INSTRUCTIONS TO STUDENTS
- This paper has two sections A and B
- Answer ALL the questions in section A. In section B answer questions 6 and any other TWO questions.
FOR EXAMINERS’ USE
|
SECTION |
QUESTION |
SCORE |
|
A |
1-5 |
|
|
B |
6 |
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
9 |
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
TOTAL |
|
|

QUESTIONS
SECTION A: 25 MARKS
Answer ALL questions in this section
-
- Name three sub-branches of Human and Economic Geography. (3 marks)
- Explain the relationship between Geography and Mathematics. (2 marks)
-
- What is mining? (2 marks)
- State three ways in which minerals occur. (3 marks)
-
- Differentiate between forests and forestry. (2 marks)
- Give three importance of agro-forestry. (3 marks)
- State five characteristics of shifting cultivation. (5 marks)
- Draw an outline map of Kenya. On it mark and name Trona and Fluorspar mining areas. (5 marks)
SECTION B
Answer question 6 and any other TWO questions from this section.
-
- The table below shows horticultural crop produced in Kenya in the year 2010.
Crop
Quantity in tonnes
Flowers
52,500
Oranges
32,600
Tomatoes
30,300
Carrots
25,400
- Draw a divided rectangle 15cm long to represent horticultural crop production in Kenya in the year 2010 using the data above. (8 marks)
- Calculate the range of the above data. (2 marks)
- What is the percentage of the horticultural crop with the highest tonnage? (2 marks)
- State two advantages of using divided rectangles to represent statistical data. (2 marks)
-
- What is plantation farming? (2 marks)
- Name two crops grown under plantation farming in Kenya. (2 marks)
- Identify four characteristics of plantation farming in Kenya. (4 marks)
- State three problems facing plantation farming in tropical regions. (3 marks)
- The table below shows horticultural crop produced in Kenya in the year 2010.
-
- Explain how the following factors influence the exploitation of minerals.
- Transport (4 marks)
- Level of technology (4 marks)
- Mode of occurrence of minerals. (4 marks)
- Describe the processing of Trona in Lake Magadi. (6 marks)
-
- Name two methods used in underground mining. (2 marks)
- Describe how minerals are obtained through open cast mining. (5 marks)
- Explain how the following factors influence the exploitation of minerals.
-
-
- Differentiate between afforestation and re-afforestation. (2 marks)
- Explain how the following factors influence forest distribution in Kenya:
- Altitude (2 marks)
- Precipitation. (2 marks)
-
- Name three equatorial rain forest reserves found along the Kenya coastal belt. (3 marks)
- State four ways in which clearing forests affect the natural environment. (4 marks)
- Explain four measures taken by the government of Kenya to control encroachment on forested areas. (8 marks)
-
- Name two areas under forests in Canada. (2 marks)
- Compare forestry in Kenya and Canada under the following sub- headings:
- Period of harvesting. (2 marks)
- Tree harvesting (2 marks)
-
-
-
- Name three counties where maize is grown on commercial scale in Kenya. (2 marks)
- State the physical conditions necessary for maize cultivation in Kenya. (5 marks)
-
- Describe the stages involved in maize production in Kenya from land preparation to harvesting. (6 marks)
- Explain three problems facing maize farming in Kenya. (6 marks)
-
- What is mixed farming? (2 marks)
- State four characteristics of mixed farming. (4 marks)
-
-
-
- Distinguish between horticulture and market gardening. (2 marks)
- Give the characteristics of horticultural farming in Kenya. (4 marks)
-
- State four factors which favour horticultural farming in Kenya. (4 marks)
- Explain three measures taken by the government of Kenya to promote horticultural farming. (6 marks)
- What are the similarities between horticultural farming in Kenya and Netherlands? (4 marks)
- A form three geography class intend to carry out a field study in a horticultural farm near their school.
- State three methods of data collection they are likely to use. (3 marks)
- Give two follow-up they are likely to undertake after the study. (2 marks)
- Give two methods they used to present their data. (2 marks)
-

MARKING SCHEME
-
- Name three sub-branches of human and economic geography. (3 marks)
- Economic geography
- Historical geography
- Agricultural geography
- Population geography
- Political geography
- Explain the relationship between geography and mathematics. (2 marks)
- Mathematical formulae and principals are used in geography to calculate area, distance, mean, bearing and population density
- Name three sub-branches of human and economic geography. (3 marks)
-
- What is mining? (2 marks)
- It is a process of extracting valuable minerals that occur on or below the earth’s crust.
