in layers. Over long period of time the remains are compacted into hard rocks
- chemically formed sedimentary rocks; dissolved minerals are transported into water bodies. They are then precipitated/evaporated over time. Precipitates or evaporates are compacted to form hard rocks.
3×3=9 marks
- Explain four significance of rocks to the economy of Kenya.
- some rocks form unique features that attract tourists earning the country foreign exchange/income
- some sedimentary rocks contains fossil fuels which are sources of energy for domestic/industrial use e.g. coal
- some rocks act as storage for ground water which can exploited for domestic/industrial/agriculture
- some rocks e.g. phonolites are exploited for building ad construction
- rocks weather to form fertile soils that support crop farming
- some rocks are ores with valuable minerals that are exploited and sold to generate income
4×2=8 marks
- What is a mineral?
-
-
- State three causes of faulting.
- earth movements causing tension within rocks
- earth movements causing compression within rocks
- faulting can occur when rocks shear
- vertical movement in the rocks cause rocks to fracture
3×1=3 marks
- Differentiate between a normal fault and a reverse fault.
- a normal fault is caused by tensional forces while reverse fault is caused by compressional forces
- in a normal fault, the upthrow moves away from the downthrow while in a reverse fault, the upthrow rides over the downthrow.
2×2=4 marks
- State three causes of faulting.
-
- A part from rift valley, give three other relief features formed due to faulting.
- tilt block
- escarpment/scarp slope
- block mountain/horst
- fault steps
3×1=3 marks
- With the aid of diagrams, describe how compressional forces can lead to formation of a rift valley.
- When layers of crustal rocks are subjected to compressional forces, lines of weakness occur and forms adjacent reverse faults
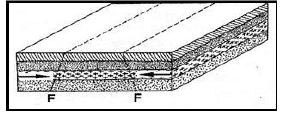
- Continued compression pushes out/thrusts the outer blocks over the central/middle block to form the floor of the rift valley.
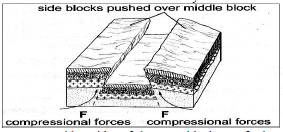
- The steep fault scarps on either sides of the outer blocks are further worn out by denudation (erosion, mass wasting, and transportation) to form gentle slopes.
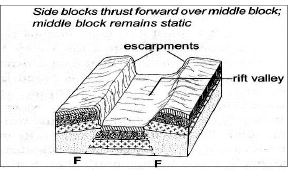
Text – 5 marks Diagrams – 3 marks
- When layers of crustal rocks are subjected to compressional forces, lines of weakness occur and forms adjacent reverse faults
- A part from rift valley, give three other relief features formed due to faulting.
- Students from your class are planning to carry out a field study on an area affected by faulting.
- State four reasons why it is important to have a pre-visit to the area.
- to draw route map
- prepare a working schedule
- identify relevant tools/equipment for the study
- identify suitable methods of collecting data
- seek permission from the authorities at the area of study
- prepare budget for the study
4×1=4 marks
- Give three reasons why it would be inappropriate to use observation to collect data during the field study.
- expensive to travel long distances
- time consuming
- limited to primary sources
- only suitable to the sighted people
3×1=3 marks
- State four reasons why it is important to have a pre-visit to the area.
-
-
-
- What are ocean tides?
ocean tides are periodic rise and fall in the level of ocean waters as a result of the gravitational attraction of the sun and the moon.
1×2=2 marks - Name two ocean currents along the western coast of Africa.
- Benguela
- Guinea
- Cannary
2×1=2 marks
- What are ocean tides?
- State three factors that determine the rate of coastal erosion.
- duration of exposure of coast to wave erosion
- degree of exposure of the coast to wave erosion
- nature of materials transported by waves
- structure/nature of the coastal rocks
- nature/strength of the waves
3×1=3 marks
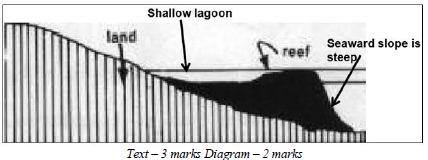
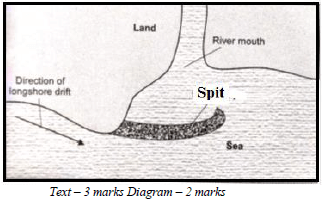
- With the aid of labeled diagrams, describe the formation of the following coastal features:
- Fringing reef
- This is a platform of coral which forms when coral polyps start building a reef near the shore.
- The reef extends seawards where the building is faster because of more food and the water is clearer.
- As the reef builds seawards, it encloses a shallow lagoon with the coast.
- Spit
- The movement of materials by the longshore drift is halted by a headland and the materials piled up/deposited in the sea/ocean water.
- This continues until they bulge out with the accumulation growing towards the sea
- Fringing reef
- Explain the significance of oceans to human activities.
- Presence of oceans modifies climatic conditions of an area through land and sea breezes.
- Oceans provide rich grounds for subsistence and commercial fishing.
- Ocean tides and waves can be harnessed to produce tidal power.
- Oceans are natural habit for marine life/ Biodiversity conservation.
- Provides cheap free water ways to transport goods and services across continents.
- Oceans provide sites for a variety of recreational activities e.g. water skiing, cruising sport fishing and tourism.
- Oceans provide grounds for navy/ military activities
- Ocean water can be distilled to provide fresh water
- Ocean water provide grounds for scientific/ educational research
4×2=8 marks
-
-
- Name three components of soil.
- soil air
- soil water/moisture
- soil organic matter/humus
- soil inorganic matter/minerals
3×1=3 marks
- Explain how the following factors influence the formation of soil:
- Climate
- Areas with heavy precipitation (rainfall) are heavily leached and weathered compared to drier areas, they therefore have deep soils
- High temperatures promote rapid faster weathering and chemical changes in the soil/cold temperatures slow these processes
- Winds act as agents of soil erosion, blowing fine sand and dust and depositing them far away forming rich fertile soils 2×2=4 marks
- Topography
- valley bottoms/gentle slopes encourage formation of deep and fertile soils due to deposition/accumulation of materials
- steep slopes encourages erosion of top layer of soil slowing down formation of soil/have thin soils
- flat areas/flood plains are saturated with water slowing down soil formation
- slope influence the arrangement of soil.
2×2=4 marks
- Climate
- Describe how laterization occurs.
- during wet season, mineral salts in the top layer of the soil dissolve in the rain water
- dissolved minerals percolate or seep downwards from the top soil to the sub-soil
- the dissolved minerals are further moved downwards to lower layer
- Insoluble minerals such as iron and aluminium accumulate on the top layer to form a crust of laterites hence laterization.
6×1=6 marks
- Explain four ways in which human activities contribute to soil erosion.
- cultivation on steep slopes increases the rate of soil erosion
- shifting cultivation/bush fallowing may leave land unprotected against agents of erosion
- cutting down trees exposes the soil to agents of erosion
- continuous ploughing weakens the soil structure, making it easy for the agents of erosion to carry it away.
- overgrazing leads to the removal of the protective cover of grass exposing the soil to agents of erosion
- overstocking leads to many animals trampling on the topsoil, loosening the particles and making it easy for them to be carried away.
4×2=8 marks
- Name three components of soil.
Download Geography Paper 1 Questions and Answers - Maranda Pre-Mock Examinations 2022.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students

