INSTRUCTIONS TO CANDIADATES
- Answer all question in section A and B
- In section C answer any two questions
- Candidates should check the question paper to ascertain that all pages are printed as indicated and that no questions is missing
- Candidates must answer all the questions in English
For examiner’s use only
|
Section |
Questions |
Maximum score |
Candidate score |
|
A |
1 -17 |
30
|
|
|
B |
18 -21 |
20
|
|
|
C |
|
20
|
|
|
|
|
20
|
|
|
Total score |
90
|
|
|

QUESTIONS
SECTION A (30marks).
Answer all Questions in this section
- Name two branches of horticulture. (1marks)
- List two advantages of mixed farming. (1 mark)
- State two advantages of metal water pipes over plastic pipes in piping water in the farm. (1 mark)
-
- State two characteristics of extensive farming system. (1marks)
- List four characteristic of fertile soil (2maks)
- Give four advantages of raising cabbage seedlings in a nursery before transplanting (2maks)
- State four benefits of a land title deed to a farmer (2marks)
- State four factors which should be considered when deciding type of irrigation on crop production (2marks)
- Give two ways by which overstocking encourage soil erosion. (1mark)
- State two physical agent of weathering (1mark)
- State four objectives of the million-acre scheme. (2marks)
- State four symptoms of attack by the bean fly in bean production. (2marks)
-
- State any four measures that are taken to minimize water pollution in the farm. (2 marks)
- Outline four ways through which soil loses its fertility. (2 marks)
- List Four practices that achieve minimum tillage. (2 marks)
- List four farming practices that can be carried out to increase the amount of light harnessed by crops. (1 marks)
- State two ways of preparing planting materials before planting (1mark)
- State four ways of increasing labour efficiency on the farm (2marks)
- State four factors which may affect the quality of Hay. (2 marks)
SECTION B (20 MARKS)
Answer ALL the questions in this section in the spaces provided.
- The diagram below shows an experiment set up using three different sets of soil, and the observations made after 24hrs. Study the diagram and answer the questions that follow.
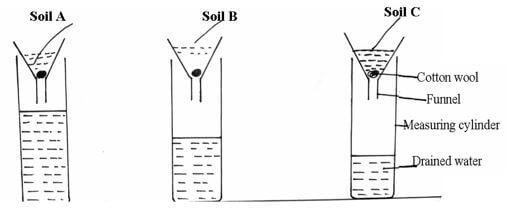
- What is the experiment set up above designed to study. (1 mark)
- Name soil types B and C. (2 marks)
C
B - What are the characteristic textures of the soil type A and C (2 marks)
Soil type A
Soil type C
- The diagrams below show a practice carried out on various crops on the farm. Study them carefully and answer the questions that follow.
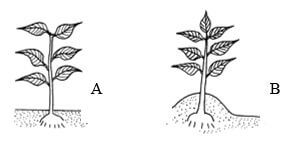
- Identify the farm practice represented by B. (1mark )
- State one the importance of the above practice in the following crops. (3marks)
- Maize
- Irish Potatoes
- Tobacco
- At what stage of growth should the above practice be carried out in maize. (1mark )
- Study the farm record below and the questions that follow:
Date
Disease symptoms
Animals affected
Drug used
Cost of treatment
Remarks
- Identity of the record (1mark)
- State two different information that should be entered in the remarks column (2marks)
- Give two importance of keeping the farm record illustrated above (2marks)
- The diagram below illustrates common weeds in arable land, study them carefully and answer the questions that follow.
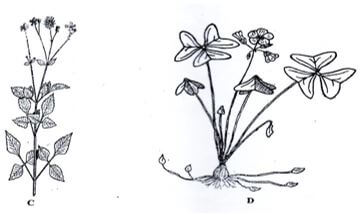
- Identify the weed labeled C and D (2marks)
C...
D... - Classify the weed labeled C according to plant morphology. (1 mark)
- Explain the reason why it is difficult to control the weed labeled D. (2 marks)
- Identify the weed labeled C and D (2marks)
SECTION C ANSWER ONLY TWO QUESTION 40 MARKS
- Describe the management of cabbages under the following sub-headings.