- State three ways in which mineral occur. (3 marks)
- Some occur in veins and lodes
- Some occur in seams and beds
- Some occur as alluvial deposits
- Some occur as weathered products
- Some occur as evaporates
- What is mining? (2 marks)
-
- Differentiate between a forests and forestry. (2 marks)
- A forest is an extensive tree cover on the earth’s surface which could be growing naturally or planted by man while forestry is the science of planting, managing and exploitation of forest resources.
- Give three importance of agro-forestry. (3 marks)
- It maximizes land use as both crops and trees are a source of income.
- It provides raw materials for the industries
- It promotes high water retention on the land
- The trees supply woof fuel needs.
- The leaf litter decomposes thus adding humus to the soil
- Livestock waste is used as manure.
- Some trees provide fodder for the animals.
- Some trees have medicinal value
- Trees provide aesthetical beauty
- It helps to conserve soil by minimizing soil erosion
- Trees act as wind breakers to the young crops
- Trees creates a micro climate
- Differentiate between a forests and forestry. (2 marks)
-
- State five characteristics of shifting cultivation. (5 marks)
- Usually practiced on small plots
- Vegetation is cleared by slashing and burning
- Simple tools are used.
- labor is usually provided by immediate family members.
- Only a limited number of food crops is cultivated to feed the family
- Land is owned communally
- Both the plots and settlements are temporary.
- State five characteristics of shifting cultivation. (5 marks)
- Draw an outline map of Kenya. On it mark and name Trona and fluorspar mining areas. (5 marks)
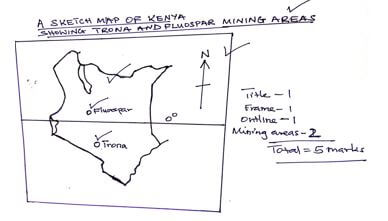
-
- The table below shows horticultural crop produced in the year 2010.
Crop
Quantity in tonnes
Flowers
52,500
Oranges
32,600
Tomatoes
30,300
Carrots
25,400
- Draw a divided rectangle 15cm long to represent horticultural crop production in Kenya in the year 2010 using the data above. (8 marks)
A DIVIDED RECTRANGLE REPRESENTING HORTICULTUREAL CROP PRODUCTION IN 2010 IN KENYA
- Flowers = 52,000/140,800 ×15=5.59 cm
- Oranges = 32,600/140,800 ×15=3.47 cm
- Tomatoes = 30,000/140,800 ×15=3.2 cm
- Carrots = 25,400/140,800 ×15=2.7 cm
- Calculate the range of the above data. (2 marks)
- Range; 52,500 – 25,400 = 27,100
- What is the percentage of the horticultural crop with the highest tonnage? (2 marks)
- 52,500/140,800 ×100=32.29%
- Draw a divided rectangle 15cm long to represent horticultural crop production in Kenya in the year 2010 using the data above. (8 marks)
- State two advantages of using divided rectangles to represent geographical data. (2 marks)
- Gives a clear visual impression
- Easy to draw/construct
- Easy to read/interpret
- Easy to compare components
- Takes up less space
-
- What is plantation farming? (2 marks)
- It is the commercial cultivation of cash crops on large tracts of land
- Name two crops grown under plantation farming in Kenya. (2 marks)
- Tea
- Coffee
- Sugar cane
- Sisal
- Sunflower
- Identify four characteristics of plantation farming in Kenya. (4 marks)
- Farms are large in size
- Farms are owned by rich individuals/groups/companies
- Farms are managed scientifically
- One single crop is grown on a large area/monoculture
- Farming activities are highly mechanized
- The produce is for commercial purposes/market oriented
- There is heavy application of fertilizers for high yields
- Requires high/heavy capital investment
- What is plantation farming? (2 marks)
- State three problems facing plantation farming in tropical regions. (3 marks)
- Insects/pests/disease attack
- Price fluctuation in the world market
- Stiff competition from other countries producing the same commodities.
- Inadequate land for expansion
- Inadequate capital
- Soil exhaustion/soil degeneration
- Climatic/frost/draught
- The table below shows horticultural crop produced in the year 2010.
-
- Explain how the following factors influence the exploitation of minerals.
- Transport (4 marks)
- Efficient transport links allow mineral products to be moved from the mining site to the ports/market without delay.
- Minerals that are bulky require railway/water/cheap transport system to reduce the total cost of production.
- Mineral deposits in remote areas/poorly developed transport system are less likely to be exploited.
- Level of technology (4 marks)
- Advanced technology has improved mining operations thus leading to high quality/large quantity mineral products.
- High level technology allows for effective exploration of minerals leading to accurate location of minerals.
- Advanced technology boost effectiveness in production hence reducing wastage.
- Low level technology limits exploitation/low quantity mined.