- Nursery preparation and establishment (7 marks)
- Management of seedlings in the nursery (5 marks)
- Transplanting of seedlings (8 marks)
-
- Explain five ways government policy contributes to Agriculture. (5 marks)
- Explain any five factors considered when spacing crops. (10marks)
- Describe the advantages of mixed grass -legume pasture over a pure grass pasture (5marks)
-
- State and explain four ways in which soil loses its fertility (8marks)
- State the precautions that should be observed when harvesting cotton. (4marks)
- Explain four importance of crop rotation. (8marks)

MARKING SCHEME
- Name two branches of horticulture. ( 2x ½ = 1 marks)
- Pomoculture / Growing of fruits
- Olericulture / growing of vegetables
- Floriculture / growing of flowers
- State two advantages of mixed farming ( 2 x ½ = 1 mark)
- Mutual benefit between crops and livestock
- Better utilization of labour
- Assured of income throughout the year
- Diversification /insurance against total loss
- Advantages of metal water pipes over plastic pipes in piping water . (2 x ½ = 1mark)
- Higher pressure tolerant
- Resistant to rodent damage
- Durable /long lasting
-
- Two characteristics of extensive farming system ( 2x ½ = 1marks)
- Practiced on large tract of land
- Low capital investment
- Low labour requirement per unit area
- Low yields per unit area.
- List four characteristic of fertile soil ( 4x ½ = 2marks)
- Correct PH
- Good water holding capacity
- Adequate plant nutrients
- Free from pest and diseases
- Good depth
- Well drained
- Two characteristics of extensive farming system ( 2x ½ = 1marks)
- Advantages of raising cabbage seedlings in a nursery before transplanting (4x ½ = 2marks)
- Easy to carry out management practices
- Better conditions are provided for seedling
- It takes short time in the field
- Excess seedling is sold to earn income.
- Easy to establish small seeds into seedlings
- A farmer is able to select strong and health seedlings for transplanting.
- State four benefits of a land title deed to a farmer. (4x ½ = 2marks)
- One can sell land and earn income
- No dispute of land/offers security of tenure
- Can develop permanent project on land
- Motivated to conserve soil and water
- Security to get a loan
- State four factors which should be considered when deciding type of irrigation on crop production ( 4x ½ = 2marks)
- Slope of land/Topography
- Type of crop to be planted
- Availability of water
- Type of soil
- Availability of capital
- ways overstocking encourage soil erosion. (2 x ½ = 1mark)
- Animals remove all forage cover and expose soil to agents of soil erosion.
- Intensive trampling loosen soil making it easily carried by agent of soil erosion
- Intensive trampling occurs and vegetation is destroyed exposing the soil to agent of soil erosion.
- Physical weathering agents (2 x½ = 1 mark)
- Wind
- Glaciations/moving ice
- Temperature change
- Running water(reject water alone)
- Objectives of million acre scheme. ( 4x ½ = 2marks)
- To transfer land from white settlers (Europeans) to Africans.
- Reduce population pressure in the African reserves.
- To solve the unemployment problems.
- To increase agricultural production,Through better methods of land utilization.
- To maintain production levels maintained by former white settlers and also earn foreign exchange from the sale of cash crops.
- State four symptoms of attack by the bean fly in bean production. ( 4x ½ = 2marks)
- Holes in stem/tunnels in stem.
- Stem swells at the base.
- Cracking of stem at the base
- Stunted growth.
-
- measures which are taken to minimize water pollution . ( 4x ½ = 2marks)
- Fencing off water sources to keep off pollutants
- Application of soil conservation measures to control soil erosion
- Avoid watering animals directly from water sources
- Good disposal of effluents from processing factories
- River banks should be vegetated by planting grass to minimize siltation in rivers.
- Employing adequate storm water control methods and disposal systems especially in areas with heavy rains.