- Mode of occurrence of minerals. (4 marks)
- Minerals that occur in small quantities /lodes/veins may limit exploitation since they are of low commercial value unless the mineral is of high value, they will be exploited.
- Large deposits are extracted as they are likely to be profitable/can sustain the mining process over a long time.
- Minerals at or near the surface/alluvial deposits are easier to extract.
- Deep seated minerals are expensive in extract.
- Transport (4 marks)
- Describe the processing of trona in Lake Magadi. (6 marks)
- A mixture of trona and liquor is pumped through a pipeline to the factory
- On reaching the factory, trona is separated from water by put on large sieve-like trays.
- The water from trona is directed back into the lake.
- The trona is then washed to remove impurities such as mud and sort. It is heaped on the ground to dry.
- After drying, trona is heated in huge cylinders called desiccators. The heating separates sodium carbonate (soda ash) and sodium bicarbonate.
- When heating is completed, the soda ash id allowed to cool.
- Soda ash is then ground into powder and sieved.
- The powder is packed in paper or jute bags ready for transportation to the market.
-
- Name two methods used in underground mining. (2 marks)
- Drift or adit method
- Shaft method
- Solution method
- Drilling method
- Describe open cast method of mining. (5 marks)
- The mineral deposits are within a few metres from the ground
- The unwanted materials on top of the mineral are removed.
- The soft minerals ore is removed by digging/quarrying/stripping/drooping. Any hard rock/mineral ore is broken up by busting with explosives.
- Huge power shovels are used to dig up minerals deposits.
- The mineral are loaded on to the trucks/railway wagon to be transported to the processing plant.
- Name two methods used in underground mining. (2 marks)
- Explain how the following factors influence the exploitation of minerals.
-
-
- Differentiate between afforestation and re-afforestation. (2 marks)
- Afforestation refers to planting trees in an area which had no trees while re-afforestation refers to planting trees in an area where trees have been cut down.
- Explain how the following factors influence forest distribution in Kenya:
- Altitude (2 marks)
- Very high altitude areas such as high mountain tops are bare due to presence of very low temperatures e.g. summits of Mt. Mt. Kenya and Mt. Kilimanjaro.
- High altitude areas experiences low temperature and thus supports growth of coniferous forests.
- Moderate altitude areas receives high rainfall and thus supports dense forest cover such as tropical rain forest and bamboo forests.
- Low altitude areas receive low to moderate rainfall and therefore supports scattered trees known as woodlands.
- Precipitation. (2 marks)
- There are dense forest cover in areas experiencing high rainfall/less dense forest cover consisting of stunted trees in areas receiving low rainfall.
- Coniferous forest have cone-shaped crowns to allow snow to slide off so as not to accumulate on the branches and cause them to break off.
- Altitude (2 marks)
- Differentiate between afforestation and re-afforestation. (2 marks)
-
- Name three equatorial rain forest reserves found along the Kenya coastal belt. (3 marks)
- Kenya forest
- Arabuko Sokoke forest
- Shimba hills
- Tana River forsts
- Boni Dodori forest
- Mangrove forests
- State four ways in which clearing forests affect4ed the natural environment. (4 marks)
- It has led to drying up of some rivers
- It has disrupted the ecosystem/it has led to destruction of natural habitat of some wildlife.
- It has accelerated soil erosion
- It has interfered with environmental beauty
- It has led to changes in rainfall patterns
- Name three equatorial rain forest reserves found along the Kenya coastal belt. (3 marks)
- Explain four conservation measures undertaken by the government of Kenya to control encroachment on forested areas. (8 marks)
- Gazetting the forested areas to create forest reserves to reduce encroachment by the public.
- Creating awareness through the mass media on the importance of conserving forests resources.
- Enacting laws to prohibit cutting of trees without licence to protect the indigenous tree species.
- Establishing Ministry of Environment and Natural Resources to coordinate all activities on forest conservation.
- Setting aside tree planting days for people to plant more trees.
- Employing forest guards to prevent illegal logging
- Encouraging recycling of wood products to reduce demand on forest trees.
- Establishing Nyayo tea zones to create buffer zones to prevent people from encroaching into forests.
- Fencing forest reserves to minimize illegal logging.
- Evicting people out of forested areas to allow rehabilitation of destroyed forest areas.
-
- Name two areas under forests in Canada. (2 marks)
- New found land
- New Brunswick
- Nova scotia
- Prince Edward Island
- British Columbia
- Compare forestry in Kenya and Canada under the following sub- headings:
- Period of harvesting. (2 marks)
- In Canada logging is done in winter and early spring while in Kenya cutting is done throughout the year.
- Tree harvesting (2 marks)
- In Canada, it is done through clear cutting while in Kenya it is done through selective cutting
- Period of harvesting. (2 marks)
- Name two areas under forests in Canada. (2 marks)
-
-
-
- Name three counties where maize is grown on commercial scale in Kenya. (2 marks)
- Nakuru
- Trans Nzoia
- Uasin Gishu
- Bungoma
- State physical conditions necessary for maize cultivation in Kenya.
- Moderate to high rainfall.
- Moderate to high temperature.
- Gentle sloping land/undulating land.
- Deep soils.
- Volcanic/light loamy soils.
- Sunny/dry season for ripening.
- Well drained soils.
- Name three counties where maize is grown on commercial scale in Kenya. (2 marks)
-
- Describe the stages involved in maize production from land preparation to harvesting. (6 marks)
- Land is cleared to remove vegetation.
- Land is ploughed by use of tractors/jembes/ox drawn plough
- Land is harrowed to loosen soil particles
- Holes are dug to correct depth
- The seeds are placed manually into the holes that have been dug and covered.
- Weeding is done severally as top dressing is done at the knee high.
- After 4 – 6 months, the crop is ready for harvesting
- The crop is harvested manually/using combine harvester.
- Explain three problems facing maize farming in Kenya. (6 marks)
- Pests e.g. cornea warms/weevils/destroy the crop lowing the yields.
- Diseases e.g. smut destroy the crop lowing the yields
- High cost of farm inputs increases production cost hence reducing profit margin
- Poor storage facilities
- Poor feeder roads in some maize growing areas leads to delay in delivery of the crop hence wastage
- Adverse weather conditions such as long draught lead to destruction of the crop/lower production.
- Describe the stages involved in maize production from land preparation to harvesting. (6 marks)
-
- What is mixed farming? (2 marks)
- Is the growing of crops and rearing of livestock on the same farm.
- State four characteristics of mixed farming. (4 marks)
- Both crops are grown and livestock reared on the same piece of land
- Crop rotation is practiced.
- It is labour intensive/utilizes manual labour
- Fodder crops are grown to supplement natural pasture
- It is scientifically managed
- There is maximum utilization of land.
- What is mixed farming? (2 marks)
-
-
-
- Distinguish between horticulture and market gardening. (2 marks)
- Horticulture is the cultivation of fruits vegetable and flowers while market gardening is the cultivation of fruits and vegetables.
- Give the characteristics of horticultural farming in Kenya. (4 marks)
- Located near transport routes
- Located near urban centres
- It requires skilled labour for breeding and management of crops.
- It requires advanced technology
- Farms under cultivation are usually large.
- It is labour intensive due weeding, spraying, harvesting and packaging.
- Distinguish between horticulture and market gardening. (2 marks)
-
- State four factors favouring horticultural farming in Kenya. (4 marks)
- Fertile volcanic soils
- Hot climate which favours crop growth
- Moderate – high rainfall
- High demand local and abroad
- Availability of capital
- Accessibility by road and air to market
- Well developed marketing system
- Adequate labour
- Explain three measures taken by the government of Kenya to promote horticultural farming. (6 marks)
- Improving roads for easy transport
- Encouraging diversification
- providing of loans to enable farmers buy inputs
- Providing pesticides to farmers to control pests and diseases.
- Encouraging farmers to form cooperatives to help them sell their crops.
- Providing refrigerators in vehicles to reduce perishability.
- State four factors favouring horticultural farming in Kenya. (4 marks)
- What are the similarities between horticultural farming in Kenya and Netherlands? (4 marks)
- On both countries, similar crops are grown
- In both countries crops are grown in open and green houses.
- Scientific farming methods are used
- Farming is carried our extensively to reap maximum returns.
- In both countries crops are grown on reclaimed land.
- A form three geography class intend to carry out a field study in a horticultural farming near their school.
- State three methods of data collection they are likely to apply. (3 marks)
- Observing
- Interviewing
- Reading from the books
- Taking photograph
- Administering questionnaires
- Collecting samples
- Give two follow-up they are likely to undertake after the study. (2 marks)
- More discussion in class.
- Displaying the photographs taken..
- Comparing notes in their groups/more consultations with teachers.
- Writing field reports.
- reading more on the topic.
- Analyzing the data collected.
- Give two methods they used to present their data. (2 marks)
- Displaying collected samples.
- Displaying photographs.
- In form of written study reports.
- Viewing the videos recorded.
- In form of drawn graphs/charts.
- In form of sketch diagrams/maps.
- State three methods of data collection they are likely to apply. (3 marks)
-
Download Geography Paper 2 Questions and Answers - Asumbi Girls Pre Mock Examinations 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