- state four importance of drainage as a land reclamation method ( 4x ½ = 2marks)
- To increase soil volume
- To raise soil temperature
- To increase soil aeration by removing excess water
- To reduce soil erosion
- To remove toxic substances
- To increase microbial activities
- measures which are taken to minimize water pollution . ( 4x ½ = 2marks)
- List four practices that achieve minimum tillage. (4x½=2marks)
- Application of herbicides in controlling weed
- Use of mulch on the soil surface
- Timing cultivation
- Establishing a cover crop on the field
- Uprooting or slashing weeds in perennial crops
- Restricting cultivation to the area where seeds are to be planted
- List four farming practices that can be carried out to increase the amount of light harnessed by crops ( 4 x ½ = 2 marks)
- Prunning
- Thinning
- Weeding
- Wider spacing
- Two ways of preparing planting materials before planting (2 x ½ = 1mark)
- Breaking seed dormancy
- Seed dressing
- Chitting/ sprouting
- Seed inoculation
- four ways of increasing labour efficiency on the farm (4x½=2marks)
- Training them
- Giving incentives
- Supervision
- Good operator – worker relationship
- Farm mechanization
- Assigning tasks according to skills & specialization
- Proper remuneration /Attractive salaries
- State four factors which may affect the quality of Hay. (2 x ½=1marks)
- Forage species used
- Stage of harvesting (leaf: stem ration)
- Length /period of storage
- Weather condition during drying period
- Condition of the storage structure
-
- What is the experiment set up above designed to study. (1 mark)
- To compare porosity / water holding capacity of different soils
- Name the three soil types B and C. (2 marks)
- C- Clay
- B- Loam
- What are the characteristic textures of the soil type A and C (2 marks)
- A- Coarse texture
- C – Fine textured
- What is the experiment set up above designed to study. (1 mark)
-
- Identify the farm practice represented by B. (1mark )
- Earthing up
- State one the importance of the above practice in the following crops. (3marks)
- Maize - provides support to prevent lodging
- Irish potatoes - Improves tuber formation/expansion
- Tobacco – Improves drainage around the plant
- At what stage of growth should the above practice be carried out in maize. (1mark )
- During second weeding /knee high/45 cm in height
- Identify the farm practice represented by B. (1mark )
-
- Identity of the record (1mark)
- Health record
- State two different information that should be entered in the remarks column (2marks)
- Occurrence of the disease
- Response to treatment
- Next date of treatment /vaccination
- Give two importance of keeping the farm record illustrated above (2marks)
- Know the course of action to be taken in the event of a disease and maintenance of good health
- Know the prevalent disease
- Calculate cost of treatment
- Select and cull animals on health ground
- Identity of the record (1mark)
-
- Identify the weed labeled (2marks)
- C-Black jack Biden pilosa
- D- Oxalis
- Classify the weed labeled C according to plant morphology. (1 mark)
- Broad leaf
- .Explain the reason why it is difficult to control the weed labeled D. (2 marks)
- Has the underground structure (bulbs) which goes deep/spread hence difficult to control
- Identify the weed labeled (2marks)
-
- Nursery Preparations and establishment (7x1=7marks)
- Clear the place if bushy
- Dig the land to remove perennial weed
- Break soil clods to a fine tilth
- Remove roots and stones from site
- Prepare nursery bed 1m wide by any convenient length
- Prepare raised or sunken depending on moisture available
- Level nursery bed
- Make shallow drills about 10cm apart
- Apply phosphatic fertilizer in drills and mix through with soil
- Sow seeds by drilling
- Cover the seeds lightly with soil
- Apply some thin layer of mulch after sowing
- Water the seeds
- Management of seedlings in the nursery (5x1=5marks)
- Remove the mulch as soon as seedlings emerge
- Water nursery twice a day – morning and late evening
- Remove weeds as they come up.
- Prick out of overcrowded seedlings
- Control pests using appropriate pesticide
- Control diseases using appropriate fungicide
- Hardening off the seedlings by gradual removal of the shade & reduction in frequency watering.
- Erect a shade to protect the seedlings from direct sunlight.
- Transplanting of seedlings (8x1=8 marks)
- Water nursery thoroughly before transplanting
- Dig planting holes of appropriate depth and correct spacing (60-90)cm x 60cm
- Select healthy and vigorously growing seedling only
- Lift seedlings carefully with a garden trowel.
- Ensure the seedling is lifted with lamp of soil around the roots
- Transport seedlings carefully to the field
- Transplant on a cloudy day or late afternoon
- Place phosphatic fertilizer and well rotten manure in the planting holes and mix with soil
- Plant seedling same depth as they were in the nursery bed
- Fill the holes with soil and firm around the base seedlings
- Apply mulch or erect a shade
- Water the seedlings thoroughly.
- Nursery Preparations and establishment (7x1=7marks)
-
- Explain five ways government policy contributes to Agriculture. (5 x1=5marks)
- Subsidize the price of inputs to ensure production is affordable.
- Conservation of natural resources to ensure sustainability
- Imposition of high tax imports to promote local products
- Stepping up control of diseases and pest to prevent spread and high quality products
- Quality control to ensure effective competition in both local and international market
- Explain any five factors considered when spacing crops.
- Soil fertility – Crops can be spaced wider if the soil is infertile and close if soil is very fertile.
- Soil moisture content – Drier areas require wider spacing than wet areas.
- Machinery to be used in subsequent farm operation - Crop whose operation will be mechanized is given wider space to allow for movement of machinery than that which will be manually managed.
- Intended purpose of the crop – Crops requires different spacing depending on their purpose e.g. maize for silage is spaced closer than that grown for grains.
- Growth habit of the crop/ size/ suckering/ tillering – plants that tiller or produce suckers tend to occupy a bigger area. they thus require wider spacing.
- Height/size of plant – Shorter crops require narrower spacing than taller crops.
- Number of seeds per hole – If more seeds are planted per hole, the spacing should be wider than if fewer or one seed is planted per hole.
- Pest and disease control-when crop are properly spaced, pest may find it difficult to move from one plant to another
- Stating 1 mark explanation 1 mark total 10 marks
- Describe the advantages of mixed grass -legume pasture over a pure grass pasture ( 5x1=marks)
- Mixed pasture yields more per unit areas of land
- It is more nutritious /has higher nutrition value
- Make maximum use of soil Nutrients
- Helps to reduce soil erosion because of good coverage
- Has better weed control
- Increases soil fertility because of Nitrogen fixation
- Explain five ways government policy contributes to Agriculture. (5 x1=5marks)
-
- State and explain four ways in which soil loses ferttility (4x2=8 marks)
- Leaching – As water infiltrates into the soil it moves together with dissolved soluble minerals to lower horizon beyond the reach of many plant roots.
- Soil Erosion – Carrying away of top soil rich in nutrients by agents.
- Monocropping – the crop grown will use the same nutrients till exhausted leaving out other nutrients, remain unused
- Continous cropping-cultivation on the same piece of land over a long period of time exhaust all the nutrients
- Burning of the vegetation – burning destroys organic matter leading to destruction of soil fertility.
- Accumulation of salts that lead to salinity. This change leads to loss of soil fertility.
- Change in soil pH – increase or decrease in soil pH as a result of use of different fertilizers affects the activity of soil microorganisms as well as availability of soil nutrients.
- State the precautions that should be observed when harvesting cotton. (4x1marks)
- Picking should be done immediately the bolls open/split to prevent staining by dust.
- Picking should be done when the lint is dry to prevent fibres from sticking together.
- Use clean containers for picking to avoid contamination.
- Hands should be clean to avoid staining of the lint.
- Do not mix cotton with foreign matter eg leaves and small twigs.
- Use separate containers for separate cotton grades to ensure quality
- Avoid using sisal bags for collecting the bolls because their fibres may mix with the seed cotton thus creating problems during ginning.
- Explain four importance of crop rotation. (8marks)
- Maximum utilization of nutrients- Alternating shallow with deep rooted crops ensures that nutrients from different layers are well utilized.
- Control of soil borne pests and disease build up- Eg root eelworms in pyrethrum. Pests and diseases are specific to various crops.
- Control of weeds -Parasitic weeds eg witch weed (Striga weed) are specific to grass family crops and can be controlled by planting non grass crops for some time.
- Improvement of soil fertility-When leguminous crops are included in the rotation programme, they help in fixing nitrogen with the help of Rhizobium bacteria. This nitrogen is made available for subsequent crops.
- Improvement of soil structure- It is recommended that at the end of the rotation programme a grass ley be established. The roots of grass are so extensive that they bind soil particles together.
- Control of soil erosion-If crops planted in rows eg maize is alternated with cover crops eg sweet potatoes providing good ground cover reducing soli erosion.
- Stating 1mark explanation 1 mark 4x2=8 marks
- State and explain four ways in which soil loses ferttility (4x2=8 marks)
Download Agriculture Paper 1 Questions and Answers - MECS Pre Mock Exams 2023.
Tap Here to Download for 50/-
Get on WhatsApp for 50/-
Why download?
- ✔ To read offline at any time.
- ✔ To Print at your convenience
- ✔ Share Easily with Friends / Students
